Essay Papers Writing Online
10 effective strategies for writing a successful synthesis essay that will impress your readers.

In the realm of written expression, the fusion of ideas from various sources has long been regarded as one of the most intellectually stimulating endeavors. Being able to synthesize information from disparate fields of knowledge not only demonstrates a profound understanding of the subject matter, but also enables the author to introduce novel insights and perspectives. A synthesis essay, as its name suggests, requires a writer to assimilate and integrate ideas, arguments, and evidence from multiple sources into a cohesive and compelling piece of writing. This type of essay invites writers to harness their analytical skills and creative thinking abilities to produce a work that advances a unique and persuasive viewpoint.
Central to the craft of writing a synthesis essay is the utilization of synthesis techniques, which allow the author to achieve the desired integration of ideas. By employing these techniques, such as comparison and contrast, analysis and evaluation, and critique and synthesis, the writer can effectively merge ideas from different sources in a clear and coherent manner. Through the skillful application of these techniques, the writer can establish connections, draw parallels, and highlight the interrelationships of ideas, thereby creating a nuanced and sophisticated argument.
Examples serve as valuable tools in illustrating the principles and techniques of crafting a successful synthesis essay. For instance, consider a synthesis essay on the topic of climate change. In this essay, the writer integrates scientific research papers, political speeches, and personal testimony to create a comprehensive and persuasive argument for the urgent need for global action on climate change. By skillfully weaving together these diverse sources, the writer is able to present a multi-dimensional perspective on the issue while maintaining a clear and compelling narrative.

How to Write a Synthesis Essay: Step-by-Step Guide
In the process of crafting a synthesis essay, you will be tasked with combining information from multiple sources to create a cohesive and well-supported argument. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the process, providing helpful tips and examples along the way.
Step 1: Understand the Assignment
Before diving into the writing process, it is crucial to fully comprehend the assignment. Read through the prompt carefully, identifying the main question or topic, as well as any specific sources or guidelines provided. This will help you determine the scope and direction of your essay.
Step 2: Conduct Research
Once you have a solid grasp of the assignment, it’s time to gather information from various sources. This can include articles, books, interviews, or even online resources. Make sure to select sources that are reputable, current, and relevant to your topic. Take detailed notes as you read, highlighting key ideas and evidence.
Step 3: Develop a Thesis Statement
Based on your research, develop a clear and concise thesis statement that encapsulates your argument. This statement should present your position on the topic and preview the main points you will explore in your essay. Keep in mind that a strong thesis statement will guide the entire writing process.
Step 4: Create an Outline
Organize your thoughts and ideas by creating an outline for your essay. This will serve as a roadmap for your writing, ensuring that each point flows logically and effectively supports your thesis. Divide your essay into sections and subsections, assigning each one a specific focus.
Step 5: Write the Introduction
Begin your essay with a captivating introduction that grabs the reader’s attention. Provide some background information on the topic and present your thesis statement. Be sure to include a hook that entices the reader to continue reading.
Step 6: Craft the Body Paragraphs
The body of your essay should consist of several paragraphs, each dedicated to a specific point or subtopic. Begin each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea, then support it with evidence from your sources. Be sure to cite your sources properly to give credit to the original authors.
Step 7: Write the Conclusion
Wrap up your essay with a strong conclusion that reinforces your thesis statement and summarizes your main points. Avoid introducing new information in this section, and instead focus on leaving a lasting impression on the reader.
Step 8: Revise and Edit
Once you have completed a draft of your essay, take the time to revise and edit it. Check for clarity, coherence, and overall effectiveness of your arguments. Also, review your grammar, spelling, and punctuation to ensure your essay is error-free.
Step 9: Proofread and Polish
Before submitting your final essay, proofread it one last time to catch any lingering errors. Pay attention to spelling, grammar, and punctuation mistakes. Additionally, ensure that your formatting and citations are consistent throughout the essay.
Step 10: Seek Feedback
Finally, seek feedback from others, such as peers, teachers, or writing tutors. Their fresh perspective can help you identify any areas that need improvement and provide valuable suggestions for strengthening your essay.
By following this step-by-step guide, you will be well-equipped to write a successful synthesis essay that effectively combines multiple sources and supports your argument. Remember to take your time, conduct thorough research, and carefully craft each section of your essay to achieve the best possible result.
Understanding the Purpose of a Synthesis Essay
Exploring the Rationale Behind Composing a Synthesis Paper
A synthesis essay is a unique form of academic writing that requires students to combine information from multiple sources to support a thesis statement. In this type of essay, the writer needs to analyze various perspectives and synthesize them into a coherent argument. The purpose of a synthesis essay is to demonstrate a deep understanding of a topic by presenting a well-structured and balanced synthesis of different viewpoints or approaches.
When writing a synthesis essay, it is essential to understand the purpose behind this type of assignment. The primary goal is not merely to summarize the information from the sources but to present an original perspective that emerges from the synthesis of these sources. By carefully analyzing and evaluating the information from various sources, students can develop a unique understanding of the topic and present their own insights.
Moreover, a synthesis essay allows students to demonstrate critical thinking and analytical skills. It requires them to evaluate the credibility and relevance of the sources used and to consider how different ideas and perspectives relate to one another. By carefully selecting and integrating information from diverse sources, students can create a cohesive argument that goes beyond a mere summary of the sources.
Another important purpose of a synthesis essay is to foster effective communication and persuasive writing skills. Through the synthesis process, students learn how to effectively convey their ideas and support them with evidence from the sources. They need to consider the audience and tailor their argument to appeal to the readers. By organizing their thoughts and ideas in a logical and coherent manner, students can make a persuasive case for their thesis statement.
In summary, the purpose of a synthesis essay is to demonstrate a deep understanding of a topic by synthesizing information from multiple sources into a cohesive argument. It requires students to analyze and evaluate various viewpoints and to develop their own unique perspective. Additionally, a synthesis essay cultivates critical thinking skills and effective communication abilities. By mastering the art of synthesis writing, students can become more proficient in academic research and persuasive writing, making their essays more compelling and insightful.
Choosing a Relevant Topic for Your Synthesis Essay

When embarking on a journey of writing a synthesis essay, one of the most crucial steps is selecting a pertinent topic that encompasses the essence of your discussion. This stage requires careful consideration and evaluation in order to ensure that you have a solid foundation on which to build your argument.
To begin, it is essential to understand that a relevant topic should address the central theme or question that you are exploring in your synthesis essay. It should encapsulate the diverse perspectives and ideas that you aim to synthesize in your composition. By choosing a topic that is pertinent to your thesis statement, you can create a cohesive and persuasive argument.
When selecting a topic, it is important to choose something that is not only interesting to you but also holds relevance to the current context. Consider the current societal issues, scientific advancements, or technological developments that are shaping the world around us. By delving into a topic that is timely and impactful, you can engage your readers and make your synthesis essay more compelling.
Furthermore, it is crucial to choose a topic that allows for a variety of sources and perspectives to be integrated into your essay. Look for subjects that have a wealth of research materials available from reputable sources such as academic journals, books, and established experts in the field. This will provide you with a diverse range of perspectives to consider and synthesize in your argument.
In conclusion, choosing a relevant topic for your synthesis essay is a critical step in the writing process. By selecting a topic that aligns with your thesis statement, holds relevance in the current context, and allows for a variety of perspectives to be included, you can create a well-rounded and persuasive synthesis essay that effectively conveys your argument.
Gathering and Evaluating Sources for Your Essay
When embarking on writing a synthesis essay, it is crucial to gather and evaluate reliable sources to support your arguments effectively. A successful essay depends on the quality and relevance of the sources you include. This section will provide you with some valuable tips on how to gather and evaluate sources for your essay.
1. Determine the scope of your essay: Before you start collecting sources, it is important to have a clear understanding of the scope and topic of your essay. This will help you narrow down your search and choose sources that are most relevant to your argument.
2. Use a variety of sources: In order to provide a well-rounded view on the topic, it is recommended to include a mix of primary and secondary sources. Primary sources can include original research studies, interviews, or firsthand accounts, while secondary sources can be scholarly articles, books, or reputable websites that analyze and interpret the primary sources.
3. Evaluate the credibility of the sources: It is essential to evaluate the credibility and reliability of the sources you find. Consider the author’s credentials, the reputation of the publication or website, and whether the information has been peer-reviewed or fact-checked. Avoid relying heavily on sources that lack authority or have a bias.
4. Check for currency: Ensure that the sources you choose are up to date and reflect the most current research and information on the topic. This is particularly important if you are writing about a rapidly evolving field or a current issue.
5. Take notes and keep track of your sources: As you gather your sources, it is crucial to take detailed notes and keep track of the bibliographic information. This will make it easier to properly credit your sources and create an accurate bibliography later on.
6. Consider diverse perspectives: While it can be tempting to rely on sources that align with your own views, it is important to consider diverse perspectives. Including sources with differing opinions can strengthen your argument and demonstrate that you have considered multiple viewpoints.
By following these tips and gathering a range of reliable sources, you will be well-equipped to write a compelling synthesis essay that is backed by solid evidence and argumentation.
Developing a Thesis Statement for Your Synthesis Essay
In the process of writing a synthesis essay, one of the most crucial steps is developing a strong thesis statement. A thesis statement sets the tone and direction for your essay, guiding the reader on what to expect and how the different sources you will be synthesizing contribute to your overall argument.
When developing a thesis statement for your synthesis essay, it is important to consider the main idea you want to convey and the point you want to make. Your thesis statement should be clear, concise, and specific, providing a roadmap for your essay and outlining the main arguments you will be making.
One approach to developing a thesis statement is to carefully analyze the sources you will be synthesizing and identify common themes or patterns. Look for similarities and differences among the sources and identify the main ideas that emerge. Your thesis statement can then highlight these main ideas and showcase how they intersect and contribute to your overall argument.
Another approach to developing a thesis statement is to consider the main arguments or perspectives presented in the sources and craft a statement that expresses your position on the topic. Your thesis statement can be a synthesis of these different perspectives, presenting a nuanced and balanced argument that incorporates multiple viewpoints.
Remember, a strong thesis statement is essential for a successful synthesis essay. It provides a clear roadmap for your essay and allows your reader to understand the main arguments you will be making. Take the time to carefully craft your thesis statement, ensuring it is specific, concise, and reflective of the main ideas you will be exploring in your essay.
Structuring Your Synthesis Essay for Effective Organization
Creating a well-structured synthesis essay is crucial for effective organization and a clear presentation of your ideas. A strong structure allows your readers to easily follow your argument and understand the connections between different sources and viewpoints. In this section, we will explore some key strategies for structuring your synthesis essay to ensure a cohesive and persuasive piece of writing.
1. Introduction: Start your essay with a compelling introduction that grabs your reader’s attention and clearly presents the topic you will be discussing. Provide some background information on the issue, highlight its significance, and state your thesis statement, which will guide your argument throughout the essay.
2. Body paragraphs: Divide your essay into several body paragraphs, each addressing a specific aspect of your topic. Begin each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea or argument you will be discussing. Support your points with evidence from your sources, making sure to cite them properly. Use transitions between paragraphs and within sentences to create a smooth flow of ideas and to establish connections between different viewpoints.
3. Analysis and synthesis: While presenting the ideas from your sources, make sure to analyze and evaluate them critically. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of each source, identify any biases or limitations, and consider how they contribute to your overall argument. Aim to synthesize the information from your sources, combining different perspectives to support your own viewpoint.
4. Counterarguments: Address and refute counterarguments to strengthen your argument and demonstrate a thorough understanding of the topic. Anticipate possible objections and provide evidence or reasoning to counter them. Acknowledging opposing viewpoints but explaining why they are flawed further strengthens your own argument and credibility.
5. Conclusion: Wrap up your essay with a strong conclusion that summarizes your main points and restates your thesis in a clear and compelling manner. Avoid introducing new information in the conclusion, but instead, emphasize the significance of your argument and its implications.
By structuring your synthesis essay in an organized and logical manner, you can ensure that your ideas are presented cohesively and persuasively. Remember to revise and edit your essay for clarity, coherence, and grammar, and proofread it carefully before submission. With a well-structured essay, you can effectively convey your argument and convince your readers of your viewpoint.
Writing and Revising Your Synthesis Essay
Crafting and fine-tuning your synthesis essay is an essential step in the writing process. Once you have conducted comprehensive research and gathered a plethora of sources, it’s time to consolidate your findings and present them in a cohesive and persuasive manner.
When it comes to writing your synthesis essay, it is crucial to lay a solid foundation. Begin by organizing your thoughts and ideas into an outline, creating a clear and logical structure for your essay. This framework will serve as a roadmap, guiding you through the writing process and ensuring that your arguments flow smoothly.
Once your outline is complete, you can begin the actual writing process. Start with a strong introduction that captures the reader’s attention and clearly states your thesis statement. From there, proceed to develop your ideas in a series of well-crafted paragraphs, each with its own topic sentence and supporting evidence.
As you write, remember to maintain a formal and academic tone, using appropriate language and avoiding slang or colloquialisms. Your synthesis essay should demonstrate your understanding of the topic and your ability to effectively analyze and synthesize information from a variety of sources.
Once you have completed your initial draft, it is essential to revise and edit your synthesis essay to ensure its clarity and coherence. Begin by reviewing the overall structure and organization of your essay. Check that your paragraphs flow smoothly and logically, and ensure that your thesis statement is well-supported by the evidence presented.
Next, focus on the content of your essay. Review each paragraph to ensure that it contributes to the overall argument and that the evidence presented is relevant and persuasive. Consider whether there are any gaps in your analysis or any areas that could benefit from further development.
In addition to content, pay attention to the style and mechanics of your writing. Check for grammatical and spelling errors, and ensure that your sentences are clear, concise, and varied. Consider the use of appropriate transitions to guide your reader through your essay and help them follow your line of reasoning.
Lastly, take the time to proofread your essay carefully. Read it aloud, or have someone else read it to you, to catch any errors or areas that could be strengthened. Remember, the revision process is an opportunity to refine and improve your essay, so take the time to make necessary changes and ensure that your synthesis is well-crafted and compelling.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Synthesis Essay

4-minute read
- 31st May 2023
Are you writing a synthesis essay? This is a paper that combines information from a variety of sources to form a new idea. Essentially, you’re synthesizing existing concepts and arguments to create something original.
As a student, you’ll probably have to write a synthesis essay at some point. Read on for our step-by-step guide on how to write one effectively.
Step 1. Define Your Idea or Argument
If you haven’t done so already, decide on a topic to write about. Read up about it using a variety of credible sources and make detailed notes while you research. Make sure you keep track of the sources you decide to pull information from so that you can cite them properly later.
Make a list of key points from your research. Once you have a good selection of material to work with, start developing your own idea or argument. This will be the focus of your essay.
Step 2. Create an Outline
Synthesis essays generally follow this format: an introduction, a handful of main body paragraphs, and a conclusion. It’s a good idea to come up with an essay plan before you start writing so that you can keep things organized while you work.
The outline is mainly helpful for deciding what to include in your body paragraphs. Decide what supporting points (and counterarguments ) from your research you want to include, and which order you want to discuss them in. You should have enough information to flesh out one paragraph for each point.
Step 3. Write Your Introduction
In your introduction, you should open with something that hooks the reader and captures their attention. Then, state your argument or idea (i.e., your thesis statement) and briefly summarize the material you’ll be including in your essay. You should also include any relevant background information here.
Step 4. Write the Body Paragraphs
Using your outline, discuss each point from your source material in more depth, devoting a body paragraph to each. Explain the information from the outside source, including appropriate citations, and discuss how it connects with your idea.
It’s a good idea to mostly focus on points that support your argument, but you should also include a paragraph with a counterargument or two. This means discussing a perspective that doesn’t necessarily align with your idea, and then explaining why your argument still works.
Step 5. Tie It All Together With a Conclusion
The conclusion should leave the reader feeling convinced of your idea. Restate your point clearly and summarize the main points you’ve discussed. You could also offer any concluding reflections on the topic.
Different Types of Synthesis Essays
While you can follow our steps for any type of synthesis essay, yours will probably fall under one of two categories: explanatory or argumentative.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Argumentative essays are as they sound – they present an argument. With an argumentative essay, you’ll take a more definitive stance on something and use your supporting material to persuade the reader.
Explanatory essays don’t necessarily take a side one way or the other. Rather, they focus on developing and explaining a concept thoroughly. Knowing which type of essay you’re writing will help you to gather more effective source material for your purpose.
Cite Your Sources
Since synthesis essays are particularly dependent on outside material, it’s especially important that you cite your sources correctly. Familiarize yourself with your referencing system before you start researching so you know what information you need to keep track of, and include appropriate citations whenever you use someone else’s work.
At the end of the essay, you’ll need to compile your sources into a reference list following the requirements of your style guide.
Summary: Writing a Synthesis Essay
Hopefully, this post has helped you to feel more confident in writing a synthesis essay. Choose a topic first, do your research, keep track of your sources, and develop an argument or idea. From there, you can organize your thoughts into an outline and get to writing!
Once you’ve created a first draft, make sure you send it our way! We’ll check it for errors in grammar, spelling, referencing, and more. Try it out for free today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a synthesis essay.
A synthesis essay gathers ideas and viewpoints from several different sources and ties them together to form a new concept.
How long is a synthesis essay?
Synthesis essays usually follow the five-paragraph format, with an introduction, three main body paragraphs discussing different points, and a conclusion.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
5-minute read
Free Email Newsletter Template
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

Synthesis Essays: A Step-by-Step How-To Guide
A synthesis essay is generally a short essay which brings two or more sources (or perspectives) into conversation with each other.
The word “synthesis” confuses every student a little bit. Fortunately, this step-by-step how-to guide will see you through to success!
Here’s a step-by-step how-to guide, with examples, that will help you write yours.
Before drafting your essay:
After reading the sources and before writing your essay, ask yourself these questions:
- What is the debate or issue that concerns all of the writers? In other words, what is the question they are trying to answer?
- On what points do they agree?
- On what points do they disagree?
- If they were having a verbal discussion, how would writer number one respond to the arguments of writer number two?
In a way, writing a synthesis essay is similar to composing a summary. But a synthesis essay requires you to read more than one source and to identify the way the writers’ ideas and points of view are related.
Sometimes several sources will reach the same conclusion even though each source approaches the subject from a different point of view.
Other times, sources will discuss the same aspects of the problem/issue/debate but will reach different conclusions.
And sometimes, sources will simply repeat ideas you have read in other sources; however, this is unlikely in a high school or AP situation.
To better organize your thoughts about what you’ve read, do this:
- Identify each writer’s thesis/claim/main idea
- List the writers supporting ideas (think topic sentences or substantiating ideas)
- List the types of support used by the writers that seem important. For example, if the writer uses a lot of statistics to support a claim, note this. If a writer uses historical facts, note this.
There’s one more thing to do before writing: You need to articulate for yourself the relationships and connections among these ideas.
Sometimes the relationships are easy to find. For example, after reading several articles about censorship in newspapers, you may notice that most of the writers refer to or in some way use the First Amendment to help support their arguments and help persuade readers. In this case, you would want to describe the different ways the writers use the First Amendment in their arguments. To do this, ask yourself, “How does this writer exploit the value of the First Amendment/use the First Amendment to help persuade or manipulate the readers into thinking that she is right?
Sometimes articulating the relationships between ideas is not as easy. If you have trouble articulating clear relationships among the shared ideas you have noted, ask yourself these questions:
- Do the ideas of one writer support the ideas of another? If so, how?
- Do the writers who reach the same conclusion use the same ideas in their writing? If not, is there a different persuasive value to the ideas used by one writer than by the other?
- Do the writers who disagree discuss similar points or did they approach the subject from a completely different angle and therefore use different points and different kinds of evidence to support their arguments?
- Review your list of ideas. Are any of the ideas you have listed actually the same idea, just written in different words?

- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Synthesis Essay
Last Updated: April 7, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 11 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,127,978 times.
Writing a synthesis essay requires the ability to digest information and present it in an organized fashion. While this skill is developed in high school and college classes, it translates to the business and advertising world as well. Scroll down to Step 1 to begin learning how to write a synthesis essay.
Examining Your Topic

- Argument synthesis: This type of essay has a strong thesis statement that presents the writer's point of view. It organizes relevant information gathered from research in a logical manner to support the thesis' point of view. Business white papers known as position papers often take this form. This is the type of synthesis essay that students will write during the AP test.
- Review: Often written as a preliminary essay to an argument synthesis, a review essay is a discussion of what has been written previously on a topic, with a critical analysis of the sources covered. Its unstated thesis is usually that more research needs to be done in that area or that the topic problem has not been adequately addressed. This type of paper is common in social science classes and in medicine.
- Explanatory/background synthesis: This type of essay helps readers understand a topic by categorizing facts and presenting them to further the reader's understanding. It does not advocate a particular point of view, and if it has a thesis statement, the thesis is a weak one. Some business white papers take this form, although they are more likely to have a point of view, if understated.

- Example of a broad topic narrowed down into a reasonable synthesis essay topic: Instead of the broad topic of Social Media, you could discuss your view on the effects texting has had on the English language.
- If you've been assigned a topic as part of a class, make sure you read the prompt carefully and fully understand it.

- Keep in mind that it's better to do three sources well than to do five sources incompletely.
- Annotate each source by writing notes in the margins. This allows you to keep track of your train of thought, developing ideas, etc.

- Example: Texting has had a positive impact on the English language as it has helped the millennial generation create their own form of the language.

- If you wish to take on a claim by an opponent of your idea, and to poke holes in it, you should also find some ideas or quotes that go against your thesis statement, and plan ways to disprove them. This is called a concession, refutation, or rebuttal, which can strengthen your argument if you do it well.
- Example : For the thesis statement listed above, excellent sources would include quotes from linguists discussing the new words that have developed through 'text-speak', statistics that show the English language has evolved with almost every generation, and facts that show students still have the ability to write with the use of grammar and spelling (which your opponents would bring up as the main reason texting has had a negative effect on the English language).
Outlining Your Essay

- The introductory paragraph: 1. An introductory sentence that acts as a hook, capturing the reader's interest. 2. Identification of the issue you will be discussing. 3. Your thesis statement.
- The body paragraphs: 1. Topic sentence that gives one reason to support your thesis. 2. Your explanation and opinion of the topic sentence. 3. Support from your sources that backs up the claim you just made. 4. Explanation of the significance of the source(s).
- The conclusion paragraph: 1. State further significance of your topic from the evidence and reasons you discussed in the essay. 2. A profound thought or thoughtful ending for your paper.

- Example/illustration. This may be a detailed recount, summary, or direct quote from your source material that provides major support for your point of view. You may use more than one example or illustration, if your paper calls for it. You should not, however, make your paper a series of examples at the expense of supporting your thesis.
- Straw man. With this technique, you present an argument opposed to the argument stated in your thesis, then show the weaknesses and flaws of the counter-argument. This format shows your awareness of the opposition and your readiness to answer it. You present the counter-argument right after your thesis, followed by the evidence to refute it, and end with a positive argument that supports your thesis. [5] X Research source
- Concession. Essays with concessions are structured similar to those using the straw man technique, but they acknowledge the validity of the counter-argument while showing that the original argument is stronger. This structure is good for presenting papers to readers who hold the opposing viewpoint.
- Comparison and contrast. This structure compares similarities and contrasts differences between two subjects or sources to show the facets of both. Writing an essay with this structure requires a careful reading of your source material to find both subtle and major points of similarity and difference. This kind of essay can present its arguments source-by-source or by points of similarity or difference.

- Summary. This structure presents summaries of each of your relevant sources, making a progressively stronger argument for your thesis. It provides specific evidence to support your point of view, but usually omits presenting your own opinions. It's most commonly used for background and review essays.
- List of reasons. This is a series of sub-points that flow from the main point of your paper as stated in its thesis. Each reason is supported with evidence. As with the summary method, reasons should become progressively more important, with the most important reason last.
Writing Your Essay

- Your essay should have an introductory paragraph that includes your thesis , a body to present evidence that supports your thesis, and a conclusion that summarizes your point of view.

- Lengthy quotes of three lines or more should generally be set off as block quotes to better call attention to them. [7] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
Finalizing Your Essay

- Ask someone else to proofread your paper. The saying “two heads are better than one” still holds true. Ask a friend or colleague what would they add or remove from the paper. Most importantly, does your argument make sense, and is it clearly supported by your sources?

- Read the paper aloud to guarantee that you don't accidentally add in or take out words when reading in your head.
- If you can, get a friend or classmate to proofread your essay as well.

- Example of citing in an AP synthesis essay: McPherson claims “texting has changed the English language in a positive way--it has given a new generation their own unique way to communicate” (Source E).
- For college essays, you'll most likely use MLA format. Whichever format you use, be consistent in its use. You may also be asked to use APA or Chicago style.

- Example title: : English and the iPhone: Exploring the Benefits of 'Text-Speak'
Outline Template

Community Q&A
- Just as your title should fit your essay instead of writing your essay to fit the title, your thesis, once chosen, should direct your subsequent research instead of subsequent research altering your thesis � unless you find you've adopted an unsupportable thesis. Thanks Helpful 21 Not Helpful 8

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://success.uark.edu/get-help/student-resources/synthesis-paper.php
- ↑ https://www.unr.edu/writing-speaking-center/student-resources/writing-speaking-resources/mapping-a-synthesis-essay
- ↑ https://www.bgsu.edu/content/dam/BGSU/learning-commons/documents/writing/synthesis/planning-synthesis-essay.pdf
- ↑ https://writingcenterofprinceton.com/synthesis-essays-a-step-by-step-how-to-guide/
- ↑ https://owl.excelsior.edu/argument-and-critical-thinking/logical-fallacies/logical-fallacies-straw-man/
- ↑ https://writingcommons.org/section/rhetoric/rhetorical-stance/point-of-view/third-person-point-of-view/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_formatting_quotations.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/steps_for_revising.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/proofreading_suggestions.html
- ↑ https://www.edhs.org/ourpages/auto/2010/5/17/41759867/Synthesis%20Essay%20Introduction.pdf
- ↑ https://writing.umn.edu/sws/assets/pdf/quicktips/titles.pdf
About This Article

To write a synthesis essay, start by coming up with a thesis statement that you can support using all of the sources you've read for your essay. For example, your thesis statement could be "Texting has had a positive impact on the English language." Once you've got your thesis, go through your sources to find specific quotes, facts, and statistics that back up your claim. Structure your essay so it has an introduction that includes your thesis statement, a body that includes your arguments and evidence, and a conclusion that wraps everything up. For more tips on structuring your synthesis essay, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Aug 8, 2016
Did this article help you?
Adrian Mastrocola
Sep 29, 2016
Emmanuel Amoatey Djaba
Nov 26, 2016
Anna VonLeader
Jun 6, 2016
May 7, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve

How to Write a Synthesis Essay
it requires researching several sources to come up with your idea, but it isn’t very different than a research essay or other academic writing assignments that students will be familiar with. This article will guide you through all the elements of a synthesis essay, including the various types, formats, citation styles, outlines, topics, guides, and tips.
At Studyfy, we understand that writing a synthesis essay can be a challenging task. That's why we offer a custom essay writing service to assist students with their assignments. Our team of expert writers has experience in writing various types of essays, including synthesis essays, and can help you with your assignment. With our online paper writing service , you can be sure that your paper will be well-researched, properly formatted, and tailored to your specific needs. Contact us today and let us help you write a top-quality synthesis essay that meets all your requirements.
What is a Synthesis Essay?
At its core, a synthesis essay asks the writer to analyze several sources and come up with their own opinion on a subject. Think of it as creating your thesis statement based on the information you have collected from several places. It’s actually not unlike any other essay. Synthesis means combining elements of separate materials or abstract entities into a single or unified entity, and that’s what a synthesis essay does.
Types of Synthesis Essay
There are three main types of synthesis essays:
A Review Essay
A review essay collects available information about a topic to suggest what further research needs to be done. It focuses on analyzing available sources rather than making a point of its own.
An Argument Essay
These types of essays use multiple sources to back up a claim or argument. Like a typical argumentative essay, the goal is to convince the reader that your viewpoint on an issue is correct providing evidence from research.
An Explanatory Essay
The goal of this type of essay is to present information about a specific topic from various perspectives. Do not make an argument, just explain the topic with every point of information backed by research.
Synthesis Essay Structure
A synthesis essay follows the traditional structure of a 5 paragraph essay but with a few modifications. An outline is always helpful to plan any form of writing, but it is especially useful when writing this type of essay because of the many sources and various arguments to keep track of. An outline helps plan an essay and ensures that all the major points are covered as well as helps develop a flow to the paper.
The basic synthesis essay structure follows the 5 paragraph essay format.
Introduction - Briefly describe what the paper will be about. Start with a hook to engage the reader from the very beginning, followed by a brief description, and make sure to include your thesis statement.
Body Paragraphs - The first body paragraph typically contains a counterargument to your thesis. Comprehensive research and proper analysis of a subject requires understanding the issue from the opposing viewpoint as well. By presenting the most popular counterargument and debunking it, you make your overall case stronger. The next body paragraphs should present information supporting your thesis.
Conclusion - The conclusion wraps up your paper by summarizing the main points and stating how you proved your thesis with facts.
Synthesis Essay Outline
Here’s an outline template for you to use. As you do your research and come up with arguments, fill this template with information.
Introduction
- Background information
- The importance of the issue
- Thesis statement
Body Paragraph 1
- Topic sentence with a counterargument
- Evidence for the counterargument
- Invalidate the counterargument
- Evidence and facts backing your claim
Conclusion
- Transition to body paragraph 2
Body Paragraph 2
- Topic sentence supporting your thesis
- Quote a source
- Evidence for your claim
- Analysis of your claim
- How it connects to and supports your claim
- One sentence summary
- Transition to body paragraph 3
Body Paragraph 3
- Quote a different source
- How it connects to and supports your claim
- One sentence summary
- Connect all research backing your claim
- Transition to the conclusion
- Summary of the main points made in the essay
- Restate your thesis
- Your main argument and the most important evidence
- One sentence about why our view is important
Struggling with your Synthesis Essay Homework?
Get your assignments done by real pros. Save your precious time and boost your marks with ease.
How to Write a Synthesis Paper
Now that you know what a synthesis essay is, what the structure should be, and have an outline to fill, let’s get to how to write a synthesis essay!
How to Start a Synthesis Essay
The first thing you need to do is come up with an appropriate topic. If you’ve been given a prompt, make sure to read it carefully and follow all the instructions.
If you have to choose your own topic make sure that the issue you choose has opposing views so that you can find research backing both sides.
Find the sweet spot between a topic that’s too broad, which can be difficult to address fully, and a topic that’s too marrow, which might not have enough available information.
Explore our lists of possible essay topics to get an idea of what you may want to write about and read some example essays to become familiar with the structure and style.
Once you have a topic in mind, find at least 3 sources and read them thoroughly while taking notes on specific facts to help build your thesis statement.
Writing a Synthesis Essay Thesis
After you’ve found a topic you find interesting and that complies with the prompt, your research should guide your thesis statement. What does your research say about the topic you’ve chosen? Your thesis is the main claim you are making in the essay. This doesn’t have to mean that you follow what a majority of the research says, just make sure you have enough evidence to back up your perspective as well as evidence to refute the main counter-arguments.
Your thesis statement should be written as a complete sentence, identifying the subject and stating your viewpoint on it. This will be the guiding idea and the main point you will try and prove through the body paragraphs.
Body Paragraphs
Body paragraphs are the main text of your essay. This is where you will present your research, support your thesis, and build your case.
The first body paragraph usually describes a major argument against your thesis to show why the argument is wrong, or why your argument is better. There are several different approaches you can take to achieve this.
The straw man technique involves presenting the main counterargument and then destroying it with evidence showing its flaws. It can be a powerful way to strengthen your claim and it shows that you have researched opposing views. End a body paragraph using this technique with a transition sentence that introduces your main statement supporting your thesis.
The concession technique can be thought of as a softer version of the straw man. You present evidence that goes against your thesis and acknowledges that it makes sense, but show that your argument is stronger. This technique is useful for convincing people that hold the opposing view to what you believe. By agreeing with and accepting that the opposing viewpoints have some merits, it put the reader in a less hostile frame of mind.
The comparison and contrast technique presents a nuanced analysis of both sides. This is the most difficult technique because it requires a deep understanding of the issue as well as careful analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of both sides of the argument. When pulled off successfully though, it is incredibly powerful and shows an in-depth understanding of the issue.
The body paragraphs after the first should provide evidence supporting your thesis. These can contain direct quotes from your sources. Your analysis should be clear and flow logically from the research. Towards the end of each paragraph connect the evidence directly to the thesis statement to build a strong case for your claim.
Your conclusion should state all the main points of the essay as well as the main takeaways. Summarize the evidence that backs your claim and reiterate your thesis statement. Make sure to acknowledge the opposing viewpoint and state why your perspective is either correct or stronger.
Synthesis Essay Format
Citation is important for any paper, but especially for one that is research-driven. The three main citation styles are MLA, APA, and Chicago. Each one has its own synthesis essay format and conventions described below.
MLA stands for Modern Language Association and is a citation style used for papers in the Humanities like art, literature, and philology. These are the key formatting rules for MLA:
- Font should be Times New Roman
- Font size should be 12
- The entire paper should be double-spaced
- Margins should be 1 inch
- Titles should be centered
- Include your last name and the page number on each page
- The header should contain your name, your professor’s name, the date, and the course code
- The research page at the end should be titled “Works Cited”
- Journal Citation Format: Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Journal Title Series Volume. Issue (Year Published): Page(s). Database Name. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
- Newspaper (Print) Citation Format: Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Article: Subtitle if Any." Name of Newspaper, Date of Publication, p. Page Number.
- Newspaper (Online) Citation Format: Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Article: Subtitle if Any." Title of Website, Date of Publication, URL. Accessed Day Month Year site was visited.
- Website Citation Format: Author's Last Name, First Name. Title of Website, Name of Organization Affiliated with the Website, Date of copyright or date last modified/updated, URL. Accessed Day Month Year site was visited.
APA stands for American Psychological Association and is a citation style used for science, education, and psychology. These are the key formatting rules for APA:
- Include a Title Page
- Include an Abstract
- Include the page number on each page
- The header should contain the page number and the paper’s title
- The research page at the end should be titled “References”
- Journal Citation Format: Author’s last name, Author’s first initial. Author’s middle initial. (Year, Month Date Published). Article title. Journal Name, Volume (Issue), page number(s).
- Newspaper Print Citation Format: Author, A. (Year, Month Date of Publication). Article title. Newspaper Title, pp. Xx-xx.
- Newspaper Online Citation Format: Author, A. (Year, Month Date of Publication). Article title. Newspaper Title, Retrieved from newspaper homepage URL
- Website Citation Format: Author’s last name, Initial(s). (Year, Month Day of publication). Title of work. Website. https://URL
The Chicago style is used for history, business, and the fine arts. These are the key formatting rules for the Chicago style:
- The space between lines should be double-spaced
- Use half-inch indents for the beginning of every paragraph
- Use the full names of people and organizations
- The research page at the end should be titled “Bibliography”
- There are 2 main ways of citing sources, Author-Dates and Notes-Bibliography
- Author-Dates uses parenthetical citations in the text referencing the source's author's last name and the year of publication.
- Notes-Bibliography uses numbered footnotes in the text to direct readers to a short citation at the bottom of the page.
- Both styles have a full bibliography as well
- Full source citations are in alphabetical order
Did you like our inspiring Synthesis Essay Guide?
For more help, tap into our pool of professional writers and get expert essay editing services!
Synthesis Essay Topics
Here are 30 topics to inspire you. You can think of these as brief synthesis essay thesis examples.
What is the impact of culture on academic success?
How does social media influence feelings of loneliness?
How does human crated sound pollution impact urban wildlife?
What will the impact of self-driving cars be on the trucking industry?
Were superheroes better role models in the past as compared to now?
How can private drones be policed?
Will machine learning ever be able to make human artists obsolete?
Does privatization of infrastructure make sense for developing countries?
What would be the best way to communicate with aliens?
Are there negative aspects of meditation?
What is the biggest potential reason for a potential World War III?
Do tall people make better leaders?
Self-fulfilling prophecies and confirmation bias explain why some predictions come true.
What can we learn from interactions with indigenous tribes?
What are the key steps developed countries must take to manage future pandemics?
How have volcanos shaped the Earth’s climate?
What is the impact of snow on overall mood?
Is it possible to reduce the wage gap fairly?
Does having pets enhance the quality of life?
Has the rise of visual media killed imagination?
Which societies in the past have been matriarchal?
How can video games help those with mental disorders?
Which is the worst seven deadly sin?
Why Anime is better than western animation
Is honor beneficial or detrimental in sports?
What are the problems with social Darwinism?
Can anyone become a model now?
What does it take to be considered an expert?
Where is the line between advertising and manipulation?
Is there an objective idea of ethical behavior?
Here are some tips to keep in mind when writing your essay.
- Write in the third person
- Make sure your research comes from credible sources
- Cite every fact
- Write multiple drafts of your essay
- Spend time editing and proofreading
- Organize your arguments clearly
- Think about your audience
- Use technical terms
- Use paragraph transitions
- Use a synthesis essay outline template
- Use present tense for MLA
- Use past tense for APA
What Not To Do
- Use informal language
- Rely only on opinion
- Use the passive voice
- Stick to the outline template exactly
- Use fewer than three sources
- Use more than five sources
- Submit the first draft
A synthesis essay might be more technical than the types of writing you’re used to, but don’t stress too much. If you think about it as any other essay, but just a little more research-intensive, it’ll be easy to write. Choose a topic that you are interested in to make the research more fun. If you know about the topic, it will guide your research and make the writing flow more smoothly as well. Citations may seem daunting, but using a citation generator will make it a cinch!
If you need assistance with writing a synthesis essay, Studyfy has a team of qualified coursework writers who can provide you with high-quality, custom essays. Whether you need to order an essay online, or require help with essay editing or proofreading, our experts are available to assist you. Don't hesitate to contact us and say " write my essay for me " if you need any kind of academic assistance.
Featured Posts
How to write a scholarship essay.

How to Write a Movie Review

How to Write an Argumentative Essay

How to Write a Cause and Effect Essay
.jpg)
How to Write an Expository Essay

How to Write an Analytical Essay

)
How to write a good AP synthesis essay
Published September 27, 2020. Updated June 7, 2022.
Synthesis Essay Definition
A synthesis essay uses information from multiple sources to support an argument or explanation.
Overview of Synthesis Essay Writing
First, take some time to develop a thorough understanding of what you will be writing about. Take notes as you go, keeping track of points you want to make and evidence you want to include in the essay. While you read, you can begin to brainstorm a thesis statement and outline for the essay. Writing an outline will help structure your essay and keep you on track. The standard synthesis essay outline includes an introduction, body, and conclusion. Spend adequate time reviewing the instructions, sources, and prompts.
The AP English Language and Composition (also known as AP Lang) exam is composed of two sections: a Multiple Choice section and a Free Response section. It’s normal to be nervous before an exam, especially an AP exam. If you’re not sure what to expect from the AP Lang synthesis essay, never fear. Here you can read about everything you need to know before exam day, including:
- the purpose of the synthesis essay
- what to expect from the sources and prompt
- a sample prompt and response
- how the synthesis essay is scored
- how to write a high-scoring synthesis essay
Worried about your writing? Submit your paper for a Chegg Writing essay check , or for an Expert Check proofreading . Both can help you find and fix potential writing issues.
Synthesis essay
The College Board describes the synthesis essay this way:
“After reading 6–7 texts about a topic (including visual and quantitative sources), students will compose an argument that combines and cites at least 3 of the sources to support their thesis.”
You will have 45 minutes to complete the synthesis essay. How you use this time is up to you, but below we’ve included a timeline for how you might choose to use your 45 minutes.
What will the sources and prompt be like?
The six to seven sources will all be centered on a specific topic. In past exams, the prompt has been focused on subjects like alternative energy and eminent domain. At least two of the sources will be visual, and at least one will be numerical (a chart or graph). The others will be text passages of roughly 500 words.
Before the sources, you’ll be given directions and a writing prompt. The prompt will explain the topic, then present a claim for you to respond to. Your response should synthesize material from at least three of the sources, forming a full-fledged essay.
See a sample synthesis essay prompt directly from the College Board linked here.
Following the directions in this sample prompt, you’ll find Sources A-F. Click here to view sample student responses.
How will my synthesis essay be scored?
Synthesis essays will be scored on a range from 0 to 6 based on an analytic rubric. This score will be the total of three scores based on three categories: your thesis, your evidence and commentary, and your sophistication.
Click here to review the complete free-response scoring guidelines for the 2020 AP Lang exam. As a quick summary, we’ll provide the College Board’s descriptions for what warrants the highest and lowest points in each category.
According to the AP English Language Scoring Rubrics, 0 points in the thesis category will be given “for any of the following”:
- There is no defensible thesis.
- The intended thesis only restates the prompt.
- The intended thesis provides a summary of the issue with no apparent or coherent claim.
- There is a thesis, but it does not respond to the prompt.
1 point in the thesis category will be given to essays that respond “to the prompt with a thesis that presents a defensible position.”
0 points will be given in the evidence and commentary section to any essay that “Simply restates thesis (if present), repeats provided information, or references fewer than two of the provided sources.”
4 points will be given in the evidence and commentary section to an essay that “Provides specific evidence from at least three of the provided sources to support all claims in a line of reasoning” and “Consistently explains how the evidence supports a line of reasoning.”
Finally, in the sophistication category , 1 point will be given to an essay that demonstrates “sophistication of thought and/or develops a complex understanding of the rhetorical situation.” 0 points will be given to essays that do not meet that criteria.
While it’s natural to worry about your score, keep in mind that your scorers know you have less than an hour to complete your synthesis essay. They know it is essentially a first draft, and they will pay more mind to what you do right than what you do wrong. Even the highest-scoring essays will contain occasional errors, so worry less about perfection than your holistic argument and synthesis.
How to write a high-scoring synthesis essay
Before we dive into what makes a high-scoring synthesis essay, let’s cover the basics. What is a synthesis essay?
Basically, a synthesis essay uses information from multiple sources to support an argument or explanation. However, when it comes to the AP Lang exam, you will be writing an argumentative synthesis essay.
You’ll take an argumentative stance, which you will express via your thesis statement, and argue in favor of that stance using evidence from multiple sources.
Outstanding AP Lang synthesis essays tend to do the following things very well. They:
- demonstrate an understanding of the topic at hand.
- express understanding of the topic’s importance.
- make the writer’s opinion on the topic clear early on.
- frequently cite examples from the sources, such as statistics and quotes.
- conclude with a strong “so what” point.
To write an essay that succeeds in all of these areas, you should use a few strategies on exam day.
Read, read, and read again
One of the worst mistakes you can make is to jump into outlining and writing before you’ve read and analyzed the directions, prompt, and sources. Though you have limited time, it’s worth taking some time to develop a thorough understanding about what you’ll be writing about.
Take notes as you go, keeping track of points you want to make and evidence you want to include in your essay. While you read, you can begin to brainstorm a thesis statement and outline for your essay.
Follow an outline
Even if you’re more of a “fly by the seat of your pants” type, an outline will help structure your essay and keep you on track.
Below is a standard synthesis essay outline to keep in mind. However, this is only an example, and your argument may not fit this outline exactly.
- Give a bit of context on the subject, demonstrating the knowledge you gained from reviewing the sources.
- Give a clear and concise thesis statement that presents your argument.
- Topic sentence
- Evidence #1
- Evidence #2
- Sum up the main points made in the essay.
- Restate the thesis statement
- End on a “so what?” statement.
Don’t lose track of time
While it’s vital you spend adequate time reviewing the instructions, sources, and prompt, it’s a lost cause if you don’t leave yourself enough time to outline and write!
Here’s a handy timeline to keep in mind during the 55-minute-long synthesis essay portion of the AP Lang exam:
- Reading the directions, sources, and prompt: 15 minutes
- Analyzing the sources and outlining your response: 10 minutes
- Drafting your response: 25 minutes
- Reviewing and revising your response: 5 minutes
Before you turn in that paper, don’t forget to cite your sources in APA format , MLA format , or a style of your choice.
Sample synthesis essay
Although you cannot know what your prompt and sources will be before exam day, you can prepare beforehand by reading sample synthesis essays and writing practice essays from past questions .
AP synthesis example essay
Based on the 2020 prompt :
The impact of television on political matters has been under debate for years. Television provides a low-cost method to stay informed about policy changes and receive important announcements, and it often offers a path to learn more about political figures and their plans for the United States. However, critics of television believe that there is a strong psychological and marketing strategy in play, which presents false images of personalities and is commonly used as a tool to sway public opinion. While there are drawbacks to broadcasting debates and politics , it positively influences presidential elections by providing accessible information to viewers , shar ing the candidate s’ personali ties , plans, and ideals during their potential role as president, and ultimately assisting citizens in casting their vot e.
The primary benefit of televising politics is t hat it provides accessible information . Television, as s ource A explains , provides an opportunity for citizens to be more involved in political matters than ever before, specifically by adding to their knowledge. With public speeches and political events televised, viewers can learn about the structure of the U.S. political system and build a better understanding of how legislation is created, in addition to their representative s’ contribution s to political matters. The reach of television is clear, as shown in Source D, where millions of viewers tune in every four years for the presidential debates. T he data reports that 80.6 million people view ed the debates in 1980, and even in 1996, the chart’s lowest year of ratings, 46.1 million viewers tuned in — all who may have been influenced to vote ! The data shows that television is unmatched in its ability to reach voters , proving that it is a beneficial tool for providing information to help citizens make their choices .
Television also works as a trust-building tool between the viewer and the presidential candidate s . Although the criticism from Source C — which claim s that televised debates are largely focused on image instead of content — is noteworthy, we must also consider the relationship development that occurs between the constituent and the politician. For example, consider the story of Walter Cronkite, who performed investigat ive journalism on-site in Vietnam to deliver a message about his opinion of the war. In doing so, he was able to shift the support for the ongoing war into a national call for closure, resulting in the end of the United States ’ presence in Vietnam and potentially saving thousands of live s (Source E) . For presidents, their arguments, vision, and speeches can establish trust with the viewers, raising citizens’ confidence in their ability to do the job successfully. Though televised appearances do result in investment in public relation campaigns and sometimes support an inauthentic view of their subjects , at the same time, television serves as an important tool to connect citizens with their president and candidates .
Perhaps the most troubling element of televisi ng presidential elections is the threat of commercialism. With the variety of issues and complaints regarding legislation and public policy, presidential candidates may use their live airtime to tackle only the most popular economic and social issues. T ed Koppel analyzed this phenomenon during a past presidential debate, in which the television station structured the debate to limit responses from the candidates (Source F) . This approach is somewhat deceptive, forcing the candidates to come up with quick answers while masking other issues. For example, only the most popular social issues may have been brought up, sidelining complex political matters and policy problems that may have been ongoing for years. However, while this format surely limits candidates ’ ability to share their opinions on a wide variety of issues, television does allow the candidates to connect with the masses, which may not be possible through other forms of communication. I f necessary , the format of future debates could be restructured to create more space for complex argumentation without sacrificing the benefits of televised communication.
In summary, t he influence of television is unprecedented, allowing presidential candidates and other politicians to connect with viewers from across the nation. The critics are justified in remarking that televised debates may mislead citizens through their emphasis on public image. However, if audiences analyz e the debates, announcements, and other such matters with a critical approach, this highly accessible form of communication encourages people to build trust with presidential candidates, enhance their worldview, and feel more involved in political matters.
Works cited
“AP English Language.” AP Central , 13 Aug. 2020, apcentral.collegeboard.org/courses/ap-english-language-and-composition/exam.
“AP English Language and Composition Free-Response Questions Scoring Rubrics, Effective Fall 2019.” The College Board, 2019, https://apcentral.collegeboard.org/pdf/ap-english-language-and-composition-frqs-1-2-3-scoring-rubrics.pdf
“AP English Language and Composition 2020 Free-Response Scoring Guidelines Applied to the 2019 Exam Questions.” The College Board, 2019, https://apcentral.collegeboard.org/pdf/ap-english-language-and-composition-2020-frq-scoring-guidelines-2019-exam-questions-0.pdf
Published September 8, 2020.
By Jolee McManus. Jolee earned a BA in English from the University of Georgia. She has several years of experience as a writing tutor and freelance copywriter and editor.
Common Writing Assignments, Apps & Tests
- Analytical Essay
- AP synthesis Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Book Report
- Compare and Contrast Essay
- Cause and Effect Essay
- College Admissions Essay
- Critical Analysis Essay
- Definition Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Dissertation
- Explanatory Essay
- Expository Essay
- Informative Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Opinion Essay
- Personal Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Reflective Essay
- Research Paper
- Rhetorical Analysis
- Scholarship Essay
- Short Essay
- Thesis Paper

What’s included with a Chegg Writing subscription
- Unlimited number of paper scans
- Plagiarism detection: Check against billions of sources
- Expert proofreading for papers on any subject
- Grammar scans for 200+ types of common errors
- Automatically create & save citations in 7,000+ styles
- Cancel subscription anytime, no obligation
How to Synthesize Written Information from Multiple Sources
Shona McCombes
Content Manager
B.A., English Literature, University of Glasgow
Shona McCombes is the content manager at Scribbr, Netherlands.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
On This Page:
When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you’ve read – you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own research fits in).
Synthesizing simply means combining. Instead of summarizing the main points of each source in turn, you put together the ideas and findings of multiple sources in order to make an overall point.
At the most basic level, this involves looking for similarities and differences between your sources. Your synthesis should show the reader where the sources overlap and where they diverge.
Unsynthesized Example
Franz (2008) studied undergraduate online students. He looked at 17 females and 18 males and found that none of them liked APA. According to Franz, the evidence suggested that all students are reluctant to learn citations style. Perez (2010) also studies undergraduate students. She looked at 42 females and 50 males and found that males were significantly more inclined to use citation software ( p < .05). Findings suggest that females might graduate sooner. Goldstein (2012) looked at British undergraduates. Among a sample of 50, all females, all confident in their abilities to cite and were eager to write their dissertations.
Synthesized Example
Studies of undergraduate students reveal conflicting conclusions regarding relationships between advanced scholarly study and citation efficacy. Although Franz (2008) found that no participants enjoyed learning citation style, Goldstein (2012) determined in a larger study that all participants watched felt comfortable citing sources, suggesting that variables among participant and control group populations must be examined more closely. Although Perez (2010) expanded on Franz’s original study with a larger, more diverse sample…
Step 1: Organize your sources
After collecting the relevant literature, you’ve got a lot of information to work through, and no clear idea of how it all fits together.
Before you can start writing, you need to organize your notes in a way that allows you to see the relationships between sources.
One way to begin synthesizing the literature is to put your notes into a table. Depending on your topic and the type of literature you’re dealing with, there are a couple of different ways you can organize this.
Summary table
A summary table collates the key points of each source under consistent headings. This is a good approach if your sources tend to have a similar structure – for instance, if they’re all empirical papers.
Each row in the table lists one source, and each column identifies a specific part of the source. You can decide which headings to include based on what’s most relevant to the literature you’re dealing with.
For example, you might include columns for things like aims, methods, variables, population, sample size, and conclusion.
For each study, you briefly summarize each of these aspects. You can also include columns for your own evaluation and analysis.
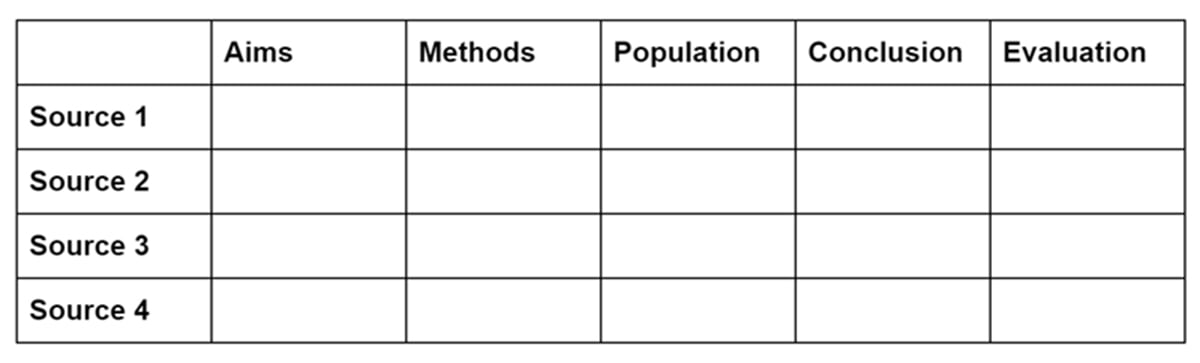
The summary table gives you a quick overview of the key points of each source. This allows you to group sources by relevant similarities, as well as noticing important differences or contradictions in their findings.
Synthesis matrix
A synthesis matrix is useful when your sources are more varied in their purpose and structure – for example, when you’re dealing with books and essays making various different arguments about a topic.
Each column in the table lists one source. Each row is labeled with a specific concept, topic or theme that recurs across all or most of the sources.
Then, for each source, you summarize the main points or arguments related to the theme.
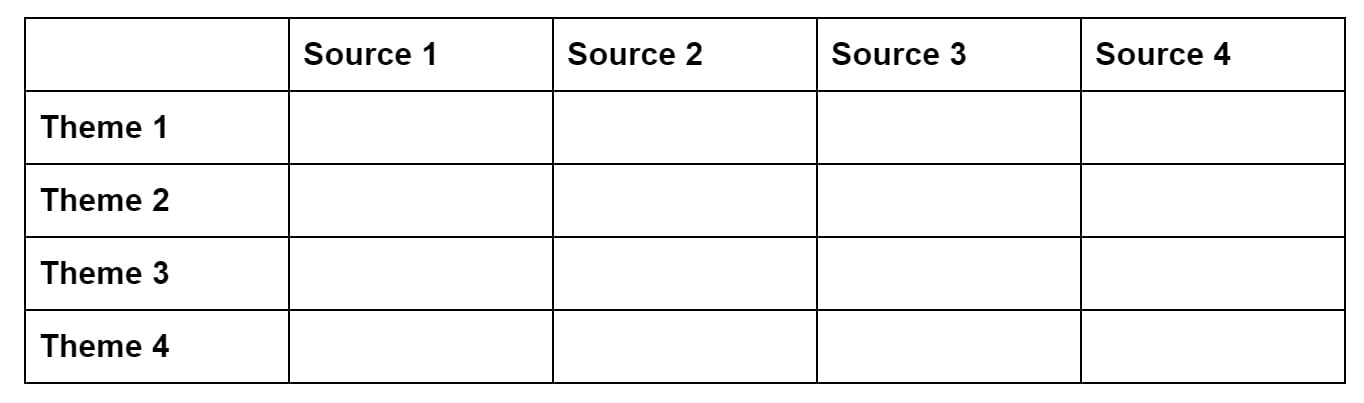
The purposes of the table is to identify the common points that connect the sources, as well as identifying points where they diverge or disagree.
Step 2: Outline your structure
Now you should have a clear overview of the main connections and differences between the sources you’ve read. Next, you need to decide how you’ll group them together and the order in which you’ll discuss them.
For shorter papers, your outline can just identify the focus of each paragraph; for longer papers, you might want to divide it into sections with headings.
There are a few different approaches you can take to help you structure your synthesis.
If your sources cover a broad time period, and you found patterns in how researchers approached the topic over time, you can organize your discussion chronologically .
That doesn’t mean you just summarize each paper in chronological order; instead, you should group articles into time periods and identify what they have in common, as well as signalling important turning points or developments in the literature.
If the literature covers various different topics, you can organize it thematically .
That means that each paragraph or section focuses on a specific theme and explains how that theme is approached in the literature.
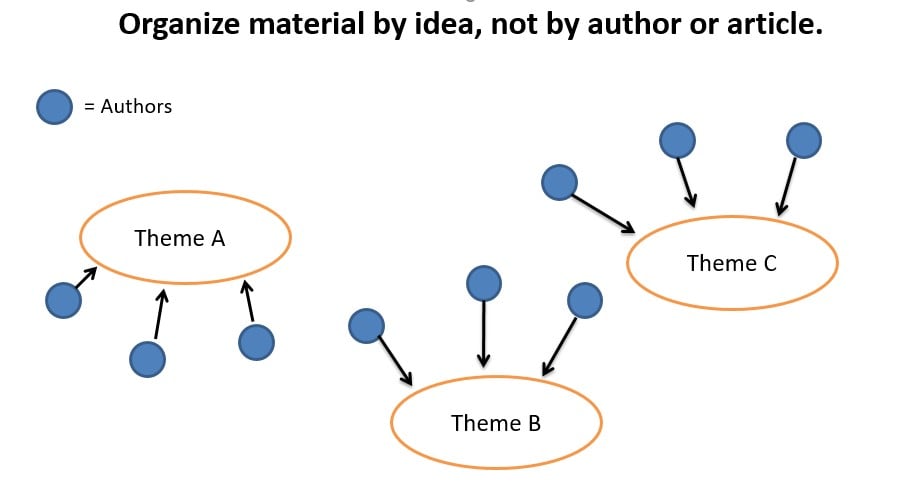
Source Used with Permission: The Chicago School
If you’re drawing on literature from various different fields or they use a wide variety of research methods, you can organize your sources methodologically .
That means grouping together studies based on the type of research they did and discussing the findings that emerged from each method.
If your topic involves a debate between different schools of thought, you can organize it theoretically .
That means comparing the different theories that have been developed and grouping together papers based on the position or perspective they take on the topic, as well as evaluating which arguments are most convincing.
Step 3: Write paragraphs with topic sentences
What sets a synthesis apart from a summary is that it combines various sources. The easiest way to think about this is that each paragraph should discuss a few different sources, and you should be able to condense the overall point of the paragraph into one sentence.
This is called a topic sentence , and it usually appears at the start of the paragraph. The topic sentence signals what the whole paragraph is about; every sentence in the paragraph should be clearly related to it.
A topic sentence can be a simple summary of the paragraph’s content:
“Early research on [x] focused heavily on [y].”
For an effective synthesis, you can use topic sentences to link back to the previous paragraph, highlighting a point of debate or critique:
“Several scholars have pointed out the flaws in this approach.” “While recent research has attempted to address the problem, many of these studies have methodological flaws that limit their validity.”
By using topic sentences, you can ensure that your paragraphs are coherent and clearly show the connections between the articles you are discussing.
As you write your paragraphs, avoid quoting directly from sources: use your own words to explain the commonalities and differences that you found in the literature.
Don’t try to cover every single point from every single source – the key to synthesizing is to extract the most important and relevant information and combine it to give your reader an overall picture of the state of knowledge on your topic.
Step 4: Revise, edit and proofread
Like any other piece of academic writing, synthesizing literature doesn’t happen all in one go – it involves redrafting, revising, editing and proofreading your work.
Checklist for Synthesis
- Do I introduce the paragraph with a clear, focused topic sentence?
- Do I discuss more than one source in the paragraph?
- Do I mention only the most relevant findings, rather than describing every part of the studies?
- Do I discuss the similarities or differences between the sources, rather than summarizing each source in turn?
- Do I put the findings or arguments of the sources in my own words?
- Is the paragraph organized around a single idea?
- Is the paragraph directly relevant to my research question or topic?
- Is there a logical transition from this paragraph to the next one?
Further Information
How to Synthesise: a Step-by-Step Approach
Help…I”ve Been Asked to Synthesize!
Learn how to Synthesise (combine information from sources)
How to write a Psychology Essay

How to Write a Synthesis Essay: Your Guide From Start to Finish

Today, we're swamped with information, like reading 174 newspapers every day. It comes from all over—news, social media, science, and more. This flood might make you feel overwhelmed and lost in a sea of facts and opinions. But being able to make sense of it all is crucial.
In this guide, we'll show you steps for choosing the right topic and organizing your essay. Let's dive in and learn how to turn scattered facts into powerful essays that really stand out. If you're looking for assistance in writing a paper, you can consider the option to order essay from our expert writing service.
What Is a Synthesis Essay
Synthesis essay is an academic assignment where you take information from several sources and combine it to create a new, unified argument. Throughout the essay, you'll weave in evidence and insights from your sources to support your thesis, explaining how each source contributes to your overall argument.
Synthesis essays are commonly assigned in high school and undergraduate courses across various disciplines. They are a great way to develop critical thinking, research, and writing skills. They are particularly useful when a topic has multiple angles or ongoing debates, as they train you to analyze information objectively and form your own well-supported conclusions.
If you're struggling with this task, just ask us to ' write paper for me ,' and we'll handle your assignment for you.
How to Write a Synthesis Essay with Easy Steps
Writing a synthesis essay requires a methodical approach to blend information from different sources into a strong and persuasive argument. Here are steps to help you along the way.
1. Choose Your Topic:
- Make sure it's broad enough to allow for multiple perspectives but specific enough for focused research.
- Look for topics with ongoing debates or with room for your own interpretation.
2. Research and Gather Sources:
- Use credible sources like academic journals, books, and reputable news websites. Aim for a variety of perspectives to ensure a well-rounded analysis.
- Take notes while researching! Focus on key points, evidence, and the author's main arguments.
3. Develop Your Thesis Statement:
- This is the central argument of your essay, informed by your research.
- It should clearly state how the different sources will be used to create a unified perspective.
4. Structure Your Essay:
- Introduction: Briefly introduce the topic, highlight the various perspectives, and present your thesis statement.
- Topic Sentence: Briefly introduce the point you'll be making in this paragraph.
- Analysis & Evidence: Integrate information from your sources, explaining how they support your point. Use in-text citations and proper formatting.
- Commentary: Explain the significance of the source material and how it contributes to your overall argument.
- Conclusion: Summarize your main points and reiterate the importance of your thesis statement. You can also offer further implications or remaining questions on the topic.
5. Write and Revise:
- Draft your essay, ensuring smooth transitions between your ideas and source integration.
- Revise for clarity, proper citation format, and strong argument flow.
For a more detailed explanation on how to write a conclusion , check out our special guide.
Synthesis Essay Example
Here are a couple of synthesis essay examples that demonstrate how to apply the synthesis process in real life. See how they tackle a wide range of issues by drawing on diverse perspectives.
Ready to Transform Your Synthesis Essay from Bland to Grand?
Let's tap into the magic of our expert wordsmiths, who will create an essay that dances with ideas and dazzles with creativity!
Synthesis Essay Thesis Statement
A strong thesis statement for a synthesis essay is more nuanced than a simple opinion. It acknowledges the complexities of the topic and positions your essay as a bridge between existing perspectives. Here's how to craft an effective thesis:
- Avoid extremes: Statements like "Social media is destroying society" are too broad and lack specific arguments. Saying "Taxes are bad" ignores potential benefits or complexities.
- Acknowledge Nuance: Show you understand different viewpoints by using qualifiers like "often," "in some cases," or "to a certain extent."
- Bridge the Gap: Your thesis should connect various source viewpoints to create a new perspective.
Example transformation:
Original (weak): Video games are a waste of time.
Improved: While video games can be a source of leisure, their excessive use can negatively impact academic performance and social interaction. (This acknowledges the entertainment value while highlighting potential drawbacks.)
- Your thesis should be specific to your topic and the sources you'll use.
- It should be clear, concise, and directly address the prompt.
- It sets the stage for your argument by outlining the connections between your chosen sources.
Synthesis Essay Checklist
Writing a strong synthesis essay requires careful attention to detail. Use this checklist to ensure you've covered all the bases:
| Criteria | Questions |
|---|---|
| Clear Thesis Statement 📜 | Does your thesis clearly state how you'll use multiple sources to create a unified perspective? |
| Source Integration 🔗 | Do you seamlessly weave evidence and insights from your sources throughout the essay? |
| Balanced Analysis ⚖️ | Do you acknowledge different viewpoints and offer fair treatment to all sources? |
| Strong Argument Flow 🌊 | Do your ideas transition smoothly, building a cohesive argument towards your thesis? |
| Grammar and Punctuation ✅ | Is your essay free of grammatical errors and typos? |
| Word Count 📏 | Does your essay meet the required word count? |
Synthesis Essay Format
A well-structured synthesis essay guides the reader through your analysis of multiple sources and effectively builds your argument. Here's a breakdown of the typical format:
- Double-space your essay unless otherwise instructed.
- Use a standard font (e.g., Times New Roman, Arial) and font size (e.g., 12 pt).
- Maintain consistent margins (e.g., 1 inch).
- Include page numbers in the top right corner (optional, but often recommended).
- Introduction (10-15% of word count):
- Body Paragraphs (60-70% of word count)
- Conclusion (10-15% of word count):
- The specific word count breakdown might vary based on your assignment instructions.
- Always follow the formatting guidelines provided by your instructor.
For a deeper understanding of a compare and contrast essay , including format and writing process, consult our dedicated article.
Explanatory vs. Argumentative Synthesis Essays
In synthesis writing, there are two main types: explanatory and argumentative. While both involve analyzing multiple sources, their ultimate goals differ. Here's a breakdown of the key distinctions between explanatory and argumentative synthesis essays:
| Criteria | Explanatory Synthesis | Argumentative Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Goal 🎯 | To clearly explain and compare/contrast different perspectives on a complex topic. | To develop a specific argument on a debatable topic, supported by evidence from multiple sources. |
| Focus 🔍 | Presents a balanced overview of various viewpoints without taking a strong personal stance. | Persuades the reader by integrating source material that strengthens your chosen position. |
| Structure 🏗️ | Highlights key arguments, evidence, and conclusions from each source, demonstrating their connections and potential contradictions. | Selectively emphasizes information from sources that align with your argument, while acknowledging and addressing opposing viewpoints. |
| Thesis Statement 📜 | Outlines the key points of comparison or contrast between the sources. | States your position on the topic and outlines how the sources will be used to support your claim. |
| Example 💡 | "This essay will explore the different approaches to tackling climate change, analyzing the proposals put forth by environmental scientists, economists, and social scientists." | "While some argue for a complete ban on social media, a more measured approach that encourages responsible use and promotes digital literacy is a more effective solution." |
And if you're keen on knowing how to write an informative essay , we've got you covered on that, too!
Synthesis Essay Topics
Picking essay topics is just the beginning. To write a great synthesis essay, you need to carefully evaluate and connect different sources to build a strong argument or viewpoint. Here's a step-by-step infographic guide to help you choose the right synthesis essay topics wisely.
There are myriads of essay topics , so how do you choose the right one? Don’t waste your time, here we offer some great ideas:
- What role does effective communication play in resolving international conflicts?
- Are video games a legitimate form of art?
- Does standardized testing hinder critical thinking skills?
- Is cultural appropriation a valid concern or does it stifle artistic exchange?
- Should economic growth outweigh environmental sustainability and social welfare?
- Is the traditional family structure the best model for child-raising?
- Should social media platforms curb misinformation?
- Is artificial intelligence a boon for scientific discovery, or does it pose ethical challenges?
- Is globalization more about economic prosperity or cultural homogenization?
- Should controversial historical monuments be preserved?
- Can renewable energy alone combat climate change, or are more drastic measures necessary?
- Should artistic expression face censorship or enjoy complete freedom?
- How can national security and individual privacy be balanced in the digital age?
- Does the cost of higher education hinder social mobility?
- Does automation threaten jobs or create new opportunities?
If you’re interested in persuasive essays topics , this guide's got your back.
Concluding Thoughts
Writing a synthesis essay is a great way to learn about a topic. It lets you explore different viewpoints and see how they fit together. This guide gives you the steps to follow for a strong essay. Remember, the goal is to use what you learn from your sources to create your own unique understanding. So next time you have a complex topic, give a synthesis essay a try! You might be surprised by what you learn.
Want an Essay that Sings, Sparkles, and Stuns?
Fear not! Our expert wordsmiths are here to turn your thoughts into a symphony of ideas!
How Should You Conclude a Synthesis Essay?

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
.webp)
How to Write a Synthesis Essay: Examples, Topics, & Outline
A synthesis essay requires you to work with multiple sources. You combine the information gathered from them to present a well-rounded argument on a topic. Are you looking for the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing? You’ve come to the right place!
In this guide by our custom writing team, you will find:
- a step-by-step writing guide;
- a list of 34 synthesis essay topics;
- a full essay sample in MLA format.
- 📚 Synthesis Essay Definition
- 📝 Essay Types
- ✅ Step-by-Step Guide
- ✍️ Topics & Prompts
- 📑 Example & Formatting Tips
📚 What Is a Synthesis Essay?
A synthesis essay is an assignment that requires a unique interpretation of a particular topic using several reliable sources. To write it, you need to understand, analyze, and synthesize information. That is why this type of essay is used in the AP Lang exam to assess students’ reasoning skills.
The key features of the synthesis essay are:
- Debatable topic . If your goal is to write a good synthesis essay, it’s necessary to choose an arguable topic. It’s best to choose something that people have different opinions about. This will allow you to use many sources with various viewpoints for your synthesis.
- Clear thesis statement. It’s a sentence that briefly describes the main idea of your essay.
- Reliable sources to prove your thesis . For a synthesis essay, your opinion is not enough. You also need to find the evidence. Keep in mind that simply reading an online encyclopedia won’t do; make sure to choose only reliable sources.
What Does It Mean to Synthesize Information?
Synthesis is a process that has huge importance in nature, science, and our everyday life. The word stems from Ancient Greek “synthesis,” which means “putting together.” In general, synthesis is the combination of components to form a connected whole.
In everyday life, we usually resort to it to synthesize information . This means taking the data from different sources and bringing it together. This process is the opposite of analyzing:
- For an analysis , you break problems into pieces,
- For a synthesis , you combine separate elements into a whole.
We use synthesis for analysis papers, research papers, argument papers, and business reports.
What Does Synthesis Mean in Writing?
Synthesis in writing means summarizing and connecting different sources considering a particular topic. Although synthesis and analysis are two opposite things, they usually go together in synthesis essays. The process consists of 2 stages:
- Conduct the analysis. For that, you break down a problem into parts and analyze the sources. It’s helpful to highlight everything regarding your topic while reading.
- Carry out the synthesis. The next step is to formulate an opinion and combine the highlighted information from the sources.
Synthesis is not only used in writing but also in reading comprehension . It’s useful to do this kind of reading while studying your sources. There are three reading comprehension stages:
- Your previous knowledge about the topic.
- Expansion of your knowledge while you are reading.
- Understanding of the problem when you have finished reading.
So, synthesized reading comprehension means combining three stages in one and formulating one statement.
Synthesis vs Summary: What Is the Difference?
A summary is a paraphrasing of the written source in your own words. For a good summary, it’s necessary to include all of the text’s key elements. Meanwhile, synthesis means combining different ideas from different sources. You don’t have to include all the key points; just choose everything related to your topic.
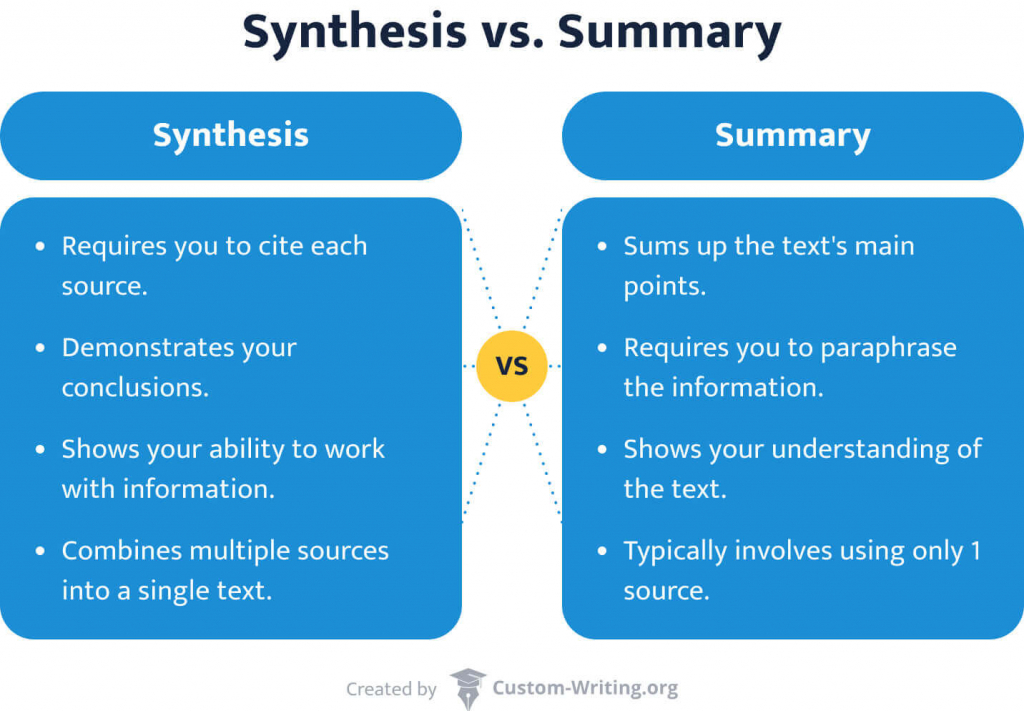
Both of these techniques are used for the synthesis essay:
- The summary goes in the conclusion. You briefly sum up your paper’s main ideas.
- Synthesis goes in the body paragraphs. Here, you combine multiple sources to prove a point.
📝 Synthesis Essay Types
There are two main types of a synthesis essay: argument and explanatory synthesis.
Both of them require working with multiple reliable sources and analyzing information. The only difference is that an argument synthesis essay requires your own opinion, while an explanatory synthesis essay does not.
Argument Synthesis Essay: Outline and Definition
As you already know, an argument synthesis essay requires you to state your own opinion about the given topic and back it up with several reliable sources. The purpose of such an essay is to persuade the reader that your point is correct.
Here’s what an argument synthesis essay consists of:
Explanatory Synthesis Essay: Definition and How to Write
An explanatory informative synthesis essay requires you to stay neutral towards the problem you are discussing. This means you cannot express your own opinion considering the given question or a problem. Your task is just to inform the reader. That’s why this essay type is also called informative synthesis.
Check out this explanatory essay outline:
✅ How to Write a Synthesis Essay Step by Step
When it comes to the synthesis essay outline, it’s not too different from other assignments. Have a look at this template:
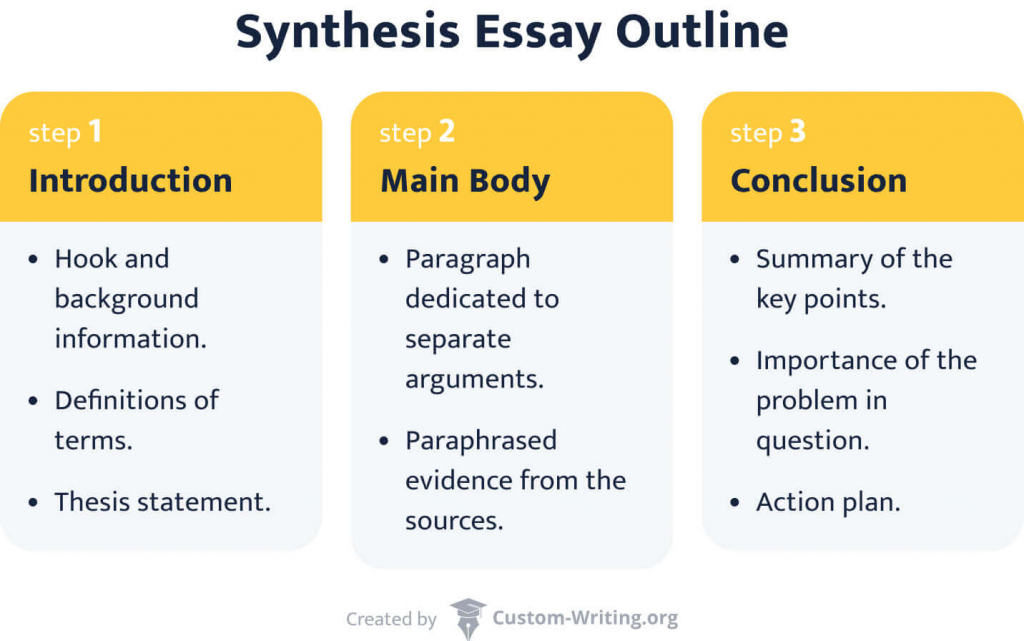
How to Synthesize: Working with Sources
After you’ve decided on your topic, it’s time to figure out how to synthesize articles into one text. This is how you do it:
- Choose reliable sources: the ones printed in journals or published on academic websites.
- Become familiar with them and see if they fit into your essay.
- Try to find a few sources for each point. It will increase your essay’s reliability.
- Relate each source to your arguments and see similarities between them.
- Don’t forget to list every source in the references.
When you are done with a comprehensive analysis of related literature, try to step back and imagine a person who has a different opinion on this topic. Think of some arguments that they can provide to prove their opinion. After you have the list of arguments, find the written evidence of why they are wrong and put them in your essay.
Analyzing and organizing sources is the first and very important step for the synthesis essay. So make sure you do understand what the text means before using it as a reference.
Synthesis Essay Outline: How to Write
For structuring your essay, it’s useful to try mapping . This technique means combining the information from different sources and rearranging it to create a new direction. To do it, you need to analyze the authors’ ideas and come up with your own conclusions.
The best way to do that is called synthesis matrix or graphic organizer. It’s a chart that you can make when you start working on your essay. Here you have a horizontal column that states the main ideas and a few vertical columns that present sources. Your task is to take sources you have chosen and write down the main ideas from them.
Here’s an example of a matrix chart:
| Topic: The influence of technologies on teenagers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
While doing that, you will see how many sources contain the same ideas. When you analyze them, you will be able to formulate your thesis backed up with evidence. The synthesis matrix also helps to see new arguments you can cover in your synthesis paper.
How to Write an Introduction for a Synthesis Essay
Now it’s time to start writing the paper. In the introductory part of the essay, you can include:
- A short yet catchy sentence or a quotation that would present the topic. The start of your essay should make people interested. It’s best to make the first sentence not only informative but also easy to understand.
- The texts that are used for the essay. Provide the titles and the authors’ names (use the appropriate guidelines depending on the writing style.)
- The background information which is needed to understand your essay. Definitions of terms or unknown words considering the topic can be included in this part. Otherwise, people may find it hard to understand what they are reading about.
How to Write a Thesis for a Synthesis Essay
A thesis statement is a point of view on a certain problem that you will defend in your essay. It should contain the key points that you want to include in your paper. Here’s how to create a perfect thesis statement:
- Find several central ideas in the chart.
- Choose the ones that are repeated the most often and the ones that you feel need to be in your essay.
- Combine them, and you have a thesis statement with all the key points.
- Make a draft of the thesis statement. Try to formulate the main idea you want to present in your essay.
- Elaborate on this idea. Add some details and expand it a bit further.
If the whole picture is coherent, and it conveys exactly what you wanted, then this is your perfect thesis statement. See the example below:
Gender inequality still exists at the workplace: women are less likely to get the most responsible positions, easily lose careers due to maternity leave, and often receive less pay for the same amount of work.
How to Write Synthesis Paragraphs for the Main Body
Your essay’s main body consists of a few paragraphs. Each of them presents a different argument considering the topic. When you start a paragraph, make sure to begin with a topic sentence, which informs the reader about the paragraph’s main idea. Then, include the synthesized sources and elaborate on them.
Here’s what you should and shouldn’t do when writing the main body:
| ✔️ Dos | ❌ Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Make sure you make the essay as informative as possible. Try to show various opinions of the authors. Avoid shuffling unrelated information into it. Try to make smooth transitions from one paragraph to another. | Instead, show your understanding and present the conclusions you’ve drawn from the texts. If you do that, you are involved in plagiarism. This would damage your credibility. |
You can use the following words to present the ideas from your sources. They will help you reflect the authors’ tone:
| Talking about arguments | Talking about research | Adding emphasis |
|---|---|---|
| The author: | The author: | The author: |
How to Conclude a Synthesis Essay
There are quite a few ways to conclude the synthesis paper. Have a look at some of the options:
- Paraphrase the thesis. As you remember, the thesis is the main idea of your essay. The conclusion is a good place to remind your readers about it. When they are done with the reading, they remember the most important thing from your essay.
- Synthesize the arguments. There is no need to repeat everything you wrote in your essay. Just briefly summarize the most crucial points.
- Answer the “So what” question. Tell the readers why this topic matters, why you’ve chosen it, and why it’s valuable for the reader.
- Provide a closure. It’s an effective strategy when you want to make the reader think. Leave them with a strong statement at the end of your essay.
Synthesis Paper Proofreading Tips
When you have finally written your paper, there is still one important thing left to do. You need to check your paper for any grammatical and contextual mistakes. You certainly can do it yourself, but it would be perfect if you could ask somebody else to read it.
The first thing you need to check grammar-wise is the tense you are using. There is no single tense you need to use for the synthesis essay. It depends on the format:
- If you’re writing in MLA format, use the present tense;
- For APA essays, you use the past tense.
The next step is to check whether your synthesis essay has everything that’s required. For that, we have prepared the checklist of questions you can ask yourself to proofread your essays.
- Is there a clear thesis statement?
- Did you include all of the key points from the synthesis?
- Are there clear transitions between paragraphs?
- Did you organize a paragraph around a single idea?
- Did you use reliable and up-to-date sources?
- Did you analyze sources rather than just summarize them?
- Did you mention every source you’ve used?
If you’ve answered “yes” to all the questions—congratulations, you are done with the essay! Otherwise, you need to come back and fix everything that you’ve answered “no” to.
✍️ Synthesis Essay Topics and Prompts
Sometimes, when you don’t have a topic , it is tough to come up with a suitable idea. That is why we have prepared two lists of topics that you can use for any synthesis essay type.
Explanatory Synthesis Essay Topics
The topics below are suitable for an explanatory synthesis essay:
- The beginning of Hollywood cinema. Cinema is a huge industry in the USA. Tell the readers about its history. Describe what it was like in the beginning, which movie was the first one, and who started this industry.
- Tactics on dealing with noisy children. Sometimes kids can be very loud, especially in public places. Write about different tactics that can help with this issue.
- The effects of climate change on the water cycle. Climate change has affected the water cycle significantly. Your task is to explain how.
- The best American cities to live in. Provide the list of the best cities and explain why you’ve included them.
- The importance of a healthy diet . Keeping a healthy diet is beneficial in many ways. Write about all the advantages it brings.
- Who can become an entrepreneur? Entrepreneurship is not for everybody. In this essay, you can describe the qualities needed for having your own business.
- The correlation between overpopulation and poverty . Describe how overpopulation leads to poverty and vice versa.
- The advantages of taking an active vacation.
- Cultural shock as a part of moving to a different country.
- The consequences of the first wave of feminism.
- Synthesis of Tan and Rodriguez’ essays ideas.
- Difficulties you may encounter during the job interview.
- How does reading prevent Alzheimer’s disease?
- The effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on businesses.
- The connection between religion and politics in ruling the country.
- What can non-verbal signals tell you about a person?
- The psychology of leadership .
- The origins of the most common stereotypes about Americans.
- Role of social media in business communication.
- The synthesis of personal nursing philosophy concept.
- Behavioral components of schizophrenia and psychosis.
- Main components of successful entrepreneurship.
- Critical components of scientific research.
- Change in religion and human beliefs throughout history.
- The effect of global warming on modern life.
Argument Synthesis Paper Topics
The list of topics for the Argument Synthesis Essay:
- Vaping is better than smoking. People are starting to exchange cigarettes for vapes and e-cigarettes. In what ways are they less harmful?
- Rich people should pay higher taxes. The same percentage of money doesn’t equal for rich and poor people. Explain why the ones who can afford more should share with others.
- Depression is a disease. Prove that psychological problems must be recognized as real health issues that should be cured and not ignored.
- Social media affects young people’s lives. Social media has a massive influence on people. In this essay, you can discuss which life spheres are the most affected.
- Beauty pageants should be banned. Provide the reasons why they should be banned and tell the reader about psychological problems they can cause.
- People should cut meat from their diet to stop global warming. Describe how the meat industry influences climate change.
- The voting age should be 25+. Your task is to show the reasons why the votes of people under 25 should not be taken into account during elections.
- A healthy lifestyle requires a lot of money.
- Each healthy man should serve in the military.
- School bullying should be punished by immediate exclusion.
- Does friendship exist between men and women?
- Drinking coffee is a bad habit.
- Working hard is more important than being talented.
- Everybody should visit a therapist at least once.
- Should universities be free?
- Artificial intelligence will cause huge unemployment rates.
- Gaming should not be allowed to children under 18.
- Components and strategies of social responsibility
- Integration of relevant ethical theory and conceptual principles in health care
- Children under 10 should be banned from gadgets.
- Social media platforms facilitate cyberbullying.
- Issues of distance education.
- Social media addiction is a serious disease.
- Deforestation critically contributes to global warming.
- Healthcare should be free for everyone.
📑 Synthesis Essay Example & Synthesis Essay Format Tips
Now let’s talk about formatting. There are two writing styles you can use for a synthesis essay: APA or MLA. You need to choose the one that is required for your assignment.
We will start with the paper in APA format. It is usually used in science and education.
| Format | |
| Title page | |
| In-text citations | Example: The artworks from the past are entirely different from the modern ones (Benjamin, 1935) Example: According to Benjamin (1935), “Mechanical reproduction of a work of art…” (p.7) |
| References | Example: Benjamin, W. (1935). The Work of Art in the Age of Mechanical Reproduction. Random House |
And these are MLA formatting rules:
| Format | |
| Title page | |
| In-text citations | Example: The artworks from the past are entirely different from the modern ones (Benjamin 7) |
| References | Example: Benjamin, Walter. Random House, 1935 |
Finally, we’ve prepared a synthesis essay sample for you to check out. Feel free to download the PDF file below:
First introduced in the Civil Rights Act of 1964, affirmative action policies aim to mitigate the discrepancy in opportunities available for underrepresented social groups by taking into account one’s minority background. The policies have become a pressing public issue that obstructs previously marginalized individuals, particularly in the educational environment.
Thank you for reading the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing. We hope you found it helpful. Don’t forget to share it with your friends. Good luck with your assignments!
🔍 References
- Writing a Synthesis Essay: Bowling Green State University
- What Is Synthesis: University of Manitoba
- Synthesis: Biology Online
- Reading Strategies: Difference Summarizing and Synthesizing: WordPress
- Summary, Analysis, Synthesis Definitions: University of Utah
- Argumentative Synthesis: University of Arkansas
- How to Synthesize Written Information: Simply Psychology
- Mapping of Synthesis Essay: University of Nevada, Reno
- Writing a Literature Review and Using a Synthesis Matrix: Florida International University
- Synthesis Essay: Cleveland State University
- Literature Review: Synthesizing Multiple Sources: Louisiana State University
- Writing a Conclusion: Texas Women’s University
- General APA Guidelines: Purdue University
- Share to Facebook
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Do you know how to make your essay stand out? One of the easiest ways is to start your introduction with a catchy hook. A hook is a phrase or a sentence that helps to grab the reader’s attention. After reading this article by Custom-Writing.org, you will be able to...

A critical analysis essay is an academic paper that requires a thorough examination of theoretical concepts and ideas. It includes a comparison of facts, differentiation between evidence and argument, and identification of biases. Crafting a good paper can be a daunting experience, but it will be much easier if you...

Critical thinking is the process of evaluating and analyzing information. People who use it in everyday life are open to different opinions. They rely on reason and logic when making conclusions about certain issues. A critical thinking essay shows how your thoughts change as you research your topic. This type...

Process analysis is an explanation of how something works or happens. Want to know more? Read the following article prepared by our custom writing specialists and learn about: So, let’s start digging deeper into this topic! ♻️ What Is Process Analysis? A process analysis describes and explains the succession of...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any...
![what does the synthesis essay entail Critical Writing: Examples & Brilliant Tips [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/fingers-note-report-journalist-filling-284x153.jpg)
Any critique is nothing more than critical analysis, and the word “analysis” does not have a negative meaning. Critical writing relies on objective evaluations of or a response to an author’s creation. As such, they can be either positive or negative, as the work deserves. To write a critique, you...

If you are assigned to write a rhetorical analysis essay, you have one significant advantage. You can choose a text from an almost infinite number of resources. The most important thing is that you analyze the statement addressed to an audience. The task of a rhetorical analysis essay is to...

Any literary analysis is a challenging task since literature includes many elements that can be interpreted differently. However, a stylistic analysis of all the figurative language the poets use may seem even harder. You may never realize what the author actually meant and how to comment on it! While analyzing...

As a student, you may be asked to write a book review. Unlike an argumentative essay, a book review is an opportunity to convey the central theme of a story while offering a new perspective on the author’s ideas. Knowing how to create a well-organized and coherent review, however, is...

The difference between an argumentative and persuasive essay isn’t always clear. If you’re struggling with either style for your next assignment, don’t worry. The following will clarify everything you need to know so you can write with confidence. First, we define the primary objectives of argumentative vs. persuasive writing. We...
Mapping a synthesis essay
When asked to write a synthesis essay, many students question the word “synthesis.” What does it mean to synthesize? Well, the dictionary tells us that synthesis is the combination of ideas to form a theory; the thesaurus provides synonyms such as fusion, blend, and creation. So ultimately, you are creating a combination of what your sources are conversing about (subject X) and how you have rearranged what is being said to create a new direction for that subject. This quick outline should get you well on your way to synthesizing.
Read your sources carefully and annotate as you go.
- Read through once for a general understanding of the source.
- Use a highlighter to call your attention to specific passages that you feel are key to this issue.
- Make summary notes as you go, so you remember why you highlighted those passages.
Analyze the data you are getting.
- Ask yourself what the author’s claim is–make note of it.
- When the author brings in evidence, what is it? How does this evidence support the claim?
- Note any common beliefs or assumptions embedded in the author’s use of evidence and claims.
What are sources “saying” to each other?
- When you can summarize what each source is saying, then you can take a step back and ask yourself: Is there a pattern; how are these sources communicating/responding to each other?
- Example: If The New York Times is speaking on gun control, they may say “X.” Later, Fox News may also be talking about gun control, but they are saying “Y.” Both are discussing gun control as the “conversation,” just in different ways and at different times.
- Example: So, when you arrange the above example’s conversation, you can see that these sources are talking about “X” and “Y,” in terms of gun control, but no one seems to be specifying about “Z”. “Z” will be the gap in the conversation (you can suggest it as a new research area, new point to consider, etc.).
Figure out what your particular stand is on this issue.
- After seeing where others stand, where do you stand?
- If you agree or disagree, why?
- If you agree, but not quite, what could be done differently? How could you make a position that might be a bit different than what other authors are saying?
Take a moment to consider how others in the conversation might respond to your position.
- Why would article X’s author argue with you?
- How would this author argue with you?
- If the author would agree with you, same thing –how and why?
After this imaginary conversation with your sources, you should be getting an idea about your thesis and where it fits into the “conversation” that your sources are having.
- Research about topic A is currently indicating…
- Maybe a lot of people are saying X about topic A, but you have found research that is actually indicating Y as the real problem of topic A, so you say that new research needs to be done…
Work on incorporating those “conversations” you just had into your essay.
- Although many researchers are indicating “X,” in discussions involving topic A, many of those research methods are faulty in that…
- When researchers in the field of topic A argue with researchers studying topic B, I am seeing that these two fields are actually linked in that…
- Aside from topic A, some researchers are finding a trend that (topic B) is actually more…
- In consideration of both topics A & B, I am led to believe that there is a vital resource that hasn’t been considered…
When incorporating conversations as you write, argue your thesis claim.
- Many who deal with topic A take a position similar to mine in that…; however, I would argue that new research needs to be done in the field of topic B.
- Although some who argue about topic A would oppose my position on developing new research in this field, here is why I still uphold its legitimacy…
- Only a few researchers offer a slightly different perspective from topic A, and one perspective that I would call attention to is...
- When sources A and B were doing the specific types of studies on subject X, there were two different research methods: method 1 and method 2. Of these methods, there are the following common themes… (and) the usual points of disagreements are… which justifies the need for new research in…
The successful synthesis essay will show readers how you have reasoned about the topic at hand by taking into account the sources critically and creating a work that draws conversations with the sources into your own thinking.
Contributor: Derrian Goebel

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
How to Write a Perfect Synthesis Essay for the AP Language Exam
Advanced Placement (AP)

If you're planning to take the AP Language (or AP Lang) exam , you might already know that 55% of your overall exam score will be based on three essays. The first of the three essays you'll have to write on the AP Language exam is called the "synthesis essay." If you want to earn full points on this portion of the AP Lang Exam, you need to know what a synthesis essay is and what skills are assessed by the AP Lang synthesis essay.
In this article, we'll explain the different aspects of the AP Lang synthesis essay, including what skills you need to demonstrate in your synthesis essay response in order to achieve a good score. We'll also give you a full breakdown of a real AP Lang Synthesis Essay prompt, provide an analysis of an AP Lang synthesis essay example, and give you four tips for how to write a synthesis essay.
Let's get started by taking a closer look at how the AP Lang synthesis essay works!
Synthesis Essay AP Lang: What It Is and How It Works
The AP Lang synthesis essay is the first of three essays included in the Free Response section of the AP Lang exam.
The AP Lang synthesis essay portion of the Free Response section lasts for one hour total . This hour consists of a recommended 15 minute reading period and a 40 minute writing period. Keep in mind that these time allotments are merely recommendations, and that exam takers can parse out the allotted 60 minutes to complete the synthesis essay however they choose.
Now, here's what the structure of the AP Lang synthesis essay looks like. The exam presents six to seven sources that are organized around a specific topic (like alternative energy or eminent domain, which are both past synthesis exam topics).
Of these six to seven sources, at least two are visual , including at least one quantitative source (like a graph or pie chart, for example). The remaining four to five sources are print text-based, and each one contains approximately 500 words.
In addition to six to seven sources, the AP Lang exam provides a written prompt that consists of three paragraphs. The prompt will briefly explain the essay topic, then present a claim that students will respond to in an essay that synthesizes material from at least three of the sources provided.
Here's an example prompt provided by the College Board:
Directions : The following prompt is based on the accompanying six sources.
This question requires you to integrate a variety of sources into a coherent, well-written essay. Refer to the sources to support your position; avoid mere paraphrase or summary. Your argument should be central; the sources should support this argument .
Remember to attribute both direct and indirect citations.
Introduction
Television has been influential in United States presidential elections since the 1960's. But just what is this influence, and how has it affected who is elected? Has it made elections fairer and more accessible, or has it moved candidates from pursuing issues to pursuing image?
Read the following sources (including any introductory information) carefully. Then, in an essay that synthesizes at least three of the sources for support, take a position that defends, challenges, or qualifies the claim that television has had a positive impact on presidential elections.
Refer to the sources as Source A, Source B, etc.; titles are included for your convenience.
Source A (Campbell) Source B (Hart and Triece) Source C (Menand) Source D (Chart) Source E (Ranney) Source F (Koppel)
Like we mentioned earlier, this prompt gives you a topic — which it briefly explains — then asks you to take a position. In this case, you'll have to choose a stance on whether television has positively or negatively affected U.S. elections. You're also given six sources to evaluate and use in your response. Now that you have everything you need, now your job is to write an amazing synthesis essay.
But what does "synthesize" mean, exactly? According to the CollegeBoard, when an essay prompt asks you to synthesize, it means that you should "combine different perspectives from sources to form a support of a coherent position" in writing. In other words, a synthesis essay asks you to state your claim on a topic, then highlight the relationships between several sources that support your claim on that topic. Additionally, you'll need to cite specific evidence from your sources to prove your point.
The synthesis essay counts for six of the total points on the AP Lang exam . Students can receive 0-1 points for writing a thesis statement in the essay, 0-4 based on incorporation of evidence and commentary, and 0-1 points based on sophistication of thought and demonstrated complex understanding of the topic.
You'll be evaluated based on how effectively you do the following in your AP Lang synthesis essay:
Write a thesis that responds to the exam prompt with a defensible position
Provide specific evidence that to support all claims in your line of reasoning from at least three of the sources provided, and clearly and consistently explain how the evidence you include supports your line of reasoning
Demonstrate sophistication of thought by either crafting a thoughtful argument, situating the argument in a broader context, explaining the limitations of an argument
Make rhetorical choices that strengthen your argument and/or employ a vivid and persuasive style throughout your essay.
If your synthesis essay meets the criteria above, then there's a good chance you'll score well on this portion of the AP Lang exam!
If you're looking for even more information on scoring, the College Board has posted the AP Lang Free Response grading rubric on its website. ( You can find it here. ) We recommend taking a close look at it since it includes additional details about the synthesis essay scoring.

Don't be intimidated...we're going to teach you how to break down even the hardest AP synthesis essay prompt.
Full Breakdown of a Real AP Lang Synthesis Essay Prompt
In this section, we'll teach you how to analyze and respond to a synthesis essay prompt in five easy steps, including suggested time frames for each step of the process.
Step 1: Analyze the Prompt
The very first thing to do when the clock starts running is read and analyze the prompt. To demonstrate how to do this, we'll look at the sample AP Lang synthesis essay prompt below. This prompt comes straight from the 2018 AP Lang exam:
Eminent domain is the power governments have to acquire property from private owners for public use. The rationale behind eminent domain is that governments have greater legal authority over lands within their dominion than do private owners. Eminent domain has been instituted in one way or another throughout the world for hundreds of years.
Carefully read the following six sources, including the introductory information for each source. Then synthesize material from at least three of the sources and incorporate it into a coherent, well-developed essay that defends, challenges, or qualifies the notion that eminent domain is productive and beneficial.
Your argument should be the focus of your essay. Use the sources to develop your argument and explain the reasoning for it. Avoid merely summarizing the sources. Indicate clearly which sources you are drawing from, whether through direct quotation, paraphrase, or summary. You may cite the sources as Source A, Source B, etc., or by using the descriptions in parentheses.
On first read, you might be nervous about how to answer this prompt...especially if you don't know what eminent domain is! But if you break the prompt down into chunks, you'll be able to figure out what the prompt is asking you to do in no time flat.
To get a full understanding of what this prompt wants you to do, you need to identify the most important details in this prompt, paragraph by paragraph. Here's what each paragraph is asking you to do:
- Paragraph 1: The prompt presents and briefly explains the topic that you'll be writing your synthesis essay about. That topic is the concept of eminent domain.
- Paragraph 2: The prompt presents a specific claim about the concept of eminent domain in this paragraph: Eminent domain is productive and beneficial. This paragraph instructs you to decide whether you want to defend, challenge, or qualify that claim in your synthesis essay , and use material from at least three of the sources provided in order to do so.
- Paragraph 3: In the last paragraph of the prompt, the exam gives you clear instructions about how to approach writing your synthesis essay . First, make your argument the focus of the essay. Second, use material from at least three of the sources to develop and explain your argument. Third, provide commentary on the material you include, and provide proper citations when you incorporate quotations, paraphrases, or summaries from the sources provided.
So basically, you'll have to agree with, disagree with, or qualify the claim stated in the prompt, then use at least three sources substantiate your answer. Since you probably don't know much about eminent domain, you'll probably decide on your position after you read the provided sources.
To make good use of your time on the exam, you should spend around 2 minutes reading the prompt and making note of what it's asking you to do. That will leave you plenty of time to read the sources provided, which is the next step to writing a synthesis essay.
Step 2: Read the Sources Carefully
After you closely read the prompt and make note of the most important details, you need to read all of the sources provided. It's tempting to skip one or two sources to save time--but we recommend you don't do this. That's because you'll need a thorough understanding of the topic before you can accurately address the prompt!
For the sample exam prompt included above, there are six sources provided. We're not going to include all of the sources in this article, but you can view the six sources from this question on the 2018 AP Lang exam here . The sources include five print-text sources and one visual source, which is a cartoon.
As you read the sources, it's important to read quickly and carefully. Don't rush! Keep your pencil in hand to quickly mark important passages that you might want to use as evidence in your synthesis. While you're reading the sources and marking passages, you want to think about how the information you're reading influences your stance on the issue (in this case, eminent domain).
When you finish reading, take a few seconds to summarize, in a phrase or sentence, whether the source defends, challenges, or qualifies whether eminent domain is beneficial (which is the claim in the prompt) . Though it might not feel like you have time for this, it's important to give yourself these notes about each source so you know how you can use each one as evidence in your essay.
Here's what we mean: say you want to challenge the idea that eminent domain is useful. If you've jotted down notes about each source and what it's saying, it will be easier for you to pull the relevant information into your outline and your essay.
So how much time should you spend reading the provided sources? The AP Lang exam recommends taking 15 minutes to read the sources . If you spend around two of those minutes reading and breaking down the essay prompt, it makes sense to spend the remaining 13 minutes reading and annotating the sources.
If you finish reading and annotating early, you can always move on to drafting your synthesis essay. But make sure you're taking your time and reading carefully! It's better to use a little extra time reading and understanding the sources now so that you don't have to go back and re-read the sources later.
A strong thesis will do a lot of heavy lifting in your essay. (See what we did there?)
Step 3: Write a Strong Thesis Statement
After you've analyzed the prompt and thoroughly read the sources, the next thing you need to do in order to write a good synthesis essay is write a strong thesis statement .
The great news about writing a thesis statement for this synthesis essay is that you have all the tools you need to do it at your fingertips. All you have to do in order to write your thesis statement is decide what your stance is in relationship to the topic provided.
In the example prompt provided earlier, you're essentially given three choices for how to frame your thesis statement: you can either defend, challenge, or qualify a claim that's been provided by the prompt, that eminent domain is productive and beneficial . Here's what that means for each option:
If you choose to defend the claim, your job will be to prove that the claim is correct . In this case, you'll have to show that eminent domain is a good thing.
If you choose to challenge the claim, you'll argue that the claim is incorrect. In other words, you'll argue that eminent domain isn't productive or beneficial.
If you choose to qualify, that means you'll agree with part of the claim, but disagree with another part of the claim. For instance, you may argue that eminent domain can be a productive tool for governments, but it's not beneficial for property owners. Or maybe you argue that eminent domain is useful in certain circumstances, but not in others.
When you decide whether you want your synthesis essay to defend, challenge, or qualify that claim, you need to convey that stance clearly in your thesis statement. You want to avoid simply restating the claim provided in the prompt, summarizing the issue without making a coherent claim, or writing a thesis that doesn't respond to the prompt.
Here's an example of a thesis statement that received full points on the eminent domain synthesis essay:
Although eminent domain can be misused to benefit private interests at the expense of citizens, it is a vital tool of any government that intends to have any influence on the land it governs beyond that of written law.
This thesis statement received full points because it states a defensible position and establishes a line of reasoning on the issue of eminent domain. It states the author's position (that some parts of eminent domain are good, but others are bad), then goes on to explain why the author thinks that (it's good because it allows the government to do its job, but it's bad because the government can misuse its power.)
Because this example thesis statement states a defensible position and establishes a line of reasoning, it can be elaborated upon in the body of the essay through sub-claims, supporting evidence, and commentary. And a solid argument is key to getting a six on your synthesis essay for AP Lang!

Step 4: Create a Bare-Bones Essay Outline
Once you've got your thesis statement drafted, you have the foundation you need to develop a bare bones outline for your synthesis essay. Developing an outline might seem like it's a waste of your precious time, but if you develop your outline well, it will actually save you time when you start writing your essay.
With that in mind, we recommend spending 5 to 10 minutes outlining your synthesis essay . If you use a bare-bones outline like the one below, labeling each piece of content that you need to include in your essay draft, you should be able to develop out the most important pieces of the synthesis before you even draft the actual essay.
To help you see how this can work on test day, we've created a sample outline for you. You can even memorize this outline to help you out on test day! In the outline below, you'll find places to fill in a thesis statement, body paragraph topic sentences, evidence from the sources provided, and commentary :
- Present the context surrounding the essay topic in a couple of sentences (this is a good place to use what you learned about the major opinions or controversies about the topic from reading your sources).
- Write a straightforward, clear, and concise thesis statement that presents your stance on the topic
- Topic sentence presenting first supporting point or claim
- Evidence #1
- Commentary on Evidence #1
- Evidence #2 (if needed)
- Commentary on Evidence #2 (if needed)
- Topic sentence presenting second supporting point or claim
- Topic sentence presenting three supporting point or claim
- Sums up the main line of reasoning that you developed and defended throughout the essay
- Reiterates the thesis statement
Taking the time to develop these crucial pieces of the synthesis in a bare-bones outline will give you a map for your final essay. Once you have a map, writing the essay will be much easier.
Step 5: Draft Your Essay Response
The great thing about taking a few minutes to develop an outline is that you can develop it out into your essay draft. After you take about 5 to 10 minutes to outline your synthesis essay, you can use the remaining 30 to 35 minutes to draft your essay and review it.
Since you'll outline your essay before you start drafting, writing the essay should be pretty straightforward. You'll already know how many paragraphs you're going to write, what the topic of each paragraph will be, and what quotations, paraphrases, or summaries you're going to include in each paragraph from the sources provided. You'll just have to fill in one of the most important parts of your synthesis—your commentary.
Commentaries are your explanation of why your evidence supports the argument you've outlined in your thesis. Your commentary is where you actually make your argument, which is why it's such a critical part of your synthesis essay.
When thinking about what to say in your commentary, remember one thing the AP Lang synthesis essay prompt specifies: don't just summarize the sources. Instead, as you provide commentary on the evidence you incorporate, you need to explain how that evidence supports or undermines your thesis statement . You should include commentary that offers a thoughtful or novel perspective on the evidence from your sources to develop your argument.
One very important thing to remember as you draft out your essay is to cite your sources. The AP Lang exam synthesis essay prompt indicates that you can use generic labels for the sources provided (e.g. "Source 1," "Source 2," "Source 3," etc.). The exam prompt will indicate which label corresponds with which source, so you'll need to make sure you pay attention and cite sources accurately. You can cite your sources in the sentence where you introduce a quote, summary, or paraphrase, or you can use a parenthetical citation. Citing your sources affects your score on the synthesis essay, so remembering to do this is important.

Keep reading for a real-life example of a great AP synthesis essay response!
Real-Life AP Synthesis Essay Example and Analysis
If you're still wondering how to write a synthesis essay, examples of real essays from past AP Lang exams can make things clearer. These real-life student AP synthesis essay responses can be great for helping you understand how to write a synthesis essay that will knock the graders' socks off .
While there are multiple essay examples online, we've chosen one to take a closer look at. We're going to give you a brief analysis of one of these example student synthesis essays from the 2019 AP Lang Exam below!
Example Synthesis Essay AP Lang Response
To get started, let's look at the official prompt for the 2019 synthesis essay:
In response to our society's increasing demand for energy, large-scale wind power has drawn attention from governments and consumers as a potential alternative to traditional materials that fuel our power grids, such as coal, oil, natural gas, water, or even newer sources such as nuclear or solar power. Yet the establishment of large-scale, commercial-grade wind farms is often the subject of controversy for a variety of reasons.
Carefully read the six sources, found on the AP English Language and Composition 2019 Exam (Question 1), including the introductory information for each source. Write an essay that synthesizes material from at least three of the sources and develops your position on the most important factors that an individual or agency should consider when deciding whether to establish a wind farm.
Source A (photo) Source B (Layton) Source C (Seltenrich) Source D (Brown) Source E (Rule) Source F (Molla)
In your response you should do the following:
- Respond to the prompt with a thesis presents a defensible position.
- Select and use evidence from at least 3 of the provided sources to support your line of reasoning. Indicate clearly the sources used through direct quotation, paraphrase, or summary. Sources may be cited as Source A, Source B, etc., or by using the description in parentheses.
- Explain how the evidence supports your line of reasoning.
- Use appropriate grammar and punctuation in communicating your argument.
Now that you know exactly what the prompt asked students to do on the 2019 AP Lang synthesis essay, here's an AP Lang synthesis essay example, written by a real student on the AP Lang exam in 2019:
[1] The situation has been known for years, and still very little is being done: alternative power is the only way to reliably power the changing world. The draw of power coming from industry and private life is overwhelming current sources of non-renewable power, and with dwindling supplies of fossil fuels, it is merely a matter of time before coal and gas fuel plants are no longer in operation. So one viable alternative is wind power. But as with all things, there are pros and cons. The main factors for power companies to consider when building wind farms are environmental boon, aesthetic, and economic factors.
[2] The environmental benefits of using wind power are well-known and proven. Wind power is, as qualified by Source B, undeniably clean and renewable. From their production requiring very little in the way of dangerous materials to their lack of fuel, besides that which occurs naturally, wind power is by far one of the least environmentally impactful sources of power available. In addition, wind power by way of gearbox and advanced blade materials, has the highest percentage of energy retention. According to Source F, wind power retains 1,164% of the energy put into the system – meaning that it increases the energy converted from fuel (wind) to electricity 10 times! No other method of electricity production is even half that efficient. The efficiency and clean nature of wind power are important to consider, especially because they contribute back to power companies economically.
[3] Economically, wind power is both a boon and a bone to electric companies and other users. For consumers, wind power is very cheap, leading to lower bills than from any other source. Consumers also get an indirect reimbursement by way of taxes (Source D). In one Texan town, McCamey, tax revenue increased 30% from a wind farm being erected in the town. This helps to finance improvements to the town. But, there is no doubt that wind power is also hurting the power companies. Although, as renewable power goes, wind is incredibly cheap, it is still significantly more expensive than fossil fuels. So, while it is helping to cut down on emissions, it costs electric companies more than traditional fossil fuel plants. While the general economic trend is positive, there are some setbacks which must be overcome before wind power can take over as truly more effective than fossil fuels.
[4] Aesthetics may be the greatest setback for power companies. Although there may be significant economic and environmental benefit to wind power, people will always fight to preserve pure, unspoiled land. Unfortunately, not much can be done to improve the visual aesthetics of the turbines. White paint is the most common choice because it "[is] associated with cleanliness." (Source E). But, this can make it stand out like a sore thumb, and make the gargantuan machines seem more out of place. The site can also not be altered because it affects generating capacity. Sound is almost worse of a concern because it interrupts personal productivity by interrupting people's sleep patterns. One thing for power companies to consider is working with turbine manufacturing to make the machines less aesthetically impactful, so as to garner greater public support.
[5] As with most things, wind power has no easy answer. It is the responsibility of the companies building them to weigh the benefits and the consequences. But, by balancing economics, efficiency, and aesthetics, power companies can create a solution which balances human impact with environmental preservation.
And that's an entire AP Lang synthesis essay example, written in response to a real AP Lang exam prompt! It's important to remember AP Lang exam synthesis essay prompts are always similarly structured and worded, and students often respond in around the same number of paragraphs as what you see in the example essay response above.
Next, let's analyze this example essay and talk about what it does effectively, where it could be improved upon, and what score past exam scorers awarded it.
To get started on an analysis of the sample synthesis essay, let's look at the scoring commentary provided by the College Board:
- For development of thesis, the essay received 1 out of 1 possible points
- For evidence and commentary, the essay received 4 out of 4 possible points
- For sophistication of thought, the essay received 0 out of 1 possible points.
This means that the final score for this example essay was a 5 out of 6 possible points . Let's look more closely at the content of the example essay to figure out why it received this score breakdown.
Thesis Development
The thesis statement is one of the three main categories that is taken into consideration when you're awarded points on this portion of the exam. This sample essay received 1 out of 1 total points.
Now, here's why: the thesis statement clearly and concisely conveys a position on the topic presented in the prompt--alternative energy and wind power--and defines the most important factors that power companies should consider when deciding whether to establish a wind farm.
Evidence and Commentary
The second key category taken into consideration when synthesis exams are evaluated is incorporation of evidence and commentary. This sample received 4 out of 4 possible points for this portion of the synthesis essay. At bare minimum, this sample essay meets the requirement mentioned in the prompt that the writer incorporate evidence from at least three of the sources provided.
On top of that, the writer does a good job of connecting the incorporated evidence back to the claim made in the thesis statement through effective commentary. The commentary in this sample essay is effective because it goes beyond just summarizing what the provided sources say. Instead, it explains and analyzes the evidence presented in the selected sources and connects them back to supporting points the writer makes in each body paragraph.
Finally, the writer of the essay also received points for evidence and commentary because the writer developed and supported a consistent line of reasoning throughout the essay . This line of reasoning is summed up in the fourth paragraph in the following sentence: "One thing for power companies to consider is working with turbine manufacturing to make the machines less aesthetically impactful, so as to garner greater public support."
Because the writer did a good job consistently developing their argument and incorporating evidence, they received full marks in this category. So far, so good!
Sophistication of Thought
Now, we know that this essay received a score of 5 out of 6 total points, and the place where the writer lost a point was on the basis of sophistication of thought, for which the writer received 0 out of 1 points. That's because this sample essay makes several generalizations and vague claims where it could have instead made specific claims that support a more balanced argument.
For example, in the following sentence from the 5th paragraph of the sample essay, the writer misses the opportunity to state specific possibilities that power companies should consider for wind energy . Instead, the writer is ambiguous and non-committal, saying, "As with most things, wind power has no easy answer. It is the responsibility of the companies building them to weigh the benefits and consequences."
If the writer of this essay was interested in trying to get that 6th point on the synthesis essay response, they could consider making more specific claims. For instance, they could state the specific benefits and consequences power companies should consider when deciding whether to establish a wind farm. These could include things like environmental impacts, economic impacts, or even population density!
Despite losing one point in the last category, this example synthesis essay is a strong one. It's well-developed, thoughtfully written, and advances an argument on the exam topic using evidence and support throughout.

4 Tips for How to Write a Synthesis Essay
AP Lang is a timed exam, so you have to pick and choose what you want to focus on in the limited time you're given to write the synthesis essay. Keep reading to get our expert advice on what you should focus on during your exam.
Tip 1: Read the Prompt First
It may sound obvious, but when you're pressed for time, it's easy to get flustered. Just remember: when it comes time to write the synthesis essay, read the prompt first !
Why is it so important to read the prompt before you read the sources? Because when you're aware of what kind of question you're trying to answer, you'll be able to read the sources more strategically. The prompt will help give you a sense of what claims, points, facts, or opinions to be looking for as you read the sources.
Reading the sources without having read the prompt first is kind of like trying to drive while wearing a blindfold: you can probably do it, but it's likely not going to end well!
Tip 2: Make Notes While You Read
During the 15-minute reading period at the beginning of the synthesis essay, you'll be reading through the sources as quickly as you can. After all, you're probably anxious to start writing!
While it's definitely important to make good use of your time, it's also important to read closely enough that you understand your sources. Careful reading will allow you to identify parts of the sources that will help you support your thesis statement in your essay, too.
As you read the sources, consider marking helpful passages with a star or check mark in the margins of the exam so you know which parts of the text to quickly re-read as you form your synthesis essay. You might also consider summing up the key points or position of each source in a sentence or a few words when you finish reading each source during the reading period. Doing so will help you know where each source stands on the topic given and help you pick the three (or more!) that will bolster your synthesis argument.
Tip 3: Start With the Thesis Statement
If you don't start your synthesis essay with a strong thesis statement, it's going to be tough to write an effective synthesis essay. As soon as you finish reading and annotating the provided sources, the thing you want to do next is write a strong thesis statement.
According to the CollegeBoard grading guidelines for the AP Lang synthesis essay, a strong thesis statement will respond to the prompt— not restate or rephrase the prompt. A good thesis will take a clear, defensible position on the topic presented in the prompt and the sources.
In other words, to write a solid thesis statement to guide the rest of your synthesis essay, you need to think about your position on the topic at hand and then make a claim about the topic based on your position. This position will either be defending, challenging, or qualifying the claim made in the essay's prompt.
The defensible position that you establish in your thesis statement will guide your argument in the rest of the essay, so it's important to do this first. Once you have a strong thesis statement, you can begin outlining your essay.
Tip 4: Focus on Your Commentary
Writing thoughtful, original commentary that explains your argument and your sources is important. In fact, doing this well will earn you four points (out of a total of six)!
AP Lang provides six to seven sources for you on the exam, and you'll be expected to incorporate quotations, paraphrases, or summaries from at least three of those sources into your synthesis essay and interpret that evidence for the reader.
While incorporating evidence is very important, in order to get the extra point for "sophistication of thought" on the synthesis essay, it's important to spend more time thinking about your commentary on the evidence you choose to incorporate. The commentary is your chance to show original thinking, strong rhetorical skills, and clearly explain how the evidence you've included supports the stance you laid out in your thesis statement.
To earn the 6th possible point on the synthesis essay, make sure your commentary demonstrates a nuanced understanding of the source material, explains this nuanced understanding, and places the evidence incorporated from the sources in conversation with each other. To do this, make sure you're avoiding vague language. Be specific when you can, and always tie your commentary back to your thesis!

What's Next?
There's a lot more to the AP Language exam than just the synthesis essay. Be sure to check out our expert guide to the entire exam , then learn more about the tricky multiple choice section .
Is the AP Lang exam hard...or is it easy? See how it stacks up to other AP tests on our list of the hardest AP exams .
Did you know there are technically two English AP exams? You can learn more about the second English AP test, the AP Literature exam, in this article . And if you're confused about whether you should take the AP Lang or AP Lit test , we can help you make that decision, too.

Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- Synthesizing Sources | Examples & Synthesis Matrix
Synthesizing Sources | Examples & Synthesis Matrix
Published on July 4, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on May 31, 2023.
Synthesizing sources involves combining the work of other scholars to provide new insights. It’s a way of integrating sources that helps situate your work in relation to existing research.
Synthesizing sources involves more than just summarizing . You must emphasize how each source contributes to current debates, highlighting points of (dis)agreement and putting the sources in conversation with each other.
You might synthesize sources in your literature review to give an overview of the field or throughout your research paper when you want to position your work in relation to existing research.
Table of contents
Example of synthesizing sources, how to synthesize sources, synthesis matrix, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about synthesizing sources.
Let’s take a look at an example where sources are not properly synthesized, and then see what can be done to improve it.
This paragraph provides no context for the information and does not explain the relationships between the sources described. It also doesn’t analyze the sources or consider gaps in existing research.
Research on the barriers to second language acquisition has primarily focused on age-related difficulties. Building on Lenneberg’s (1967) theory of a critical period of language acquisition, Johnson and Newport (1988) tested Lenneberg’s idea in the context of second language acquisition. Their research seemed to confirm that young learners acquire a second language more easily than older learners. Recent research has considered other potential barriers to language acquisition. Schepens, van Hout, and van der Slik (2022) have revealed that the difficulties of learning a second language at an older age are compounded by dissimilarity between a learner’s first language and the language they aim to acquire. Further research needs to be carried out to determine whether the difficulty faced by adult monoglot speakers is also faced by adults who acquired a second language during the “critical period.”
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
To synthesize sources, group them around a specific theme or point of contention.
As you read sources, ask:
- What questions or ideas recur? Do the sources focus on the same points, or do they look at the issue from different angles?
- How does each source relate to others? Does it confirm or challenge the findings of past research?
- Where do the sources agree or disagree?
Once you have a clear idea of how each source positions itself, put them in conversation with each other. Analyze and interpret their points of agreement and disagreement. This displays the relationships among sources and creates a sense of coherence.
Consider both implicit and explicit (dis)agreements. Whether one source specifically refutes another or just happens to come to different conclusions without specifically engaging with it, you can mention it in your synthesis either way.
Synthesize your sources using:
- Topic sentences to introduce the relationship between the sources
- Signal phrases to attribute ideas to their authors
- Transition words and phrases to link together different ideas
To more easily determine the similarities and dissimilarities among your sources, you can create a visual representation of their main ideas with a synthesis matrix . This is a tool that you can use when researching and writing your paper, not a part of the final text.
In a synthesis matrix, each column represents one source, and each row represents a common theme or idea among the sources. In the relevant rows, fill in a short summary of how the source treats each theme or topic.
This helps you to clearly see the commonalities or points of divergence among your sources. You can then synthesize these sources in your work by explaining their relationship.
| Lenneberg (1967) | Johnson and Newport (1988) | Schepens, van Hout, and van der Slik (2022) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Approach | Primarily theoretical, due to the ethical implications of delaying the age at which humans are exposed to language | Testing the English grammar proficiency of 46 native Korean or Chinese speakers who moved to the US between the ages of 3 and 39 (all participants had lived in the US for at least 3 years at the time of testing) | Analyzing the results of 56,024 adult immigrants to the Netherlands from 50 different language backgrounds |
| Enabling factors in language acquisition | A critical period between early infancy and puberty after which language acquisition capabilities decline | A critical period (following Lenneberg) | General age effects (outside of a contested critical period), as well as the similarity between a learner’s first language and target language |
| Barriers to language acquisition | Aging | Aging (following Lenneberg) | Aging as well as the dissimilarity between a learner’s first language and target language |
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Paraphrasing
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
Synthesizing sources means comparing and contrasting the work of other scholars to provide new insights.
It involves analyzing and interpreting the points of agreement and disagreement among sources.
You might synthesize sources in your literature review to give an overview of the field of research or throughout your paper when you want to contribute something new to existing research.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
Topic sentences help keep your writing focused and guide the reader through your argument.
In an essay or paper , each paragraph should focus on a single idea. By stating the main idea in the topic sentence, you clarify what the paragraph is about for both yourself and your reader.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Ryan, E. (2023, May 31). Synthesizing Sources | Examples & Synthesis Matrix. Scribbr. Retrieved September 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/synthesizing-sources/
Is this article helpful?

Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, signal phrases | definition, explanation & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, how to find sources | scholarly articles, books, etc., get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Synthesizing Sources

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
When you look for areas where your sources agree or disagree and try to draw broader conclusions about your topic based on what your sources say, you are engaging in synthesis. Writing a research paper usually requires synthesizing the available sources in order to provide new insight or a different perspective into your particular topic (as opposed to simply restating what each individual source says about your research topic).
Note that synthesizing is not the same as summarizing.
- A summary restates the information in one or more sources without providing new insight or reaching new conclusions.
- A synthesis draws on multiple sources to reach a broader conclusion.
There are two types of syntheses: explanatory syntheses and argumentative syntheses . Explanatory syntheses seek to bring sources together to explain a perspective and the reasoning behind it. Argumentative syntheses seek to bring sources together to make an argument. Both types of synthesis involve looking for relationships between sources and drawing conclusions.
In order to successfully synthesize your sources, you might begin by grouping your sources by topic and looking for connections. For example, if you were researching the pros and cons of encouraging healthy eating in children, you would want to separate your sources to find which ones agree with each other and which ones disagree.
After you have a good idea of what your sources are saying, you want to construct your body paragraphs in a way that acknowledges different sources and highlights where you can draw new conclusions.
As you continue synthesizing, here are a few points to remember:
- Don’t force a relationship between sources if there isn’t one. Not all of your sources have to complement one another.
- Do your best to highlight the relationships between sources in very clear ways.
- Don’t ignore any outliers in your research. It’s important to take note of every perspective (even those that disagree with your broader conclusions).
Example Syntheses
Below are two examples of synthesis: one where synthesis is NOT utilized well, and one where it is.
Parents are always trying to find ways to encourage healthy eating in their children. Elena Pearl Ben-Joseph, a doctor and writer for KidsHealth , encourages parents to be role models for their children by not dieting or vocalizing concerns about their body image. The first popular diet began in 1863. William Banting named it the “Banting” diet after himself, and it consisted of eating fruits, vegetables, meat, and dry wine. Despite the fact that dieting has been around for over a hundred and fifty years, parents should not diet because it hinders children’s understanding of healthy eating.
In this sample paragraph, the paragraph begins with one idea then drastically shifts to another. Rather than comparing the sources, the author simply describes their content. This leads the paragraph to veer in an different direction at the end, and it prevents the paragraph from expressing any strong arguments or conclusions.
An example of a stronger synthesis can be found below.
Parents are always trying to find ways to encourage healthy eating in their children. Different scientists and educators have different strategies for promoting a well-rounded diet while still encouraging body positivity in children. David R. Just and Joseph Price suggest in their article “Using Incentives to Encourage Healthy Eating in Children” that children are more likely to eat fruits and vegetables if they are given a reward (855-856). Similarly, Elena Pearl Ben-Joseph, a doctor and writer for Kids Health , encourages parents to be role models for their children. She states that “parents who are always dieting or complaining about their bodies may foster these same negative feelings in their kids. Try to keep a positive approach about food” (Ben-Joseph). Martha J. Nepper and Weiwen Chai support Ben-Joseph’s suggestions in their article “Parents’ Barriers and Strategies to Promote Healthy Eating among School-age Children.” Nepper and Chai note, “Parents felt that patience, consistency, educating themselves on proper nutrition, and having more healthy foods available in the home were important strategies when developing healthy eating habits for their children.” By following some of these ideas, parents can help their children develop healthy eating habits while still maintaining body positivity.
In this example, the author puts different sources in conversation with one another. Rather than simply describing the content of the sources in order, the author uses transitions (like "similarly") and makes the relationship between the sources evident.
Welcome to the new OASIS website! We have academic skills, library skills, math and statistics support, and writing resources all together in one new home.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Using Evidence: Synthesis
Synthesis video playlist.
Note that these videos were created while APA 6 was the style guide edition in use. There may be some examples of writing that have not been updated to APA 7 guidelines.

Basics of Synthesis
As you incorporate published writing into your own writing, you should aim for synthesis of the material.
Synthesizing requires critical reading and thinking in order to compare different material, highlighting similarities, differences, and connections. When writers synthesize successfully, they present new ideas based on interpretations of other evidence or arguments. You can also think of synthesis as an extension of—or a more complicated form of—analysis. One main difference is that synthesis involves multiple sources, while analysis often focuses on one source.
Conceptually, it can be helpful to think about synthesis existing at both the local (or paragraph) level and the global (or paper) level.
Local Synthesis
Local synthesis occurs at the paragraph level when writers connect individual pieces of evidence from multiple sources to support a paragraph’s main idea and advance a paper’s thesis statement. A common example in academic writing is a scholarly paragraph that includes a main idea, evidence from multiple sources, and analysis of those multiple sources together.
Global Synthesis
Global synthesis occurs at the paper (or, sometimes, section) level when writers connect ideas across paragraphs or sections to create a new narrative whole. A literature review , which can either stand alone or be a section/chapter within a capstone, is a common example of a place where global synthesis is necessary. However, in almost all academic writing, global synthesis is created by and sometimes referred to as good cohesion and flow.
Synthesis in Literature Reviews
While any types of scholarly writing can include synthesis, it is most often discussed in the context of literature reviews. Visit our literature review pages for more information about synthesis in literature reviews.
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Analysis
- Next Page: Citing Sources Properly
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Cost of Attendance
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

What Does It Mean to Synthesize for Writing Assignments?

Synthesis Writing – What It Means and How to Do it!
Have you been asked to synthesize material for a writing assignment? Are you taking a college course where your instructor doesn’t want you to use quotes but instead, write in your own words?
If the answer is yes, you’ve come to the right place. This post is all about that word “synthesize” with a specific focus on essay based writing for college students.
On this page, you will learn:
- The definition of synthesis
- What synthesis means in the context of writing assignments.
- How synthesizing looks in essays.
- How to synthesize the material you are reading and apply to your paper.
- See an example college essay written entirely through synthesis.
- Additional writing tips to help you earn the highest possible score on college papers.
You may be wondering what qualifies me to author this piece? It’s simple – I’m a college professor who has been teaching business and psychology courses at for almost twenty years. In my work, I evaluate writing submitted by students and assignment a grade.
So the bottom line is this: I know exactly what your professor is looking for when ask you to synthesize. I require the same approach to writing for my learners.
OK – now that we’ve gotten that out of the way, let’s jump right in.
What does synthesis or synthesize mean?
Synthesis is a ten-dollar word to describe the combination of two or more ideas or concepts into your writing using your own words .
Think of this as a way of bringing together different themes that you observe from your reading material and then writing about it in your own voice.
Example of synthesis in everyday life
If a friend asked you to explain the similarities and differences between Star Trek and Star Wars, how would you respond?
Whatever your answer might be, you will be synthesizing .
Here is how I might answer that question in casual conversation.
Star Trek is similar to Star Wars in that both take place in the future and presented as science fiction. Additionally, both draw upon age-old concepts of a shared journey.
But the two shows differ in that Star Trek is heavily focused on exploration. Star Wars, on the other hand, is all about survival.
See how this works? Simple, huh?
Notice how I talked about both shows without quoting anyone else. In addition, did you see how I pulled in other material I knew about (“age-old concepts”) as part of the dynamic?
Folks, I promise you synthesis is not complicated. The problem is college educators, like English professors and business instructors, don’t take the time to explain what this term means or how it works.
In fact, the very reason I am blogging about this topic is that there’s not a lot of useful resources on the web that explains – with examples – how synthesis looks.
Most sites engage in babble and use a bunch of fancy words that don’t get to the heart of what you are looking for.
What does synthesis mean when I write essays?
When your professor or teacher asks you to write an essay and synthesize , here is what they are really saying to you:
- Discuss your understanding of the material in your own words.
- Demonstrate your knowledge of key concepts in your own words.
- Apply that knowledge to your writing in your own words.
As you will see, the “in your own words” is critical. To help draw a mental picture, let’s have a little fun and go camping.
Campfire Analogy
I’d like you to imagine that we are sitting around a campfire with your fellow classmates, roasting marshmallows.
As you take in the smell of burning wood and watch golden ambers float into the air, one of your classmates asks the group a question.
“ I wonder where marshmallows come from?”
Let’s assume you know the answer to this question. How would you respond?
Would you quote, verbatim, the words of someone else or would you simply start talking about your knowledge of marshmallows?
Hopefully, the answer to that question is the later. In other words, you might say something like:
Marshmallows are kind of amazing. They have been with us for nearly 2000 years, dating back to the early Egyptians.
Believe it or not, they are made from a combination of sap from the mallow plant – plus egg whites and a little sugar. They even make them in different colors, thanks to dyes. How cool is that?
Notice how you gave that answer is a very conversational way?
While you may not have recognized it, you were synthesizing!
Just for the sake of demonstration, here’s how you wouldn’t answer that question:
According to the Encyclopedia, “Marshmallows are a sugar-based confectionery that in its modern form typically consists of sugar, water and gelatin whipped to a squishy consistency, molded into small cylindrical pieces, and coated with corn starch. Additives may be included to change the color-scheme”
The reasons you wouldn’t answer it this way is because:
1) Nobody talks like that unless they are an android.
2) Quoting doesn’t demonstrate you really know the answer. All it shows is that somebody else knows the answer and you don’t.
My point is this – Your professor will be grading you on your ability to explain different concepts in your own words.
That’s synthesis.
Let’s look at another example but this time, something more complex. Again, I’d like you to pretend we are all sitting around the campfire.
As your fellow students gossip about the latest rumors, somebody points to the sky and shouts, “Holy crap – look, it’s a shooting star!”
Suddenly you gaze towards the heavens. Your eye catches a fast-moving white light racing from east to west. Seconds later, it’s gone.
Excited, everyone starts talking about where comets come from and if they present a risk to earth. Mesmerized by the conversation, you find yourself sucked in.
That’s when somebody asks:
“Do you think an asteroid killed the dinosaurs?”
Based on your knowledge of this topic, how might you respond? Well, assuming you knew the answer, you might say something like:
A lot of people say that the dinosaurs were killed off by a huge asteroid, which blocked the sun and triggered a mass extinction event.
The problem is not everyone agrees.
There are some scientists who believe the dinosaurs died off because of massive volcanic eruptions, which made the air unbeathable.
What you just read above is an example of synthesis. In your own words, you explained two theories in a straightforward, easy to understand way.
Not so difficult, is it?

How does synthesis look in a writing assignment?
Now that you’ve grasped the basics, let’s look at an example for a writing assignment.
Pretend your instructor gives you this as homework.
Assignment Directions:
Define Freud’s theory of denial. Discuss what denial is used for. Apply denial to a hypothetical situation. Write out your thoughts about denial by answering the question: Do you believe denial serves a purpose?
Right off the top, the first thing you’ll want to do is underline the action words in the directions.
– Define
– Discuss
– Apply
Once you’ve done this, it’s time to formulate a reply using synthesis. Here’s what you might write:
Sigmund Freud is considered the father of modern psychotherapy and one of the most important contributors to the field of psychology.
As part of his extensive body of work, he postulated that human beings use various kinds of defense mechanisms as tools for coping with unpleasant life situations (Smith, 2017).
One of those defense mechanisms is called denial.
In Freudian psychology, denial simply means that a person is unable to acknowledge something negative.
For example, a college student named Ed gets caught plagiarizing on an essay. As a result, he fails the course and is told by student services that his scholarship will be canceled.
To deal with the bad news, Ed pretends everything is fine. He even registers for new courses as part of his degree program.
But the reality of his situation sets in days later.
That’s when Ed receives an email from the registrar informing him that he must use a credit card to pay for his classes. Additionally, the email states that because of plagiarism, his scholarship is no longer active.
Suddenly, he starts to feel deep shame, particularly when it dawns on him that he’ll have to beg his parents for money.
In short, denial acts as a kind of subconscious shield against psychological or emotional trauma. Sometimes, the shield is short term.
Other times, it can be extended for many years (Davis, 2018). Much depends on the person, the events, and the individual’s life history.
In the narrow sense, I believe denial allows a person to get through the present moment. The problem, however, occurs when denial is left unchecked and doesn’t allow space for the person to take responsibility for their actions.
Notice how I wrote the response. Using the action words from the directions, I synthesized material from various sources and applied it to my writing.
That’s called synthesizing.
By writing in your own voice, you demonstrate to your instructor that:
- You can define a topic
- You can discuss a concept coherently.
- You can apply the construct to a hypothetical situation.
- You can pull together different theories.
Synthesizing is not the same summarizing
I am often asked if synthesis is the same as summarizing. The answer to that question is a solid no .
When you are asked to summarize, your instructor is requesting that you break down the major highlights of a theory, case study, concept or news story.
Here’s an example of summarizing, using Freud’s theory of denial.
Freud believed that people employ denial as a shield against emotional or psychological trauma.
All I’ve done with the above example is provided a quick snapshot about Freud’s theory. In short, I’m reiterating a main point.
With synthesis, I’m pulling on different areas to create a meaningful answer. I’m also expanding the conversation with different ideas.
Additional tips when asked to synthesize
What follows are a few general essay writing tips for students who have been asked to synthesize.
- Underline all action words in the directions.
- Use those action words as a guide for what you will write.
- Never start your essay off with a quote.
- Unless absolutely necessary, don’t use quotes at all.
- NEVER copy and paste from the web and try to pass it off as your writing. With today’s plagiarism technology, there’s a good chance you will get busted.
- Write your essays in a conversational tone. This will help you to synthesize, much like the campfire examples mentioned earlier.
- When referencing the work of others, speak in your own voice and then cite at the end of the sentence.
- Break up paragraphs to help with flow
- Ask your professor if you can write in the first person.
- Expand on the topic you have been asked to write about and go beyond simply answering the essay question.
Example essay using synthesis
Because I understand it helps to see real life examples, I’m sharing an essay with you that I wrote using synthesis. Notice that I never quote in this document.
Instead, I speak in my own voice (third person) and cite where necessary.
By the way, I don’t pretend to be the perfect writer. Use the downloadable PDF below as an example of what synthesizing looks like.
Click for Example Synthesis Writing Essay
Questions about synthesis?
Are you struggling with writing in synthesis? Share your questions below and let others respond.
Share this:

Related Articles

Why Organizational Management Is a Smart Degree Choice For Your Career
Organizational Management Explored Are you considering a degree in organizational management? Do you naturally gravitate towards the world of business and psychology? Trying to better your station in life with a credential that can help […]

5 Tips When Caught Plagiarizing To Save Your Bacon!
Caught Plagiarizing? Learn What to do! You have just received a stern email from your professor who is rather upset with you because the paper you submitted several days ago appears to be plagiarized. Attached […]

Research Suggests Materialistic People Use Facebook More
Facebook User News A new study out of Europe suggest that if you are a materialistic person, you’re more likely to use Facebook more frequently and intensely. German scientists found that materialistic people view and […]
Copyright 2024 Guy Counseling. All Rights Reserved. See Disclaimer
Hot List: New launches from Lululemon, exclusive NuFace discount, more
- Share this —

- Watch Full Episodes
- Read With Jenna
- Inspirational
- Relationships
- TODAY Table
- Newsletters
- Start TODAY
- Shop TODAY Awards
- Citi Concert Series
- Listen All Day
Follow today
More Brands
- On The Show
- TODAY Plaza
‘Mi’jo’: More than just a word to a Mexican American boy like me

I was probably 4 years old the first time anyone called me “mi’jo,” colloquial Spanish for “my son.” My Mexican American family lived in the front house on a two-unit lot on the east side of Los Angeles, and our landlady Rita lived in the back house. In the afternoons, I often trotted over to her place, eager for a change of scenery. Rita spent the whole day doing housework, yet her home looked like one of those places where the government had declared a state of emergency.
I liked to arrive at Rita’s around three, when she would pull out her Lady Pall Malls and plop herself on the couch. “Mi’jo, come here,” she’d call, then scoop me into her lap so we could watch a TV show where beautiful white ladies spent a lot of time crying. I loved it here in Rita’s house, which felt cozy and chaotic at the same time. Once the show ended, Rita would send me back home, saying “See you tomorrow, mi’jo.”
“Mi’jo” is a universal Latino term of endearment. Pronounced me-ho, it’s a contraction of the words, “mi hijo” (my son). Its female counterpart is “mi’ja” (my daughter).
If you’ve ever watched a movie or TV show centered on a Mexican American family, like “Selena,” “Ugly Betty,” or any George Lopez sitcom , you’ve heard characters call each other “mi’jo” and “mi’ja.” Onscreen, these terms are usually used to delineate a relationship for the audience: Mother/son. Father/daughter.
When someone calls you “mi’jo,” it means that you are among family, that you belong, that you are loved.
In real life, the word carries much more power than its literal meaning. When someone calls you “mi’jo,” it means that you are among family, that you belong, that you are loved. It’s a term that is both casual and intimate; it can be used by a family elder, or by a total stranger. It is an everyday word in our communities, yet also one that can still tug at the heartstrings.
Although I grew up in an assimilated household in 1970s Southern California, the word “mi’jo” was always around, implanted in my consciousness nearly as far back as I can remember. As a kid, if someone called out “mi’jo,” I knew to turn around and see if they meant me. Among the people who called me “mi’jo” were my first babysitter, a nice checkout lady at the local market, a few of my mom’s friends, and random old folks in my grandpa’s barrio in El Paso.

It’s hard to come up with an English equivalent of “mi’jo.” Words like “honey,” “kid” or “dear” don’t capture its essence, because some people would be offended being called by those terms. In contrast, no one takes offense at being called “mi’jo.”
Not long after my father passed away in 2019, I went to see his barber, Richard, for a haircut. “MI’JO!” Richard exclaimed when I walked in the door. Unlike my dad, I was never a regular in Richard’s shop; this was perhaps my second or third visit ever. But Richard’s conspicuous greeting seemed a kind of benediction.
Richard’s barbershop functioned like a community man cave, with police officers, gang members and teenagers drifting in and out. There was an old-timer snoozing on a sofa, two mounted TVs playing the same baseball game, and a boxing calendar tacked to the wall. It was comforting to be here, in one of my father’s old hangouts. Being recognized as “mi’jo” by Richard, I realized, was my entree into this sanctum of masculinity, a clubhouse for male bonding at a time when I needed it.
For years, “mi’jo” was something only people like us said. Then in 2017 came “Coco,” the Disney/Pixar animated film about a young Mexican boy searching for his great-great grandfather. In the movie, “mi’jo” was bandied about so frequently that the word edged into the mainstream. Today you can buy T-shirts emblazoned with “Mi’jo,” and there are books , plays, and songs with the word in the title. Latino millennials and Gen-Z’ers sometimes call each other “mi’jo” as a synonym for “dude.” But for me, in “mi’jo” I still hear the intertwining of family and affection, tradition and culture, heritage and home.
Two years ago, my relatives and I helped my mother move into her new house in Burbank. At the end of a hot day spent carrying and unpacking boxes, I stood in the front yard and my mom’s longtime friend Irene approached me.
I’d known Irene since I was in fifth grade, when she and my mother worked in a nearby school district together. Back then, they were two fierce Latina moms navigating their careers; now they were both grandmas and retired. Irene told me to make sure that I visited my mom more often now that she would be living by herself. I nodded.
“Well, mi’jo,” Irene said, “have a good trip back to New York.”
Irene got in her car to drive home, and for a few seconds I felt a kind of lightness. Right then, I had a flashback of her and my mom, bustling around the small yellow kitchen in our old house. They were both dark-haired, bright-eyed and bursting with youthful energy. In that moment, “mi’jo” was my Mexican American madeleine, a word that transported me back, if only briefly, to childhood. It was a fleeting, lovely vision — and the magic in “mi’jo” took me there.
Raul A. Reyes, a lawyer, is a member of the USA Today Board of Contributors. He has written for The New York Times, the Los Angeles Times, The Christian Science Monitor, Texas Monthly and the Huffington Post.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Structuring your synthesis essay by topic works best for more complicated ideas with different aspects that should be explored individually. Example outline: I. Introduction A. Thesis statement. II. Topic 1 A. Source A discussing Topic 1 1. A point or piece of evidence/data from Source A about Topic 1 2.
In the process of crafting a synthesis essay, you will be tasked with combining information from multiple sources to create a cohesive and well-supported argument. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the process, providing helpful tips and examples along the way. Step 1: Understand the Assignment.
The writing process for composing a good synthesis essay requires curiosity, research, and original thought to argue a certain point or explore an idea. Synthesis essay writing involves a great deal of intellectual work, but knowing how to compose a compelling written discussion of a topic can give you an edge in many fields, from the social sciences to engineering.
As a student, you'll probably have to write a synthesis essay at some point. Read on for our step-by-step guide on how to write one effectively. Step 1. Define Your Idea or Argument. If you haven't done so already, decide on a topic to write about. Read up about it using a variety of credible sources and make detailed notes while you research.
How to write body paragraphs for synthesis essays: 1.Pick three points to write about from your list of points about which the writers agreed or disagreed. When picking three to write about, pick the three that offer you ample evidence. 2.Decide the order of the three points to be written about in your body paragraphs.
Your essay should have an introductory paragraph that includes your thesis, a body to present evidence that supports your thesis, and a conclusion that summarizes your point of view. 2. Write in the third person. Writing in the third person means using "he," "she," "it", and using complete, unambiguous sentences.
The basic synthesis essay structure follows the 5 paragraph essay format. Introduction - Briefly describe what the paper will be about. Start with a hook to engage the reader from the very beginning, followed by a brief description, and make sure to include your thesis statement. Body Paragraphs - The first body paragraph typically contains a ...
Overview of Synthesis Essay Writing. First, take some time to develop a thorough understanding of what you will be writing about. Take notes as you go, keeping track of points you want to make and evidence you want to include in the essay. While you read, you can begin to brainstorm a thesis statement and outline for the essay.
Synthesis Essay: The structure of a synthesis essay typically includes an introduction that presents the topic and thesis, followed by body paragraphs that integrate sources to support the thesis. Each paragraph may address different aspects of the topic (themes) or different viewpoints, with the writer synthesizing the information to argue for ...
Step 1 Organize your sources. Step 2 Outline your structure. Step 3 Write paragraphs with topic sentences. Step 4 Revise, edit and proofread. When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you've read - you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own ...
A well-structured synthesis essay guides the reader through your analysis of multiple sources and effectively builds your argument. Here's a breakdown of the typical format: Double-space your essay unless otherwise instructed. Use a standard font (e.g., Times New Roman, Arial) and font size (e.g., 12 pt).
A synthesis matrix will help you with that: Find several central ideas in the chart. Choose the ones that are repeated the most often and the ones that you feel need to be in your essay. Combine them, and you have a thesis statement with all the key points. Make a draft of the thesis statement.
The successful synthesis essay will show readers how you have reasoned about the topic at hand by taking into account the sources critically and creating a work that draws conversations with the sources into your own thinking. Contributor: Derrian Goebel. University Writing & Speaking Center. 1664 N. Virginia Street, Reno, NV 89557.
Paragraph 1: The prompt presents and briefly explains the topic that you'll be writing your synthesis essay about. That topic is the concept of eminent domain. Paragraph 2: The prompt presents a specific claim about the concept of eminent domain in this paragraph: Eminent domain is productive and beneficial.
Revised on May 31, 2023. Synthesizing sources involves combining the work of other scholars to provide new insights. It's a way of integrating sources that helps situate your work in relation to existing research. Synthesizing sources involves more than just summarizing. You must emphasize how each source contributes to current debates ...
Although Mehmad (2012) suggested X, O'Donnell (2013) recommended a different approach. Again, the focus of synthesis is to combine ideas on a given topic and for the writer to use that to review the existing literature or support an overall argument (i.e., in the problem statement, rationale and justification for the method, etc.).
Argumentative syntheses seek to bring sources together to make an argument. Both types of synthesis involve looking for relationships between sources and drawing conclusions. In order to successfully synthesize your sources, you might begin by grouping your sources by topic and looking for connections. For example, if you were researching the ...
When asked to synthesize sources and research, many writers start to summarize individual sources. However, this is not the same as synthesis. In a summary, you share the key points from an individual source and then move on and summarize another source. In synthesis, you need to combine the information from those multiple sources and add your ...
Basics of Synthesis. As you incorporate published writing into your own writing, you should aim for synthesis of the material. Synthesizing requires critical reading and thinking in order to compare different material, highlighting similarities, differences, and connections. When writers synthesize successfully, they present new ideas based on ...
1) Nobody talks like that unless they are an android. 2) Quoting doesn't demonstrate you really know the answer. All it shows is that somebody else knows the answer and you don't. My point is this - Your professor will be grading you on your ability to explain different concepts in your own words. That's synthesis.
nnections or putting things together. We synthesize information naturally to help othe. see the connections between things. For example, when you report to a friend the things that several other friends have said about a song or. movie, you are engaging in synthesis. However, synthesizi.
What does "mi'jo" mean? It's colloquial Spanish for "my son," though it's so much more than its literal meaning to Mexican American writer Raul A. Reyes.