How to prepare for PMP Certification?

Last updated on October-2024 by PMPwithRay, PMP

Examples of Waterfall Type Projects in Project Management
Waterfall is a project management methodology, Examples of Waterfall Type Projects in Project Management , that follows a sequential approach to project delivery, where progress flows downwards through the phases of the project. In this methodology, each phase must be completed before moving on to the next one. Waterfall projects are best suited for projects where the requirements are well defined, and the project team has a clear understanding of what needs to be done. The phases of a typical waterfall project include planning, design, development, testing, and deployment. This methodology is commonly used in projects such as construction projects, software development projects, and manufacturing projects. Waterfall projects have several advantages, such as ease of understanding and accurate estimation of resources, but they also have some disadvantages, such as inflexibility and difficulty accommodating changing requirements. Ultimately, the choice of project management methodology depends on the specific project’s requirements and the project team’s preferences and expertise.
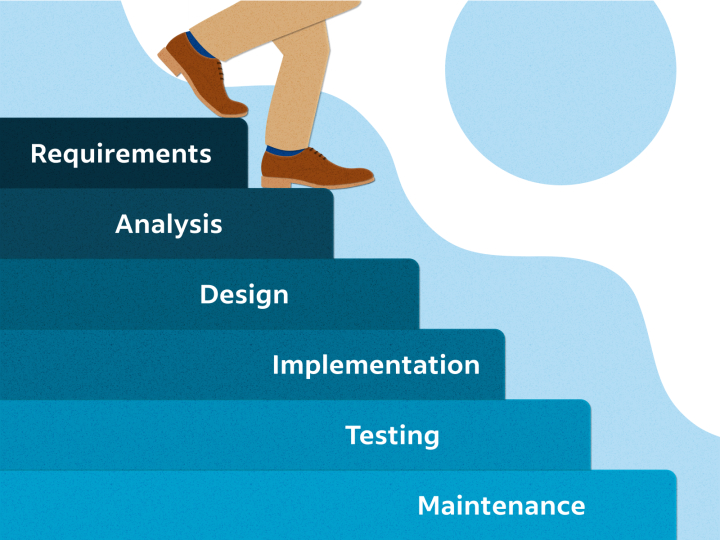
In project management, there are two primary methodologies used to complete projects: waterfall and agile. The waterfall approach is a sequential design process, where progress flows downwards through the phases of the project. Each phase must be completed before moving on to the next one. This methodology is commonly used in projects where the requirements are well defined, and the project team has a clear understanding of what needs to be done. In this blog post, we will explore examples of waterfall type projects in project management in following industries:
- Construction Projects
- Healthcare Projects
- Manufacturing Projects
1. Type of Waterfall Projects - Construction Projects

One of the most common types of waterfall projects, Examples of Waterfall Type Projects in Project Management, is construction projects. Construction projects are characterized by their linear and sequential nature, where each phase must be completed before moving on to the next. The phases of a construction project typically include planning, design, pre-construction, construction, and closeout.
During the planning phase, the project team defines the scope, requirements, and objectives of the project. In the design phase, the project team develops detailed plans and specifications for the project. The pre-construction phase involves preparing the site for construction and obtaining necessary permits and approvals. The construction phase is where the actual construction work takes place, and the closeout phase involves completing final inspections and turning over the project to the owner.
2. Type of Waterfall Projects - Healthcare Projects
The waterfall model is a traditional approach to project management that is commonly used in the healthcare industry is one of the Examples of Waterfall Type Projects in Project Management. This model is a linear sequential approach, where each phase of the project must be completed before moving onto the next phase.
In a healthcare project, the waterfall model typically consists of the following phases:
- Planning : During this phase, project managers work with stakeholders to define the project goals, objectives, and scope. They also create a detailed project plan, including timelines, resource requirements, and budget.
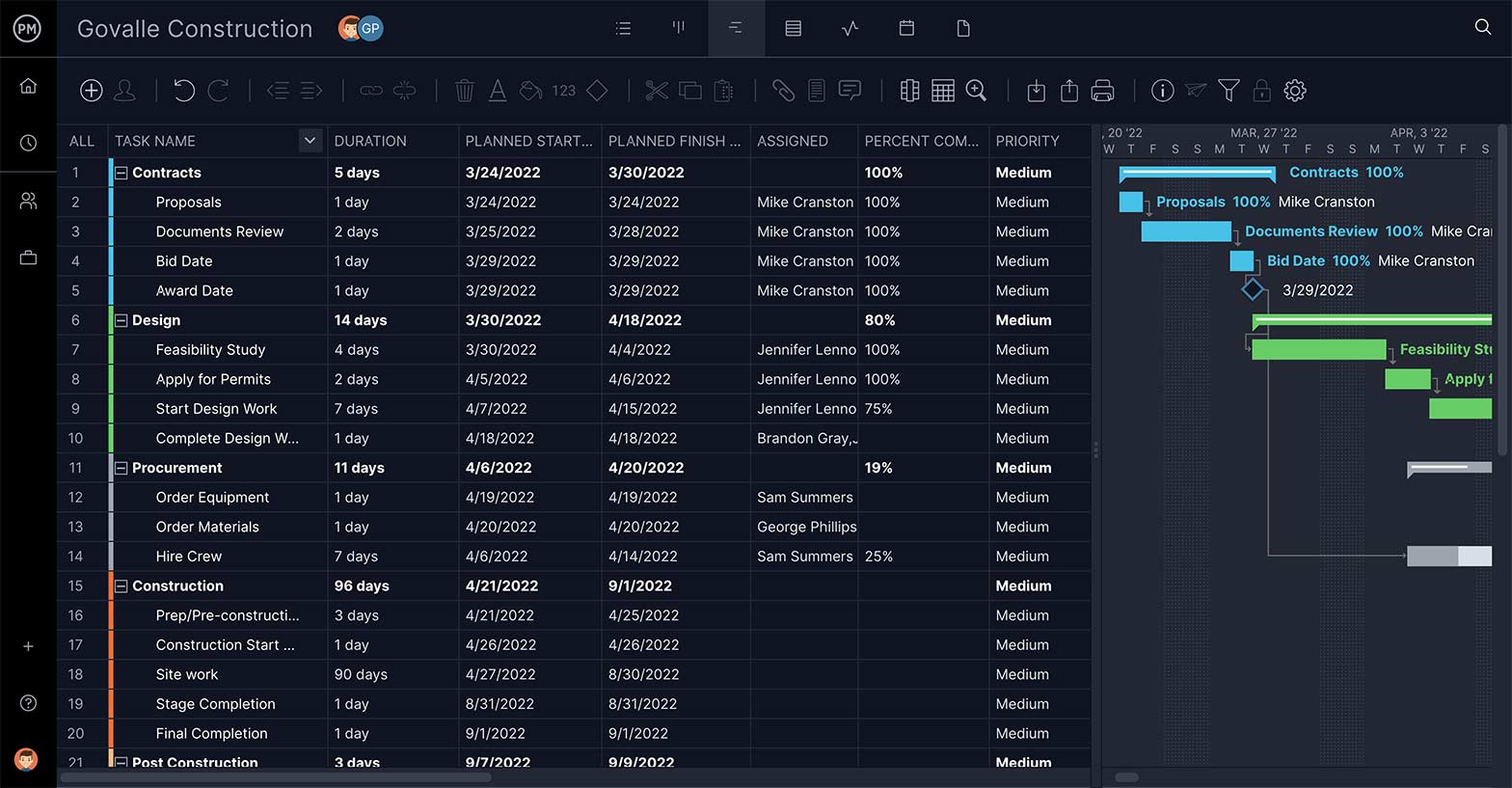
- Requirements gathering: This phase involves gathering and documenting all of the requirements for the project. This includes identifying the needs of all stakeholders, including patients, medical staff, and administrators.
- Design : During this phase, the project team creates detailed specifications for the project. This includes designing the system architecture, developing software requirements, and identifying hardware and software components.
- Implementation : The implementation phase involves building and testing the system or solution based on the design specifications. This includes installing software, configuring hardware, and integrating all components.
- Testing : Once the system or solution has been implemented, the project team performs extensive testing to ensure that it meets all of the project requirements. This includes functional testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing.
- Deployment : During the deployment phase, the project team releases the system or solution to the healthcare organization. This includes training end-users, providing technical support, and monitoring the system to ensure that it is working properly.
- Maintenance : The final phase of the waterfall model involves ongoing maintenance and support for the system or solution. This includes bug fixes, updates, and enhancements based on user feedback.
While the waterfall model can be effective in healthcare projects, it does have some drawbacks. One of the main disadvantages is that it can be inflexible, as changes to the project scope or requirements may require restarting the entire process. Additionally, the linear nature of the model may not be well-suited for complex projects or those with changing requirements.
3. Type of Waterfall Projects - Manufacturing Projects

Manufacturing projects are another example of a waterfall project. These types of projects typically involve the production of physical goods, such as cars, appliances, or electronics. The phases of a manufacturing project typically include planning, design, procurement, production, and delivery.
During the planning phase, the project team defines the scope and objectives of the project. In the design phase, the project team develops detailed plans and specifications for the product. In the procurement phase, the project team acquires the necessary materials and equipment. In the production phase, the project team manufactures the product. Finally, in the delivery phase, the product is shipped to the customer.
What are the advantages of Waterfall Projects in Project Management?
Waterfall projects have several advantages over other project management methodologies. One of the main advantages is that they are easy to understand and implement. The linear and sequential nature of the methodology makes it easy for project team members to know what needs to be done and when.
Another advantage of waterfall projects is that they are well suited for projects with clearly defined requirements. Because the requirements are well defined, the project team can accurately estimate the time and resources needed to complete the project.
What are the disadvantages of Waterfall Projects in Project Management?
While waterfall projects have several advantages, they also have some disadvantages. One of the main disadvantages is that they are not well suited for projects with changing or undefined requirements. Because the methodology is linear and sequential, any changes to the requirements can significantly impact the project’s timeline and budget.
Another disadvantage of waterfall projects is that they do not allow for much flexibility during the project. Once a phase is completed, it is challenging to go back and make changes without impacting the project’s timeline and budget.
If you are planning to write the PMP Exam, you can make the best use of the free resources on my YouTube channel PMPwithRay . Also, make sure you checkout my Udemy courses on PMP Certification as well.
Conclusion - Types of Waterfall Projects in Project Management
These Examples of Waterfall Type Projects in Project Management as mentioned are a common methodology used in project management, particularly for projects with well-defined requirements and a linear structure. We explored several examples of waterfall projects, including construction projects, software development projects, and manufacturing projects. While waterfall projects have several advantages, such as ease of understanding and accurate estimation of resources, they also have some disadvantages, such as inflexibility and difficulty accommodating changing requirements. Ultimately, the choice of project management methodology depends on the specific project’s requirements and the project team’s preferences and expertise. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of different project management methodologies, project teams can choose the best approach for their projects to ensure success.
Hope you enjoyed reading the article. If you are preparing for your PMP Exam, don’t forget to check out my Udemy Courses and Live PMP Masterclass Sessions as below:
- Udemy PMP Exam 2024 Mock Simulator
- PMP Exam 2024 Complete Training Guide – 35 PDUs
- Udemy Course: Project Management with Earned Value Management (9 PDUs)
The last one is the best if you are struggling to learn EVM during your PMP and CAPM preparation.
Cheers and I will talk to you soon!

Nilotpal Ray PMP, MBA, B.Tech
London United Kingdom
Disclaimer: PMI, PMP Certificate, PMI-PMP Badge, PMBOK, PMP, PgMP, PfMP, CAPM, PMI-SP, PMI-RMP, PMI-ACP, and PMI-PBA all are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc. Views expressed in this website are fully personal and does not guarantee any direct correlation or causation towards increased probability of passing the PMP examination.
- Contact sales
- Start free trial
The Ultimate Guide…
Waterfall Model
Brought to you by projectmanager, the online project planning tool used by over 35,000 users worldwide..
What Is the Waterfall Methodology in Project Management?
The phases of the waterfall model, waterfall software development life cycle.
- What Is Waterfall Software?
- Desktop vs Online Waterfall Software
Must-Have Features of Waterfall Software
- The Waterfall Model & ProjectManager.com
Waterfall vs. Agile
- Pros & Cons of the Waterfall Model
Benefits of Project Management Software for Waterfall Projects
Waterfall methodology resources.
The waterfall methodology is a linear project management approach, where stakeholder and customer requirements are gathered at the beginning of the project, and then a sequential project plan is created to accommodate those requirements. The waterfall model is so named because each phase of the project cascades into the next, following steadily down like a waterfall.
It’s a thorough, structured methodology and one that’s been around for a long time, because it works. Some of the industries that regularly use the waterfall model include construction, IT and software development. As an example, the waterfall software development life cycle, or waterfall SDLC, is widely used to manage software engineering projects.
Related: 15 Free IT Project Management Templates for Excel & Word
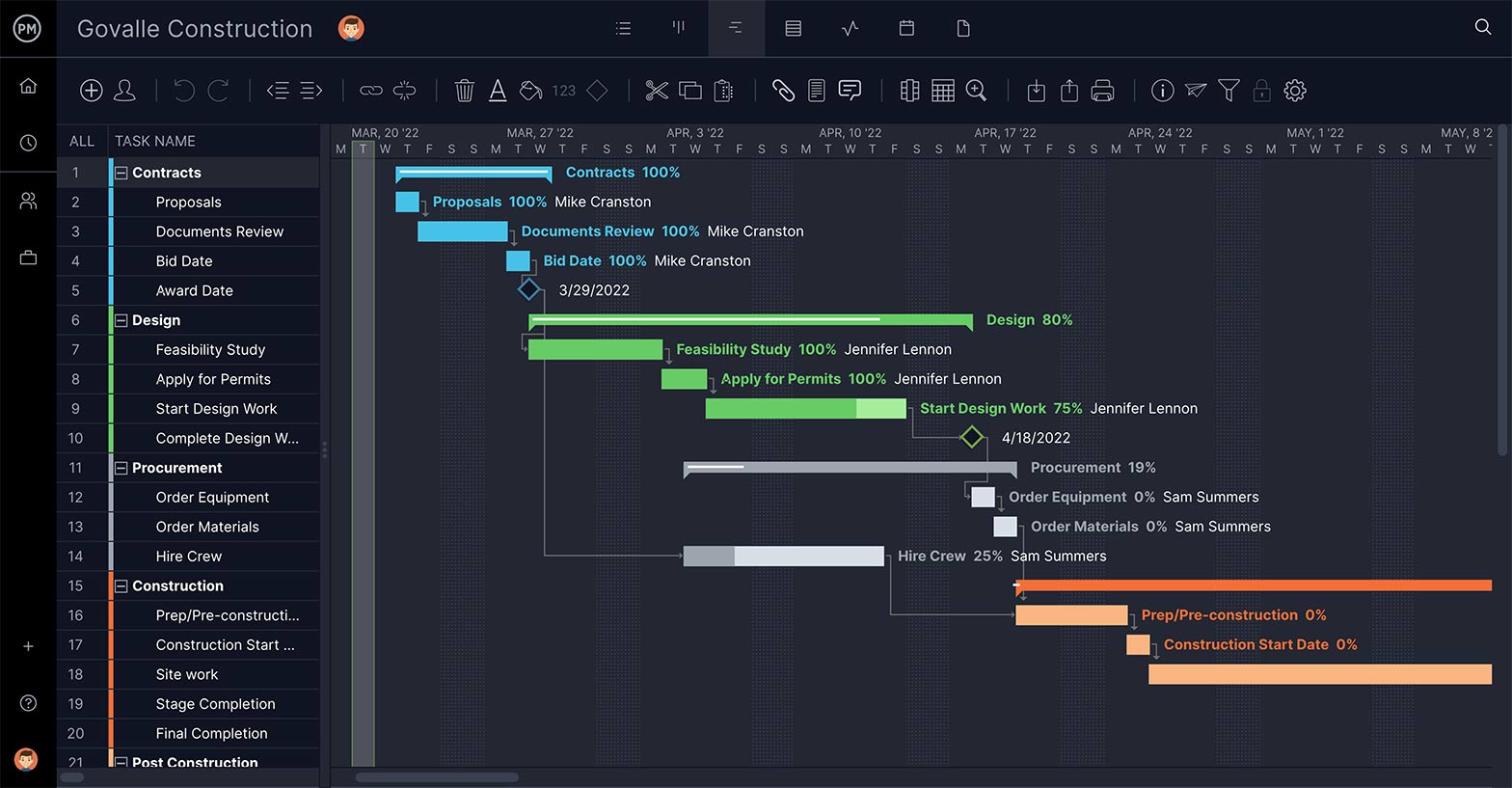
Gantt charts are the preferred tool for project managers working in waterfall method. Using a Gantt chart allows you to map subtasks, dependencies and each phase of the project as it moves through the waterfall lifecycle. ProjectManager’s waterfall software offers these features and more.
Manage waterfall projects in minutes with ProjectManager— learn more .
The waterfall approach has, at least, five to seven phases that follow in strict linear order, where a phase can’t begin until the previous phase has been completed. The specific names of the waterfall steps vary, but they were originally defined by its inventor, Winston W. Royce, in the following way:
Requirements: The key aspect of the waterfall methodology is that all customer requirements are gathered at the beginning of the project, allowing every other phase to be planned without further customer correspondence until the product is complete. It is assumed that all requirements can be gathered at this waterfall management phase.
Design: The design phase of the waterfall process is best broken up into two subphases: logical design and physical design. The logical design subphase is when possible solutions are brainstormed and theorized. The physical design subphase is when those theoretical ideas and schemas are made into concrete specifications.
Implementation: The implementation phase is when programmers assimilate the requirements and specifications from the previous phases and produce actual code.
Verification: This phase is when the customer reviews the product to make sure that it meets the requirements laid out at the beginning of the waterfall project. This is done by releasing the completed product to the customer.
Maintenance: The customer is regularly using the product during the maintenance phase, discovering bugs, inadequate features and other errors that occurred during production. The production team applies these fixes as necessary until the customer is satisfied.
Related: Free Gantt Chart Template for Excel
Let’s hypothesize a simple project, then plan and execute it with the waterfall approach phases that you just learned. For our waterfall software development life cycle example, we’ll say that you’re building an app for a client. The following are the steps you’d take to reach the final deliverable.
Requirements & Documents
First, you must gather all the requirements and documentation you need to get started on the app.
- Project Scope: This is one of the most important documents in your project, where you determine what the goals associated with building your app are: functional requirements, deliverables, features, deadlines, costs, and so on.
- Stakeholder Expectations: In order to align the project scope with the expectations of your stakeholders—the people who have a vested interest in the development of the app—you want to conduct interviews and get a clear idea of exactly what they want.
- Research: To better serve your plan, do some market research about competing apps, the current market, customer needs and anything else that will help you find the unserved niche your app can serve.
- Assemble Team: Now, you need to get the people and resources together who will create the app, from programmers to designers.
- Kickoff: The kickoff meeting is the first meeting with your team and stakeholders where you cover the information you’ve gathered and set expectations.
System Design
Next, you can begin planning the project proper. You’ve done the research, and you know what’s expected from your stakeholders . Now, you have to figure out how you’re going to get to the final deliverable by creating a system design. Based on the information you gathered during the first phase, you’ll determine hardware and software requirements and the system architecture needed for the project.
- Collect Tasks: Use a work breakdown structure to list all of the tasks that are necessary to get to the final deliverable.
- Create Schedule: With your tasks in place, you now need to estimate the time each task will take. Once you’ve figured that out, map them onto a Gantt chart , and diligently link dependencies. You can also add costs to the Gantt, and start building a budget.
Implementation
Now you’re ready to get started in earnest. This is the phase in which the app will be built and tested. The system from the previous phase is first developed in smaller programs known as units. Then each goes through a unit testing process before being integrated.
- Assign Team Tasks: Team members will own their tasks and be responsible for completing them, and for collaborating with the rest of the team. You can make these tasks from a Gantt chart and add descriptions, priority, etc.
- Monitor & Track: While the team is executing the tasks, you need to monitor and track their progress in order to make sure that the project is moving forward per your schedule.
- Manage Resources & Workload: As you monitor, you’ll discover issues and will need to reallocate resources and balance workload to avoid bottlenecks.
- Report to Stakeholders: Throughout the project, stakeholders need updates to show them progress. Meet with them and discuss a regular schedule for presentations.
- Test: Once the team has delivered the working app, it must go through extensive testing to make sure everything is working as designed.
- Deliver App: After all the bugs have been worked out, you’re ready to give the finished app to the stakeholders.
System Testing and Deployment
During this phase you’ll integrate all the units of your system and conduct an integration testing process to verify that the components of your app work properly together.
Once you verify that your app is working, you’re ready to deploy it.
Verification
Though the app has been delivered, the software development life cycle is not quite over until you’ve done some administrative tasks to tie everything up. This is technically the final step.
- Pay Contracts: Fulfil your contractual obligations to your team and any freelance contractors. This releases them from the project.
- Create Template: In software like ProjectManager, you can create a template from your project, so you have a head start when beginning another, similar one.
- Close Out Paperwork: Make sure all paperwork has been rubber stamped and archived.
- Celebrate: Get everyone together, and enjoy the conclusion of a successful project!
Maintenance
Of course, the nature of any software development project is that, through use by customers, new bugs will arise and must be squashed. So, past the verification stage, it’s typically expected that you will provide maintenance beyond launch. This is an ongoing, post-launch phase that extends for as long as your contract dictates.
What Is Waterfall Project Management Software?
Waterfall project management software is used to help you structure your project processes from start to finish. It allows managers to organize their tasks, sets up clear schedules in Gantt charts and monitor and control the project as it moves through its phases.
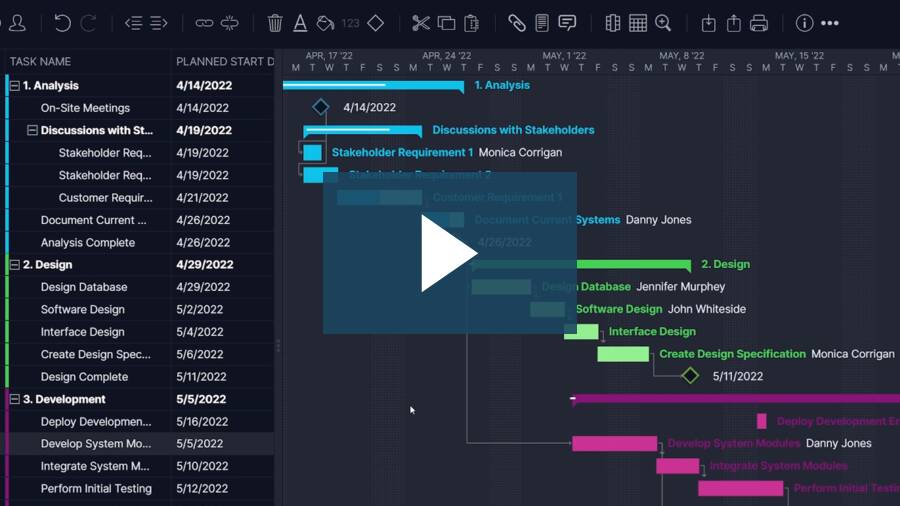
A waterfall project is broken up into phases, which can be achieved on a Gantt chart in the waterfall project management software. Managers can set the duration for each task on the Gantt and link tasks that are dependent on one another to start or finish.
While waterfall software can be less flexible and iterative than more agile frameworks, projects do change frequently—and there must be features that can capture these changes in real-time with dashboards and reports, so that the manager can clear up bottlenecks or reallocate resources to keep teams from having their work blocked. Microsoft Project is one of the most commonly used project management software, but it has major drawbacks that make ProjectManager a great alternative .
Desktop vs Online Project Management Waterfall Software
When it comes to waterfall software, you can choose from either a desktop application or online, cloud-based project management software. This might not seem to be a big issue, but there are important distinctions between these two types of offerings.
That’s because there are differences between the two applications, and knowing those differences will help you make an informed decision.
Desktop waterfall software tends to have a more expensive up-front cost, and that cost can rise exponentially if you are required to pay per-user licensing fees for every member of your team.
Online waterfall software, on the other hand, is typically paid for on a subscription basis, and that subscription is usually a tiered payment plan depending on the number of users.
Connectivity
Online software, naturally, must be connected to the internet. This means your speed and reliability can vary depending on your internet service provider. It also means that if you lose connectivity, you can’t work.
Although the difference is minor, desktop waterfall software never has to worry about connection outages.
If security is a concern, rest assured that both options are highly secure. Desktop software that operates on a company intranet is nigh impenetrable, which can provide your company with a greater sense of security.
Strides in web security, like two-factor authentication and single-sign have made online, cloud-based waterfall software far more secure. Also, online tools have their data saved to the cloud, so if you suffer a crash on your desktop that might mean the end of your work.
Accessibility
Desktops are tied to the computers they are installed to or, at best, your office’s infrastructure. That doesn’t help much if you have distributed teams or work off site, in the field, at home and so on.
Online software is accessible anywhere, any time—so long as you have an internet connection. This makes it always accessible, but even more importantly, it delivers real-time data, so you’re always working on the current state of the project.
Waterfall software helps to organize your projects and make them run smoothly. When you’re looking for the right software to match your needs, make sure it has the following features.
Keep Your Project Structured
Managing a project with the waterfall method is all about structure. One phase follows another. To break your project into these stages, you need an online Gantt chart that has a milestone feature. This indicates the date where one phase of the waterfall process stops and another begins.
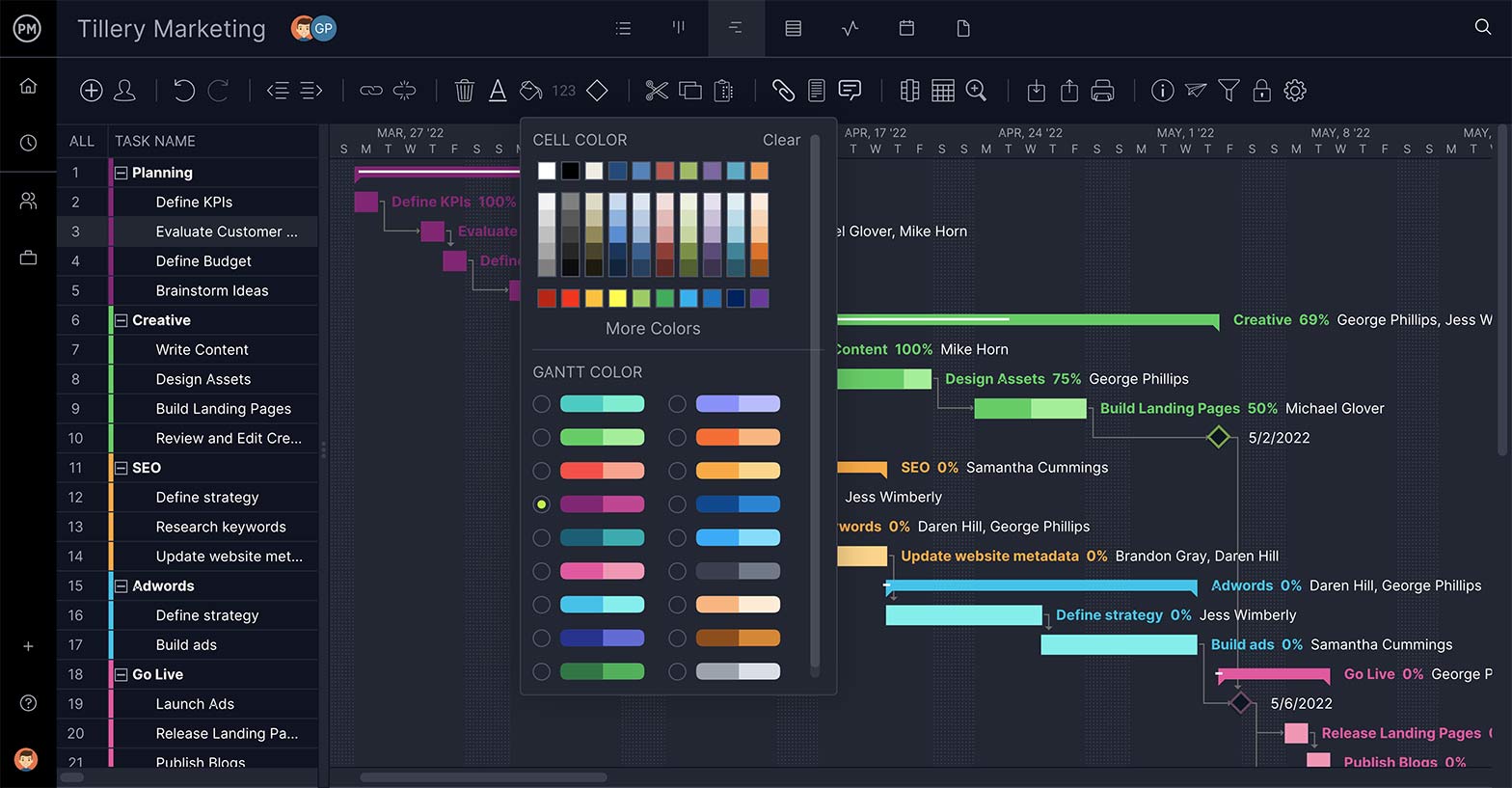
Control Your Task and Schedule
The Gantt chart is a waterfall’s best friend. It organizes your tasks, sets the duration and links tasks that are dependent to keep work flowing later on. When scheduling, you want a Gantt that can automatically calculate your critical path to help you know how much float you have.
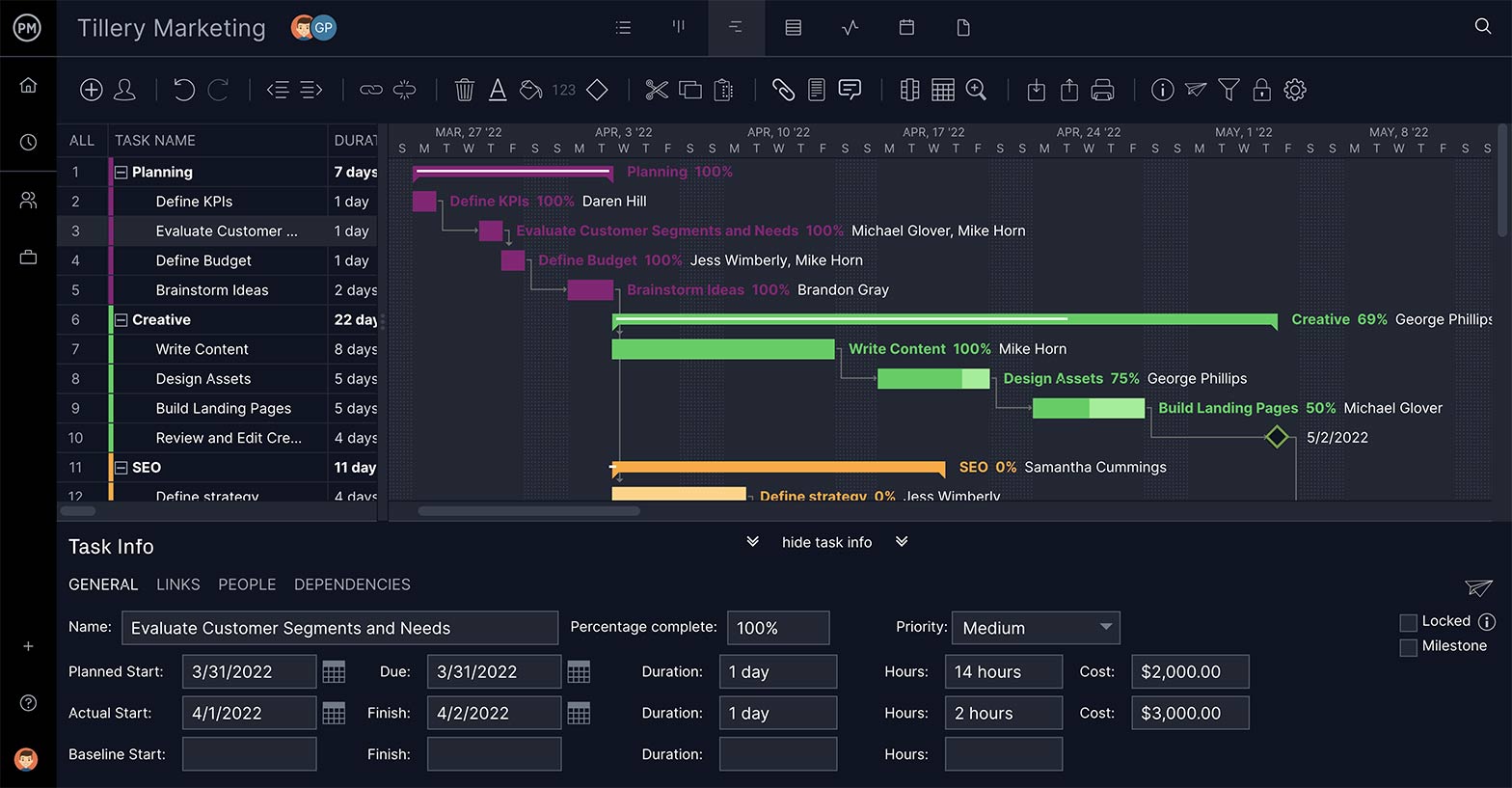
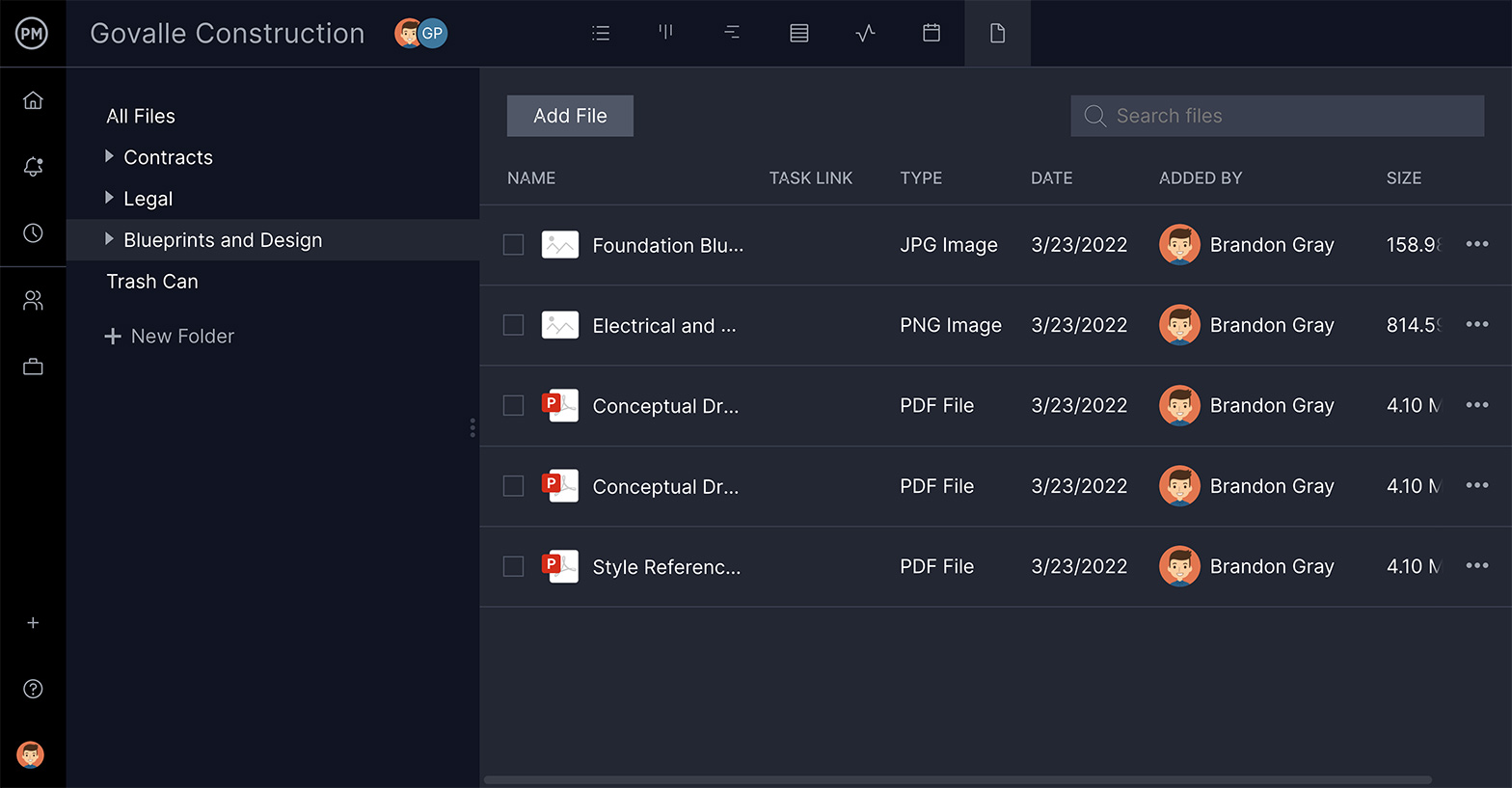
Have Your Files Organized
Waterfall projects, like all projects, collect a lot of paperwork. You want a tool with the storage capacity to hold all your documents and make them easy to find when you need them. Also, attaching files to tasks gives teams direction and helps them collaborate.
Know If You’re on Schedule
Keeping on track means having accurate information. Real-time data makes it timely, but you also need to set your baseline and have dashboard metrics and reporting to compare your actual progress to your planned progress. This makes sure you stay on schedule.
Get an Overview of Performance
Dashboards are designed to collect data and display it over several metrics, such as overall health, workload and more. This high-level view is important, so you want to have a feature that automatically calculates this data and doesn’t require you to manually input it.

Make Data-Based Decisions
Reports dive deeper into data and get more details on a project’s progress and performance. Real-time data makes them accurate. Look for ease of use—it should only take a single click to generate and share. You’ll also want to filter the results to see only what you’re interested in.
The Waterfall Model & ProjectManager
ProjectManager is an award-winning project management software that organizes teams and projects. With features such as online Gantt charts, task lists, reporting tools and more, it’s an ideal tool to control your waterfall project management.
Sign up for a free 30-day trial and follow along to make a waterfall project in just a few easy steps. You’ll have that Gantt chart built in no time!
1. Upload Requirements & Documents
Waterfall project management guarantees one thing: a lot of paperwork. All the documentation and requirements needed to address for the project can quickly become overwhelming.
You can attach all documentation and relevant files to our software, or directly on a task. Now, all of your files are collected in one place and are easy to find. Don’t worry about running out of space—we have unlimited file storage.
2. Use a Work Breakdown Structure to Collect Tasks
Getting to your final deliverable will require many tasks. Planning the waterfall project means knowing every one of those tasks, no matter how small, and how they lead to your final deliverable. A work breakdown structure is a tool to help you figure out all those steps.
To start, use a work breakdown structure (WBS) to collect every task that is necessary to create your final deliverable. You can download a free WBS template here . Then, upload the task list to our software.
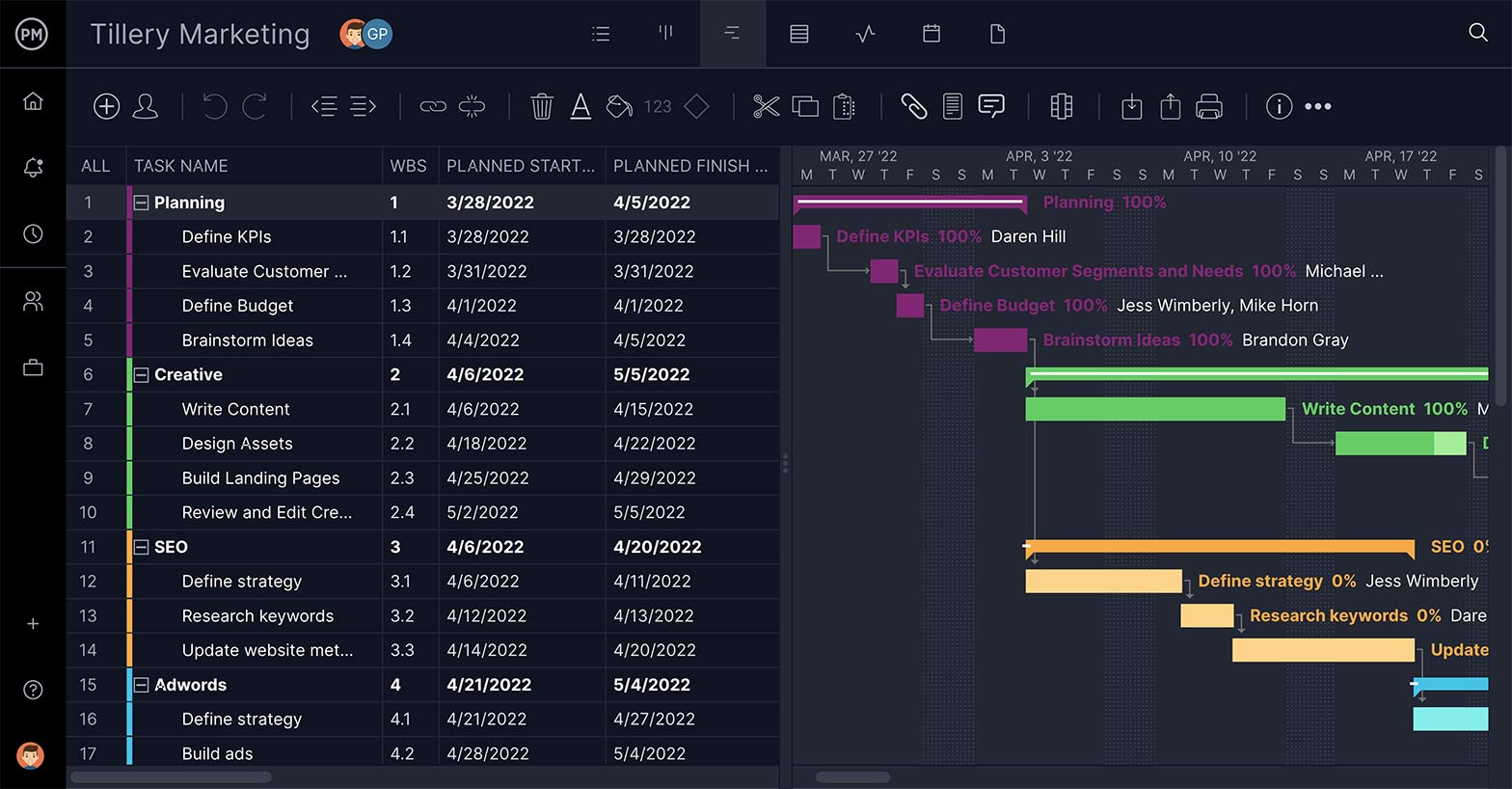
3. Open in Gantt Project View
Gantt charts are essential project management tools used for planning and scheduling. They collect your tasks in one place on a timeline . From there, you can link dependencies, set milestones, manage resources and more.
In the software, open the Gantt chart view and add deadlines, descriptions, priorities and tags to each task.
4. Create Phases & Milestones
Milestones are what separates major phases in a waterfall method project. Waterfall methodology is all about structure and moving from one phase to the next, so breaking your project into milestones is key to the waterfall method.
In the Gantt view, create phases and milestones to break up the project. Using the milestone feature, determine when one task ends and a new one begins. Milestones are symbolized by a diamond on the Gantt.
5. Set Dependencies in a Gantt Chart
Dependent tasks are those that cannot start or finish until another starts or finishes. They create complexities in managing any waterfall project.
Link dependent tasks in the Gantt chart. Our software allows you to link all four types of dependencies: start-to-start, start-to-finish, finish-to-finish and finish-to-start. This keeps your waterfall project plan moving forward in a sequential order and prevents bottlenecks.
6. Assign From Gantt Charts
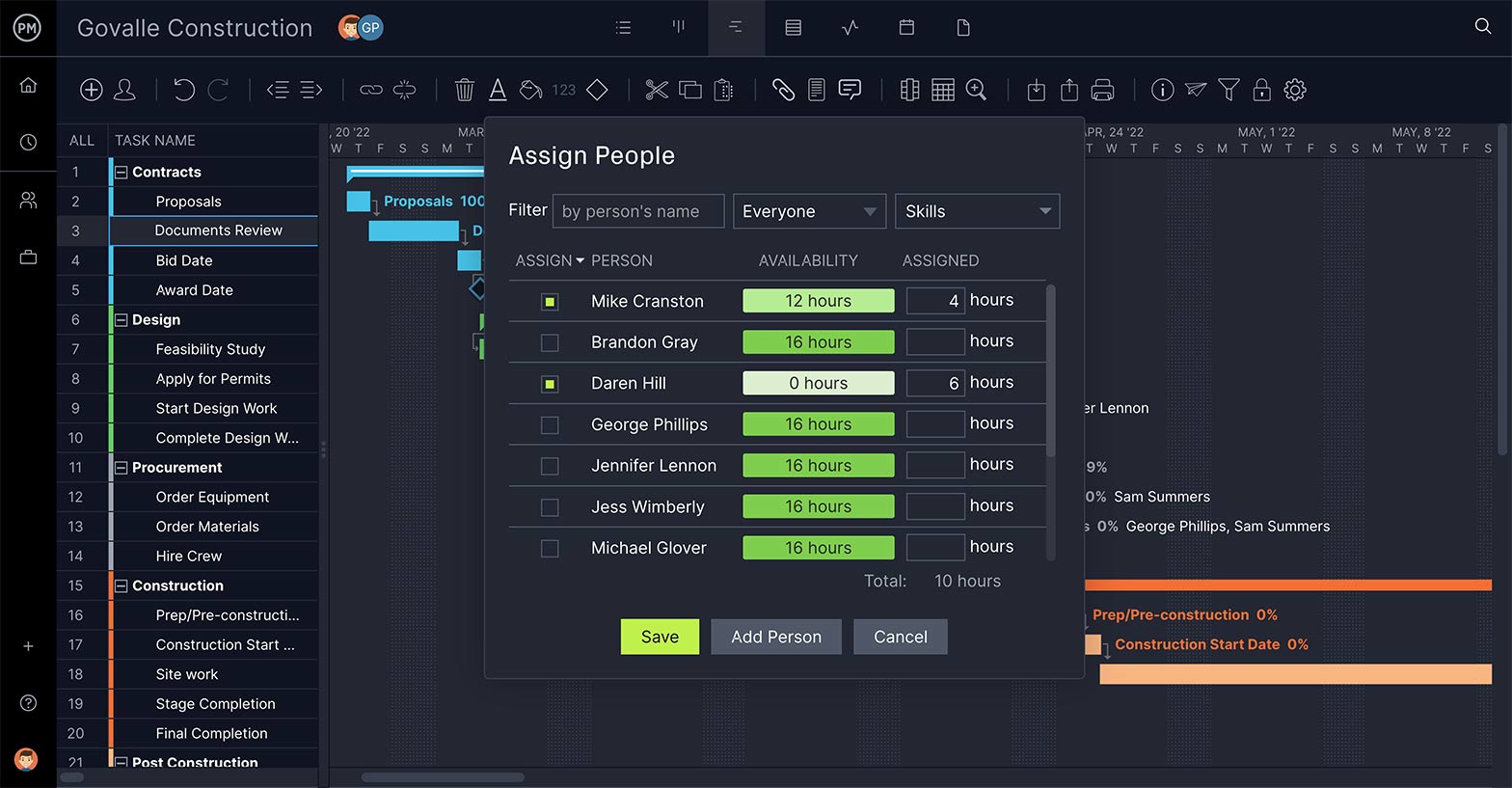
Although you’ve planned and scheduled a project, it’s still just an abstraction until you get your team assigned to execute those tasks. Assigning is a major step in managing your waterfall project and needs to happen efficiently.
Assign team members to tasks right from the Gantt chart. You can also attach any related images or files directly to the task. Collaboration is supported by comments at the task level. Anyone assigned or tagged will get an email alert to notify them of a comment or update.
7. Manage Resources & Workload
Resources are anything you need to complete the project. This means not only your team, but also the materials and tools that they need. The workload represents how many tasks your team is assigned, and balancing that work keeps them productive.
Keep track of project resources on the Workload view. See actual costs, and reallocate as needed to stay on budget. Know how many tasks your team is working on with easy-to-read color-coded charts, and balance their workload right on the page.
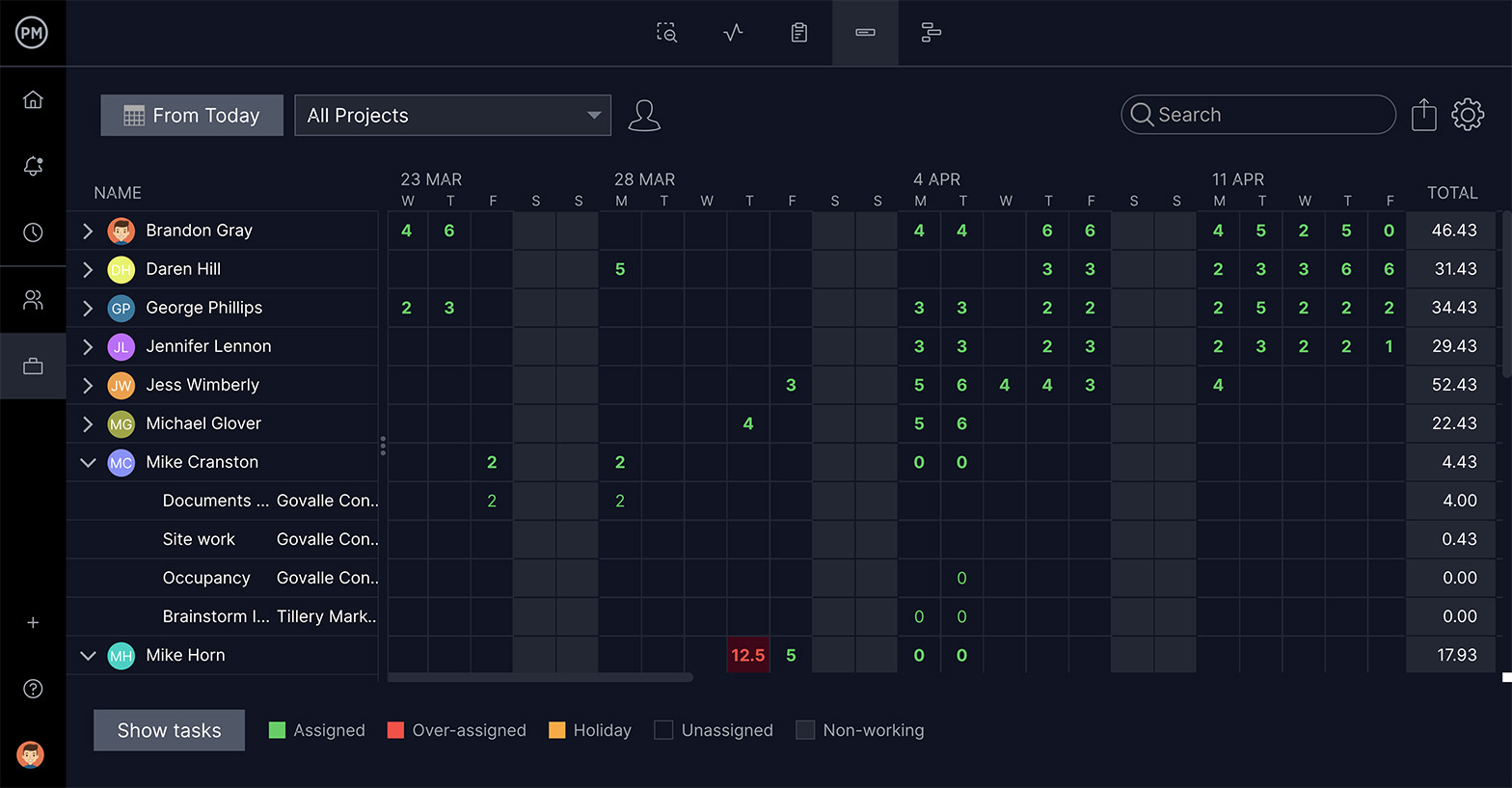

8. Track Progress in Dashboard & Gantt
Progress must be monitored to know if you’re meeting the targets you set in your waterfall method plan. The Gantt shows percentage complete, but a dashboard calculates several metrics and shows them in graphs and charts.
Monitor your project in real time and track progress across several metrics with our project dashboard . We automatically calculate project health, costs, tasks and more and then display them in a high-level view of your project. Progress is also tracked by shading on the Gantt’s duration bar.

9. Create Reports
Reporting serves two purposes: it gives project managers greater detail into the inner-workings of their waterfall project to help them make better decisions, and acts as a communication tool to keep stakeholders informed.
Easily generate data-rich reports that show project variance, timesheets , status and more. Get reports on your planned vs. the actual progress. Filter to show just the information you want. Then, share with stakeholders during presentations and keep everyone in the loop.

10. Duplicate Plan for New Projects
Having a means to quickly copy projects is helpful in waterfall methodology, as it jumpstarts the next project by recreating the major steps and allowing you to make tweaks as needed.
Create templates to quickly plan any recurring waterfall projects. If you know exactly what it takes to get the project done, then you can make it into a template. Plus, you can import proven project plans from MSP, and task lists from Excel and Word.
The waterfall methodology is one of two popular methods to tackle software engineering projects; the other method is known as Agile .
It can be easier to understand waterfall when you compare it to Agile. Waterfall and Agile are two very different project management methodologies , but both are equally valid, and can be more or less useful depending on the project.
Waterfall Project Management
If the waterfall model is to be executed properly, each of the phases we outlined earlier must be executed in a linear fashion. Meaning, each phase has to be completed before the next phase can begin, and phases are never repeated—unless there is a massive failure that comes to light in the verification or maintenance phase.
Furthermore, each phase is discrete, and pretty much exists in isolation from stakeholders outside of your team. This is especially true in the requirements phase. Once the customer’s requirements are collected, the customers cease to play any role in the actual waterfall software development life cycle.
Agile Project Management
The agile methodology differs greatly from the waterfall approach in two major ways; namely in regards to linear action and customer involvement. Agile is a nimble and iterative process, where the product is delivered in stages to the customer for them to review and provide feedback.
Instead of having everything planned out by milestones, like in waterfall, the Agile software development method operates in “sprints” where prioritized tasks are completed within a short window, typically around two weeks.
These prioritized tasks are fluid, and appear based on the success of previous sprints and customer feedback, rather than having all tasks prioritized at the onset in the requirements phase.
Understanding the Difference Between Waterfall & Agile
The important difference to remember is that a waterfall project is a fixed, linear plan. Everything is mapped out ahead of time, and customers interact only at the beginning and end of the project. The Agile method, on the other hand, is an iterative process, where new priorities and requirements are injected into the project after sprints and customer feedback sessions.
Pros & Cons of the Waterfall Project Management
There are several reasons why project managers choose to use the waterfall project management methodology. Here are some benefits:
- Project requirements are agreed upon in the first phase, so planning and scheduling is simple and clear.
- With a fully laid out project schedule , you can give accurate estimates for your project cost, resources and deadlines.
- It’s easy to measure progress as you move through the waterfall model phases and hit milestones.
- Customers aren’t perpetually adding new requirements to the project, which can delay production.
Of course, there are drawbacks to using the waterfall method as well. Here are some disadvantages to this approach:
- It can be difficult for customers to articulate all of their needs at the beginning of the project.
- If the customer is dissatisfied with the product in the verification phase, it can be very costly to go back and design the code again.
- A linear project plan is rigid, and lacks flexibility for adapting to unexpected events.
Although it has its drawbacks, a waterfall project management plan is very effective in situations where you are encountering a familiar scenario with several knowns, or in software engineering projects where your customer knows exactly what they want at the onset.
Using a project management software is a great way to get the most out of your waterfall project. You can map out the steps and link dependencies to see exactly what needs to go where.
As illustrated above, ProjectManager is made with waterfall methodology in mind, with a Gantt chart that can structure the project step-by-step. However, we have a full suite of features, including kanban boards that are great for Agile teams that need to manage their sprints.
With multiple project views, both agile and waterfall teams and more traditional ones can work from the same data, delivered in real time, only filtered through the project view most aligned to their work style. We take the waterfall methodology and bring it into the modern world.
Now that you know how to plan a waterfall project, give yourself the best tools for the job. Take a free 30-day trial and see how ProjectManager can help you plan with precision, track with accuracy and deliver your projects on time and under budget.
Start My Free Trial
- Gantt Chart Software
- Project Planning Software
- Project Scheduling Software
- Requirements Gathering Template
- Gantt Chart Template
- Change Request Form
- Project Management Trends (2022)
- SDLC – The Software Development Life Cycle
- IT Project Management: The Ultimate Guide
- Project Management Methodologies – An Overview
- Project Management Framework Types, Key Elements & Best Practices
Start your free 30-day trial
Deliver faster, collaborate better, innovate more effectively — without the high prices and months-long implementation and extensive training required by other products.
- Product overview
- All features
- Latest feature release
- App integrations
- project icon Project management
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- my-task icon Admin and security
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Project intake
- Resource planning
- Product launches
- View all use cases arrow-right icon

- Help Center
- Asana Academy
- Certifications
- Work management hub
- Customer stories
- Get support
- Developer support
- Customer Success
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Project management |
- Guide to waterfall methodology: Free te ...
Guide to waterfall methodology: Free template and examples

Waterfall project management is a sequential project management methodology that's divided into distinct phases. Each phase begins only after the previous phase is completed. This article explains the stages of the waterfall methodology and how it can help your team achieve their goals.
But what if your project requires a more linear approach? Waterfall methodology is a linear project management methodology that can help you and your team achieve your shared goals—one task or milestone at a time. By prioritizing tasks and dependencies, the waterfall method helps keep your project on track.
3 ways to transform your enterprise project management
Watch a live demo and Q&A session to help you streamline goal-setting, accelerate annual planning, and automate how teams intake strategic work.
What is waterfall methodology?
Waterfall methodology, a term coined by Dr. Winston W. Royce in 1970, is a sequential design process used in software development and product development where project progress flows steadily downwards through several phases—much like a waterfall. The waterfall model is structured around a rigid sequence of steps that move from conception, initiation, analysis, design, construction, testing, implementation, and maintenance.
Unlike more flexible models, such as Agile, the waterfall methodology requires each project phase to be completed fully before the next phase begins, making it easier to align with fixed budgets, timelines, and requirements.
By integrating comprehensive documentation and extensive upfront planning, waterfall methodology minimizes risk and tends to align well with traditional project management approaches that depend on detailed records and a clear, predetermined path to follow.
For example, here’s what a waterfall project might look like:
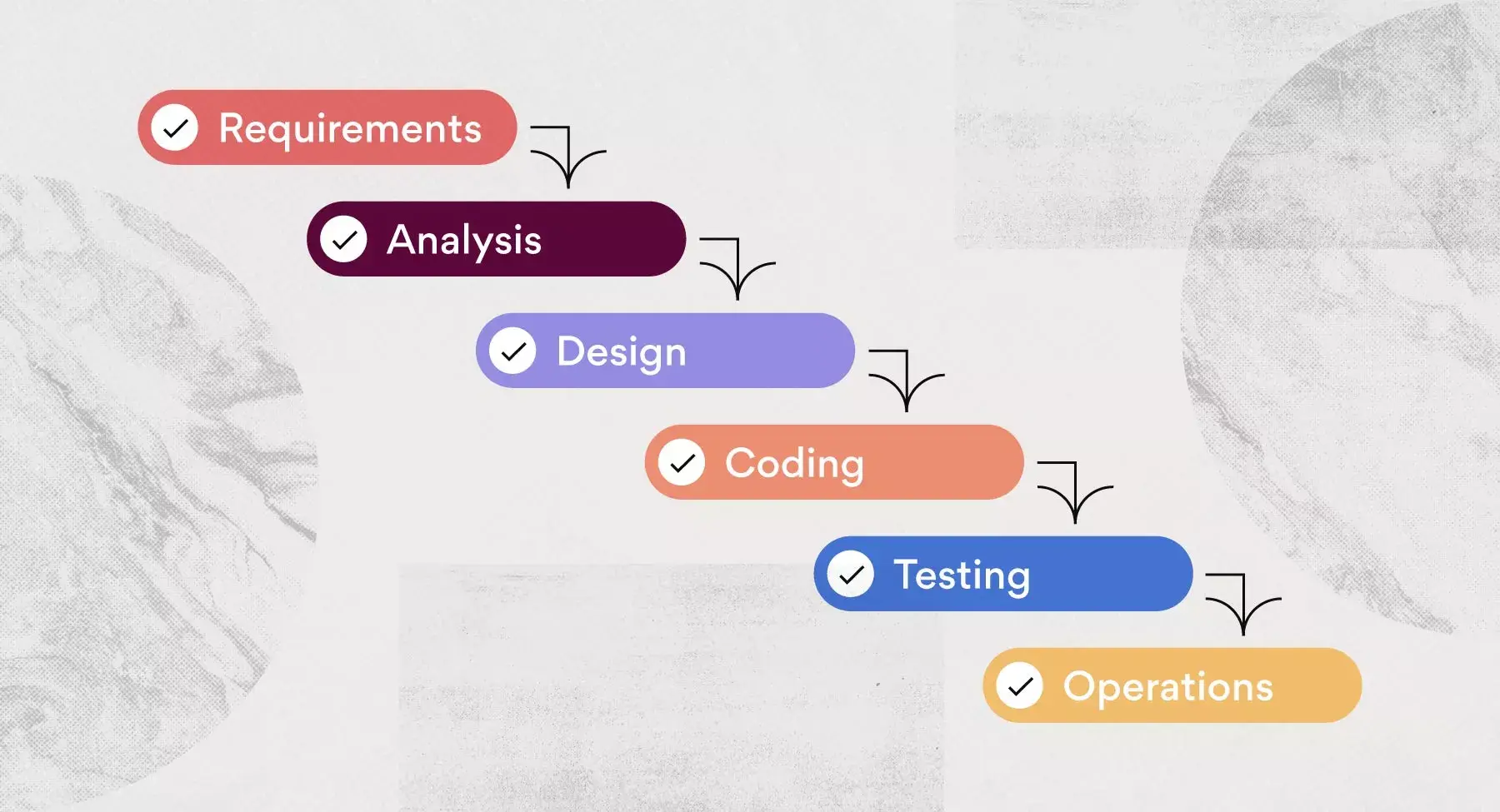
The waterfall methodology is often visualized in the form of a flow chart or a Gantt chart. This methodology is called waterfall because each task cascades into the next step. In a Gantt chart, you can see the previous phase "fall" into the next phase.
6 phases of the waterfall project management methodology
Any team can implement waterfall project management, but this methodology is most useful for processes that need to happen sequentially. If the project you’re working on has tasks that can be completed concurrently, try another framework, like the Agile methodology .
If you’re ready to get started with the waterfall methodology, follow these six steps:
1. Requirements phase
This is the initial planning process in which the team gathers as much information as possible to ensure a successful project. Because tasks in the waterfall method are dependent on previous steps, it requires a lot of forethought. This planning process is a crucial part of the waterfall model, and because of that, most of the project timeline is often spent planning.
To make this method work for you, compile a detailed project plan that explains each phase of the project scope. This includes everything from what resources are needed to what specific team members are working on the project. This document is commonly referred to as a project requirements document.
By the end of the requirements phase, you should have a very clear outline of the project from start to finish, including:
Each stage of the process
Who’s working on each stage
Key dependencies
Required resources
A timeline of how long each stage will take.
A well-crafted requirements document serves as a roadmap for the entire project, ensuring that all stakeholders are on the same page.
2. System design phase
In a software development process, the design phase is when the project team specifies what hardware the team will be using, and other detailed information such as programming languages, unit testing, and user interfaces. This phase of the waterfall methodology is key to ensuring that the software will meet the required functionality and performance metrics.
There are two steps in the system design phase: the high-level design phase and the low-level design phase. In the high-level design phase, the team builds out the skeleton of how the software will work and how information will be accessed. During the low-level design phase, the team builds the more specific parts of the software. If the high-level design phase is the skeleton, the low-level design phase is the organs of the project.
Those team members developing using the waterfall method should document each step so the team can refer back to what was done as the project progresses.
3. Implementation phase
This is the stage where everything is put into action. The team starts the full development process to build the software in accordance with both the requirements phase and the system design phase, using the requirements document from step one and the system design process from step two as guides.
During the implementation phase, developers work on coding and unit testing to ensure that the software meets the specified requirements.
4. Testing phase
This is the stage in which the development team hands the project over to the quality assurance testing team. QA testers search for any bugs or errors that need to be fixed before the project is deployed.
Testers should clearly document all of the issues they find when QAing. In the event that another developer comes across a similar bug, they can reference previous documentation to help fix the issue.
5. Deployment phase
For development projects, this is the stage at which the software is deployed to the end user. For other industries, this is when the final deliverable is launched and delivered to end customers. A successful deployment phase requires careful planning and coordination to ensure a smooth rollout.
6. Maintenance phase
Once a project is deployed, there may be instances where a new bug is discovered or a software update is required. This is known as the maintenance phase, and it's common in the software development life cycle to be continuously working on this phase.
Regular maintenance and updates are essential for keeping the software running smoothly and addressing any issues that arise post-deployment.
When to use waterfall methodology
The waterfall methodology is a common form of project management because it allows for thorough planning and detailed documentation. However, this framework isn’t right for every project. Here are a few examples of when to use this type of project management.
Project has a well-defined end goal
One of the strengths of the waterfall approach is that it allows for a clear path from point A to point B. If you're unsure of what point B is, your project is probably better off using an iterative form of project management like the Agile approach.
Projects with an easily defined end goal are well-suited for waterfall methodology because project managers can work backwards from the goal to create a clear and detailed path with all of the requirements necessary.
No restraints on budget or time
If your project has no restraints on budget or time, team members can spend as much time as possible in the requirements and system design phases. They can tweak and tailor the needs of the project as much as they want until they land on a well-thought-out and defined project plan.
Creating repeatable processes
The waterfall model requires documentation at almost every step of the process. This makes it easy to repeat your project for a new team member; each step is clearly detailed so you can recreate the process.
Creating repeatable processes also makes it easy to train new team members on what exactly needs to be done in similar projects. This makes the waterfall process an effective approach to project management for standardizing processes.
Waterfall vs. Agile methodologies
While the waterfall methodology follows a linear, sequential approach, Agile is an iterative and incremental methodology. In Agile, the project is divided into smaller, manageable chunks known as sprints. Each sprint includes planning, design, development, testing, and review phases.
The Agile method emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and rapid iteration based on continuous feedback. It allows for changes and adaptations throughout the project's lifecycle. In contrast, the waterfall model has a more rigid structure with distinct phases and limited room for changes once a phase is complete.
The choice between waterfall and Agile depends on factors such as project complexity, clarity of requirements, team size, and client involvement. The waterfall model is suitable for projects with well-defined requirements and minimal changes expected, while the Agile method is favored for projects with evolving requirements and a need for frequent client feedback and course corrections.
Benefits of waterfall methodology
Consistent documentation makes it easy to backtrack.
When you implement the waterfall project management process, you’re creating documentation every step of the way. This can be beneficial—if your team needs to backtrack your processes, you can easily find mistakes. It's also great for creating repeatable processes for new team members, as mentioned earlier.
Tracking progress is easy
By laying out a waterfall project in a Gantt chart, you can easily track project progress. The timeline itself serves as a progress bar, so it’s always clear what stage a project is in.
![what type of projects use waterfall methodology [Old Product UI] Mobile app launch project in Asana (Timeline)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/a5f7977a-e36d-43fb-89e9-ca12b741ca11/inline-visual-project-management-kanban-timeline-calendar-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Team members can manage time effectively
Because the waterfall methodology requires so much upfront planning during the requirement and design phase, it is easy for stakeholders to estimate how much time their specific part of the waterfall process will take.
Downsides of waterfall project management
Roadblocks can drastically affect timeline.
The waterfall methodology is linear by nature, so if there's a bump in the road or a task gets delayed, the entire timeline is shifted. For example, if a third-party vendor is late on sending a specific part to a manufacturing team, the entire process has to be put on hold until that specific piece is received.
Linear progress can make backtracking challenging
One of the major challenges of the waterfall methodology is that it's hard to go back to a phase once it's already been completed. For example, if someone is painting the walls of a house, they wouldn’t be able to go back and increase the size of one of the rooms.
QA is late in the process
In comparison to some of the more iterative project management methodologies like Kanban and Agile, the review stage in a waterfall approach happens later in the process. If a mistake is made early on in the process, it can be challenging to go back and fix it. Because of how the waterfall process works, it doesn’t allow for room for iteration or searching for the best solution.
Waterfall methodology examples
To better understand how the waterfall methodology is applied in practice, let's look at a couple of real-world use cases:
1. Construction Project: Building a new office complex requires careful planning and sequential execution. The project manager first gathers all the requirements, such as building specifications, timelines, and budgets. Then, architects and engineers create detailed designs. After approval, construction starts and strict quality controls follow. Finally, the building is handed over to the client for use and maintenance.
2. Software Engineering Project: A company wants to develop a new mobile application using the software development life cycle (SDLC). The project manager defines the product requirements, including features, performance metrics, and integrations. Software architects create the high-level design and technical specifications. Developers then follow the SDLC phases of coding, unit testing, and deployment. The team follows the waterfall methodology throughout the product development process, making sure that each step is finished before going on to the next. After the successful launch, the mobile app enters the maintenance phase, where the team addresses user feedback and provides updates.
Managing your waterfall project
With waterfall projects, there are many moving pieces and different team members to keep track of. One of the best ways to stay on the same page is to use project management software to keep workflows, timelines, and deliverables all in one place.
If you're ready to try waterfall project management with your team, try a template in Asana . You can view Asana projects in several ways, including Timeline view, which visualizes your project as a linear timeline.
FAQ: Waterfall methodology
How do you handle changes in requirements during a waterfall project?
Handling changes in requirements during a waterfall project can be challenging, but it's essential to assess the impact of the change, communicate with stakeholders, update project documentation, adjust the project plan, and ensure all team members are informed of the changes. Implementing a change control process can help formally manage and track changes throughout the project.
Can you combine waterfall and agile methodologies in a single project?
Yes, it is possible to combine waterfall and agile methodologies in a single project using a hybrid approach. This involves using waterfall methodology for the upfront planning and requirements gathering phases and adopting agile practices during the implementation and testing phases. The balance between the waterfall model and Agile method can be adjusted based on the project scope.
How do you ensure successful team collaboration on a waterfall project?
Ensuring successful team collaboration in a waterfall project involves establishing clear communication, defining roles and responsibilities, scheduling regular meetings, using collaborative tools, fostering a positive team culture, and providing necessary support and resources. By focusing on these key aspects, teams can work together effectively and efficiently to achieve project goals.
What are the best project management tools for waterfall methodology?
For teams following a waterfall methodology, Asana is the best project management tool available. Its comprehensive set of features, such as Timeline view for visualizing project plans, task dependencies for ensuring proper sequencing, and seamless integrations, make it the ideal choice for managing linear projects. While other tools like Microsoft Project offer waterfall-specific features, Asana's ease of use, collaboration capabilities, and flexibility make it the top choice for teams looking to streamline their waterfall project management process.
Related resources
What is a product backlog? (And how to create one)
How to use benchmarking to set your standards for success

How to scale retail management operations with Asana

How Asana’s digital team used work management to refresh our brand

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The waterfall methodology for project management follows a linear progression, in which each phase of a project is completed before moving onto the next.
In project management, there are two primary methodologies used to complete projects: waterfall and agile. The waterfall approach is a sequential design process, where progress flows downwards through the phases of the project. …
Before complex processes such as software development and technology came into play, the Waterfall model was widely used and accepted. Let’s rediscover this age-old …
What Is the Waterfall Methodology in Project Management? The waterfall methodology is a linear project management approach, where stakeholder and customer requirements are gathered at the beginning of the project, and then a …
Waterfall methodology is a linear project management methodology that can help you and your team achieve your shared goals—one task or milestone at a time. By prioritizing tasks and dependencies, the …
Waterfall project management is a linear project management methodology that moves through distinct phases of work. The next phase of work is dependent on the previous phase, so only one project phase can be …
The Waterfall Model is a linear or sequential approach to project management and works based on fixed dates, requirements, and outcomes. Teams do not require consistent communication and, unless specific …
Waterfall methodology is a widely used project management method with a linear approach. In Waterfall, each stage of the workflow needs to be completed before moving on to the next step.