Visual Aids In Presentations: The Complete Guide
@danishd This is a sample bio. You can change it from WordPress Dashboard, Users → Biographical Info. Biographical Info
Published Date : August 21, 2020
Reading Time :
A picture, they say, is worth a thousand words. Using visual aids in presentations helps you pass a lot of information in a relatively shorter time. With the right visual aids, you can create the desired impact that you want your presentation to make on your audience. Learning how to use visual aids effectively will boost the quality of your presentations. We discuss some of the top visual aids in our recent YouTube video :

Visual Aid Definition
What are visual aids? Simply put, visual aids are things that your listening can look at while you give your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech or presentation. Visual aid appeals to the audience’s vision more than any other sensory organ.
Why use visuals for presentations?
There is no such thing as a perfect Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . However, there are ways to make a presentation closer to perfection. What are they? Simple: Visual aids. Visual aids can bring life back into a tedious Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , and they take less time to come up with than long notes. This article discusses how you can use visual aids effectively and conquer an audience. Before that, we discuss how visuals can help you achieve a better presentation.
They help you structure your work.
Using the right types of visual aids can help you create a perfect picture of what you want your audience to see in your presentations. Instead of struggling to condense a lot of information into a long text, you can present your information in one straightforward image or video and save yourself the stress.
It is easier to engage the audience.
An excellent visual setup can help elicit audience interest and sometimes their input in the presentation. When the audience is engaged, they tend to be more interested in the presenter’s work. Also, an interactive audience can boost your morale and encourage you.
You save time on your presentation.
When presenting, time is of the essence. So, you can effectively reduce your presentation time if you have useful visual aids and use them properly. Would you prefer to go on and on for minutes about a topic when you can cut your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech down by inserting a few images or videos?
What are visual aids?
A visual aid is any material that gives shape and form to words or thoughts. Types of visual aids include physical samples, models, handouts, pictures, videos, infographics, etc. Visual aids have come a long way, including digital tools such as overhead projectors, PowerPoint presentations, and interactive boards.
Different Types Of Creative Visual Aid Ideas To Awe Your Audience
Have you ever been tasked with making a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech or a presentation but don’t know how to make it truly remarkable? Well, visual aid is your answer.
Giving a presentation or Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech is hard. You have to strike a balance between persuading or informing your audience while also maintaining their attention. The fear of your audience slipping away is very real. And a visual aid can help.
We surveyed the Orai community to vote for their preferred visual aid. Here are the top ten creative visual aid ideas that you could use in your next presentation:
Videos emerged as the clear winner in all our surveys. We ran these surveys on all our social handles and contacted successful speakers. 27.14% of all respondents prefer visual aids because they are easy to understand, can be paused during a presentation, and can trigger all sorts of emotions. That being said, it is also very tough to create good videos. However, more and more tools are available to help you create amazing videos without professional help.
Hans Rosling’s TED talk, titled ‘the best stats you have ever seen,’ is one of the best speeches. He uses video for the Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ’s entirety while not diverting the audience’s attention away from him. He does all this while also bringing out some optimism for the world’s future. We highly recommend this TED talk to learn how to use videos effectively as a visual aid and inject some positivity into your lives during these trying times.
2. Demonstrations
Demonstrations, also known as demos, are undoubtedly among the most effective visual aids for communication. You can use demonstrations in two ways. One as a hook to captivate your audience. Prof. Walter Lewin was famous for using demonstrations as a hook during lectures. In his most famous lecture, he puts his life in danger by releasing a heavy pendulum to show that a pendulum’s period remains constant despite the mass.
Demonstrations can also be used to show how some things are done or work. We use demonstrations to showcase how Orai works and how you can use them to improve your speaking skills.
18.57% voted for demonstrations because they are unique, interactive, up close, and have a personal touch.
3. Roleplays
Jokes aside, why do you think comedy shows are memorable? You guessed it right. Roleplays! Role – play is any speaking activity when you put yourself into somebody else’s shoes or stay in your shoes but put yourself into an imaginary situation!
Nothing is more boring than a comedian delivering lines straight from a joke book. Legendary comedians like George Carlin, Kevin Hart, Chris Rock, and Bill Burr use roleplays effectively and make a mundane joke genuinely memorable.
Jokes aside, you can use roleplays in business presentations and speeches. Use real-life stories or examples in your role plays to make them authentic.
15.71% of the survey respondents voted for roleplays because they are very close to real life and do not take the audience’s attention away from the speaker.
With 12.86% of the votes, Props is number 4. A prop is any concrete object used to deliver a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech or presentation. Props add another dimension to our Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech and help the listeners visualize abstract concepts like vision, milestones, targets, and expectations. It ties verbal to visual. Introducing a prop into your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech or presentation should not seem forced. Use them sparingly to highlight your address’s most critical points or stories.
People voted for props because they feel 3D visualization is more useful than 2D visualization. Props will make your presentations stand out because few people use them today.
When we sent out the survey to the Orai community and some highly successful speakers, we were sure that slides/presentations would come out on top. However, we were surprised by the results. With 12.86% votes, slides are number five on our list.
Presentations are effortless to create and, therefore, the most commonly used visual aid in business communications. Today, dozens of software programs are available to help you make beautiful presentations. Microsoft PowerPoint is the pioneer in the space and holds a significant market share.
Whatever is your preferred software, you need to keep your audience at the center while making presentations.
People described the ease of creation and the ability to incorporate other visual aids when asked why they chose presentations as their top visual aid.
The inclusion of Audio in this list can appear controversial. But it got a significant vote share in our survey and cannot be ignored. Audio can add a new dimension to your presentations where the audience is hearing your voice and other sound cues that can trigger various emotional responses. Especially when coupled with other visual aids, audio can be a powerful tool for making impactful presentations.
Vote share:
Audio aid is number six, with 4.29% of the votes.
7. Handouts
What is a handout.
A handout is a structured view of your presentation or Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech that you can distribute to the audience.
What are the benefits of a handout?
Like how this blog gives more information than our YouTube video on the different visual aids, handouts can be used to furnish more information than your discourse itself. They give your audience something to take away after your presentation, making you and your presentation more memorable.
Are you going to be speaking about something overly technical? Then handouts are your friends. Handouts are also an opportunity to facilitate follow-ups if you specify your contact details.
Handouts are tied with whiteboards and got 2.86% of the votes in our survey.
8. Physical & Online Whiteboards
What is a whiteboard.
Traditionally, whiteboards are white, shiny, and smooth boards on which texts and diagrams are made using non-permanent markers. It is widely used in professional presentations, Brainstorming <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:132">A collaborative process to generate ideas freely and spontaneously, fostering creative thinking and problem-solving.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:12"><strong>Purpose:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73">Develop a wide range of innovative ideas without judgment or criticism.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:60">Overcome creative blocks and stimulate fresh perspectives.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:67">Encourage participation and engagement from diverse team members.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0">Build upon and combine individual ideas to reach breakthrough solutions.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:17"><strong>Key elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:96"><strong>Openness:</strong> All ideas are welcomed, regardless of their initial feasibility or practicality.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:109"><strong>Quantity over quality:</strong> Focus on generating as many ideas as possible, even if they seem unconventional.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:93"><strong>Spontaneity:</strong> Encourage quick thinking and rapid-fire suggestions without overanalyzing.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:114"><strong>Building upon ideas:</strong> Combine, adapt, and improve upon existing ideas to generate even more unique solutions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Positive environment:</strong> Maintain a supportive atmosphere where participants feel comfortable sharing their thoughts freely.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:13"><strong>Benefits:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:68">Sparks creativity and innovation, leading to unexpected solutions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:95">Encourages participation and team building, fostering collaboration and a sense of ownership.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:78">It breaks down communication barriers and allows diverse perspectives to shine.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0">It helps identify potential flaws and roadblocks early in the ideation process.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:16"><strong>Application:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-32:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:69">Idea generation for new products, projects, or marketing campaigns.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:78">Problem-solving for existing challenges or obstacles within an organization.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-32:0">Developing communication strategies or messaging frameworks.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="33:1-33:38"><strong>Brainstorming for Public Speaking:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="35:1-38:0"> <li data-sourcepos="35:1-35:86">Use brainstorming with your team to research and develop <strong>public speaking topics</strong>.</li> <li data-sourcepos="36:1-36:122">Generate creative ideas for introductions, transitions, and conclusions in your <strong>professional speaking</strong> presentations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="37:1-38:0">Brainstorm innovative ways to incorporate storytelling, humor, or visuals into your speeches.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="39:1-39:190"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="39:1-39:190">While brainstorming offers numerous advantages, it's crucial to have a strong facilitator, clear objectives, and a follow-up process to evaluate and refine the generated ideas.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/brainstorming/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">brainstorming sessions, and group discussions. Post-COVID, more and more companies are moving to online whiteboards. Online whiteboards are software that provides a space where individuals across the globe can collaborate online. Many companies have moved beyond the whiteboard and started using online whiteboards for meetings and discussions.
What are the benefits of a whiteboard?
A whiteboard helps listeners better visualize thoughts, concepts, and ideas. It is also a better alternative to the blackboard for a smaller audience as it is tidier and easier to use. Online whiteboards can be used instead of traditional whiteboards without being limited by space constraints. Online whiteboards will transform virtual meetings into a collaborative experience.
With 2.86% of the votes, whiteboards stand at eight on our list.
9. Blackboard
What is a blackboard.
A blackboard (aka chalkboard) is a surface on which texts or diagrams are made using chalk made from calcium sulfate or calcium carbonate. Blackboards are typically used in classrooms for large groups of students.
What are the benefits of blackboards?
Blackboard is one of the foremost and most popular teaching aids. Blackboard is useful for teaching as it helps instructors move from easy to complex topics in an organized manner. Diagrams, symbols, charts, and drawings can be introduced in discourse to bring life to rather dull topics. Blackboards are highly interactive, where the teacher and students can participate during a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech .
With 1.43% of the vote share, the blackboard stands at the bottom, along with flipcharts.
10. Flipchart
What is a flipchart.
Flipcharts consist of a pad of large sheets of paper bound together. It is typically fixed to the upper edge of a whiteboard or canvas. Flipcharts are easy to create and inexpensive fit for small groups of people.
What are the benefits of presenting using a flipchart?
Nowadays, everybody seems only interested in making presentations powered by computer-generated slide decks. However, the flip chart has its charm. Since most presentations consist of less than ten people, flip charts can be a refreshing change to the standard slide deck. Moreover, flipchart does not require electricity. No electricity and no software means fewer of those last-minute hick-ups.
Flipchart got 1.43% of the vote and shared the bottom position with its counterpart, which we will discuss in the next section.
Master the art of Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , practice with Orai
How to make an informative speech with visual aids in presentations
If you have a presentation coming up soon, you can follow the instructions below to learn how you can take advantage of visual aids:
Determine your overall objective
The aim of your presentations depends on you, what information is being presented, and your audience. The motivational speaker and the classroom teacher may approach the same types of visual aids differently due to differences in overall objectives. For instance, if you aim to inspire and remind your audience of salient points, a poster template should serve well; infographics work well when trying to show relationships between complex information. A chart will be quite effective if you seek to explain a given data set. For additional inspiration, you might consider using an AI poster generator to create visually appealing and informative posters that captivate your audience.
Choose appropriate visual aids in presentations.
After identifying the overall aim of your presentation, you have to match it with the right visual aids example. Will a graph, picture, or video suffice?
If you use the PowerPoint Presenter, focus mainly on the media that best conveys your message. Make sure that the notes you add are bold and brief. Try to keep your sentence in one line of text.
Prepare thoroughly
You will spend some time preparing your visual aids before the day of your presentation. It is good to allow yourself enough time to prepare so you can perfect your work accordingly. Take note of when, where, and how you will use your visual aids. If you discover some inconsistencies, you can compensate for them by adjusting your choice or using visual aids in presentations.
After you have a final draft of your visual aids, run a series of sessions with them. Let your friends or colleagues be your audience and ask for their honest feedback. Make appropriate adjustments where necessary.
During presentation
First, you need to be comfortable and confident. A neat and appropriate dress should boost your Confidence <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:305">In the context of <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>confidence</strong> refers to the belief in one's ability to communicate effectively and deliver one's message with clarity and impact. It encompasses various elements, including self-belief, composure, and the ability to manage one's <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:16"><strong>Key Aspects:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-12:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:108"><strong>Self-belief:</strong> A strong conviction in your knowledge, skills, and ability to connect with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:95"><strong>Composure:</strong> Maintaining calmness and poise under pressure, even in challenging situations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:100"><strong>Assertiveness:</strong> Expressing your ideas clearly and concisely, avoiding hesitation or self-doubt.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:104"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Countering negative thoughts with affirmations and focusing on your strengths.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-12:0"><strong>Strong body language:</strong> Using gestures, posture, and eye contact that project confidence and professionalism.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="13:1-13:27"><strong>Benefits of Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="15:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:99"><strong>Reduced anxiety:</strong> Feeling confident helps manage <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and stage fright.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Confident speakers project their voices, hold eye contact, and connect with their audience more effectively.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:137"><strong>Increased persuasiveness:</strong> A confident presentation inspires belief and motivates your audience to listen and remember your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Greater impact:</strong> Confidently delivered speeches leave a lasting impression and achieve desired outcomes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:112">Overcoming <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>: Many people experience some level of anxiety when speaking publicly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:101"><strong>Imposter syndrome:</strong> Doubting your abilities and qualifications, even when objectively qualified.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:92"><strong>Negative self-talk:</strong> Internalized criticism and limiting beliefs can hamper confidence.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Past negative experiences:</strong> Unsuccessful presentations or negative feedback can erode confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:24"><strong>Building Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-36:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:102"><strong>Practice and preparation:</strong> Thoroughly rehearse your speech to feel comfortable with the material.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:101"><strong>Visualization:</strong> Imagine yourself delivering a successful presentation with confidence and poise.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:100"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Actively replace negative thoughts with affirmations about your abilities.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Ask trusted individuals for constructive criticism and use it to improve your skills.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:157">Consider a <strong>speaking coach</strong>: Working with a coach can provide personalized guidance and support to address specific challenges and confidence barriers.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-34:114"><strong>Start small:</strong> Gradually increase the size and complexity of your speaking engagements as you gain experience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="35:1-36:0"><strong>Focus on progress:</strong> Celebrate small successes and acknowledge your improvement over time.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Confidence</strong> in public speaking is a journey, not a destination. By actively practicing, embracing feedback, and focusing on your strengths, you can overcome <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and develop the <strong>confidence</strong> to deliver impactful and memorable presentations.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/confidence/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">confidence . Follow the tips below during presentations.
- Keep your face on your audience. It may help to look a little above their heads while presenting.
- Only point to or take the visual aid when needed. When you do, explain what you mean immediately.
- Do not read texts on your visual aids verbatim.
- Once a visual aid has served its purpose, you should keep it away from your audience’s view.
If you need more help boosting your Confidence <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:305">In the context of <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>confidence</strong> refers to the belief in one's ability to communicate effectively and deliver one's message with clarity and impact. It encompasses various elements, including self-belief, composure, and the ability to manage one's <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:16"><strong>Key Aspects:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-12:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:108"><strong>Self-belief:</strong> A strong conviction in your knowledge, skills, and ability to connect with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:95"><strong>Composure:</strong> Maintaining calmness and poise under pressure, even in challenging situations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:100"><strong>Assertiveness:</strong> Expressing your ideas clearly and concisely, avoiding hesitation or self-doubt.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:104"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Countering negative thoughts with affirmations and focusing on your strengths.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-12:0"><strong>Strong body language:</strong> Using gestures, posture, and eye contact that project confidence and professionalism.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="13:1-13:27"><strong>Benefits of Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="15:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:99"><strong>Reduced anxiety:</strong> Feeling confident helps manage <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and stage fright.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Confident speakers project their voices, hold eye contact, and connect with their audience more effectively.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:137"><strong>Increased persuasiveness:</strong> A confident presentation inspires belief and motivates your audience to listen and remember your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Greater impact:</strong> Confidently delivered speeches leave a lasting impression and achieve desired outcomes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:112">Overcoming <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>: Many people experience some level of anxiety when speaking publicly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:101"><strong>Imposter syndrome:</strong> Doubting your abilities and qualifications, even when objectively qualified.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:92"><strong>Negative self-talk:</strong> Internalized criticism and limiting beliefs can hamper confidence.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Past negative experiences:</strong> Unsuccessful presentations or negative feedback can erode confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:24"><strong>Building Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-36:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:102"><strong>Practice and preparation:</strong> Thoroughly rehearse your speech to feel comfortable with the material.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:101"><strong>Visualization:</strong> Imagine yourself delivering a successful presentation with confidence and poise.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:100"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Actively replace negative thoughts with affirmations about your abilities.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Ask trusted individuals for constructive criticism and use it to improve your skills.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:157">Consider a <strong>speaking coach</strong>: Working with a coach can provide personalized guidance and support to address specific challenges and confidence barriers.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-34:114"><strong>Start small:</strong> Gradually increase the size and complexity of your speaking engagements as you gain experience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="35:1-36:0"><strong>Focus on progress:</strong> Celebrate small successes and acknowledge your improvement over time.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Confidence</strong> in public speaking is a journey, not a destination. By actively practicing, embracing feedback, and focusing on your strengths, you can overcome <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and develop the <strong>confidence</strong> to deliver impactful and memorable presentations.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/confidence/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">confidence , we have written a detailed piece on how to conquer your fear of speaking in front of people.
What is the importance of using visuals in giving a presentation?
Visual aids in presentations are invaluable to you and the audience you hope to enlighten. They make the job easier for you, and the audience leaves feeling like they learned something. Apart from their time-saving abilities, here are some reasons why you need to incorporate visual aids in your presentations:
- Visual aids can help your audience retain the information long-term.
- The human brain processes images faster than text, so visuals make us understand things faster.
- Using visual aids makes your presentations more enjoyable, interactive, and memorable.
- Visual aids help your audience connect and relate with you better
- Presentations with visual aids are less likely to be misunderstood or misrepresented. They are usually easier to understand and leave little room for confusion
- Visual designs help stimulate cognition and they are great for people with learning disabilities.
- Visual aids act as key cards and pointers for the presenter and help you keep track of what you’re saying
What are the ideas for speech topics using visual aids?
- Use a picture or image that closely represents the topic. A one-hundred-dollar note can suggest topics revolving around money and finances.
- Use a chart showing trends or statistics that your audience finds appealing. You can use popular sayings or quotes to generate topics your audience can relate to.
- Newspaper headlines on related issues can be good starters for opinion-based topics.
Why is the use of color important in presentations, according to research?
Color plays a crucial role in presentations, boosting audience engagement with its ability to enhance motivation and create visually appealing visuals. By understanding color theory and using shades thoughtfully, presenters can ensure their work is professional and organized and accessible to a diverse audience, considering color blindness and cultural associations.
What are the key points to consider when using visual aids in a presentation?
Ensure effective and engaging visuals in your presentation by considering the space, practicing beforehand, utilizing and limiting color strategically (considering color blindness), and maintaining consistency throughout your presentation.
What are some tips for using objects or artifacts as visual aids in presentations?
Objects in presentations can captivate your audience! Choose relevant objects for demonstrations or explanations. In small groups, pass the object around but manage time. For larger audiences, move it around for clear visibility. Reveal the object at the right moment with context and explanation. If demonstrating, use deliberate movements and explain each step clearly to keep them engaged.
What are some tips for using visual aids to engage the audience and maintain their interest?
Capture and keep your audience’s attention with impactful visuals! Ensure clear visibility, maintain eye contact, and use visuals to complement your spoken words, not replace them. Explain each visual promptly and remove it seamlessly when finished to refocus attention on your message.
How can visual aids be tailored to suit the audience and make the presentation more effective?
Craft impactful presentations by tailoring visuals to your audience and goals. Choose relevant and resonant visuals, be it a graph, picture, or video, accompanied by clear, concise notes. Prepare thoroughly, refining visuals and considering timing, context, and integration. Seek feedback to fine-tune for optimal audience connection.
How should one prepare and use visual aids effectively during a presentation?
Prepare polished visuals beforehand, considering timing, context, and integration. Seek feedback. During your presentation, prioritize Clarity <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:269">In <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>clarity</strong> refers to the quality of your message being readily understood and interpreted by your audience. It encompasses both the content and delivery of your speech, ensuring your message resonates and leaves a lasting impact.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:16"><strong>Key Aspects:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-13:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:133"><strong>Conciseness:</strong> Avoid unnecessary details, digressions, or excessive complexity. Focus on delivering the core message efficiently.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:149"><strong>Simple language:</strong> Choose words and phrases your audience understands readily, avoiding jargon or technical terms unless you define them clearly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:145"><strong>Logical structure:</strong> Organize your thoughts and ideas logically, using transitions and signposts to guide your audience through your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:136"><strong>Effective visuals:</strong> If using visuals, ensure they are clear, contribute to your message, and don't distract from your spoken words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-11:144"><strong>Confident delivery:</strong> Speak clearly and articulately, avoiding mumbling or rushing your words. Maintain good eye contact with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="12:1-13:0"><strong>Active voice:</strong> Emphasize active voice for better flow and avoid passive constructions that can be less engaging.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="14:1-14:24"><strong>Benefits of Clarity:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="16:1-20:0"> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:123"><strong>Enhanced audience engagement:</strong> A clear message keeps your audience interested and helps them grasp your points easily.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:123"><strong>Increased credibility:</strong> Clear communication projects professionalism and expertise, building trust with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-18:111"><strong>Improved persuasiveness:</strong> A well-understood message is more likely to resonate and win over your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="19:1-20:0"><strong>Reduced confusion:</strong> Eliminating ambiguity minimizes misinterpretations and ensures your message arrives as intended.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="21:1-21:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="23:1-27:0"> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:129"><strong>Condensing complex information:</strong> Simplifying complex topics without sacrificing crucial details requires skill and practice.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:128"><strong>Understanding your audience:</strong> Tailoring your language and structure to resonate with a diverse audience can be challenging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:85"><strong>Managing nerves:</strong> Nerves can impact your delivery, making it unclear or rushed.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-27:0"><strong>Avoiding jargon:</strong> Breaking technical habits and simplifying language requires constant awareness.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="28:1-28:22"><strong>Improving Clarity:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="30:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:117"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> The more you rehearse your speech, the more natural and clear your delivery will become.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:107"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech with others and ask for feedback on clarity and comprehension.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:161"><strong>Consider a public speaking coach:</strong> A coach can provide personalized guidance on structuring your message, simplifying language, and improving your delivery.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:128"><strong>Join a public speaking group:</strong> Practicing in a supportive environment can help you gain confidence and refine your clarity.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Listen to effective speakers:</strong> Analyze how clear and impactful others achieve communication.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:250"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="36:1-36:250"><strong>Clarity</strong> is a cornerstone of impactful <strong>public speaking</strong>. By honing your message, focusing on delivery, and actively seeking feedback, you can ensure your audience receives your message clearly and leaves a lasting impression.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/clarity/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">clarity , avoid overwhelming the audience, and use visuals purposefully to enhance, not replace, your message. Practice beforehand and maintain audience engagement through confident delivery.
The visual aid definition is very clear on how much impact using visual aids in Public Speaking <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking refers to any live presentation or speech. It can cover a variety of topics on various fields and careers (you can find out more about public speaking careers here: https://orai.com/blog/public-speaking-careers/. Public speaking can inform, entertain, or educate an audience and sometimes has visual aids.</p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking is done live, so the speakers need to consider certain factors to deliver a successful speech. No matter how good the speech is, if the audience doesn't connect with the speaker, then it may fall flat. Therefore, speakers have to use a lot more nonverbal communication techniques to deliver their message. </p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:heading --> <h2>Tips for public speaking</h2> <!-- /wp:heading --><br /><!-- wp:list --> <ul> <li>Have a sense of humor.</li> <li>Tell personal stories that relate to the speech you're giving.</li> <li>Dress appropriately for the event. Formal and business casual outfits work best.</li> <li>Project a confident and expressive voice.</li> <li>Always try to use simple language that everyone can understand.</li> <li>Stick to the time given to you.</li> <li>Maintain eye contact with members of your audience and try to connect with them.</li> </ul> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/public-speaking/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">public speaking has on an audience. With a great selection of visual aids, you can transform your presentations into a pleasant experience that you and your audience will always look forward to.
Become a confident speaker. Practice with Orai and get feedback on your tone, tempo, Conciseness <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:326">In the realm of <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>conciseness</strong> refers to the ability to express your message clearly and effectively using the fewest possible words. It's about conveying your ideas precisely, avoiding unnecessary details and rambling while maintaining your message's essence and impact.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:33"><strong>Benefits for Public Speakers:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:137"><strong>Engaged audience:</strong> A concise speech keeps your audience focused and prevents them from losing interest due to excessive information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:117"><strong>Increased clarity:</strong> By removing unnecessary clutter, your core message becomes clearer and easier to understand.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:137"><strong>Enhanced credibility:</strong> Concise communication projects professionalism and efficiency, making you appear more confident and prepared.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Reduced anxiety:</strong> Knowing you have a clear and concise message can help manage <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong> by minimizing the pressure to fill time.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:35"><strong>Challenges for Public Speakers:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:126"><strong>Striking a balance:</strong> Knowing where to draw the line between conciseness and omitting important information can be tricky.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:115"><strong>Avoiding oversimplification:</strong> Complex topics may require elaboration to ensure clarity and understanding.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Overcoming natural tendencies:</strong> Some speakers naturally use more words than others, requiring a conscious effort to be concise.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:41"><strong>Strategies for Achieving Conciseness:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="20:1-25:0"> <li data-sourcepos="20:1-20:92"><strong>Identify your core message:</strong> What is your audience's main point to remember?</li> <li data-sourcepos="21:1-21:128"><strong>Prioritize and eliminate:</strong> Analyze your content and remove any information not directly supporting your core message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:133"><strong>Use strong verbs and active voice:</strong> This makes your sentences more impactful and avoids passive constructions that can be wordy.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:109"><strong>Simplify your language:</strong> Avoid jargon and technical terms unless they are essential and clearly defined.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-25:0"><strong>Practice and refine:</strong> Rehearse your speech aloud and identify areas where you can tighten your wording or eliminate redundancies.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="26:1-26:20"><strong>Additional Tips:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="28:1-31:0"> <li data-sourcepos="28:1-28:93"><strong>Use storytelling:</strong> Engaging narratives can convey complex ideas concisely and memorably.</li> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:110"><strong>Focus on the visuals:</strong> Powerful visuals can support your message without extensive explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-31:0"><strong>Embrace silence:</strong> Pausing deliberately can emphasize key points and give your audience time to absorb your message.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="32:1-32:404"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="32:1-32:404"><strong>Conciseness</strong> is a powerful tool for <strong>public speakers</strong>. By eliminating unnecessary words and focusing on your core message, you can create a more engaging, impactful, and memorable presentation for your audience. This can also help manage <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong> by reducing the pressure to fill time and enabling you to focus on delivering your message with clarity and confidence.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/conciseness/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">conciseness , and Confidence <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:305">In the context of <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>confidence</strong> refers to the belief in one's ability to communicate effectively and deliver one's message with clarity and impact. It encompasses various elements, including self-belief, composure, and the ability to manage one's <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:16"><strong>Key Aspects:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-12:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:108"><strong>Self-belief:</strong> A strong conviction in your knowledge, skills, and ability to connect with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:95"><strong>Composure:</strong> Maintaining calmness and poise under pressure, even in challenging situations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:100"><strong>Assertiveness:</strong> Expressing your ideas clearly and concisely, avoiding hesitation or self-doubt.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:104"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Countering negative thoughts with affirmations and focusing on your strengths.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-12:0"><strong>Strong body language:</strong> Using gestures, posture, and eye contact that project confidence and professionalism.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="13:1-13:27"><strong>Benefits of Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="15:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:99"><strong>Reduced anxiety:</strong> Feeling confident helps manage <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and stage fright.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Confident speakers project their voices, hold eye contact, and connect with their audience more effectively.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:137"><strong>Increased persuasiveness:</strong> A confident presentation inspires belief and motivates your audience to listen and remember your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Greater impact:</strong> Confidently delivered speeches leave a lasting impression and achieve desired outcomes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:112">Overcoming <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>: Many people experience some level of anxiety when speaking publicly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:101"><strong>Imposter syndrome:</strong> Doubting your abilities and qualifications, even when objectively qualified.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:92"><strong>Negative self-talk:</strong> Internalized criticism and limiting beliefs can hamper confidence.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Past negative experiences:</strong> Unsuccessful presentations or negative feedback can erode confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:24"><strong>Building Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-36:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:102"><strong>Practice and preparation:</strong> Thoroughly rehearse your speech to feel comfortable with the material.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:101"><strong>Visualization:</strong> Imagine yourself delivering a successful presentation with confidence and poise.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:100"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Actively replace negative thoughts with affirmations about your abilities.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Ask trusted individuals for constructive criticism and use it to improve your skills.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:157">Consider a <strong>speaking coach</strong>: Working with a coach can provide personalized guidance and support to address specific challenges and confidence barriers.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-34:114"><strong>Start small:</strong> Gradually increase the size and complexity of your speaking engagements as you gain experience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="35:1-36:0"><strong>Focus on progress:</strong> Celebrate small successes and acknowledge your improvement over time.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Confidence</strong> in public speaking is a journey, not a destination. By actively practicing, embracing feedback, and focusing on your strengths, you can overcome <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and develop the <strong>confidence</strong> to deliver impactful and memorable presentations.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/confidence/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">confidence .
You might also like
2024 complete guide to presentation templates 📊, how to improve your speaking skills: 50 experts reveal their secrets [in..., quick links.
- Presentation Topics
Useful Links
- Start free trial
- The art of public speaking
- improve public speaking
- mastering public speaking
- public speaking coach
- professional speaking
- public speaking classes - Courses
- public speaking anxiety
- © Orai 2023
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance

10 Presentation Aids To Enhance Your Presentation
Table of contents.
You’re putting together a presentation and you’ve considered using presentation aids but don’t know where to begin?
Whether you’re a seasoned veteran presenter or new to the industry and looking on how to become a better presenter , we’ve got you covered with tips and tricks and everything you need to know about presentation aids.
We’ve put together this comprehensive list of 10 presentation aids you should incorporate in your next presentation, seminar, public speaking event or any other audience engagement to ensure your key messages are retained and you remain at the forefront of people’s minds.
Whether it’s visual aids, creative design or new ideas you wouldn’t necessarily think of to use in your line of work, we’ve broken down the bias to help give you a fresh mind on some presentation aids you should use.
What Are Presentation Aids?

A presentation aid is a complementary tool you can and should use in order to have your presentation stand out and enhance it.
They are sensory aids to help elevate your speech, performance or powerpoint presentation.
Where words fail, presentation aids come in to support.
A presentation aid can be used alone or in combination with other presentation aids. More often than not, it is encouraged to combine a couple of presentation aids to target the different senses – hearing, vision, smell, & taste.
The more senses you target, the more likely your presentation will be remembered.
For example, audio and video clips might be sprinkled throughout your presentation slide deck. Although these are all different presentation aids, using them in a combined way will enhance the overall presentation and increase audience engagement.
Presentation aids work because they tap into the presentation psychology ; the underpinning of our minds and how we perceive and remember great presentations. Whether someone is an auditory or visual learner, using additional presentation aids that target these senses will help take your presentation from average to phenomenal.
Why Do Presenters Use Presentation Aids?

Every presenter has their reasoning for selecting the presentation aids they use.
With the advancement of technology, presenters have been using more and more visual aids in their presentations in order to enhance the overall audience experience and create a great visual presentation .
Whether your presentation is in-person or instead a virtual presentation , the objective is always the same. Get your key messaging across with minimal miscommunication. Getting your key message across to your audience members can be done with the help of effective presentation aids.

Both informal and formal presentations incorporate some degree of presentation aids.
Presentation aids provide many benefits to a presenter. A presenter may use a combination of both visual aids and auditory aids to increase audience engagement and to help deliver their message.
Let’s break it down as to why a presenter would use visual aids and why a presenter would use auditory aids.
At a high level, it first depends on the audience. You should always begin crafting your presentation by understanding who your audience is and what you want them to take away from your presentation. This will help define the aids you select.
If your audience has a shorter attention span such as young adults or children, consider using more visual aids like videos or imagery. You may do this by adding videos into your PowerPoint presentation or adding images.
Perhaps you want your audience to remember things or act on something after the presentation has already concluded. A brochure or presentation handout might be a great aid to use as it leaves a physical, tangible item with the audience.
Trying to get funding or convert audience members into sales? A demonstration or live performance of the product can help people envision themselves using the product.
Presentation aids are used to help deliver your message and influence people. Understand your audience and the message you want them to take away and you’re halfway done deciding which complementary presentation tool you should use.
10 Types Of Presentation Aids

Before we begin going through the list of presentation aids you should use, we want to first preface with a word of caution.
Don’t overdo it.
As tempting as it may be to incorporate all 10 presentation types of presentation aids into your allotted time, don’t. You may be doing yourself a disservice.
Too many presentation aids may begin to distract your audience rather than support your messaging.
If you give your audience a handout, have them glance at an image with some written text all on one slide all the while you’re speaking over everything, there is too much going on. Your audience won’t know where to place their attention.
Also, some presentation aids don’t work in the environment in which the presentation is being held.
For example, if your presentation is virtual with absolutely no in-person audience members, a demonstration or live performance might not make practical sense.
Use these tools sparingly.
With that being said, let’s dive into the top 10 types of presentation aids we believe you should incorporate into your next presentation based on presentation feedback we’ve received over the years as presentation designers.
1 – PowerPoint Slides, Google Slides & Prezi Slides

One of the very first presentation aids we’ve all been taught to use and have more than likely used at least once in a school or work environment is a presentation slide deck.
Almost all presentations nowadays have a slide deck accompanying the presentation since it has been engrained in our minds as an essential for every presentation.
Whether it’s a motivational speech, client pitch presentation , RFP presentation , virtual presentation or an investment pitch presentation , they typically always use a slide deck.
Slide decks are great because they’re often easily customizable and there are plenty of well designed templates you can find online.

Slide decks such as PowerPoint Slides, Google Slides and Prezi Slides also allow a presenter to incorporate additional presentation aids such as videos, images or graphs seamlessly. Rather than having to jump back and forth between tabs, monitors or computers, a presentation slide deck consolidates all the information into one place.
When presenting to a large audience, a slide deck also allows audience members who are seated at the back of the venue to still take away the key points you’re trying to highlight. When highlighting key points, they will often be mentioned in the slide deck which is often displayed using a large projector and screen or video monitor.
Lastly, a presentation slide deck is a great tool to use as a reference.
The key details should be illustrated in the slide deck. Once the presentation is over, the slide deck can be a stand alone takeaway the audience or client can reference at a later date once the presentation has long past.
2 – Visual Aids, Audio And Video Clips

At a minimum, you should have at least one of the following presentation aids – imagery, audio or video.
Imagery can be more than just a photo. Imagery encompasses your slide deck, the color theory you use such as brand colors, how you embellish quotes and more.

For example, rather than sticking a text block on your slide deck with a quote, try enhancing the quote with the some visual appeal. You may consider adding a photo of the person who said the quote, stylizing the font with script writing so it seems more humanized and lastly using colors to highlight key words you want to bring to the audience’s attention.
Audio is another great tool to use, especially if you plan on incorporating motion graphics in your presentation. It also adds a layer of depth.
Since the audience will likely be hearing you speak for a majority of the presentation, having a pre-recorded narration over motion graphics will help create a “unique moment” in your presentation – almost like a bookmark. This will help your audience segment your presentation and retain information better.
Finally, videos have continued to grow in popularity as it is a combination of both visual aids and auditory aids.
Your video can be a live action video with real actors or it can be a stop motion animation. Whatever video style you decide, a video clip will help get your message across and enhance audience memory.
By combining all three aids, you’re targeting a combination of both visual and auditory senses. This combination will help your presentation stick out as human learning occurs visually and through auditory.
3 – Sizzle Reels
Although similar to videos, sizzle reels add a bit of flair traditional videos often lack.
Sentiment wise, videos can be positive, neutral or even negative while a sizzle reel’s sentiment is usually always positive.
Sizzle reels are very promotional in the sense that they are created with an intended purpose to have the audience act or feel in a certain way.
Unlike a video which may be used to support an argument or provide raw, unfiltered visual dialogue, a sizzle reel is typically created with a specific purpose for persuasion or selling.
Oftentimes, a sizzle reel is used to demonstrate or highlight a specific idea, product or sample of work usually presented with positive connotation. The presenter is trying to get the audience to be on the same page as them.
Like a video, a sizzle reel can be live action or animated – it is the intention of the video which makes it a sizzle reel or not.
4 – Motion Graphics
Keep your audience’s eyes stimulated by incorporating motion graphics into your presentation.
Motion graphics use the illusion of motion or rotation to make something which is typically stationary to appear as though it’s moving.
Motion graphics are great when they are used effectively. Too much motion graphics or improperly used motion graphics takes away your presentation’s credibility as it may begin to appear too animated and comical.
Depending on your presentation niche, motion graphics can really help enhance your presentation.
If your presentation primarily deals with lots of text, consider using motion graphics to help liven things up.
PresGeek Portfolio - Flowmill Explainer Video from Presentation Geeks on Vimeo .
You may be thinking to yourself, “Well, why not just use video?”. To that we say video isn’t for every industry. Although video may seem like the best option, it can often hurt your presentation more than it benefits it.
Consider a historical speech, one with a powerful message. Would you rather just watch a video of the person speaking, or perhaps a carefully curated kinetic typography motion graphic?
In this instance, although a video is still acceptable, you would be better off with motion graphics.
Motion graphics aren’t to be confused with animation. The difference between motion graphics and animation is motion graphics convert a typically stationary object into a moving one. Motion graphics don’t follow a typical storytelling narrative.
Animation on the other hand takes the audience on an emotional journey through storytelling which is an additional presentation aid we will discuss.
5 – 3D Modeling & Animation
If motion graphics aren’t enough, try using 3D Modeling and animation to bring your ideas to life and help tell a story!
3D Modeling and animation help bring hard to conceptualize ideas into a more tangible reality.
For example, if you’re presenting a prototype of a car, home or the latest piece of tech, spending money into developing a fully functional or full-scale product may not be feasible – especially if you’re merely pitching the idea to get funding in the first place.

3D modeling allows your audience to see how the product will look and perform if it were real.
Animation helps connect your messaging to your audience through the art of storytelling. Animation allows you to tell stories far beyond the scope of what is in our reality and can really help emphasize your brand’s essence.
For example, Red Bull did a great job with their advertising using the art of animation. Red Bull’s slogan of “Red Bull gives you wings” is personified through animation as their animated characters are given wings after drinking their product. They’re also put in high-intensity situations. Although often comical, animation helped bring the brand essence to life.
This could still be done with live-action actors and CGI, but the cost is far more than animation.
Animation is a cost-effective storytelling tool to bring even the most extremes of situations into a digestible reality.
6 – Maps
Our world has shifted to become a global village.
It is almost impossible to go about your day without hearing a piece of international news.
Whether it’s news, politics, culture or business, we are connected to different nations around the world. As you progress in your life, you’ll soon encounter yourself presenting to people around the world whether virtually or in-person.
If you are presenting to people around the world whether it be for politics, culture or business, adding a map is another great presentation aid to help visualize the interconnectedness between each other.
A map can be used to highlight geographical hotspots, geographical trends and more.
Here are some examples we’ve put together of when you would use a map.
Planning to expand your business? Why not include a map pinpointing all your existing locations relative to your new expansion.
Planning to show how diseases spread throughout the world and relative hotspots of infections? Consider adding a map with varying degrees of color to highlight infection densities.
Maps don’t need to be international either depicting every country – they can be used for small businesses showcasing a localized region.
Lastly, maps help put things into perspective. Tying back to presentation psychology, people are more likely to express emotions or feel connected to something the closer they are to it, physically. By using a map, you can put your message into perspective for your audience.
7 – Infographic Charts & Graphs
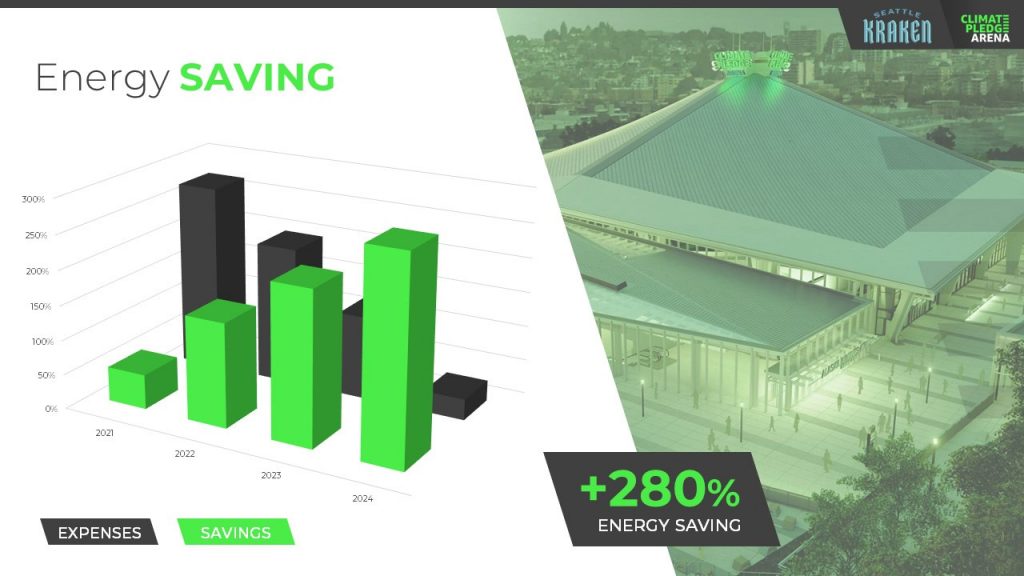
Rather than simply putting a few numbers up on a slide deck and calling it a day, try inputting these numbers in a chart or graph.
You have to consider your audience and not everyone learns or absorbs information by simply reading. They need to visualize comparisons and differences. Charts and graphs are one great way to do this.
Let’s take a look at the example above. It could’ve been easy enough to show there was a 280% increase in energy saving, but we were missing a big chunk of the story which was expenses were declining. You also don’t see the scale of energy savings relative to expenses with just words.
Instead, opting to put numbers into a visual format, the audience members can easily understand the advantages and compare it to the change over time.
Remember – try and avoid very complex graphs. When you start to input complex graphs into a presentation, you’ll begin to lose the audience as they will be too busy focusing on understanding the graph.
If possible, leave the audience with resources they can look back to after the presentation such as a brochure or handout where they can take as much time as they need to digest more robust graphs.
8 – Infographic Diagrams
Unlike charts and graphs which primarily focus on data and numbers, a diagram focuses on the appearance, structure, flow or workings of something.
A diagram is a great presentation aid to use as it helps break complex ideas into step-by-step sections the audience can follow along with.
Not only does it provide clear steps, but it can help speak to key points of a product or timeline.

For example, this diagram goes over the structure of an EV charger.
Rather than just showing an image of the charger with bullet points off to the side, a diagram provides clear connection lines from the point being made and where it’s located on the final product.
Diagrams also help illustrate flow. Whether it be the customer journey, your product development or your company’s growth, diagrams are great ways to show consistent progression in a logical, step-by-step pattern.
9 – Brochures & Presentation Handouts
One way to really connect with your audience and almost guarantee they’ll leave the presentation remembering something is with a brochure or handout.
A brochure or handout is a physical printout which could be a combination of images, written text and diagrams.
Oftentimes, brochures and handouts are used to elaborate on information already being presented but in further detail. Depending on the scope of your presentation, you may want to opt to have a brochure or presentation handout.
If the nature of your presentation requires thorough research, data and insight such as business or healthcare, a handout can allow your audience to review the information at their own pace at a later time.
A brochure or handout also allows audience members to jot down information.
This is important if you’re trying to encourage audience participation.
By enabling the audience to jot down their own notes and have time near the end of your presentation for them to collaborate and speak to points throughout your presentation, you’ll be engaging in a discourse with your audience.
10 – Demonstration or Live Performance

The last presentation aid we recommend is also one of the hardest to pull off – a demonstration or live performance.
A demonstration or live performance is when you’re presenting the truth and validity of something. For example, you might do a demonstration of how your product performs. Or, instead of playing music, you could have a live performance.
One of the most well-known presenters to do demonstrations or live performances is Steve Jobs. At the unveiling of any new Apple product, Steve Jobs was there on stage with the product in-hand ready to demonstrate its state of the art capabilities.
Demonstration or live performances are one of the best presentation aids to use as they often go hand in hand with public relations. Whether the performance goes well or bad, you can almost be sure there will be press coverage of it afterwards.
A great example of a demonstration which went south was Tesla’s Cybertruck and their armored windows . What was supposed to be strong, armored glass came to a shattering end when a Tesla employee threw a steel ball at not just one window, but both the front and rear window leaving both of them shattered. The hope was for the steel ball to ricochet off the window to demonstrate their durability, but instead they failed.
Although this might seem like a failure, the coverage it got after the presentation was a complete publicity success.
Advantages & Disadvantages Of Using Presentation Aids
As with everything in life, there are always two sides of the coin – positives and negatives.
The same goes for using presentation aids.
Rather than experimenting yourself and learning the hard way of advantages and disadvantages, we’ve put together this short yet informative section to help guide your decision making.
Presentation aids are great complementary tools you should use in every presentation. They allow you to connect with audience members in new and unique ways.
One of the advantages of using presentation aids is to appeal to different audiences.
Everyone has a different attention span. Everyone also learns and absorbs information differently. By disseminating your key message using new and unique methods, you’re able to appeal to a larger audience.
Secondly, presentation aids allow the lifespan of your presentation to be extended.
Imagine your presentation was only you speaking. The moment you’re done talking, the presentation is over and it begins to fade from people’s memory. With the help of presentation aids, you avoid this outcome and extend how long your presentation is remembered for.
For example, if you used a slide deck to accompany your presentation, the slide deck can be made available to audience members after the presentation to reference.
Lastly, presentation aids help reduce the attention that’s put on you and allow you to take breaks while presenting.
If you’re a beginner, it can be intimidating to be the center of attention. With the added use of presentation aids, you can break up your presentation to allow the aids to do the work. If you have a video, once you begin to play it, the audience’s attention will be redirected to the video. This will allow you time to pause, recollect your thoughts, take a drink of water if needed and continue on with the presentation afterwards.
Disadvantages
Presentation aids are not the miracle solution.
If you don’t have a solid foundation on which your presentation is built upon, it doesn’t matter how many or which presentation aids you decide to use. You need to ensure your presentation is properly structured from the beginning.
Presenters can also get carried away with using too many presentation aids.
When you don’t take the time to reflect on the presentation aids you are using and just begin spitballing every presentation aid into your presentation just because you know of these tools, doesn’t mean you should. They begin to become a distraction and takeaway from the messaging you’re trying to get across.
Conclusion – Should You Use Presentation Aids?
The short and sweet answer is yes. You should absolutely use presentation aids.
Unless your plan is to only be a storyteller letting the audience create an image in their mind, then you should consider using at least one of the presentation aid types mentioned above.
Not only will presentation aids help your audience learn and retain the information better, it may actually help you!
Presentation aids require you to contribute more work to the final product. It requires you to carefully think of the story you’re trying to convey to your audience and which best method to do so. By taking this extra bit of time to sit down and reflect on your presentation and actually produce well-crafted aids, you’ll be setting yourself up as a thought-leader on the topic.
If You’re looking for a Pitch Deck Design Agency , we can help. Just click the button below to start your journey!
Author: Ryan
Related posts.

FREE PROFESSIONAL RESOURCES DELIVERED TO YOUR INBOX.
Subscribe for free tips, resources, templates, ideas and more from our professional team of presentation designers.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Graphic Design Visual Presentation: Tips, Types and Examples
Visual Presentation: Tips, Types and Examples
Written by: Krystle Wong Sep 28, 2023

So, you’re gearing up for that big presentation and you want it to be more than just another snooze-fest with slides. You want it to be engaging, memorable and downright impressive.
Well, you’ve come to the right place — I’ve got some slick tips on how to create a visual presentation that’ll take your presentation game up a notch.
Packed with presentation templates that are easily customizable, keep reading this blog post to learn the secret sauce behind crafting presentations that captivate, inform and remain etched in the memory of your audience.
Click to jump ahead:
What is a visual presentation
15 effective tips to make your visual presentations more engaging, 6 major types of visual presentation you should know , what are some common mistakes to avoid in visual presentations, visual presentation faqs, 5 steps to create a visual presentation with venngage.
A visual presentation is a communication method that utilizes visual elements such as images, graphics, charts, slides and other visual aids to convey information, ideas or messages to an audience.
Visual presentations aim to enhance comprehension engagement and the overall impact of the message through the strategic use of visuals. People remember what they see, making your point last longer in their heads.
Without further ado, let’s jump right into some great visual presentation examples that would do a great job in keeping your audience interested and getting your point across.
In today’s fast-paced world, where information is constantly bombarding our senses, creating engaging visual presentations has never been more crucial. To help you design a presentation that’ll leave a lasting impression, I’ve compiled these examples of visual presentations that will elevate your game.
1. Use the rule of thirds for layout
Ever heard of the rule of thirds? It’s a presentation layout trick that can instantly up your slide game. Imagine dividing your slide into a 3×3 grid and then placing your text and visuals at the intersection points or along the lines. This simple tweak creates a balanced and seriously pleasing layout that’ll draw everyone’s eyes.
2. Get creative with visual metaphors
Got a complex idea to explain? Skip the jargon and use visual metaphors. Throw in images that symbolize your point – for example, using a road map to show your journey towards a goal or using metaphors to represent answer choices or progress indicators in an interactive quiz or poll.
3. Engage with storytelling through data
Use storytelling magic to bring your data to life. Don’t just throw numbers at your audience—explain what they mean, why they matter and add a bit of human touch. Turn those stats into relatable tales and watch your audience’s eyes light up with understanding.

4. Visualize your data with charts and graphs
The right data visualization tools not only make content more appealing but also aid comprehension and retention. Choosing the right visual presentation for your data is all about finding a good match.
For ordinal data, where things have a clear order, consider using ordered bar charts or dot plots. When it comes to nominal data, where categories are on an equal footing, stick with the classics like bar charts, pie charts or simple frequency tables. And for interval-ratio data, where there’s a meaningful order, go for histograms, line graphs, scatterplots or box plots to help your data shine.
In an increasingly visual world, effective visual communication is a valuable skill for conveying messages. Here’s a guide on how to use visual communication to engage your audience while avoiding information overload.

5. Employ the power of contrast
Want your important stuff to pop? That’s where contrast comes in. Mix things up with contrasting colors, fonts or shapes. It’s like highlighting your key points with a neon marker – an instant attention grabber.
6. End with a powerful visual punch
Your presentation closing should be a showstopper. Think a stunning clip art that wraps up your message with a visual bow, a killer quote that lingers in minds or a call to action that gets hearts racing.

7. Tell a visual story
Structure your slides like a storybook and create a visual narrative by arranging your slides in a way that tells a story. Each slide should flow into the next, creating a visual narrative that keeps your audience hooked till the very end.
Icons and images are essential for adding visual appeal and clarity to your presentation. Venngage provides a vast library of icons and images, allowing you to choose visuals that resonate with your audience and complement your message.
8. Show the “before and after” magic
Want to drive home the impact of your message or solution? Whip out the “before and after” technique. Show the current state (before) and the desired state (after) in a visual way. It’s like showing a makeover transformation, but for your ideas.
9. Add fun with visual quizzes and polls
To break the monotony and see if your audience is still with you, throw in some quick image quizzes or polls. It’s like a mini-game break in your presentation — your audience gets involved and it makes your presentation way more dynamic and memorable.
10. Use visuals wisely
Your visuals are the secret sauce of a great presentation. Cherry-pick high-quality images, graphics, charts and videos that not only look good but also align with your message’s vibe. Each visual should have a purpose – they’re not just there for decoration.
11. Utilize visual hierarchy
Employ design principles like contrast, alignment and proximity to make your key info stand out. Play around with fonts, colors and placement to make sure your audience can’t miss the important stuff.
12. Engage with multimedia
Static slides are so last year. Give your presentation some sizzle by tossing in multimedia elements. Think short video clips, animations, or a touch of sound when it makes sense, including an animated logo .
For those dealing with multilingual audiences, consider the use of an AI image translator to seamlessly convert text within images to various languages, enhancing accessibility and understanding. There are tons of video and clip creator tools like HubSpot or Adobe But remember, these are sidekicks, not the main act, so use them smartly.
13. Interact with your audience
Turn your presentation into a two-way street. Start your presentation by encouraging your audience to join in with thought-provoking questions, quick polls or using interactive tools. Get them chatting and watch your presentation come alive.

When it comes to delivering a group presentation, it’s important to have everyone on the team on the same page. Venngage’s real-time collaboration tools enable you and your team to work together seamlessly, regardless of geographical locations. Collaborators can provide input, make edits and offer suggestions in real time.
14. Incorporate stories and examples
Weave in relatable stories, personal anecdotes or real-life examples to illustrate your points. It’s like adding a dash of spice to your content – it becomes more memorable and relatable.
15. Nail that delivery
Don’t just stand there and recite facts like a robot — be a confident and engaging presenter. Lock eyes with your audience, mix up your tone and pace and use some gestures to drive your points home. Practice and brush up your presentation skills until you’ve got it down pat for a persuasive presentation that flows like a pro.
Venngage offers a wide selection of professionally designed presentation templates, each tailored for different purposes and styles. By choosing a template that aligns with your content and goals, you can create a visually cohesive and polished presentation that captivates your audience.
Looking for more presentation ideas ? Why not try using a presentation software that will take your presentations to the next level with a combination of user-friendly interfaces, stunning visuals, collaboration features and innovative functionalities that will take your presentations to the next level.
Visual presentations come in various formats, each uniquely suited to convey information and engage audiences effectively. Here are six major types of visual presentations that you should be familiar with:
1. Slideshows or PowerPoint presentations
Slideshows are one of the most common forms of visual presentations. They typically consist of a series of slides containing text, images, charts, graphs and other visual elements. Slideshows are used for various purposes, including business presentations, educational lectures and conference talks.

2. Infographics
Infographics are visual representations of information, data or knowledge. They combine text, images and graphics to convey complex concepts or data in a concise and visually appealing manner. Infographics are often used in marketing, reporting and educational materials.
Don’t worry, they are also super easy to create thanks to Venngage’s fully customizable infographics templates that are professionally designed to bring your information to life. Be sure to try it out for your next visual presentation!
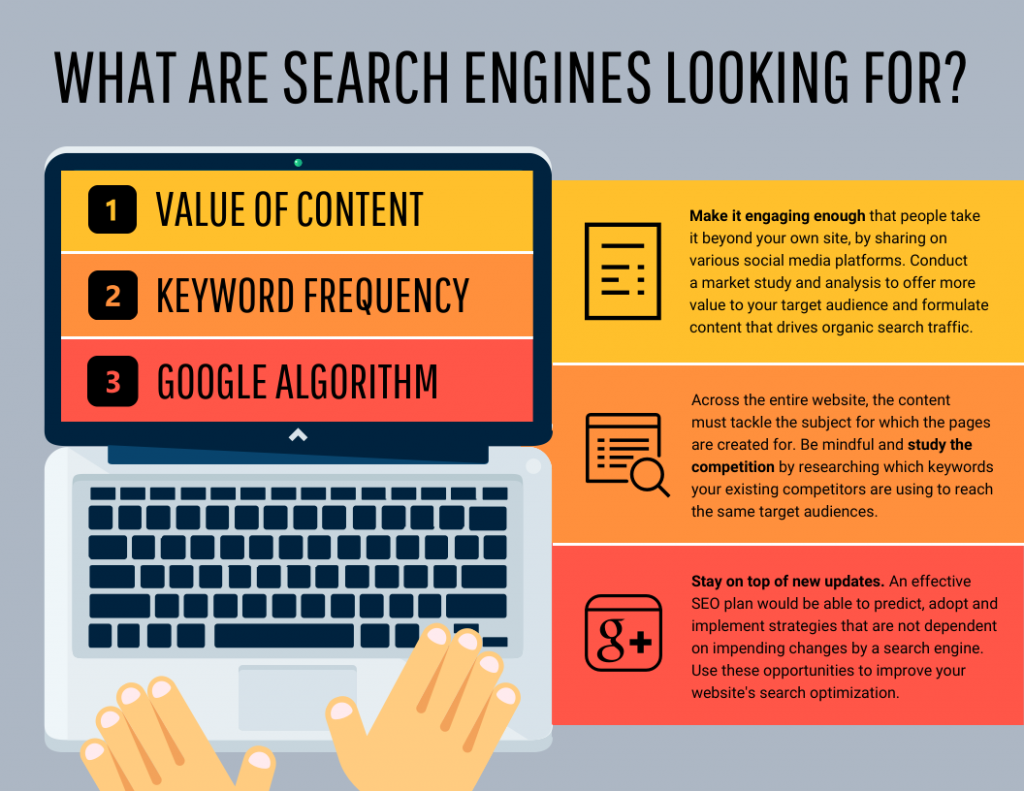
3. Video presentation
Videos are your dynamic storytellers. Whether it’s pre-recorded or happening in real-time, videos are the showstoppers. You can have interviews, demos, animations or even your own mini-documentary. Video presentations are highly engaging and can be shared in both in-person and virtual presentations .
4. Charts and graphs
Charts and graphs are visual representations of data that make it easier to understand and analyze numerical information. Common types include bar charts, line graphs, pie charts and scatterplots. They are commonly used in scientific research, business reports and academic presentations.
Effective data visualizations are crucial for simplifying complex information and Venngage has got you covered. Venngage’s chart templates enable you to create engaging charts, graphs,and infographics that enhance audience understanding and retention, leaving a lasting impression in your presentation.

5. Interactive presentations
Interactive presentations involve audience participation and engagement. These can include interactive polls, quizzes, games and multimedia elements that allow the audience to actively participate in the presentation. Interactive presentations are often used in workshops, training sessions and webinars.
Venngage’s interactive presentation tools enable you to create immersive experiences that leave a lasting impact and enhance audience retention. By incorporating features like clickable elements, quizzes and embedded multimedia, you can captivate your audience’s attention and encourage active participation.
6. Poster presentations
Poster presentations are the stars of the academic and research scene. They consist of a large poster that includes text, images and graphics to communicate research findings or project details and are usually used at conferences and exhibitions. For more poster ideas, browse through Venngage’s gallery of poster templates to inspire your next presentation.

Different visual presentations aside, different presentation methods also serve a unique purpose, tailored to specific objectives and audiences. Find out which type of presentation works best for the message you are sending across to better capture attention, maintain interest and leave a lasting impression.
To make a good presentation , it’s crucial to be aware of common mistakes and how to avoid them. Without further ado, let’s explore some of these pitfalls along with valuable insights on how to sidestep them.
Overloading slides with text
Text heavy slides can be like trying to swallow a whole sandwich in one bite – overwhelming and unappetizing. Instead, opt for concise sentences and bullet points to keep your slides simple. Visuals can help convey your message in a more engaging way.
Using low-quality visuals
Grainy images and pixelated charts are the equivalent of a scratchy vinyl record at a DJ party. High-resolution visuals are your ticket to professionalism. Ensure that the images, charts and graphics you use are clear, relevant and sharp.
Choosing the right visuals for presentations is important. To find great visuals for your visual presentation, Browse Venngage’s extensive library of high-quality stock photos. These images can help you convey your message effectively, evoke emotions and create a visually pleasing narrative.
Ignoring design consistency
Imagine a book with every chapter in a different font and color – it’s a visual mess. Consistency in fonts, colors and formatting throughout your presentation is key to a polished and professional look.
Reading directly from slides
Reading your slides word-for-word is like inviting your audience to a one-person audiobook session. Slides should complement your speech, not replace it. Use them as visual aids, offering key points and visuals to support your narrative.
Lack of visual hierarchy
Neglecting visual hierarchy is like trying to find Waldo in a crowd of clones. Coupling this with video transcription can make your presentation more comprehensive and engaging. Use size, color and positioning to emphasize what’s most important. Guide your audience’s attention to key points so they don’t miss the forest for the trees.
Ignoring accessibility
Accessibility isn’t an option these days; it’s a must. Forgetting alt text for images, color contrast and closed captions for videos can exclude individuals with disabilities from understanding your presentation.
Relying too heavily on animation
While animations can add pizzazz and draw attention, overdoing it can overshadow your message. Use animations sparingly and with purpose to enhance, not detract from your content.
Using jargon and complex language
Keep it simple. Use plain language and explain terms when needed. You want your message to resonate, not leave people scratching their heads.
Not testing interactive elements
Interactive elements can be the life of your whole presentation, but not testing them beforehand is like jumping into a pool without checking if there’s water. Ensure that all interactive features, from live polls to multimedia content, work seamlessly. A smooth experience keeps your audience engaged and avoids those awkward technical hiccups.
Presenting complex data and information in a clear and visually appealing way has never been easier with Venngage. Build professional-looking designs with our free visual chart slide templates for your next presentation.
What is a visual presentation?
A visual presentation is a method of presenting information through visual aids such as slides, images, charts and videos. It enhances understanding and retention by illustrating key points and data visually. Visual presentations are commonly used in meetings, lectures, and conferences to engage and inform the audience effectively.
What is the role of storytelling in visual presentations?
Storytelling plays a crucial role in visual presentations by providing a narrative structure that engages the audience, helps them relate to the content and makes the information more memorable.
What software or tools can I use to create visual presentations?
You can use various software and tools to create visual presentations, including Microsoft PowerPoint, Google Slides, Adobe Illustrator, Canva, Prezi and Venngage, among others.
What is the difference between a visual presentation and a written report?
The main difference between a visual presentation and a written report is the medium of communication. Visual presentations rely on visuals, such as slides, charts and images to convey information quickly, while written reports use text to provide detailed information in a linear format.
How do I effectively communicate data through visual presentations?
To effectively communicate data through visual presentations, simplify complex data into easily digestible charts and graphs, use clear labels and titles and ensure that your visuals support the key messages you want to convey.
Are there any accessibility considerations for visual presentations?
Accessibility considerations for visual presentations include providing alt text for images, ensuring good color contrast, using readable fonts and providing transcripts or captions for multimedia content to make the presentation inclusive.
Most design tools today make accessibility hard but Venngage’s Accessibility Design Tool comes with accessibility features baked in, including accessible-friendly and inclusive icons.
How do I choose the right visuals for my presentation?
Choose visuals that align with your content and message. Use charts for data, images for illustrating concepts, icons for emphasis and color to evoke emotions or convey themes.
How can I adapt my visual presentations for online or virtual audiences?
To adapt visual presentations for online or virtual audiences, focus on concise content, use engaging visuals, ensure clear audio, encourage audience interaction through chat or polls and rehearse for a smooth online delivery.
What is the role of data visualization in visual presentations?
Data visualization in visual presentations simplifies complex data by using charts, graphs and diagrams, making it easier for the audience to understand and interpret information.
How do I choose the right color scheme and fonts for my visual presentation?
Choose a color scheme that aligns with your content and brand and select fonts that are readable and appropriate for the message you want to convey.
How can I measure the effectiveness of my visual presentation?
Measure the effectiveness of your visual presentation by collecting feedback from the audience, tracking engagement metrics (e.g., click-through rates for online presentations) and evaluating whether the presentation achieved its intended objectives.
Follow the 5 simple steps below to make your entire presentation visually appealing and impactful:
1. Sign up and log In: Log in to your Venngage account or sign up for free and gain access to Venngage’s templates and design tools.
2. Choose a template: Browse through Venngage’s presentation template library and select one that best suits your presentation’s purpose and style. Venngage offers a variety of pre-designed templates for different types of visual presentations, including infographics, reports, posters and more.
3. Edit and customize your template: Replace the placeholder text, image and graphics with your own content and customize the colors, fonts and visual elements to align with your presentation’s theme or your organization’s branding.
4. Add visual elements: Venngage offers a wide range of visual elements, such as icons, illustrations, charts, graphs and images, that you can easily add to your presentation with the user-friendly drag-and-drop editor.
5. Save and export your presentation: Export your presentation in a format that suits your needs and then share it with your audience via email, social media or by embedding it on your website or blog .
So, as you gear up for your next presentation, whether it’s for business, education or pure creative expression, don’t forget to keep these visual presentation ideas in your back pocket.
Feel free to experiment and fine-tune your approach and let your passion and expertise shine through in your presentation. With practice, you’ll not only build presentations but also leave a lasting impact on your audience – one slide at a time.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
Home Blog Presentation Ideas Presentation Aids: A Guide for Better Slide Design
Presentation Aids: A Guide for Better Slide Design

During a speech or presentation, information is conveyed orally. When relying solely on spoken words, a speaker may confuse and make it difficult for listeners to remember key facts. Therefore, combining presentation aids with oral explanations can improve the audience’s understanding and help them retain the main points.
This article defines what presentation aids are, their uses, different types of presentation aids, and their advantages and disadvantages.
Table of Contents
What is a Presentation Aid?
Are presentation aids the same as visual aids.
- Why Should we use Presentation Aids?
When Should Presentation Aids be Used When Delivering a Presentation?
Types of presentation aids, recommended ppt & google slides templates for presentation aids.
According to Leon, presentation aid refers to the tools and materials used by a speaker beyond spoken words to enhance the communicated message to the audience [1]. These tools comprise templates, multimedia, and visual elements to improve engagement and clarity. Presentation aids act as a bridge between the speaker and the audience, facilitating a presentation.
For instance, the strategic use of templates and multimedia elements can elevate a presentation from a mere speech to a compelling narrative. Integrating these aids is rooted in established practices, ensuring a comprehensive and impactful message delivery. The proper use of presentation aids can improve the quality of the presentation.
No, presentation aids differ from visual aids. Visual aid is also a type of presentation aid mainly used by speakers [1]. Examples of visual aids include images, tables, maps, charts, and graphs. In contrast, presentation aid is a broader category, including templates, 3D models, transitions, audio clips, and multimedia elements. The use of presentation aids goes beyond visuals, offering a diverse set of resources to enhance engagement and communication effectiveness [2].
Why Should we use Presentation Aids?
Presentation Aids are used for specific purposes in a presentation. To enhance audience understanding and retention can be one of the primary purposes. In addition, presentation aids guide transitions so the audience may remain focused [1]. For instance, charts and maps allow speakers to communicate complex information quickly.

Templates and multimedia elements advance the professionalism of a presentation. At the same time, using slideshows clarifies a presentation’s organization In short, a presentation aid ensures a lasting impact on the audience [3].
Presentation aids must be used when a speaker wants to emphasize critical points or evoke an emotional response from the audience. Integrate presentation aids when conveying a complex concept . The strategic use of presentation aids, in line with speech, complements spoken words without overshadowing them. Whether visualizing data or incorporating multimedia elements, presentation aids are most effective when seamlessly integrated into a presentation.
Therefore, presentation aids must be used when the speaker is presenting a specific idea relevant to an aid [4]. Consider a scenario where a speaker delivers a presentation on renewable energy sources. If one of the key points involves the efficiency of solar panels. He can use, for example, a graph or chart illustrating the comparative efficiency rates of various types of solar panels and contrast that with their average lifespan.

Some types of presentation aids can be used in various presentations to assist the speaker. Highlighted advantages and disadvantages of various presentation aids allow presenters to use these presentational aids best.
When considering visual aids for a presentation, one immediately thinks of a slideshow. Slide presentation software, such as PowerPoint, Prezi, and Google Slide, is commonly used by speakers. A slideshow consists of slides containing words, images, or a blend of both, serving as a primary presentation aid [1]. Slide and slide-show design has a greater impact on the effectiveness of conveying a message to the audience.
PowerPoint and similar slideware offer easily editable templates for a consistent slide show appearance. These PowerPoint templates provide a structured framework reorganizing the design process and ensuring a consistent visual identity. Templates are easy to use and helpful for a consistent slideshow.

When using slide templates, a presenter needs to place images or graphs according to the message, medium, and audience. Each slide reinforces the key message, so a conscious decision about each element and concept is essential [5].
Place one idea or concept per slide to keep it simple and understandable. Do not overcrowd it with images or text. However, slideshows limit the audience’s participation which may cause boredom or confusion among the audience. At the same time, the strict order of slides bounds the presenter. He won’t be able to explain the topic openly [6]. Therefore, a presenter should be aware of the background and needs of the audience. By blending different flexible techniques, a presenter can elaborate his slideware presentation.
Charts and Graphs
Graphs and charts are essential for precise data visualization. They simplify complex information for clearer communication. In business presentations , where data-driven decisions are paramount, these visual aids offer advantages in conveying key insights concisely.
Graphs and charts extract complex numerical data into accessible formats and provide precision in representation. These are used to present trends, comparisons, and relationships, particularly in contexts requiring nuanced data analysis. Different charts have distinct purposes. Choosing the one that aligns with your data is essential to ensure clarity [3]. Pie charts, for instance, depict the relationship between parts and the whole. It is ideal to present up to eight visually distinct segments. A line graph effectively illustrates trends over time, while a bar chart facilitates direct comparisons between variables [3].

When creating charts, use different colors and provide clear labels. Maintain consistency in both colors and data groupings. For clarity, refrain from using 3-D graphs and charts. Minimize background noise, such as lines and shading [7]. Ensure that all elements of your graph are distinguishable from the background color. Remove unnecessary clutter. Keep graphs straightforward. Prioritize clarity in conveying your message and visually emphasize the intended conclusion for the audience [7].
Using graphs and charts can be challenging regarding effectiveness and ethics. Therefore, a solid grasp of statistical concepts is essential, and the chosen graphs should clearly represent quantities [3].
Align visual presentation aids to the audience and topic for optimal impact. In business scenarios, the ability to convey data insights efficiently improves decision-making processes. Beyond representation, graphs, and charts enhance audience understanding [2]. Visual learners benefit from the graphical depiction of information. The choice of graph or chart type should align with the audience’s familiarity with the subject matter.
3D Modeling
3D modeling implies creating realistic or abstract representations of objects, fictional characters, environments, or concepts through digital tools [9]. 3D modeling enhances visualization, making complex concepts more accessible. It is mainly used in the Engineering and Architectural fields. It improves audience understanding and visual engagement. Presenters can use this technique to provide a clearer understanding of intricate details. It allows the audience to visualize the inner workings of machinery, architectural designs, or scientific processes [8]. The dynamic nature of three-dimensional visuals captures and sustains the audience’s attention. This engagement is particularly beneficial in holding the audience’s interest throughout the presentation and prevents attention fatigue. However, presenters should be cautious to avoid visual overload. Ensure that the 3D elements enhance rather than distract from the main message.
Creating a 3D model for a presentation requires basic skills and knowledge of 3D modeling techniques. It includes modeling, texturing, lighting, and rendering [9]. Modeling involves shaping and structuring 3D models. Texturing applies color, pattern, or material using images or shaders. Lighting incorporates light sources and shadows to build the desired mood or atmosphere. However, for basic 3D models, a presenter can use PowerPoint to create or access available designs from online sources.

Moreover, these models enhance communication by creating animations, simulations, or demonstrations for understanding a point or process. The versatility of 3D models allows for generating various views, angles, or perspectives of a subject, facilitating customization based on audience or purpose.
Maps are highly valuable to use when information is clear and concise [3]. Different types of maps include population, geographical, political, climate, and economic maps [3]. Therefore, select the one that aligns with the presentation. Choose a map that highlights the specific information the speaker intends to convey. If a speech necessitates geographic reference, a map is an effective tool [7].
Maps provide precise visual communication of geographical data and help convey spatial relationships effectively.

Maps communicate information with clarity [7]. They are used to present global market trends, regional analyses, or any scenario where location-based insights matter. For instance, a world map can highlight key regions of interest when presenting global market trends. It helps the audience grasp the distribution of market opportunities.
The visual appeal of maps enhances audience engagement, particularly when presenting data tied to specific locations [10]. For a marketing presentation , a map showcasing the distribution of target demographics can capture attention and reinforce the spatial context of the campaign.
However, overly complex maps can confuse the audience. Similarly, relying on maps for all data types can lead to oversimplification.
Dry-Erase Board
The Dry-Erase Board is useful for brainstorming and note-taking. It is one of the ideal presentation materials for spontaneous discussions and audience engagement. It allows the presenter to make live diagrams and emphasize key points. At the same time, it is cost-effective and user-friendly.
Suppose a presenter chooses a dry-erase board. He needs to ensure that the board is presentable, rehearsed, and clear [7]. There are a few rules to remember before using a Dry-Erase Board as a presentation aid [3]. First, ensure legible writing is large enough for everyone to see. Use clear printing instead of cursive script. Use short phrases rather than complete sentences. Avoid turning away from the audience while speaking. Use markers that are functional and clean the board afterward.
The drawback of the Dry-Erase Board is that it has limited visibility in large settings. When using a Dry-Erase board, a presenter may seem less prepared. However, many speakers effectively use these boards for interactive elements in their speeches [3]. It is great for dynamic presentations, but space and audience size should be considered.
Brochures and Handouts
Brochures and handouts are tangible takeaways for the audience. They enhance information retention and serve as lasting references [11]. These presentation materials are effective in educational presentations or seminars, offering supplementary details for in-depth understanding.
There are a few things to consider when distributing handouts to the audience [7]. Provide a handout for each audience member, avoiding the need for sharing. Never distribute a single copy to pass around, as it detracts from a professional image. Handouts should be distributed before, during, or after the presentation. If audience participation is required, distribute handouts before starting or have a volunteer distribute them. Include only essential information, organized for clarity. If the handout is meant for audience follow-along, inform them of this and mention specific references during the speech [7].
Check our article about how to create handouts for a presentation .
However, potential disadvantages include the timing of distribution. Handing out materials at the wrong moment can distract the audience.
Audio Clips
Using an audio clip in a presentation introduces an auditory dimension. It evokes emotions and enhances the overall experience.
When using an audio clip, select a clip of appropriate length for your speech duration. Prior to speaking, familiarize yourself with audio or video equipment to avoid disruptions and maintain credibility. Ensure computer speakers are on and set to the right level of volume level [7].
However, potential disadvantages of audio include technical issues with sound playback. It requires presenters to ensure seamless integration. Besides, overuse of audio clips can also be overwhelming, requiring careful selection and timing.
Integrating prerecorded videos offers a dynamic means of presenting information, catering to visual learners, and capturing audience attention. Prepare short videos from platforms like YouTube or Vimeo, song segments, or podcasts before your speech [7]. Cue the clip to the right spot and ensure the browser window is open. Before playing the clip, Provide the audience with context about its relevance to the speech. Explain its connection and significance. Ensure the video enhances the message without duplicating information already conveyed [3].
A video demonstration of a complex process can significantly enhance understanding in a training session. However, presenters should be mindful of timing and integration to avoid disruptions. Technical issues during playback can also pose challenges. It requires thorough testing beforehand.
1. Price Corridor of the Target Mass Presentation Aid Template

For presenters looking to implement the Blue Ocean Strategy in their organization, this presentation aid material gives emphasis on the potential pricing tiers and the difficulty of adapting that solution. Ideal for sales teams looking to innovate their pricing strategy.
Use This Template
2. Innovation Strategy Diagram Presentation Aid Material Template

Professionals seeking to introduce new strategy models can benefit from this highly visual strategy diagram template for PowerPoint & Google Slides. By using this matrix PPT slide, we can compare approaches and leverage them regarding the effort required for their implementation.
3. AIDAL Model Funnel Sales Presentation Aid

Whether your project requires brand awareness analysis or the steps that lead to customer loyalty, this funnel diagram for PowerPoint & Google Slides based on the AIDAL model is the ideal resource for your presentation. We can go stage by stage on the customer buyer journey, expanding details on the horizontal timeline shown right next to it.
4. Opportunities Solution Tree Template Presentation Aid for Product Development

Showcase your product discovery process by using our Opportunities Solution Tree PPT template. With this tree diagram presentation aid, we can easily arrange the customer pain points and streamline ideas that offer solutions to those emerging opportunities.
5. Business Brochure Aid for Presentation Handouts

Say goodbye to boring presentation handouts with this business-tailored brochure template for PowerPoint and Google Slides. In a two-sided format, companies can add relevant information about their activities, value proposals, and contact data.
6. Atlanta City Map and City Skyline Illustration Aids for Presentations

Among the multiple product offerings we have for map templates , we would like to highlight the particular style of this slide deck of Atlanta City. By accessing this product, you can get skyline silhouettes of Atlanta City, the Georgia State Capitol Building, maps in white and dark blue tones, bar charts, etc. They can be an ideal presentation aid example for users looking to deliver talks about local politics, new business venues, and more.
7. 3D Tetris Cube Visual Aid for a Presentation

How many times have you looked to create a 3D model to express an idea or concept made of different components? If so, this template ranks among the best examples of a visual aid. It’s almost instant to edit, as you just need to change the content in placeholder text areas and the colors, and that’s it.
8. Sprint Retrospective Presentation Aid Template for PowerPoint & Google Slides

This Sprint board template is the answer to the lack of clarity during sprint retrospective meetings. Scrum Masters can discuss in detail the aspects of the project covering what was considered a good job during the sprint, what was missing, what the team learned, and which are the new goals to achieve.
Turn your Agile presentations into powerful tools for action with this visual presentation aid!
[1] Leon, M., 2023. Presentation Aids. Public Speaking as Performance . https://opentext.ku.edu/publicspeakingperformance/chapter/presentation-aids/
[2] Shier, M. 2020. 11.3 Presentation Aids. Student Success . https://opentextbc.ca/studentsuccess/chapter/presentation-aids/
[3] Mapes, M. 2019. Presentation AIDS. Speak Out Call in Public Speaking as Advocacy. https://opentext.ku.edu/speakupcallin/chapter/chapter-10-presentation-aids/
[4] Functions of Presentation Aids. 2016. Public Speaking . https://open.lib.umn.edu/publicspeaking/chapter/15-1-functions-of-presentation-aids/#:~:text=Presentation%20aids%20can%20help%20clarify,process%20is%20a%20complex%20one .
[5] Gruber, K. 2022. Chapter Fourteen – Presentation Aids, Principles of Public Speaking . https://mtsu.pressbooks.pub/principlesofpublicspeaking/chapter/chapter-fourteen-presentation-aids/
[6] Xingeng, D. and Jianxiang , L. 2012. Advantages and Disadvantages of PowerPoint in Lectures to ScienceStudents. I.J. Education and Management Engineering. MECS press. https://www.mecs-press.org/ijeme/ijeme-v2-n9/IJEME-V2-N9-10.pdf
[7] Goodman, Dr.L. and Amber Green, M.A. Presentation AIDS, Public Speaking . https://open.maricopa.edu/com225/chapter/need-presentation-aids/
[8] Vincenti, G. and Braman, J. 2011. Teaching through multi-user virtual environments: Applying dynamic elements to the modern classroom , Google Books. Available at: https://www.google.com.pk/books/edition/Teaching_through_Multi_User_Virtual_Envi/sekY2Iy5LdcC?hl=en&gbpv=1&dq=3d%2Bmodelling%2Bas%2Ba%2Bpresentation%2Baid&pg=PA389&printsec=frontcover (Accessed: 27 November 2023).
[9] Mamgain, P., 2020. Autodesk 3ds Max 2020: A Detailed Guide to Modeling, Texturing, Lighting, and Rendering . Padexi Academy.
[10] 15.1 Functions of Presentation Aids. 2016. Public Speaking. Available at: https://open.lib.umn.edu/publicspeaking/chapter/15-1-functions-of-presentation-aids/#:~:text=Presentation%20aids%20can%20help%20clarify,process%20is%20a%20complex%20one .
[11] Chapter 15 Presentation AIDS: Design and Usage . ( https://saylordotorg.github.io/text_stand-up-speak-out-the-practice-and-ethics-of-public-speaking/s18-presentation-aids-design-and-u.html ).
Like this article? Please share
Communication, Presentation Tips Filed under Presentation Ideas
Related Articles

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • September 9th, 2024
How to Convert Canva to Google Slides
Need to switch from Canva to Google Slides? Follow this guide to easily convert your Canva designs into Google Slides in minutes.

Filed under Presentation Ideas • August 29th, 2024
How to Make a Presentation Longer: 7 Strategies to Master
Extend your talk in style. Join us to discover how to make a presentation longer while providing a high-end experience to your audience.

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • August 29th, 2024
How to Insert an Equation in Google Slides
Make your math-related slides stand out by learning the different methods for how to insert an equation in Google Slides.
Leave a Reply

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
Using visual aids during a presentation or training session
June 21, 2018 - Gini Beqiri
Visual aids can enhance your presentations – they can increase the audience’s understanding of your topic, explain points, make an impact and create enthusiasm. It has become more important to make information visual:
“Something is happening. We are becoming a visually mediated society. For many, understanding of the world is being accomplished, not through words, but by reading images” – ( Lester, 2006 )
In this article, we discuss how to use visual aids for presentations or training sessions.
What are visual aids?
Visual aids are items of a visual manner, such as graphs, photographs, video clips etc used in addition to spoken information. Visual aids are chosen depending on their purpose, for example, you may want to:
- Summarise information.
- Reduce the amount of spoken words, for example, you may show a graph of your results rather than reading them out.
- Clarify and show examples.
- Create more of an impact, for example, if your presentation is on the health risks of smoking, you may show images of the effects of smoking on the body rather than describing this. You must consider what type of impact you want to make beforehand – do you want the audience to be sad, happy, angry etc?
- Emphasise what you’re saying.
- Make a point memorable.
- Enhance your credibility .
- Engage the audience and maintain their interest.
- Make something easier for the audience to understand.

Preparation and use of visual aids
Once you have decided that you want to use a visual aid, you must ensure that the audience is able to quickly understand the image – it must be clear. They can be used throughout your speech but try to only use visual aids for essential points as it can be tiring for the audience to skip from one visual to another.
Preparation
- Think about how can a visual aid can support your message. What do you want the audience to do?
- Ensure that your visual aid follows what you’re saying or this will confuse the audience.
- Avoid cluttering the image as it may look messy and unclear.
- Visual aids must be clear, concise and of a high quality.
- Keep the style consistent, such as, the same font, colours, positions etc
- Use graphs and charts to present data.
- The audience should not be trying to read and listen at the same time – use visual aids to highlight your points.
- One message per visual aid, for example, on a slide there should only be one key point.
- Use visual aids in moderation – they are additions meant to emphasise and support main points.
- Ensure that your presentation still works without your visual aids in case of technical problems.
- Practice using the visual aids in advance and ask friends and colleagues for feedback. Ask them whether they can clearly see the visual aid and how they interpret it.
During the presentation
- Ensure that the visual aids can be seen by everyone in the audience.
- Face the audience most of the time rather than the image.
- Avoid reading from the visual aid.
- As soon as you show the visual aid the audience’s attention will be drawn to it so you must immediately explain it. You will be ignored if you talk about something else.
- Make it clear to the audience why you are using it.
- When you no longer need the visual aid ensure that the audience can’t see it.
Tailor to your audience
Choose your visual aids tactically so you appeal to your audience. This means finding images your audience can relate to, images they will find familiar and images they will like. Also think about what style of visual aid is suitable for the audience; is it quite a serious presentation? Can you be humorous? Is it more formal or informal?
Example of using visual aids
When watching this video, notice how the presenters:
- Talk to the audience while writing
- Turn their body to the audience while writing
- Don’t spend too long writing in one session
Types of visual aids
There are a variety of different types of visual aids, you must decide which will suit your presentation and your audience.
Microsoft PowerPoint is widely used for presentations because it’s easy to create attractive and professional presentations and it’s simple to modify and reorganise content compared to other visual aids. You can insert a range of visual items into the slides which will improve the audience’s focus. Also, the audience can generally see slideshows better than other visual aids and you don’t have to face away from them. However, your presentation can look unprofessional if this software is used poorly.
- Have a clear and simple background.
- Avoid using too many different types of fonts or font sizes.
- Only use animations for a purpose, such as, to reveal the stages of a process, otherwise this can be distracting and look amateurish.
- Use a large font size – a minimum of 24pt.
- Use bullet points to summarise key points.
- Consider providing handouts of diagrams because the audience will find the diagrams easier to read.
- Avoid putting too much text on a slide.
- Avoid using red or green text as it’s difficult to read.
- There should only be one key point for each slide.
- Always have a back-up plan in case there is a technical issue and you cannot show the visuals on the day, for example, bring handouts or a poster.
Whiteboards
Whiteboards are great for providing further explanations, such as, showing the order of a process, creating diagrams or explaining complex words or phrases. They’re often used to display headings and write down audience suggestions. Whiteboards are also ideal for displaying important information for the entire duration of the presentation, such as, key definitions, because the audience can just glance at the whiteboard for a reminder.
- Ensure that enough time has passed for the audience to take notes before rubbing something off of the whiteboard.
- Write concisely to avoid facing away from the audience for too long.
- Handwriting must be large and legible.
- Practice beforehand as you may feel nervous about writing in front of an audience at the time.
Handouts are papers that contain key information from your presentation or they may provide further information. They prevent you from overwhelming the audience as there will be less information on the slides and therefore less information they need to write down.
You must consider when you want to give the audience the handouts:
- If given at the beginning and middle of your presentation the audience may be reading rather than listening to you or they might not pay attention to what you’re saying as they already have the information.
- If given at the end of your presentation the audience may be trying to take lots of notes which may reduce the amount of information they are actually understanding.
To manage this, provide the audience with partially completed handouts so they will have to listen to what you’re saying to be able to fill in the gaps. Providing the audience with graphs and charts beforehand is also beneficial because the audience will find them easier to read than, for example, from a slide.
- Tips on creating handouts for your presentation

Video clips
Using videos are a great wait to engage the audience and increase their interest. Use video to bring motion, images and audio into your presentation.
- Ensure that any videos used are relevant to the presentation’s content.
- Only show as much of the video as necessary.
- Never show a really long clip.
- Videos can be difficult to fit into the structure of a presentation so ensure that you tell that audience why you’re showing them a clip and tell them what to look for.
- Inform the audience how long the video will last.
Flip charts offer a low cost and low tech solution to record and convey information as you speak. They’re more beneficial for smaller audiences and they are favoured for brainstorming sessions as you can gather ideas easily. Flip charts are also widely used for summarising information and, like with a whiteboard, you can use them to show permanent background information.
- Before your presentation, place the flip chart in a location that you can easily access.
- Prepare any sheets you can in advance, even if you can only write down the headings.
- Flip charts can be moved so you can avoid facing away from the audience – stand next to it and continue to face the audience.
- Have only one main idea per sheet.
- Write legibly, largely and in block capitals so it’s more visible.
- Check with the audience that they can read the text – do not use a flipchart if there is a large audience.
- Only write in black and blue ink. Red ink is good for circling or underlining.
- Using a pencil write notes to yourself beforehand so you remember what to include – the audience will not see this writing. Also drawing lines in pencil beforehand can keep your handwriting straight.
- Flip back through the sheets to consolidate points.
- Practice writing on the flip chart advance as you may feel nervous at the time of presenting.
Poster boards can be created using a variety of visual devices, such as graphs and images. They’re generally quite portable and you can make them as elaborate as you want. However, they can be expensive to produce if the poster is quite complex.
- One poster per message or theme
- Use block capitals
- Avoid using posters when presenting to large audiences as they will not be able to see the content
Product, objects or artefacts
Objects can be useful tools for making an impact or even for making a dull topic more interesting. Sometimes they’ll be needed for technical and practical reasons, such as, showing a model or conducting an experiment.
- If you are presenting to a small audience consider passing the object around but provide enough time so they won’t have to divide their attention between the object and what you’re saying.
- If the audience is large ensure that you move the object around so everyone sees it.
- The audience will be more distracted from what you’re saying when they’re looking at the object so keep it hidden until the right time and provide the background information before revealing it.
- Explain why you’re using the object.
- If you are conducting an experiment or demonstration, move slowly with exaggerated movements so the audience can follow. Also explain precisely what’s going on.
Two examples of live product demos:
Key points for using visual aids
Try to find out what the presentation room is like beforehand, such as, the layout of the room, the equipment etc, so you can see if your visual aids are appropriate and whether they will work there but always have a contingency plan regardless. Also remember that the audience should be able to understand an image almost immediately.
Before your presentation, ensure that you practice with your visual aids so you know how to operate the equipment. If something goes wrong you’ll have a better chance of solving the problem.
Research suggests that using colour increases people’s motivation to read and their enthusiasm for a presentation. Software like PowerPoint is great for producing colour visuals.
Using the colour wheel can help when choosing your presentation’s colours:
- Colours opposite each other in the wheel are complementary and they create contrast. Using complementary colours makes your text more readable.
- Colours next to each other are analogous and they are harmonious. Using analogous colours makes your presentation more unified.
The Adobe colour wheel , which helps you pick complementary colours for your presentation design.
Avoid using too many colours in your presentation as this can look cluttered and unprofessional and keep your colour themes continuous, for example, if you highlight all the key words on one slide in blue, continue to do this throughout the presentation. Also be careful with colour associations, for example, in many cultures red is linked to danger. Try to represent your words and topics with colours that make sense and are appropriate.
Many people are blue-green or red-green colour-blind so avoid putting these colours next to each other’s in, for example, a graph. If you cannot avoid placing these colours next to each other then use text to clearly label items.
Research suggests that information displayed visually is well remembered: “retention of information three days after a meeting or other event is six times greater when information is presented by visual and oral means than when the information is presented by the spoken word alone.” ( U.S. Department of Labor OSHA Office of Training and Education, 1996 )
There is also significant evidence suggesting that most learning occurs visually – some researchers suggest that 83% of human learning happens visually. The psychologist Bruner conducted multiple studies which suggest that people remember 80% of what they see and do, 20% of what they read and only 10% of what they hear.
Visual aids are worth including in your presentations because they can help you explain information more coherently which makes presenting easier for you and learning easier for the audience. They also help add variety to your presentation thus making it more interesting for the audience. If the audience understand what you’re saying and they are more engaged, they’re more likely to be persuaded by you.

10 Best Visual Aids to Drive Home Your Presentation
Feb 22, 2023 | Deliver a Presentation
Even more impactfully, you can generate greater understanding in your audience. For example, if you’re discussing a company’s finances, having a set of graphs and charts can convey a greater grasp of the figures.
Visual Aids Examples
Visual aids are more than just PowerPoint presentations. To help spark some ideas, here are ten visual aids examples to try out.
What is a visual aid?
A visual aid is anything you use in a presentation to visually drive home your point. Using visual aids can improve attention and engagement with your presentation. They’re also quite fun!
If a picture tells a thousand words, a video tells a thousand pictures. You could pause your talk at the start to show a video demonstrating an idea or concept. It can help ground your presentation and provide context for what you’re going to say next.
In one particularly spectacular example, Hans Rosling’s TED talk, The Best Stats You Have Ever Seen , uses video continuously throughout the presentation. The result: a deeper understanding of a complex topic.
Don’t just describe your product: show it! Having a tactile prop you can hand around or demonstrate isn’t just informative; it’s one of the most engaging visual aid examples around. It draws the eye and captivates your audience.
For example, if you’re giving a talk on African History, showing a traditional artifact (even a replica) can go a long way towards conveying your ideas.
Just don’t overdo it. Too many props can distract your audience from the main thrust of your presentation.
3. Handouts
Are you discussing a complex topic? If so, a handout can help break down the more complex aspects of your talk. It can contain pictures and diagrams for you to refer to in your presentation. It’s also something your audience can take away at the end. And what better way to drive home your message than a lasting reminder.
That’s not to say every presentation could benefit from a handout. But when used prudently, this visual aid example can help make your presentation that bit more memorable.
4. Demonstrations
This visual aid example blurs into props a little bit. Where it differs is in its dynamic character. Think back to your school days – aren’t the lessons you remember best, the ones with a bang?
Demonstrations can serve as the hook to draw your audience into a complicated concept. You could show off how your product works in practice. Or set up a small scientific experiment to get across the core concept of your talk.
And it’s a great way to end a presentation – no other visual aid example is as memorable.
Everyone might use slides – but that’s for a reason. Slides are a simple but effective way to convey your ideas visually throughout a presentation. They can give key statistics or contain charts, graphs, or pictures.
Nor do you need to settle solely for PowerPoint. If you fancy trying something different, check out Prezi. It lets you create an interactive and fluid presentation at the click of a button.
6. Whiteboards
There’s a reason why classrooms have whiteboards. To explain a new idea or spark a discussion, there’s no better visual aid example than a whiteboard.
How about having a pause midway through your presentation to have a brainstorm? Or start off the discussion by jotting down people’s initial impression of an idea. Then, at the end, you can revisit what you wrote down and see if people’s perspective has changed.
Even better, with virtual meetings now the go-to way to conduct a presentation, many video conferencing software contains virtual whiteboards.
7. Posters and boards
If you go to a scientific conference, posters are the primary way to present. When big and visually engaging, they can help introduce an idea. Alternatively, like a lawyer in a courtroom, you can use pre-made boards throughout your presentation. It’s a little more dramatic than a PowerPoint, creating a more memorable experience.
8. Roleplay
Before you roll your eyes – stay with me. Roleplays, when done right, can be the most memorable part of a presentation (for the right reasons). It’s a chance to put yourself in someone else’s shoes. Think about how a roleplay can show a social situation. It could be a person trying to buy a product. By walking through the customer’s shoes, you could demonstrate to a prospective client just why your product or service is essential.
9. Blackboards
If you don’t have a whiteboard, blackboards are the next best thing. Though they function pretty similarly, the blackboard has an older aesthetic many remember from their schooldays. Draw diagrams, symbols, charts, and drawings with the classic chalk.
In fact, one of the benefits blackboards have over whiteboards is the ease with which you can draw. Plus, it’s always a great tool for interactive learning.
10. Flipcharts
If a room doesn’t have a blackboard or whiteboard, try a flipchart – it’s the next best thing. Unlike the other two, you can prepare some of the pages beforehand. For example, you can draw a table of pros and cons, ready for your audience to shout out their ideas.
For many, it’s just a refreshing change from the tired slide presentations.
Need more visual aids examples?

About the Author
For over 20 years Elizabeth Peterson , has enjoyed supporting individuals and companies with their communication and voice needs. Speech and Voice Enterprises, her private practice, has been in operation for over 15 years in Denver, Colorado. Ms. Peterson is heavily involved in her field and has numerous published books, therapy programs and articles in the areas of accent reduction, public speaking, leadership and communication, traumatic brain injury, stroke recovery and pediatric therapy programs.
At Speech and Voice Enterprises, we offer custom-tailored business communication classes with several training options available... Get started now with
More Articles from Our Blog!

Who Can Benefit from Foreign Accent Reduction Classes?
Aug 23, 2024 | Accent Reduction
In today’s ever-shrinking world, clear communication is more important than ever. Whether you're navigating a professional environment or simply engaging in daily conversations, the ability to express yourself clearly can make all the difference. For many, an accent...

Empowering Women’s Voices: Private Coaching for Public Speaking Success
Aug 12, 2024 | Public Speaking
It’s not uncommon to feel uncomfortable speaking in front of large groups. Indeed, the pressure to present yourself well can make it feel almost impossible. Unfortunately, many women have to engage in some form of public speaking nearly every day. From group fitness...

Mastering the Art of Persuasion: Insights from Online Public Speaking Courses
Jun 21, 2024 | Public Speaking
The fear of public speaking, also known as glossophobia, is surprisingly common. Studies reveal that a staggering 77% of the general public experiences this fear to varying degrees, from mild nervousness to outright panic. This anxiety often stems from the fear of...

- PRESENTATION SKILLS
- Working With Visual Aids
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Presentation Skills:
- A - Z List of Presentation Skills
- Top Tips for Effective Presentations
- General Presentation Skills
- What is a Presentation?
- Preparing for a Presentation
- Organising the Material
- Writing Your Presentation
- Deciding the Presentation Method
- Managing your Presentation Notes
Working with Visual Aids
- Presenting Data
- Managing the Event
- Coping with Presentation Nerves
- Dealing with Questions
- How to Build Presentations Like a Consultant
- 7 Qualities of Good Speakers That Can Help You Be More Successful
- Self-Presentation in Presentations
- Specific Presentation Events
- Remote Meetings and Presentations
- Giving a Speech
- Presentations in Interviews
- Presenting to Large Groups and Conferences
- Giving Lectures and Seminars
- Managing a Press Conference
- Attending Public Consultation Meetings
- Managing a Public Consultation Meeting
- Crisis Communications
- Elsewhere on Skills You Need:
- Communication Skills
- Facilitation Skills
- Teams, Groups and Meetings
- Effective Speaking
- Question Types
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Visual aids are an important part of presentations. They can help to keep your audience engaged, make your point for you—there is a reason why people say that a picture tells a thousand words—and remind you what you want to say.
However, you can also take them too far.
If good use of visual aids can make a presentation, poor use can ruin it. Who, after all, has not be subject to ‘death by PowerPoint’, in one of its many forms? This page explains more about how to use visual aids effectively in presentations and helps you to avoid being remembered for all the wrong reasons.

What Are Visual Aids?
Visual aids are exactly what they sound like: a visual support to you standing up and speaking.
They are commonly something like slides setting out your main points, or a video. They can also take the form of a handout, either of your slides, or a summary of your presentation, the use of a flip chart, or even something interesting that you have brought along to show your audience and make a point.
If visual aids are used well they will enhance a presentation by adding impact and strengthening audience involvement. They can also be a helpful to reminder to you of what you wanted to say.
You should only use visual aids if they are necessary to maintain interest and assist comprehension in your presentation.
Do not use visual aids just because you can, or to demonstrate your technological competence. Doing so may make it harder to get your messages across clearly and concisely.
For each visual aid or slide, ask yourself why you are using it. If there is no real purpose, don’t include it.
Thinking Ahead—Planning Your Visual Aids
Most visual aids will need advance preparation. You will need to know how to operate the equipment effectively.
Check beforehand what facilities are available so that you can plan your presentation accordingly.
Also check whether you need to send your presentation in advance to be loaded up, or whether you can bring it on a memory stick or similar.
You can find more about preparing a presentation in our dedicated page on the subject.
Presentation software
It is now common to use presentation software such as PowerPoint.
Indeed, few presenters would dare to attend an event without a PowerPoint file. However, it is still possible to manage without. Some of the very best lecturers and speakers do not use PowerPoint. At most, they might draw on a flip chart or whiteboard. What they have to say, and the style in which they say it, is compelling enough to hold their audience.
For most of the rest of us, PowerPoint is likely to be the way forward, however.
Top tips for using PowerPoint
Keep it simple. Use no more than three to five bullet points per slide and keep your bullet points to a line of text, if possible. Your slides should be a guide to what you are going to say, not a verbatim account.
Don’t use visual effects unless they actually add to your presentation. PowerPoint has some very nice options for adding and subtracting text, but they can be very distracting. Stay away unless you really know what you’re doing.
Keep it short. A half-hour presentation can usually be summarised into six to ten slides at most.
Don’t use the notes function. PowerPoint has a ‘notes’ function that allows you to write notes under the slides for your benefit. Don’t. You will try to read them off the screen, and stop talking to your audience. Instead, use cue cards held in your hands and focus on your audience.
Other common visual aids include:
- Whiteboards and interactive whiteboards
- Flip charts
Whiteboards and Interactive Whiteboards
Whiteboards are good for developing an explanation, diagrams and simple headings.
They can also be used for recording interaction with, and comments from, the audience during brainstorming sessions .
Remember that writing on a whiteboard takes time and that you will have to turn your back to the audience to do so. If using a whiteboard, you should ensure that your handwriting is legible, aligned horizontally, and is sufficiently large to be seen by all the audience. Also ensure that you use non-permanent pens (sometimes referred to as dry-wipe pens) rather than permanent markers so that your writing can be erased later.
Bear in mind that the white background of a whiteboard can cause contrast problems for people with impaired vision.
Interactive whiteboards can be used for PowerPoint presentations, and also to show videos, as well as to write on and record interactions with the audience. They are, effectively, projector screen/whiteboard combinations, with attitude. If you plan to use an interactive whiteboard, you should make sure you know how it works, and practice using it, before your presentation. It is NOT a good idea to make first use of one in a major presentation.
Flip Charts
A flip chart is a low cost, low tech solution to recording interactive meetings and brainstorming sessions.
At many venues, however, they have been replaced by interactive whiteboards.
A flip chart can be prepared in advance and is portable, it requires no power source and no technical expertise. Flip charts are ideal for collecting ideas and responses from the audience and are good for spontaneous summaries. However, if the audience is large, a flip chart will be too small to be seen by everyone.
Top tips for the effective use of a flip chart:
Arrive early and position the flip chart so that you can get to it easily when you need it.
Position the flip chart so that you can stand next to it and write while still at least half-facing your audience. Do not turn your back on your audience.
Make sure you have several marker pens that work.
Only use blue or black marker pens. It will be difficult for those at the back of the room to see any other colours. You can use red pens to accentuate blue or black.
Make your letters at least 2-3 inches tall so that everybody can see what you have written.
Draw lines in pencil on blank pages before your presentation, to help you keep your writing legible and straight.
If you are using a flip chart as an alternative to PowerPoint:
- Plan out your pages as you are writing the outline for your presentation;
- Write notes to yourself, in pencil, on the flip chart to remind you of the points you want to make. Your audience will not see the pencil notes.
If you have something that you want to present and then accentuate during the presentation or discussion, write out the flip chart page beforehand so that you can just flip the page to it—or just use a PowerPoint slide.
If you need to refer to something that you wrote on a page at a later point in your presentation, rip off the page and fix it to the wall.
Videos are particularly good for training purposes. Short videos can also be embedded into a PowerPoint presentation to make a point, or provide an example. This is becoming increasingly popular with the advent of YouTube, because far more videos are available. Smartphones have also made recording your own videos much easier.
However, as with any visual aid, make sure that you are using video for a purpose, not just because you can.
Handouts summarising or including the main points of a presentation are an excellent addition, but must be relevant.
Presentation software packages such as PowerPoint can automatically generate handouts from your presentation slides. You can also prepare a one-page summary of your presentation, perhaps as a diagram, if that seems more appropriate. This may be particularly useful if you are asked to do a presentation as part of an interview .
If you do provide handouts, it is worth thinking carefully about when to distribute them.
Giving out handouts at the start of a talk will take time and the audience may start to read these rather than listen to what the speaker is saying. However, if your presentation contains complex graphs or charts, the audience will appreciate receiving the handout before the presentation starts since they may find it easier to view these on paper than on the projection screen. The audience may also appreciate being able to make their own notes on the printed handout during the presentation.
Consider the best time and method to distribute any handouts, including either placing them on seats prior to the start or giving them out at the end of your presentation. You may also consider emailing copies of handouts to participants after the event. If your talk includes questions or discussion this will give to time to summarise this and communicate it back to the attendees.
A final take-away
There is no question that visual aids, used well, will enhance your presentation. They add a more visual element to the auditory aspect of you speaking. They therefore help to engage your audience on more levels, and also keep them interested.
The key to avoiding ‘death by PowerPoint’ is to focus on the purpose of each slide or visual aid, and ask yourself:
How does this add to what I am saying?
‘Adding’ may of course include ‘providing a summary’, but if your slide adds nothing to your spoken words, then do not include it.
Continue to: Managing the Presentation Event Presenting Data
See also: Preparing for a Presentation Organising the Presentation Material How You Can Improve Your Video Editing Skills Typography – It’s All About the Message in Your Slides


15 Essential Visual Aids Examples to Improve Your Presentations
Visual aids can make a world of difference in how we communicate, learn, and present ideas. Whether you’re giving a business presentation, teaching a class, or sharing information with friends, the right visuals can capture attention and make your message clear. In this article, we’ll explore various visual aids examples that can enhance your presentations and help you connect with your audience.
From charts and graphs to videos and infographics, these tools can simplify complex information and make your content more engaging and memorable. Let’s dive in and see how you can use visual aids to your advantage!
What Are Visual Aids?
Visual aids are tools that presenters use to help convey their message more effectively. These can include anything from simple charts and graphs to elaborate models and videos. The primary purpose of visual aids is to enhance understanding by providing a visual representation of the information being presented.
They can help clarify complex concepts, highlight important points, and keep the audience engaged. By appealing to the visual sense, these aids can make information more accessible and memorable, making them an essential part of effective communication.
Types of Visual Aids
- Charts and Graphs: These are used to represent data and statistics visually. Examples include bar charts for comparing quantities and pie charts for showing proportions.
- Diagrams and Illustrations: Diagrams and illustrations help explain processes, structures, or concepts. Flowcharts, for instance, can show steps in a process, while anatomical diagrams can explain parts of the body.
- Photographs and Images: High-quality photographs and images can enhance storytelling and provide real-life context. They are especially useful in marketing and educational materials.
- Videos and Animations: Videos and animations are dynamic visual aids that can demonstrate processes, provide tutorials, or explain complex ideas in an engaging way.
- Models and Physical Objects: Physical models and objects can provide a tangible way to understand abstract concepts, such as architectural designs or scientific phenomena.
- Infographics: Infographics combine data and visuals to present information clearly and quickly. They are great for summarizing research findings or explaining statistical data.
- Presentations and Slideshows: Tools like PowerPoint or Keynote presentations allow for a combination of text, images, charts, and videos to support spoken content and keep the audience engaged.
Examples of Effective Visual Aids
1. charts and graphs.

Example: Bar Charts for Sales Data
Bar charts are an excellent way to compare different categories of data. For instance, in a business presentation, a bar chart can clearly show sales performance across various regions. This visual aid helps the audience quickly grasp which regions are performing well and which are lagging behind.
Example: Pie Charts for Market Share
Pie charts are useful for displaying parts of a whole. They can effectively show market share distribution among competitors in a particular industry. By using distinct colors and clear labels, pie charts can make complex data easy to understand at a glance.
2. Diagrams and Illustrations

Example: Flowcharts for Process Visualization
Flowcharts are ideal for mapping out processes. In a training session, a flowchart can illustrate the steps involved in a customer service protocol, ensuring that employees understand the sequence of actions required.
Example: Anatomical Diagrams for Biology Classes
In educational settings, anatomical diagrams can provide detailed visual explanations of biological structures. For example, a diagram of the human heart can help students learn about its various parts and functions.
3. Photographs and Images
Example: high-quality product images in marketing.
High-quality images are crucial in marketing materials. For an e-commerce website, clear and detailed photographs of products can significantly enhance the shopping experience, helping customers make informed purchasing decisions.
Example: Historical Photographs in Presentations
In a history presentation, using authentic photographs from the era being discussed can make the content more relatable and engaging. These images provide a visual connection to historical events and figures.
4. Videos and Animations
Example: tutorial videos for software training.
Videos are highly effective for training purposes. A tutorial video demonstrating how to use a specific software feature can help users follow along and learn more efficiently than through text instructions alone.
Example: Animated Explainer Videos for Complex Concepts
Animated videos can simplify complex concepts. For example, an explainer video about blockchain technology can break down the intricate details into easy-to-understand visuals, making the topic accessible to a broader audience.
5. Models and Physical Objects
Example: 3d models for architectural designs.
Physical models are invaluable in fields like architecture. A 3D model of a building can provide a tangible representation of the design, allowing clients and stakeholders to better visualize the final product.
Example: Physical Prototypes in Engineering
In engineering, physical prototypes can demonstrate how a product will function. For instance, a prototype of a new gadget allows engineers to test its usability and make necessary adjustments before mass production.
6. Infographics
Example: data-driven infographics for statistics.
Infographics are perfect for summarizing complex data in a visually appealing format. For instance, an infographic on global warming statistics can combine charts, icons, and brief text to convey key information quickly and effectively.
Example: Infographics for Educational Purposes
In educational contexts, infographics can simplify learning. An infographic explaining the water cycle can use visuals and concise explanations to help students understand the process more easily.
Example: Geographic Maps for Location-Based Data
Maps are invaluable for displaying geographical information. For example, in a business presentation, a geographic map can show sales distribution across different regions, helping the audience visualize areas of high and low performance. This can be particularly useful for identifying target markets and regional trends.
Example: Heat Maps for Data Density
Heat maps use color coding to show data density in specific areas. For instance, a heat map can illustrate population density in a city, with darker colors representing more densely populated areas. This type of visual aid is useful in urban planning, real estate, and marketing to identify hotspots of activity or interest.
8. Timelines

Image source: Pinterest
Example: Historical Event Timelines
Timelines are effective for showing events in chronological order. A timeline of significant historical events can help an audience understand the sequence and context of occurrences, providing a clear and organized way to present historical data or project milestones.
Example: Project Timelines in Business
In business, project timelines outline key milestones and deadlines. This visual aid helps teams stay on track, ensures that everyone is aware of important dates, and can highlight dependencies between tasks, making project management more efficient.
9. Mind Maps
Example: brainstorming sessions.
Mind maps are powerful tools for brainstorming and organizing ideas. During a team meeting, a mind map can visually represent thoughts and connections between concepts, fostering creativity and collaboration by showing how ideas relate to each other.
Example: Study Guides
Students can use mind maps to summarize and organize study material, making it easier to review and recall information. By breaking down complex subjects into manageable parts, mind maps can enhance learning and retention.
10. Posters
Example: educational posters.
Posters are useful in educational settings to reinforce learning. For instance, a poster displaying the periodic table of elements provides a constant visual reference for students, aiding in memorization and understanding.
Example: Informational Posters in Public Spaces
In public spaces, posters can convey important information clearly and accessibly. For example, posters detailing safety protocols or event schedules can be placed in common areas to inform and guide the public effectively.
11. Flip Charts

Example: Interactive Meetings
Flip charts are great for interactive meetings and workshops. Presenters can write and draw on flip charts in real-time, engaging the audience and encouraging participation. This allows for dynamic presentations where feedback can be incorporated on the spot.
Example: Training Sessions
In training sessions, flip charts can outline key points and concepts, making the information more interactive and memorable. Trainees can also use flip charts for group activities, fostering collaborative learning.
12. Whiteboards and Blackboards
Example: classroom teaching.
Whiteboards and blackboards are essential tools in classrooms. Teachers can write, draw, and illustrate lessons dynamically, adjusting content based on student needs. This versatility helps cater to different learning styles, whether visual, auditory, or kinesthetic.
Example: Business Meetings
In business meetings, whiteboards can be used to brainstorm ideas, outline strategies, and solve problems collaboratively. The ability to quickly jot down thoughts and make changes facilitates efficient and productive discussions.
13. Interactive Displays
Example: touchscreen displays.
Touchscreen displays offer interactive experiences. In museums or exhibitions, visitors can interact with the display to explore information at their own pace, making the learning experience more engaging and personalized.
Example: Smart Boards in Classrooms
Smart boards combine traditional whiteboards with digital technology, allowing teachers to present multimedia content, annotate slides, and interact with educational software. This technology can enhance student engagement and provide a richer learning experience.
14. Props and Demonstrations

Example: Science Experiments
Props and demonstrations bring abstract concepts to life. In science classes, demonstrating a chemical reaction with actual materials helps students understand the process better than through diagrams alone. It makes learning more tangible and exciting.
Example: Product Demonstrations
In sales presentations, demonstrating a product’s features and benefits using actual props can be much more persuasive than simply describing them. Seeing a product in action can help potential customers understand its value and functionality.
15. Presentations and Slideshows
Example: powerpoint presentations for business meetings.
PowerPoint presentations can combine text, images, charts, and videos to support spoken content in business meetings. This multimedia approach keeps the audience engaged and ensures that key points are effectively communicated.
Example: Keynote Presentations for Conferences
For conference speakers, Keynote presentations provide a polished and professional way to deliver their message. By integrating various visual aids, these presentations can enhance the overall impact and clarity of the content.

Roberta Walter is the visionary behind Content Paradise, a blog that delves into diverse topics with enthusiasm and insight. Passionate about discovery, she crafts content that educates, inspires, and entertains a community of curious minds.
Similar Posts

120 Different Ways to Say No Without Feeling Guilty
Saying no can be tough, especially when you don’t want to hurt someone’s feelings or seem rude. Whether it’s at work, with friends, or in…

How to Get Rid of Spider Webs Outside: 13 Methods to Try
Spiders are helpful little animals to have around, but that doesn’t mean they’re always pleasant. Some are venomous, they’re a little creepy and crawly, and…

What to Write in a Baby Shower Card: 125 Thoughtful Messages
Baby showers are a wonderful way to celebrate the upcoming arrival of a new baby and show support for the parents-to-be. Whether you’re a close…

30 Best Wedding Entrance Ideas for the Wedding Party
The entrance of the wedding party sets the tone for the celebration and creates lasting memories. Whether you want something classic, funny, or unique, the…

How Long Should You Stay in an Ice Bath? Best Duration for a Dip
If you’re looking into ice baths, you likely know the numerous benefits of trying them out. Unfortunately, getting started is difficult sometimes. It’s intimidating to…

How to Ask Someone to Homecoming: 27 Unique Ideas to Try
Homecoming is a special time that brings excitement and a bit of nervousness, especially when you want to ask someone to be your date. Whether…
7 Presentation Aids To Deliver A Successful Presentation
- By Judhajit Sen
- April 25, 2024
Key Takeaways
- Diverse Tools for Engagement : Different types of presentation aids, including images, graphs, diagrams, maps, audio and video aids, handouts, and demonstrations, enhance engagement by targeting various senses and learning styles and helping the audience to understand your message.
- Enhanced Comprehension : Aids simplify complex ideas, making them easier to understand and remember. They act as a bridge between abstract concepts and audience comprehension, ensuring more transparent communication.
- Strategic Selection and Integration : Choosing the right aid aligned with the speech’s purpose is crucial. Quality visuals, such as high-resolution images and clear charts, reinforce key points and maintain audience focus.
- Long-lasting Impact : Effective use of different types of presentation aids extends the presentation ‘s impact beyond its duration. Handouts and memorable demonstrations leave lasting impressions, reinforcing memory recall and audience association with the content.
What Are Presentation Aids?
Presentation aids, also known as sensory aids, are additional tools to boost good presentations. They come in various forms, such as visuals, sounds, and multimedia elements , and enhance the speech’s impact. By targeting different senses like sight and sound, different types of computer-based presentation aids ensure better audience engagement and retention. For instance, combining audio and video clips in a PowerPoint presentation slide can make your presentation more memorable.
Use of different presentation aids go beyond mere words, enriching the message and catering to diverse learning styles. Presentation aids can be used to complement spoken words, making complex ideas easier to understand. Audible aids, such as music or speech excerpts, add depth to the PowerPoint slides and make your speech more interesting.
Presentation aids tap into the psychology of presentation perception, elevating the overall quality from ordinary to extraordinary. They work hand in hand with the speaker’s delivery, enriching the audience’s experience and reinforcing key points.
Why Presenters Use Presentation Aids
Presenters choose presentation aids to enhance their message and engage the audience effectively. Whether in-person or virtual, presentation aids can help clarify complex ideas and ensure an introduction to speech communication. They help maintain focus, especially in nerve-wracking situations like public speaking , and bridge any gaps in understanding.
Use of visual aids, including slides and props, make presentations more engaging, credible, and memorable. They guide transitions, communicate data effectively, and reinforce key points, increasing the likelihood of a positive response to calls to action.
Strategic use of presentation aids helps speakers improve audience understanding, retention, and interest. While a well-prepared speech is crucial, aids further elevate its impact. They add variety, enhance credibility, and emphasize ideas, ultimately contributing to a successful presentation. As a speaker, choosing the right presentation aid tailored to various points in your speech is critical to delivering a compelling message.
Following are seven forms of presentation aids to deliver a successful presentation.
Images serve as your presentation aid in enhancing understanding and evoking emotions. Unlike words, photographs provide visual experiences, bridging the gap between description and reality. They offer a window for audiences to see and experience specific aspects throughout your presentation, ensuring more transparent comprehension.
While videos have their place, photographs capture singular moments without distractions, making them necessary to present your message. Strictly speaking, they are less likely to overwhelm or divert attention, ensuring the main speaking points remain the focus. Visual aids like photographs are cost-effective and easily editable, making them practical choices for presentations.
Quality and relevance are paramount when selecting images. High-resolution images prevent pixelation and maintain clarity, ensuring effective communication. Watermarked images should be avoided to maintain professionalism, with alternatives sought from reputable sources like iStockphoto or Creative Commons databases.
Simple images like silhouettes or diagrams can enhance understanding, particularly for complex topics, while avoiding clutter. However, they must align with the presentation’s message and evoke the desired emotions.
Presenters can create impactful presentations that resonate with audiences and enhance comprehension without distractions by using images judiciously and ensuring their compatibility with the speech.
Graphs And Charts

Graphs and charts serve as essential tools for visually presenting data and comparisons. They simplify complex information, making it easy for audiences to comprehend statistics and figures. In business contexts, they are among the most commonly used visual aids.
Long strings of numbers can overwhelm audiences, leading to disengagement. However, comparing simple shapes or lines in a chart is far easier for most people to understand. Selecting the correct types of charts or graphs is crucial to communicate your message effectively. Whether it’s a pie chart to show proportions, a line graph to illustrate trends over time, or a bar chart for precise comparisons, each presentation aid must serve a specific purpose of your speech.
When designing charts, simplicity is vital. Emphasize clarity over complexity, focusing on delivering a clear conclusion rather than cramming in excessive data. Clear labels, easily distinguishable colors, and consistent formatting enhance comprehension. Complex graphs should be avoided, as they can confuse rather than clarify.
Presenters facilitate audience understanding and engagement by transforming numerical data into visual formats , such as charts and graphs. Visualizing comparisons and trends allows audiences to grasp information more effectively, reinforcing key points and enhancing overall communication.
Diagrams serve as visual aids to elucidate the inner workings and relationships of subjects. They are distinct from mere sketches by their focus on function and connection rather than physical form. They offer flexibility in presenting complex concepts beyond physical attributes, making them invaluable for explaining intricate relationships where other visual mediums fall short.
Experimentation is key in selecting the most effective diagram type for audience comprehension. Diagrams excel in clarifying abstract concepts or unfamiliar entities, bridging understanding by relating them to familiar elements. Their step-by-step breakdown aids in following processes or sequences logically, enhancing audience retention and comprehension.
Unlike charts and graphs, which prioritize data, diagrams emphasize appearance, structure, and flow. They delineate parts, aiding in detailed explanations and mitigating potential confusion.
When incorporating diagrams, it’s crucial to articulate each component, particularly those prone to misunderstanding. Whether illustrating a product’s features or delineating a process’s steps, diagrams ensure clarity and coherence, facilitating audience understanding and engagement.
Diagrams are indispensable tools for dissecting and demystifying complex subjects, transforming abstract ideas into tangible concepts that resonate with audiences.
Maps serve as potent presentation aids, offering more than just geographical information. Maps convey relational data effectively as two-dimensional diagrams, especially when enhanced with animations or overlays. Modern presentation software makes updating map datasets seamless, ensuring real-time accuracy without manual manipulation.
Diverse types of maps, such as population, weather, political, or economic maps, cater to specific informational needs, emphasizing key aspects relevant to the speech’s purpose. In today’s interconnected world, where global interactions are commonplace, maps are crucial in visualizing relationships between nations and regions. Whether showcasing business expansions, disease spread patterns, or cultural trends, maps provide much information into geographical hotspots and trends.
Maps offer perspective, fostering emotional connections by illustrating proximity and spatial relationships. Whether presenting to a global audience or focusing on localized regions, maps help contextualize information and engage audiences more effectively. By incorporating maps into presentations, speakers can enhance comprehension and facilitate a deeper understanding of complex concepts, making them indispensable tools in communication across various domains.
Audio Visual Aids
Audiovisual aids, including video and audio clips, serve as invaluable tools to enrich presentations and enhance audience engagement . By incorporating diverse delivery methods, such as transitioning from speech to audio or video clips, speakers can more effectively captivate their audience’s attention. Videos, in particular, offer a powerful means of summarizing key points and conveying emotions beyond what speech alone can achieve.
However, while audiovisual aids can significantly elevate presentations, they also present potential challenges, such as technical compatibility issues and abrupt transitions. Integrating audiovisual elements into presentations requires adequate preparation, including familiarity with presentation software, checking the video equipment prior to speaking and practice with audio or video equipment.
To maximize the effectiveness of audiovisual aids, speakers should ensure clips are relevant in length and content, avoiding lengthy selections that distract when they give a speech. Prudent planning includes:
- Cueing clips to the appropriate starting point.
- Providing context to the audience.
- Avoiding technical mishaps that detract from credibility.
Ultimately, audiovisual aids should complement and reinforce key points of the speech, enhancing audience comprehension and retention without overshadowing the speaker’s message.
Handouts are tangible resources provided to the audience containing information relevant to the presentation. Their most significant advantage lies in the physical interaction they facilitate, allowing audiences to engage with the material through touch, sight, and reading. By involving multiple senses, handouts enhance information retention.
They also reference unclear points during the presentation, ensuring consistent audience comprehension. Additionally, handouts extend the presentation’s impact beyond its duration, as they persist in the audience’s possession long after the event. This reinforces memory recall and association with the presentation’s content.
Deciding when to distribute handouts is crucial. While providing comprehensive handouts at the end prevents distractions during the speech, offering summarized versions at the beginning aids audience comprehension and participation.
Effective handouts require careful management and consideration. Distributing enough copies for each audience member ensures professionalism and accessibility. Handouts should contain only essential information organized logically to support the presentation’s key points. Informing the audience of their purpose and how to use them effectively fosters engagement and understanding.
Brochures or detailed handouts offer additional depth, particularly in research-intensive presentations like business or healthcare topics. They enable audiences to review information at their own pace and engage in collaborative note-taking, fostering discourse and interaction.
Handouts are valuable tools for reinforcing presentation content, aiding audience comprehension, and extending engagement beyond the live event. Properly managed and designed, they contribute significantly to a speaker’s credibility and audience satisfaction.
Demonstrations

Demonstrations are dynamic tools used to illustrate and reinforce key points in presentations. They encompass various forms, including physical demonstrations, allegorical stories, or live performances, all of which aim to anchor abstract concepts in reality for audience comprehension.
Memorable examples, like those from science classes, highlight the effectiveness of demonstrations in engaging audiences. Demonstrations leave lasting impressions through sensory involvement, as they stimulate multiple senses, enhancing understanding and retention.
Personal stories or case studies serve as powerful demonstrations. They allow audiences to immerse themselves in the narrative, making the message more relatable and memorable.
However, while demonstrations can elevate presentations, they must be used judiciously. Overuse or irrelevant demonstrations can detract from the main message, undermining the presentation’s effectiveness.
Live performances, exemplified by Steve Jobs’ iconic product unveilings, showcase the potential of demonstrations in public relations. They garner attention and media coverage, even in the face of problem if your presentation aid malfunctions, as demonstrated by Tesla’s Cybertruck unveiling.
Despite setbacks, such as the unexpected failure of Tesla’s armored windows, demonstrations often generate significant publicity, underscoring their impact on audience engagement and perception.
Strategically incorporating demonstrations can transform a speaking situation from average to exceptional, leaving a lasting impression on audiences and effectively conveying key messages.
Maximizing Impact with Presentation Aids
Incorporating possible presentation aids into presentations can transform your message from average to unforgettable. From captivating images to informative graphs, these aids enhance audience understanding and engagement. They also act as a bridge between complex ideas and audience comprehension, ensuring your message resonates long after the presentation ends .
Quality visuals, such as high-resolution images and clear charts, are essential for effective communication. They help maintain focus and reinforce key points, guiding your audience through your presentation effortlessly. By strategically selecting and integrating video clips during a speech, you can enhance credibility, emphasize ideas, and leave a lasting impression on your audience.
Remember, choosing the right visual aid prior to beginning your speech is key to delivering a compelling message. So whether you’re presenting in person or virtually, consider incorporating these seven presentation aids to talk about during your speech. The right visuals can contribute positively to your speech and you can deliver a stellar presentation every time.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why should presenters use presentation aids?
Presenters use aids like visuals and sounds to boost their message and keep the audience engaged at any speaking event. These aids clarify complex ideas, especially in nerve-wracking situations like public speaking , ensuring clear communication and maintaining focus.
2. How do visuals like images contribute to presentations?
Images are powerful tools that enhance understanding and evoke emotions. They provide visual experiences, making presentations more engaging, credible, and memorable. Unlike words, photographs bridge the gap between description and reality, ensuring more transparent comprehension.
3. What role do graphs and charts play in presentations?
A: Graphs and charts simplify complex information, making it easier for audiences to grasp statistics and figures. They prioritize clarity over complexity, guiding transitions and reinforcing critical points effectively. Presenters facilitate audience understanding and engagement by transforming numerical data into visual formats.
4. How can handouts enhance presentations?
Handouts are tangible resources that aid information retention and extend engagement beyond the live event. They reference unclear points, reinforcing memory recall and association with the presentation’s content. Properly managed and designed, handouts significantly contribute to a speaker’s credibility and audience satisfaction.
Transform Your Presentations Today with Prezentium’s Interactive Workshops!
With Prezentium’s AI-powered workshops, you can learn to communicate complex ideas effortlessly using simple layouts, visualization techniques and presentation aids in a speech. Our interactive training programs are designed to help you master the art of engaging presentations, ensuring better audience comprehension and retention.
With Prezentium , you’ll discover how to utilize a variety of effective presentation aids, from captivating images to informative graphs, to enhance your message and leave a lasting impression. Elevate your presentations from ordinary to extraordinary by incorporating our proven techniques and strategies.
Don’t let your presentations fall flat—empower yourself with the skills to captivate and inspire. Join Prezentium’s interactive workshops today and unlock your full potential as a communicator!
Why wait? Avail a complimentary 1-on-1 session with our presentation expert. See how other enterprise leaders are creating impactful presentations with us.
How to Start a Presentation in English: 12 Slide Ideas
Introduction to group communication: tips and benefits, shark tank presentation tips: winning shark tank pitch elements.
- Home →
- Toastmasters →
Visual Aids Presentations: How to Make a Powerful Impact

When you step up to give a presentation, you want to make sure that your message won’t get lost in translation. Enter the power of Visual Aids.
Whether you’re giving a business presentation to a room of colleagues, or speaking to a hundred people at a seminar, using visual aids can really help capture their attention. When used effectively, visual presentations are like taking a mental roller coaster—you start with a few warm-up slides , then you’re off to the races, and by the time you finish, it feels as if you’ve been on an unforgettable journey.
But how do you make sure your visual presentation sticks the landing? In this blog post, we’ll discuss the key components of creating a powerful visual aid presentation that will have the impact you desire. So, warm up the engines, get ready for takeoff and let’s learn how to make a powerful visual presentation!
Why Use Visual Aids for Presentations?
As technologies and audiences continually evolve, visual aids play an increasingly vital role in how presenters engage with their audience. Visuals can stimulate the audience’s interest, help them stay focused, and ultimately make a far more powerful impression. Below are some of the key reasons why presenters should incorporate visuals into their presentations: 1. Enhance Comprehension: It has been shown that visuals can significantly enhance comprehension by up to 89%. This is because visuals provide a clear, easy-to-understand way of displaying complex concepts and data that would take far longer to explain using words alone. Additionally, presenting information with visuals reinforces key points and encourages viewers to remember the main message of the presentation. 2. Attention Grabbing: Because visuals can quickly capture the attention of a viewer they make it easier for presenters to focus their audience’s attention on the most important parts of the presentation. This means presenters do not need to rely solely on verbal explanations and often dramatic charts or results can draw audiences in at just the right moment. This can be especially effective during board meetings or high-level projects when stakeholders need to quickly grasp important information. 3. Improved Memorability: In an age where most of us are bombarded with information from screens, emails and text messages, simply reading aloud from a script often loses its impact over time. By leveraging visuals such as graphs, infographics and compelling images, it is much easier for speakers to keep their audience interested and engaged for extended periods of time. This helps both parties maintain a clear understanding of what is being presented and makes it easier for attendees to remember crucial facts months down the road. The potential downsides of visual aids presentations include clutter, distraction and a lack of engagement if visuals are poorly executed or there is too much discussion around individual slides that gets away from the core message or goal of each slide. To avoid this problem it is critical that the presenter prepares visuals carefully so that each one reinforces the message being conveyed without becoming overly focused on data points or causing distraction. Visual aids offer numerous benefits for improving communication , engagement, engagement and memorability when used correctly within presentations, which will be discussed further in the next section on “Improved Communication and Engagement.
Improved Communication and Engagement
For a presentation to be truly successful, communicative and engaging elements are essential. Through the use of visuals, communication during presentations can be greatly enhanced and interactive dialogue can easily be spurred. The simple addition of visual aids can help attendees pay closer attention to the speaker and better understand the main points of the presentation. This helps prevent confusion as attendees are drawn to different slides as topics transition throughout the presentation. Arguments have been raised that visual aids have a higher potential for confusing rather than clarifying content when used inappropriately. It is possible for some presenters to place too much focus on their slides, taking away from their own storytelling or providing additional and unnecessary information than what is needed. Although there is potential for visuals to obscure communication, the counter argument suggests that with appropriate preparation, visual aids can lead to deeper understanding rather than confusion. With careful preparation and understanding of one’s audience and material, presentations can be influential tools to educate attendees and draw them in with captivating visuals that engage. By understanding engagement patterns, presenters should strive for adding visuals as supplements to chosen content that further illustrate topics of discussion rather than subtracting from them. With this approach in mind, presenters should ensure they are engaging with their audience while using visuals as an extra layer of communication, rather than a distraction from their main message. The thoughtful consideration of these aspects during preparation is integral for making a powerful impact during visual aid presentations. This leads into the next section which will discuss tips on how to prepare effectively before giving a presentation with visuals.
Preparation for Visual Aids Presentations
Prior to giving a visual aid presentation, there are some key steps to ensure optimum success. An important aspect of any presentation is preparation and proper planning . Planning entails organizing the information one wishes to impart as well as understanding who the audience is and what they need or expect from the presentation. Preparation helps identify weaknesses before the day of the presentation so they can be addressed beforehand. The other key element is the content itself. When creating a presentation, it’s important to ensure that all material is accurate, relevant, and well-researched. If using graphical elements such as diagrams and images, assess their relevance and accuracy in order to make sure the visuals add value instead of detracting from your message. Furthermore, find a way to explain complex concepts in simple terms using visuals as an aid rather than relying solely on a lengthy explanation. It might also be beneficial to choose a tool that allows for interactivity with attendees . This could come in the form of an audience poll or game that engages participants and allows them to gain more insight into your topic during the presentation. When constructing the slides themselves, keep them simple with minimal text and use appropriate colors that coordinate with each other while allowing different aspects of your visuals to stand out. Also avoid long paragraphs; instead, break up content into chunks within separate slides. As a general rule of thumb, fewer slides usually means more successful presentations. Lastly, time spent rehearsing will pay off during the live performance; if you feel comfortable enough presenting to coworkers or peers beforehand, do so in order to receive feedback and perfect your craft ahead of time. In this way, you can be confident in knowing what to expect once standing in front of a larger crowd about to deliver your presentation with visual aids. Having gone through these preparatory steps for a powerful visual aid presentation, the next step is determining exactly how these visuals will communicate your message effectively: What are you trying to communicate?
What Are You Trying to Communicate?
When determining the goal of a presentation , it is important to consider what one is trying to communicate. Visual aids can be used to demonstrate an idea or concept , show relationships between data, uncover social trends and patterns, or illustrate complex information in an easier-to-understand way. Depending on the type of visual aids, presenters may opt for a straightforward approach or choose methods designed to evoke emotion from their audience. For analytical presentations where technical visuals such as graphs are used, precision and accuracy are paramount. Presenters need to ensure that their data is accurate and their visuals clearly convey the message they are trying to communicate. On the other hand, when creating emotional visuals geared towards storytelling, identifying the right images or videos to represent the story can help ensure viewers understand the desired message. Both analytical presentations using technical visuals and emotional storytelling visuals are essential tools in making an impactful and powerful presentation. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses that should be taken into consideration when deciding which format best suits the presented materials and content. With this knowledge, speakers can leverage both types of visual aids to create powerful presentations tailored to their unique needs. Finally, as a presenter, you should have a clear understanding of what you are trying to communicate in your presentation before selecting any visual aides. With this knowledge in mind, you can move forward to the next section about Visual Aids Tools and Examples for helpful tips on choosing the right tools for your presentation.
Visual Aids Tools and Examples
Visual aids – such as pictures, charts, and graphs – can be powerful tools for making presentations more effective. They are essential for helping people understand the concept being discussed, and for creating a more engaging experience. However, when used improperly, visual aids can distract from the main message or become a crutch. In order to maximize their impact, it is important to understand which types of visual aids are most appropriate for different kind of presentations. Commonly used visual aid tools include infographics, diagrams, photos, slideshows, videos, and other multimedia. Smartly designed diagrams can help simplify complex information into a graphic representation that is easier to understand and remember. Infographics are useful when you want to convey data in a visually appealing way while keeping the focus on the key points. Photos create an emotional connection with the audience and can be used to strengthen your point. Slideshows are popular options for making PowerPoint presentations more dynamic, while videos can upgrade any presentation by providing an entertaining yet informative way to engage listeners. On one hand, visuals help audiences remember information better by giving them something concrete to relate to and take away after the presentation is over. On the other hand, too many visuals may make it difficult for them to focus on what’s being said or cause confusion about which points are most important. Thus it is important to choose visuals thoughtfully and judiciously when designing a presentation in order to both capture attention and effectively convey the message intended. To make your presentation even more powerful, consider incorporating graphic design elements into the visuals you choose. Graphic design techniques such as color theory and typography can be used to help viewers recognize patterns or relationships among ideas being presented that would otherwise remain hidden beneath words alone. These techniques also create visual interest which engages viewers for longer periods of time and keeps them actively taking in new information as opposed to simply passing through it without learning anything along the way. So with careful consideration given toward both content and context of visuals selected for a presentation, combined with an understanding of how graphics design principles work together; massive impact can be created through effective visual aids. This brings us now to examine PowerPoint and graphic design in greater detail as part of our next section.
PowerPoint and Graphic Design
When considering visuals within presentations, few tools can rival the popularity of PowerPoint. Much of its success is due to its ease of use – slides are easy to create, and the program has a wealth of features that make it suitable for all levels of users. For example, the ready-made slide designs and templates can help even inexperienced presenters to create visually appealing slides in no time with minimal effort. At the same time, however, it is important to recognize that there are times when PowerPoint may be ill suited for a particular scenario. For example, when giving a lecture or seminar on a complex topic, or when wanting to engage an audience with creative visuals. In addition, though PowerPoint contains tools for incorporating graphics into slides, those tools are limited in scope and power. Creating advanced graphics and animated images often requires access to more sophisticated graphic design software. Enterprising presenters should consider taking advantage of both PowerPoint and graphic design skills when planning a presentation. When used together in tandem they can create amazing visuals that engage an audience while also conveying complex information in simple terms. With such powerful visuals it is possible to craft presentations that make lasting impressions on your audience and leave them inspired by what they have seen and heard. Having established how effective combination of PowerPoint and graphic design can be in creating presentations that make a powerful impact, the next section will discuss how to incorporate engaging visuals into a presentation so that it is truly memorable.
Engaging Visuals
Visuals can often be the most powerful and engaging element of a presentation . Using a variety of visuals, such as charts, graphs, or images, can help capture an audience’s attention in ways that words alone might not. However, some debates exists as to when and how often visuals should be used in a presentation. Those who prioritize visuals believe that they are essential in conveying a message or idea quickly and effectively. They argue that a good visual aids presentation will leave a lasting impression on the audience. Good visuals allow the presenter to focus on delivering information in an engaging manner, rather than wasting time with factual reciting. Additionally, visuals can also act as memorable reminders for what was covered during the presentation. Others point out that too many visuals can detract from the impact of each one. In overloaded presentations, each individual visual will be viewed less seriously and thus have less influence overall. The importance of visuals may also vary depending on the desired outcome for the presentation. Some audiences need more detailed factual data than others, and therefore visuals may not always be necessary. Overall, there is no single way to use visuals – every presenter needs to decide what makes the most sense for their audience and goals. But when done strategically and thoughtfully, using visuals in presentations can lead to more powerful and impactful experiences overall. As we move on to our next section about Examples and Graphic Design, let’s discuss how you can design your own unique visuals for maximum impact.
Examples and Graphic Design
The visual content in a presentation can be nearly as vital as the words. After all, a good graphic illustration can communicate complex data quickly and effectively. As such, it is important to choose your design elements and examples carefully when creating a visual aid. When it comes to examples, experts suggest keeping them to relevant, evidence-based statements that support the key points of your argument. For example, if you are making the case for why a new software system should be adopted by your company, include specific figures related to cost savings or increased productivity to back up your claim. With this type of evidence strongly displayed in graphics, it will more easily resonate with the audience and make an impact. It is also important to pay attention to the overall graphic design. That means selecting vivid colors, bold fonts, and interesting infographics. Too many images or bright colors can seem overwhelming though, so strike a balance between clear points communicated effectively and eye-catching visuals. This will help keep your audience engaged while still providing necessary information. When it comes to using visual aids effectively, there are certain tools and strategies that can make a powerful impact on how well data is received. In the next section we will discuss some of those tips for successful visual presentations.
Using Visual Aids Effectively
Using visual aids effectively is essential for a successful presentation. Visual aids can capture the audience’s attention and engage them in the material. When used correctly, visual aids can also give ideas more clarity and help to reinforce key points. Many speakers debate just how effective visual aids actually are in helping to convey a message. On one hand, many people believe that visuals are helpful to conveying a message because viewers are able to clearly understand what’s being said better than if it were presented through words alone. According to research done by the University of Minnesota, visual aids can increase the amount of information retained by viewers in comparison to solely verbal presentations. Plus, visuals can draw on viewers’ emotions, which helps them stay engaged throughout a presentation. The other side of the argument is that overusing visual aids can be distracting and take away from the primary purpose—the speech itself. Too much emphasis on visuals may lead viewers to focus solely on the graphics instead of absorbing the actual content of the presentation. Also, if visuals are too complex, viewers may not pay attention due to having trouble understanding or deciphering the data being presented. Visual aids play an important role in making a powerful impact during a presentation. It’s imperative that presenters use them effectively and strive for balance between words and visuals for a successful outcome. To learn more about how to use visual aids with professionalism, continue reading for further details in the next section.
How to Use Visual Aids With Professionalism
Visual aids can be an important component of any successful presentation; they make it easier to understand specialized topics, tell stories , and draw the audience in. When used correctly, visual aids can greatly amplify the impact of a message and help any speaker deliver a memorable lecture or speech . It is important to consider how using visual aids affects the professionalism of a presentation. Too many elements can detract from the focus or cause confusion among the audience, while too few can leave them lacking in interest or engagement. That said, some types of visuals may not be suitable for certain settings. Political cartoons, for example, could be deemed inappropriate in professional contexts. It is wise for speakers to exercise discretion when deciding what visuals are appropriate within their field. Good visual design is critical for effective presentations. Visuals should be chosen carefully based on their purpose and should follow a consistent color scheme, font size, and typographical conventions. Engaging visuals are easy to read and visually appealing, with limited use of text. Speakers should also ensure that any graphics are formatted properly so that elements do not get cut off or appear scrunched together during the presentation. When using multimedia technologies in live presentations such as slideshows or videos, it pays to plan ahead and practice using the technology beforehand. This will allow the speaker to be confident in handling technical issues should they arise during the event. Additionally, set-up steps and plugging in cables should be done before beginning a presentation as they can be disruptive if done mid-presentation. In conclusion, visual aids can go a long way toward making a powerful impact provided they are used wisely and professionally. To make sure everything looks good and works correctly before delivering a presentation with visuals, speakers should carefully plan their content and rehearse with any hardware and software prior to presenting. This will ensure that the visuals remain engaging throughout the presentation, adding to its impact instead of distracting from it. Moving on from this section about how to use visual aids with professionalism, let us now move to our conclusion which will cover key takeaways from this article:
In conclusion, visual aids are powerful tools in presentations, helping to make a lasting impression on both internal and external stakeholders. Visual aids present information effectively, allowing your audience to learn more efficiently and retain more information long-term. They can help to clarify complex concepts and bring life to otherwise mundane slides. Using visuals can also create a positive energy in the room that helps strengthen engagement among attendees. However, there are some downsides to using visuals that you should be aware of before deciding to use them in your presentation. Visual aids can take up more time during the presentation in terms of creation and incorporation into the deck, while they can also detract from the overall content if they are poorly designed or used excessively. It is important that you have a plan for incorporating visuals into your presentation and keeping it efficient instead of overwhelming the audience. Furthermore, depending on the context, you may need to consider the impact of accessibility for visual assets – for example, if you’re presenting remotely or on different devices. This is particularly important if you’re sharing sensitive or confidential information. Visual aids can be extremely beneficial when used correctly – as long as you plan ahead and manage expectations with your audience, there is no limit to how great of an impact visuals can have on your presentation and its results!
Answers to Common Questions with Detailed Explanations
What types of visual aids are most effective for a presentation.
The most effective visual aids for a presentation depend on the type of information you are presenting and your audience. For example, if you are presenting facts or data, graphs or charts are great ways to communicate that information quickly and efficiently. Animations (e.g. videos) can be used to break up monotony and add visuals that captivate the audience. Infographics can also be highly effective for summarizing complex ideas in a single image. If you have access to more sophisticated technology, 3D models and augmented reality may also be used as visual aids during presentations. Ultimately, it’s important to use visuals that will catch your audience’s attention and keep them engaged throughout the presentation.
How should visual aids be used to most effectively support the presenter’s message?
Visual aids should be used to enhance the presenter’s message, rather than overwhelm or overshadow it. Doing so effectively means including visuals that are easy to understand and relevant to the content of the presentation. This could come in the form of graphs, videos, tables, photographs, illustrations and more. The key is to ensure that the visual element is integral to the underlying message; it should complement and enhance messages as opposed to distract from them. Visuals should also be used to support key facts and figures that may be difficult for an audience to easily take on board, as well as providing an interesting talking point for further discussion with attendees during question time. In short, visuals should be used strategically to help make the presentation more memorable, engaging and informative.
What tips and tricks will help me create engaging visual aids for my presentation?
When creating visual aids for a presentation, it’s important to keep in mind how they will contribute to your overall goal. Here are some tips that can help you make engaging and effective visual aids: 1. Be aware of the environment. The size, brightness and color of the room, or even the lighting, can all affect how well your visuals pop. Take into account the physical setting when designing your visuals. 2. Keep it simple. Too much clutter on your slides can be distracting and impede understanding. Instead, keep visuals clean, with plenty of white space. Choose legible fonts and use colors sparingly—stick to 1-2 colors at most. 3. Focus on one idea per slide. Don’t try to cram too much information onto each slide; instead, break down complex topics into simple graphics or bullet points that focus on one concept at a time. That way, viewers will be more likely to comprehend what you’re presenting. 4. Get creative! Visuals don’t have to be limited to charts and graphs—think out of the box and consider incorporating multimedia elements such as videos or animations into your slides to make them more dynamic and engaging. 5. Test your visuals ahead of time. Make sure that any content you plan on displaying is optimized for the platform you’ll be using–whether it’s a laptop, projector, or something else–and test it out beforehand so you know what works best for the room setup and audience size.

Microsoft 365 Life Hacks > Presentations > 5 reasons to use visual aids for speeches and presentations
5 reasons to use visual aids for speeches and presentations
A whopping 65 percent of humans are visual learners . This makes sense, considering the brain processes visual information about 60,000 times faster than text.
It also explains why it’s so important for speakers to incorporate compelling visual aids into their presentations . Impactful visuals help us communicate our ideas and messaging more effectively—no matter what type of audience we are trying to reach.

Here are 5 facts that drill home the importance of visual aids when it comes to delivering a memorable presentation or speech.

Grow a business
Use free apps and tools from microsoft for your small business and side gig.
1. Presentation visuals grab an audience’s attention—and keep it
Human beings are naturally curious creatures but we have a short attention span—and it’s gotten worse in our current era of information overload and non-stop scrolling. When listening to a speech or presentation, audience interest peaks around the 10-minute mark and then drops precipitously depending on the content and communication style of the speaker. (A Ben Stein soundalike drolling on about duality quantum algorithms? Godspeed.) That’s why so many experts insist on capping lectures at 15 to 20 minutes or mixing up the format with 20-minute blocks. Interesting visual aids can help you do that.
They spark interest when the brain is feeling fatigued, making it easier to receive and process complex information. Think of each new visual or animation as little shots of adrenaline—capturing the waning attention of an audience and re-energizing the room. This can be especially effective when embedding picture polls, or visuals that require audience members to pull out their phones and interact with the content you’ve presented.
2. Presentation visuals make complex ideas easier to understand
Not everyone computes information at the same speed. Infographics make data-heavy presentations more digestible—breaking statistics and other figures or timelines into bite-sized chunks. They’re also more persuasive. According to a study conducted at the Wharton School of Business, 67 percent of audience members were more convinced by the content of a verbal presentation with accompanying visuals versus 50 percent with a verbal-only presentation.
3. Presentation visuals build emotional bridges with the audience
They say a picture is worth a thousand words—it’s cliché but true. Images make viewers feel things that words cannot and give presenters a way to connect with their audience on a more visceral level. (Yes, even if your audience is a bunch of humorless academics.) Instead of listing off dull facts about global warming, pop in a few slides depicting recent floods or forest fires to drive home your point. Powerful imagery, including 3D effects and visually appealing templates , resonate with audiences and makes them care more deeply about what you’re saying.
4. Presentation visuals help audiences retain information
Researchers have found that people who are asked to recall information after a three-day period retained just 10 percent of what they heard during an oral presentation, 35 percent from a visual presentation, and 65 percent from an oral presentation with visuals. You’ve worked too hard preparing your address to have the audience walk away remembering only a tiny fraction of what you said. Embracing visuals will improve the odds by six times.
5. Presentation visuals keep your speech on track
Peppering your presentation with visual aids will help you organize your talking points, avoid off-topic rambling, and even jog your memory if you get hit with a bout of stage fright.
But remember: While thoughtful visuals will make a speech or presentation much stronger, they won’t save you if you show up unprepared. The purpose of a visual aid is to engage the audience, boost their understanding of your content, ignite an emotional response, and help you convey important messaging—but it is never a substitute for preparation .

Get started with Microsoft 365
It’s the Office you know, plus the tools to help you work better together, so you can get more done—anytime, anywhere.
Topics in this article
More articles like this one.

How to introduce yourself in a presentation
Gain your audience’s attention at the onset of a presentation. Craft an impressionable introduction to establish tone, presentation topic, and more.

How to add citations to your presentation
Conduct research and appropriately credit work for your presentation. Understand the importance of citing sources and how to add them to your presentation.

How to work on a group presentation
Group presentations can go smoothly with these essential tips on how to deliver a compelling one.

How to create a sales presentation
Engage your audience and get them interested in your product with this guide to creating a sales presentation.
Everything you need to achieve more in less time
Get powerful productivity and security apps with Microsoft 365

Explore Other Categories
- Forgot your Password?
First, please create an account
Using visual aids.
1. Visual Aids
Visual communication relies on vision and is primarily presented or expressed with two-dimensional images.
Visuals with accompanying text have a greater power to inform, educate, or persuade a person or audience than text alone. One way to make your presentation vivid and memorable is through visual aids. Although computer-generated and projected visual—and presentation—aids are commonly used, it is still important to understand how to use them or any other type of visual aids in your presentation.
There are many different types of visual aids. The type of visual aid a speaker uses depends on his preference and the information he is trying to present. To determine the type of visual aid to use, begin by writing your outline first, focusing on the main points of your presentation, and considering your audience and any cultural contexts.
- Graphic design
- Illustration
- Electronic resources
- Photographs
- Drawings or diagrams
- Display charts
- Video excerpts
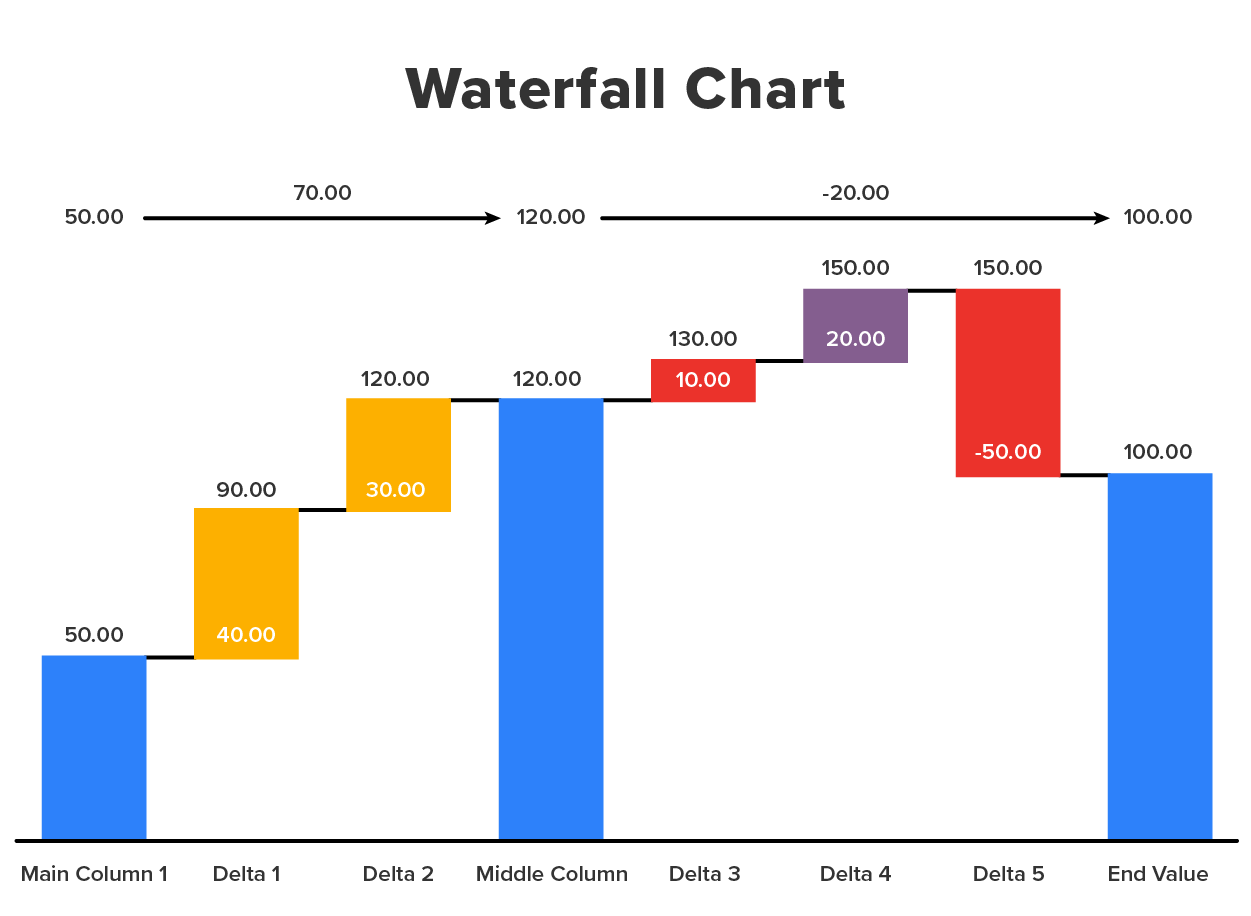
term to know Visual Communication The communication through visual aid and the conveyance of ideas and information in forms that can be read or looked upon.
1a. Selecting the Right Visual Aid
Select visual aids that are appropriate to the point that you wish to illustrate or clarify. Visual aids should support, clarify, and amplify, not repeat what you are saying. In order to make sure that the intent of your visual aid is clear, try to use only important or memorable words or phrases. For example, eliminate any unnecessary word slides or overcrowding of visual aids. Pictorial slides and appropriate color usage have the biggest impact.
1b. Testing Your Visual Aid
It is important to consider if your visual aid can be seen and understood by the member of your audience who is farthest from the screen when choosing to use it. To do this, test your visual aids in different environments. Practice with your visual aid when going through your presentation for timing and familiarity.
Introduce visual aids so that they blend smoothly with your speech and highlight your main points or provide clarity to examples. It is important to maintain eye contact; talk to your audience, not the visual aid, throughout your presentation.
Practice going through your presentation and coordinating your points with your visual aids when discussing them. Avoid passing hard copies of your visual aids around to the audience, as it is often a distraction. Try to provide interactive aspects in your visual aids that involve the audience, such as polls, feedback requests, and interactive activities.
2. The Importance of Preparation
Appropriate preparation of your visual aids is essential in making sure that they are effective in helping to improve your audience’s engagement, memory, and comprehension.
- Are your visual aids appropriate for your audience?
- Are your visual aids easy to understand and easy to read or view?
- Do you know what is on your visual aids, and can you present them effectively?
2a. Are Your Visual Aids Appropriate for Your Audience?
Once your topic has been decided upon, and your research is underway, it's time to think about how you plan to present your information in visual aids.
Of the several angles that need to be addressed in regard to delivering a speech, the most important thing to keep in mind is, "Who is my audience?" Never underestimate the importance of knowing your audience. If your audience can't understand your visuals, you'll find it much harder to accomplish your objective.
Make sure to consider the knowledge base, demographic background, occupation, and values of your audience when creating a visual aid.
Your decision to use visual aids such as PowerPoint, charts, or any kind of demonstrative props will have a sizable impact on your audience, so they should be given careful thought.
term to know Demographic A characteristic used to classify people for statistical purposes, such as age, race, or gender.
2b. Are Your Visual Aids Easy to Understand and Easy to Read or View?
When you are preparing your visual aids, you should make sure that your audience will be able to read and understand what they are saying.
Be sure to use text that is large enough and colors that do not conflict with one another. This ensures that words are legible. Make sure that any photos, charts, and diagrams are easily understood within the first few seconds of looking at them. If they are not easily understood, be sure to spend time during your presentation explaining what the photos or charts mean.
Additionally, one way to make sure that people in the back of the presentation can read your visual aids is to print off a full-page slide of your presentation, place it on the floor, and stand up and see if you can read the entire slide. If you cannot read it, people in the back of the room during your presentation will also likely not be able to read your slide.
One other consideration is to be sure that you are comfortable using any technology that you will use to assist in the presentation of your visual aids. You must also make sure that the location of your presentation has this working technology available to you.
2c. Do You Know What Is on Your Visual Aids and Can You Present Them Effectively?
An essential component of using visual aids effectively is to prepare yourself to understand what is on them and determine how you want to explain them. If you are using pictures, graphs, or charts to help you explain a point, be sure that you understand the graph or picture and that you are comfortable explaining this to an audience.
If you are confused about a graph during your presentation or do not do an adequate job of explaining a graph, your audience will likely be confused about the graph as well. Such confusion will detract from audience engagement and comprehension.
Before you present, go through your graph, charts, and pictures. In your notes, write where each visual aid is presented in your presentation, what they mean, and how you plan to present them. Be sure to rehearse this before your presentation so your visual aids can be as effective in helping your audience be engaged, understand your presentation, and remember your key points.
3. Physical and Animate Objects
In today's media-driven world, public speakers have a plethora of visual aids to choose from when augmenting their presentations.
From LCD projections to flip charts, visual aids help presenters inform and persuade audiences, as well as help them understand the presentation topic.
Physical and animate objects can also help integrate the verbal and visual elements of the speaker's presentation into one unified and memorable message.
Ultimately, objects should enhance rather than detract from a presentation. The use of objects as visual aids involves using actual objects as live demonstrations or props for the audience.
terms to know LCD A flat-panel display, electronic visual display, or video display that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly. Prop An item placed on a stage or set to create a scene or scenario in which actors perform. Contraction of "property."
3a. Choosing Objects for Presentations
Using physical objects is often necessary when demonstrating how to do something so that the audience can fully understand the procedure or process.
The use of physical and animate objects in formal presentations is the same as in stage acting, where actors use still and animated props. For the objects to be as effective as possible, they must be positioned in a way where they are quickly detected and easily understood by the audience.
A common mistake involves placing an object where it is obstructed or hidden from view or in front of a more interesting object that divides the audience's attention. Speakers must also be cognizant of objects that are too large or inconvenient for stage use.
There are many physical and animate objects available for presentations. Choosing the appropriate visual aids depends on the speaker's preference, as well as the content and setting of the presentation.
Objects can be both beneficial or distracting during speeches. Therefore, presenters should prepare and plan ahead accordingly to ensure that objects are appropriate for the audience and the material being presented.
3b. Chalkboards, Whiteboards, and Flip Charts
Visual aids such as chalkboards, whiteboards, and flip charts are used by presenters to help weave their words and images together into a cohesive message.
Using visual tools effectively during a presentation helps speakers appear prepared, professional, interesting, and credible. Writing tools and imagery also help audience members focus on and remember the presenter's major points, as well as better understand the presenter's argument.

Although we often think of chalkboards in academic or teaching settings, chalkboards are also used in business environments. However, dry-erase boards, also known as whiteboards, are becoming more common.
Chalkboards are reusable writing surfaces where text and drawings are made using chalk. Organizations typically use dry-erase whiteboards, which use dry-erase markers for easy application and removal. These boards can be used for presentations, as well as advertisements or recordkeeping.
In presentations, chalkboards and whiteboards provide significant flexibility for recording audience responses and jumpstarting discussions. This spontaneity allows for fast, simple, and easy use by presenters who may not be familiar or comfortable with presentation software tools.

Like chalkboards and whiteboards, flip charts have a low learning curve, allowing anyone with the ability to write to quickly convey information to audience members.
Flip charts are typically stationary items consisting of pads of large paper sheets fixed to the upper edge of a whiteboard. These are typically supported on a tripod or four-legged easel. Invented by Peter Kent, who built one to help him in a presentation, flip charts are commonly used for presentations.
- Stand-alone flip charts
- Metallic tripod (or easel) stands
- Metallic mounts on wheels
4. Static Presentations: Images, Drawings, and Graphs
As we’ve discussed earlier, public speakers often employ a variety of presentation tools—including drawings, paintings, and graphs—to inform, educate, or persuade a person or audience. Here is a quick review of the many ways you can use visuals to enhance your presentation.
4a. The Many Uses of Images in Presentations
Although static in nature, nonelectronic imagery has both advantages and disadvantages when used as visual aids in presentations.
- Photographs : Photographs are helpful tools to make or emphasize a point or to explain a topic when the actual object cannot be viewed. For example, photographs are particularly useful for displaying historical places and sites that no longer exist.
- Maps : Maps show geographical areas of interest. They are often used as aids when speaking of differences between geographical areas or showing the location of something.
- Handouts : Charts, graphs, pictures, illustrations, and other images can be printed on handouts for distribution before, during, or after a presentation. An important aspect of the use of a handout is that a person can keep the handout long after the presentation is over. This helps the person better remember what was discussed.
4b. Graphs and Data
Graphs are used in both static and electronic presentations to visualize relationships between different quantities.
- Line graphs
- Scatter plots
However, it is the complexity of graphs—their detailed calculations, complex data, and large figures—that causes them to become cluttered during use in a speech. Graphs often include too much detail, overwhelming the audience and making the graph ineffective.
4c. Drawings in Presentations
Drawings or diagrams can be used when photographs do not show exactly what the speaker wants to show or explain. They could also be used when a photograph is too detailed.
Nevertheless, talent and skills are usually needed for professional drawings that require significant detail or realism. If not done correctly, drawings can look sloppy, ineffective, and unprofessional.
5. Dynamic Representations: Video and Multimedia
Presenters may use navigation devices such as text links, picture thumbnails, or small screenshots to move around spontaneously within and between extensive collections of related content.
Using these relational presentation techniques allows presenters to interact with rather than "talk at" audiences.

5a. Audience Reception of Dynamic Content
Studies have revealed that audiences are more engaged during presentations that employ dynamic elements. There are also ongoing assessments as to how much using multimedia improves learning and retention of presentation material.
Regardless of whether speakers use static or dynamic content, all presentations must present consistent and compelling information within a limited time frame.
The various formats of technological or digital multimedia available to presenters may be intended to enhance the users' experience, quickly and easily convey information, or transcend everyday experiences.
term to know Multimedia The use of different media to convey information; text together with audio, graphics, and animation, often packaged on CD-ROM with links to the internet.
5b. Software Presentation Programs
Presentation software programs provide public speakers with the ability to display video, photography, and other dynamic content in slideshow formats suitable for small and large audiences.
IN CONTEXT Apple's iPhoto and Google photos are two examples of software that allow groups of digital photos to be displayed in a slideshow with options including transitions, looping functions, and the integration of music and digital images. Zooming presentation programs such as Prezi present content on one infinite canvas. This allows for nonlinear presentations where presenters can present richer detail of content, as well as provide a better overview and understanding of complex visual messages and relations. Technology keeps evolving, so we can expect new software programs to become options in the future.
5c. Multimedia Tools in Presentation Software
Many presentation programs come with predesigned images (clip art) or have the ability to import graphic images. Some tools also have the ability to search and import images from Google directly from the tool. Custom graphics can also be created in other programs, such as Adobe Photoshop or Adobe Illustrator, and then exported.
Similar to programming extensions for an operating system or web browser, plug-ins for presentation programs can be used to enhance their capabilities.
Certain presentation programs also offer an interactive, integrated hardware element designed to engage an audience (e.g., audience response systems) or facilitate presentations across different geographical locations (e.g., web conferencing).
Integrated hardware devices such as laser pointers and interactive whiteboards can ease the job of the presenter by adding emphasis and bringing attention to specific points in the presentation.
5d. Slideshows
A slideshow is an on-screen presentation of information or ideas presented on slides. Since the late 1960s, visual artists in museums and galleries have used slideshows as a device for presenting specific information about an action or research or as a phenomenological form in itself.
Before the advent of motion pictures, slides were originally projected onto a theater screen by a type of projector called a magic lantern . This practice later evolved into moving picture shows.

Even after the introduction of motion pictures, slides continued to be used between film showings to advertise for local businesses or advise on theater decorum—for example, by requesting that gentlemen remove their hats and refrain from smoking and urging mothers to remove crying infants from the auditorium.
Slideshows were later conducted using apparatuses such as a carousel slide or overhead projector. Most recently, modern slideshows are commonly assembled using presentation software such as Microsoft PowerPoint or Prezi.
Presentation software is most commonly used for instructional purposes, usually with the intention of creating a dynamic, audiovisual presentation. The relevant points and imagery of the entire presentation are placed on slides and accompanied by a spoken monologue.
The old adage "a picture is worth a thousand words" holds true, in that a single image can save a presenter from speaking a paragraph of descriptive details. As with any public speaking or lecturing, a certain amount of talent, experience, and rehearsal is required to make a successful slideshow presentation.
Slideshows have artistic uses as well. They are often used to provide dynamic imagery for museum presentations and installation art. Consumer uses of slideshows include personal screen savers and digital photo slides for display. Vendors or consumers can custom-make slideshows using their photos, music, wedding invitations, birth announcements, or other digital files. The slideshows are typically placed onto DVDs, converted into HD video format, or saved in an executable file for computer use.
Ultimately, photo slideshow software—coupled with digital cameras and computer technology—has made it easier to create photo slideshows, eliminating the need for expensive color reversal film.
terms to know Phenomenological Using the method of phenomenology, by which the observer examines the data without trying to provide an explanation of them. Magic Lantern An early form of slide projector that could achieve simple animation by moving and merging images.
summary In this lesson, you learned how to choose the right visual aid for your presentation. Visual aids should support, clarify, and amplify, not repeat what you are saying. Selecting the right visual aid requires you to understand your audience’s needs. When preparing and testing your visual aids , you should consider three important components: whether your visual aids are appropriate for your audience, whether your visual aids are easy to understand and easy to read or view , and whether you know what is on your visual aids and can present them effectively . Using physical and animate objects in a presentation requires the speaker to analyze the content and setting of the presentation first. You should choose objects used as visual aids that enhance rather than detract from a presentation. Chalkboards, whiteboards, and flip charts are examples of objects that can support your presentation. Static imagery can either serve as a useful visual tool to emphasize further or support a speaker's point or confuse audiences and detract from the speaker's message. There are many ways to use static images in presentations . Graphs, data, and drawings are all examples of visual aids that employ static imagery. For example, graphs and data can support a presentation of research, while drawings help to visualize concepts for your audience. Dynamic representations such as video and multimedia are also commonly used in public speaking. Studies have revealed that audiences are more engaged during presentations that employ dynamic elements. Integrating multimedia with presentation software can ease the job of presenters by adding emphasis and bringing attention to specific points in the presentation. Slideshows are used to provide dynamic imagery for museum presentations and installation art and for saving personal memories as digital photo albums.
Source: THIS TUTORIAL HAS BEEN ADAPTED FROM "BOUNDLESS COMMUNICATIONS" PROVIDED BY BOUNDLESS.COM. ACCESS FOR FREE AT oer commons. LICENSED UNDER CREATIVE COMMONS ATTRIBUTION-SHAREALIKE 4.0 INTERNATIONAL.
A characteristic used to classify people for statistical purposes, such as age, race, or gender.
A flat-panel display, electronic visual display, or video display that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly.
An early form of slide projector that could achieve simple animation by moving and merging images.
The use of different media to convey information; text together with audio, graphics, and animation, often packaged on CD-ROM with links to the internet.
Using the method of phenomenology, by which the observer examines the data without trying to provide an explanation of them.
An item placed on a stage or set to create a scene or scenario in which actors perform. Contraction of "property."
The communication through visual aid and the conveyance of ideas and information in forms that can be read or looked upon.
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
© 2024 SOPHIA Learning, LLC. SOPHIA is a registered trademark of SOPHIA Learning, LLC.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
15.1 Functions of Presentation Aids
Learning objectives.
- List four reasons why presentation aids are important in public speaking.
- Explain two ways in which presentation aids can increase audience understanding of a message.
Why should you use presentation aids? If you have prepared and rehearsed your speech adequately, shouldn’t a good speech with a good delivery be enough to stand on its own? While it is true that impressive presentation aids will not rescue a poor speech, it is also important to recognize that a good speech can often be made even better by the strategic use of presentation aids.
Presentation aids can fulfill several functions: they can serve to improve your audience’s understanding of the information you are conveying, enhance audience memory and retention of the message, add variety and interest to your speech, and enhance your credibility as a speaker. Let’s examine each of these functions.
Improving Audience Understanding
Human communication is a complex process that often leads to misunderstandings. If you are like most people, you can easily remember incidents when you misunderstood a message or when someone else misunderstood what you said to them. Misunderstandings happen in public speaking just as they do in everyday conversations.
One reason for misunderstandings is the fact that perception and interpretation are highly complex individual processes. Most of us have seen the image in which, depending on your perception, you see either the outline of a vase or the facial profiles of two people facing each other. This shows how interpretations can differ, and it means that your presentations must be based on careful thought and preparation to maximize the likelihood that your listeners will understand your presentations as you intend them to.
As a speaker, one of your basic goals is to help your audience understand your message. To reduce misunderstanding, presentation aids can be used to clarify or to emphasize.
Clarification is important in a speech because if some of the information you convey is unclear, your listeners will come away puzzled or possibly even misled. Presentation aids can help clarify a message if the information is complex or if the point being made is a visual one.
If your speech is about the impact of the Coriolis effect on tropical storms, for instance, you will have great difficulty clarifying it without a diagram because the process is a complex one. The diagram in Figure 15.1 “Coriolis Effect” would be effective because it shows the audience the interaction between equatorial wind patterns and wind patterns moving in other directions. The diagram allows the audience to process the information in two ways: through your verbal explanation and through the visual elements of the diagram.
Figure 15.2 “Model of Communication” is another example of a diagram that maps out the process of human communication. In this image you clearly have a speaker and an audience (albeit slightly abstract), with the labels of source, channel, message, receivers, and feedback to illustrate the basic linear model of human communication.
Figure 15.1 Coriolis Effect
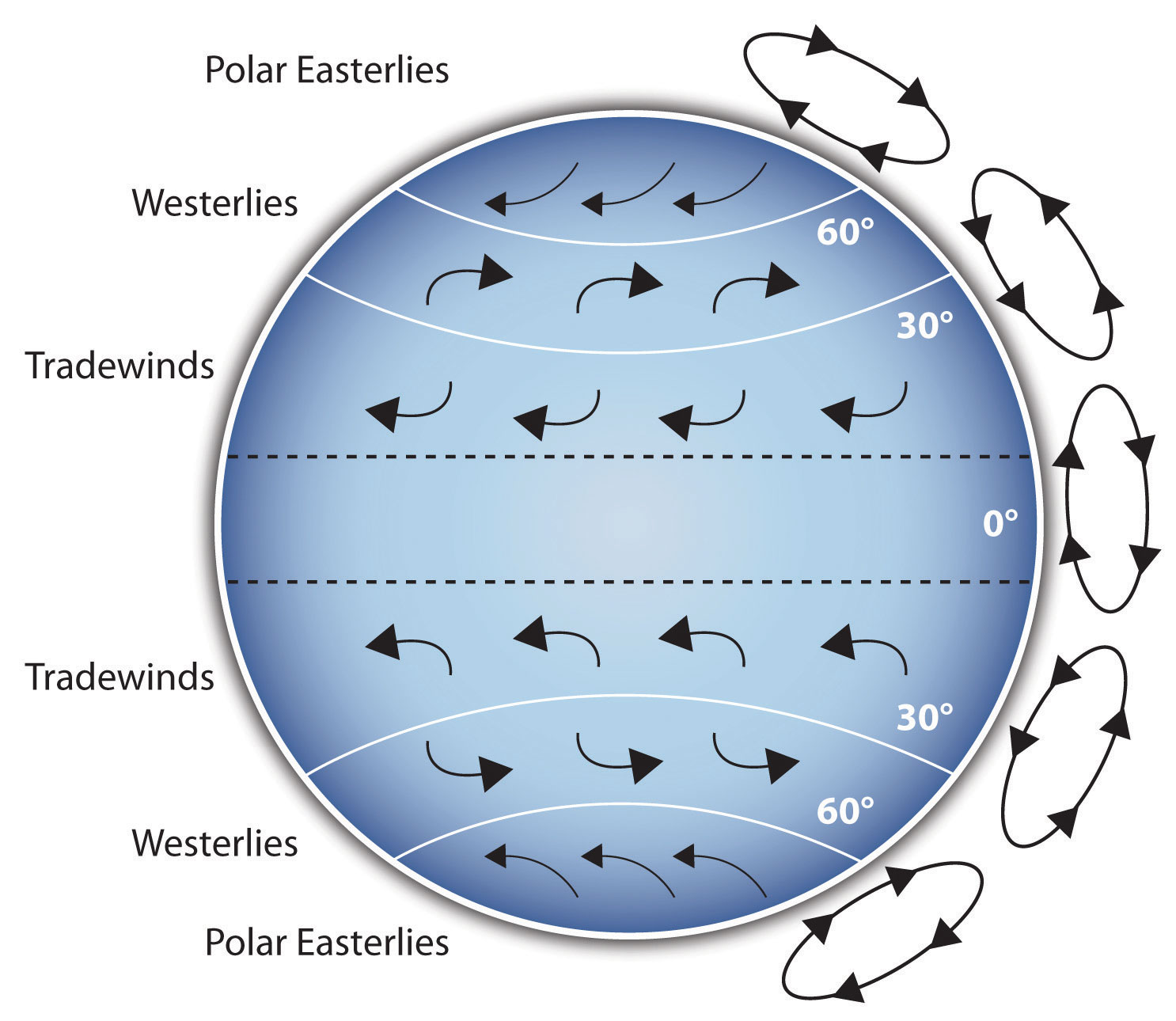
Figure 15.2 Model of Communication
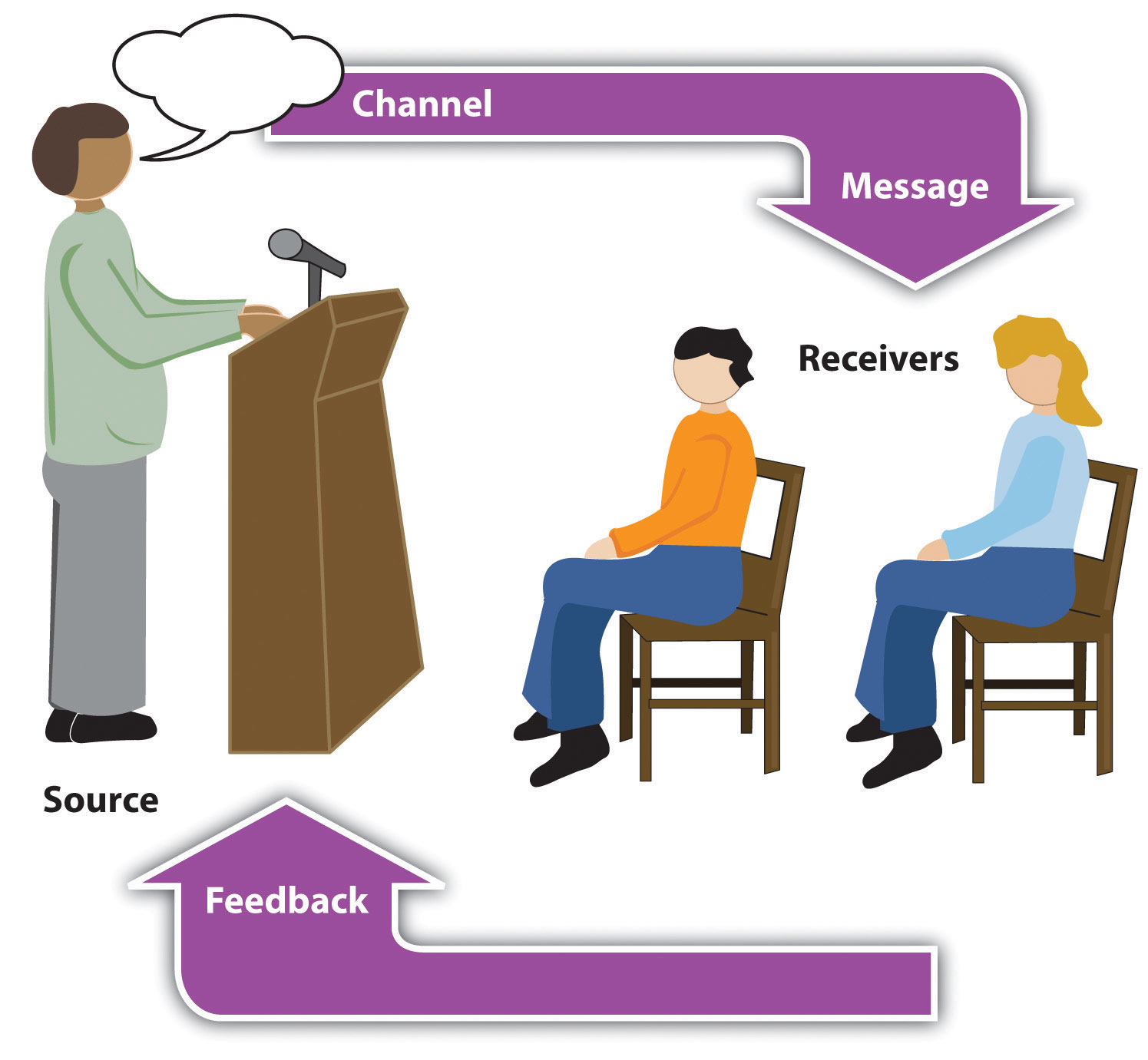
Figure 15.3 Petroglyph

Another aspect of clarifying occurs when a speaker wants to visually help audience members understand a visual concept. For example, if a speaker is talking about the importance of petroglyphs in Native American culture, just describing the petroglyphs won’t completely help your audience to visualize what they look like. Instead, showing an example of a petroglyph, as in Figure 15.3 “Petroglyph” , can more easily help your audience form a clear mental image of your intended meaning.
Emphasizing
When you use a presentational aid for emphasis , you impress your listeners with the importance of an idea. In a speech on water conservation, you might try to show the environmental proportions of the resource. When you use a conceptual drawing like the one in Figure 15.4 “Planetary Water Supply” , you show that if the world water supply were equal to ten gallons, only ten drops would be available and potable for human or household consumption. This drawing is effective because it emphasizes the scarcity of useful water and thus draws attention to this important information in your speech.
Figure 15.4 Planetary Water Supply
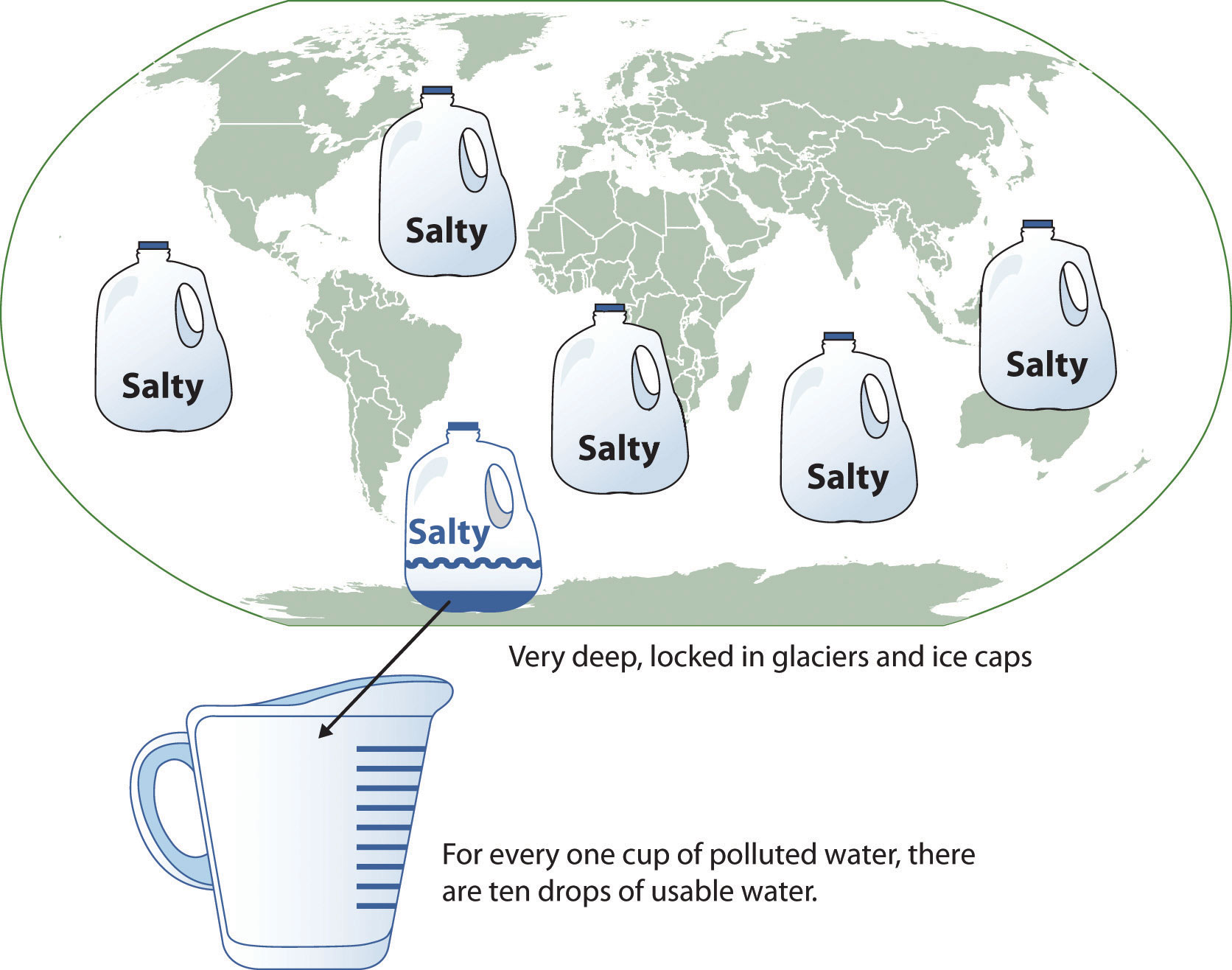
Figure 15.5 Chinese Lettering Amplified

Wikimedia Commons – public domain.
Another way of emphasizing that can be done visually is to zoom in on a specific aspect of interest within your speech. In Figure 15.5 “Chinese Lettering Amplified” , we see a visual aid used in a speech on the importance of various parts of Chinese characters. On the left side of the visual aid, we see how the characters all fit together, with an emphasized version of a single character on the right.
Aiding Retention and Recall
The second function that presentation aids can serve is to increase the audience’s chances of remembering your speech. A 1996 article by the US Department of Labor summarized research on how people learn and remember. The authors found that “83% of human learning occurs visually, and the remaining 17% through the other senses—11% through hearing, 3.5% through smell, 1% through taste, and 1.5% through touch” (United States Department of Labor, 1996). Most of how people learn is through seeing things, so the visual component of learning is very important. The article goes on to note that information stored in long-term memory is also affected by how we originally learn the material. In a study of memory, learners were asked to recall information after a three day period. The researchers found that they retained 10 percent of what they heard from an oral presentation, 35 percent from a visual presentation, and 65 percent from a visual and oral presentation (Lockard & Sidowski, 1961). It’s amazing to see how the combined effect of both the visual and oral components can contribute to long-term memory.
For this reason, exposure to a visual image can serve as a memory aid to your listeners. When your graphic images deliver information effectively and when your listeners understand them clearly, audience members are likely to remember your message long after your speech is over.
Moreover, people often are able to remember information that is presented in sequential steps more easily than if that information is presented in an unorganized pattern. When you use a presentation aid to display the organization of your speech, you will help your listeners to observe, follow, and remember the sequence of information you conveyed to them. This is why some instructors display a lecture outline for their students to follow during class.
An added plus of using presentation aids is that they can boost your memory while you are speaking. Using your presentation aids while you rehearse your speech will familiarize you with the association between a given place in your speech and the presentation aid that accompanies that material. For example, if you are giving an informative speech about diamonds, you might plan to display a sequence of slides illustrating the most popular diamond shapes: brilliant, marquise, emerald, and so on. As you finish describing one shape and advance to the next slide, seeing the next diamond shape will help you remember the information about it that you are going to deliver.
Adding Variety and Interest
A third function of presentation aids is simply to make your speech more interesting. While it is true that a good speech and a well-rehearsed delivery will already include variety in several aspects of the presentation, in many cases, a speech can be made even more interesting by the use of well-chosen presentation aids.
For example, you may have prepared a very good speech to inform a group of gardeners about several new varieties of roses suitable for growing in your local area. Although your listeners will undoubtedly understand and remember your message very well without any presentation aids, wouldn’t your speech have greater impact if you accompanied your remarks with a picture of each rose? You can imagine that your audience would be even more enthralled if you had the ability to display an actual flower of each variety in a bud vase.
Similarly, if you were speaking to a group of gourmet cooks about Indian spices, you might want to provide tiny samples of spices that they could smell and taste during your speech. Taste researcher Linda Bartoshuk has given presentations in which audience members receive small pieces of fruit and are asked to taste them at certain points during the speech (Association for Psychological Science, 2011).
Enhancing a Speaker’s Credibility
Presentation aids alone will not be enough to create a professional image. As we mentioned earlier, impressive presentation aids will not rescue a poor speech. However, even if you give a good speech, you run the risk of appearing unprofessional if your presentation aids are poorly executed. This means that in addition to containing important information, your presentation aids must be clear, clean, uncluttered, organized, and large enough for the audience to see and interpret correctly. Misspellings and poorly designed presentation aids can damage your credibility as a speaker. Conversely, a high quality presentation will contribute to your professional image. In addition, make sure that you give proper credit to the source of any presentation aids that you take from other sources. Using a statistical chart or a map without proper credit will detract from your credibility, just as using a quotation in your speech without credit would.
If you focus your efforts on producing presentation aids that contribute effectively to your meaning, that look professional, and that are handled well, your audience will most likely appreciate your efforts and pay close attention to your message. That attention will help them learn or understand your topic in a new way and will thus help the audience see you as a knowledgeable, competent, credible speaker.
Key Takeaways
- Presentation aids should help audiences more thoroughly understand a speaker’s basic message.
- There are four basic reasons to use presentation aids. First, they increase audience understanding of a speaker’s message. Second, they help audiences retain and recall a speaker’s message after the fact. Third, they make a speech more interesting by adding variety. Lastly, by making a speaker’s overall speech more polished, presentation aids can increase an audience’s perception of the speaker’s credibility.
- Presentation aids help an audience more clearly understand a speaker’s message in two ways: they help clarify and they help emphasize. Presentation aids can help the audience to understand complex ideas or processes and can also show which ideas are most important in the speech.
- Look at the outline you have prepared for a classroom speech. Where in the speech would it be appropriate to use presentation aids? Why would presentation aids help at the points you identify?
- Presentational slides from speeches are sometimes available online. Search for and evaluate three sets of presentation slides you find online. Identify three ways that the slides could be improved to be more effective presentation aids.
Association for Psychological Science. (2011, May 28). Miracle fruit and flavor: An experiment performed at APS 2010 [Video file]. Retrieved from http://www.psychologicalscience.org/index.php/publications/observer/obsonline/miracle-fruit-and-flavor-an-experiment-performed-at-aps-2010.html
Lockard, J., & Sidowski, J. R. (1961). Learning in fourth and sixth graders as a function of sensory mode of stimulus presentation and overt or covert practice. Journal of Educational Psychology, 52 (5), 262–265. doi: 10.1037/h0043483
United States Department of Labor. (1996). Presenting effective presentations with visual aids . Retrieved from http://www.osha.gov
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Presentation Training Institute
A division of bold new directions training, the role of visual aids in presentations.
Did you know that 65% of people are visual learners? This makes sense, considering the fact that the brain processes visual information nearly 60,000 times faster than text. It also explains why it is so important for presenters to incorporate visual aids into their presentations. Visual aids are powerful tools that enhance your message and clarify your key points. Good visual aids help you communicate more effectively and make your presentation more engaging. Here are a few reasons why visual aids are so important in presentations.
They Capture Attention
One of the most important tasks for a presenter is to capture and maintain the attention of the audience. Visual aids are a great way to attract attention and peak interest. They also break up the monotony of spoken word and text and add a little variety to your presentation. Visual aids help to make your presentation a multi-sensory experience and keeps the audience engaged in your topic.Â
They Clarify Your Message
Not everyone understands information the same way and at the same speed. Visual aids make it easier for the audience to understand complex or abstract concepts or data in a clear and concise way. They are especially useful for explaining statistics, timelines, or other figures.Â
They Build an Emotional Connection with the Audience
As the saying goes, “A picture is worth a thousand words.†It may be cliche but it’s true. Images make people feel things that words cannot and it allows presenters to connect with their audience on a deeper level. Instead of listing dull facts, photographs and powerful imagery will resonate with the audience and get them to care more deeply about your message.
They Help Audiences Retain Information
Research has shown that after three days people can only recall about 10% of what they heard during an oral presentation but 65% from a presentation that included both oral and visual content. You’ve worked too hard creating a presentation just to have your audience forget the majority of what you said.
They Reinforce and Emphasize Key Points
Visual aids are useful for reinforcing your key points and making them more memorable. They help you to highlight important information and increase audience engagement and retention.Â
.css-1qrtm5m{display:block;margin-bottom:8px;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:14px;line-height:1.5714285714285714;-webkit-letter-spacing:-0.35px;-moz-letter-spacing:-0.35px;-ms-letter-spacing:-0.35px;letter-spacing:-0.35px;font-weight:300;color:#606F7B;}@media (min-width:600px){.css-1qrtm5m{font-size:16px;line-height:1.625;-webkit-letter-spacing:-0.5px;-moz-letter-spacing:-0.5px;-ms-letter-spacing:-0.5px;letter-spacing:-0.5px;}} Best Practices The #1 rule for improving your presentation slides
by Tom Rielly • May 12, 2020

When giving presentations, either on a video conference call or in person, your slides, videos and graphics (or lack of them) can be an important element in helping you tell your story or express your idea. This is the first of a series of blog posts that will give you tips and tricks on how to perfect your visual presentations.
Your job as a presenter is to build your idea -- step-by-step -- in the minds of your audience members. One tool to do that is presentation graphics, such as slides and videos.
Why graphics for your presentation?
A common mistake is using slides or videos as a crutch, even if they don’t actually add anything to your presentation. Not all presentations need graphics. Lots of presentations work wonderfully with just one person standing on a stage telling a story, as demonstrated by many TED Talks.
You should only use slides if they serve a purpose: conveying scientific information, art, and things that are hard to explain without pictures. Once you have decided on using slides, you will have a number of decisions to make. We’ll help you with the basics of making a presentation that is, above all, clear and easy to understand. The most important thing to remember here is: less is more.
Less is so much more
You want to aim for the fewest number of slides, the fewest number of photos, the fewest words per slide, the least cluttered slides and the most white space on your slides. This is the most violated slide rule, but it is the secret to success. Take a look at these examples.

As you can see in the above example, you don’t need fancy backgrounds or extra words to convey a simple concept. If you take “Everything you need to know about Turtles”, and delete “everything you need to know about” leaving just “turtles”, the slide has become much easier for your audience to read, and tells the story with economy.

The above example demonstrates that a single image that fills the entire screen is far more powerful than a slide cluttered with images. A slide with too many images may be detrimental to your presentation. The audience will spend more mental energy trying to sort through the clutter than listening to your presentation. If you need multiple images, then put each one on its own slide. Make each image high-resolution and have it fill the entire screen. If the photos are not the same dimensions as the screen, put them on a black background. Don’t use other colors, especially white.
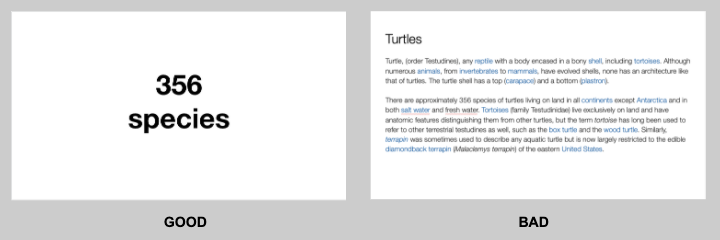
Your slides will be much more effective if you use the fewest words, characters, and pictures needed to tell your story. Long paragraphs make the audience strain to read them, which means they are not paying attention to you. Your audience may even get stressed if you move on to your next slide before they’ve finished reading your paragraph. The best way to make sure the attention stays on you is to limit word count to no more than 10 words per slide. As presentation expert Nancy Duarte says “any slide with more than 10 words is a document.” If you really do need a longer explanation of something, handouts or follow-up emails are the way to go.
Following a “less is more” approach is one of the simplest things you can do to improve your presentation visuals and the impact of your presentation overall. Make sure your visuals add to your presentation rather than distract from it and get your message across.
Ready to learn more about how to make your presentation even better? Get TED Masterclass and develop your ideas into TED-style talks.
© 2024 TED Conferences, LLC. All rights reserved. Please note that the TED Talks Usage policy does not apply to this content and is not subject to our creative commons license.
Ace your presentation with these 6 different presentation aids

You’re preparing for a presentation, and you know you need to do more than stand in front of your audience and talk — you need something for them to look at.
Visual aids not only make your presentation more engaging, but they also make the information more memorable.
One study found that a mere three hours after your presentation, only 70% of people are able to recall the information that was presented verbally. However, that number gets a boost when you incorporate visual aids. 85% of people are able to recall information that was presented visually.
But, here’s the thing: You don’t want to paste a few stock images onto some PowerPoint slides just for the sake of having visual aids. You want them to serve a purpose, to educate your audience and complement your content.
Stumped for ideas? We’ve pulled together some clever suggestions for presentation aids below.

1. Perform a demonstration
When thinking of presentation aids, slides are often the first thing to jump into people’s minds. And, without a doubt, they definitely have their time and place. However, don’t hesitate to think outside the box (or, in this case, the slide) and use real objects or even people to get a point across.
For example, maybe rather than talking about how your product works, you can do a simple demonstration. Or, perhaps you can ask for some volunteers from the audience to help you teach a lesson about how to make proper business introductions.
There are plenty of options, so get creative and remember that your visual aids don’t need to only live on slides — you can create some real action too.
2. Use charts and graphs
Imagine that I were standing in front of you, rattling off a bunch of statistics right in a row. How likely are you to remember those digits one minute later? Not very likely.
This is why charts and graphs can be such a helpful addition to your presentation. They allow you to display a lot of information in a far more comprehensible (not to mention memorable) way. Using Poll Everywhere , you can even create these types of visual aids right on the spot by polling your audience and then immediately pulling those results into an animated graph or chart. That not only simplifies your information, but actually involves your audience in the process as well.

Read more: How to choose the best format for your presentation
3. Share a handout
Your presentation shares tons of valuable information that you know could be a huge help to your attendees, yet you’re frustrated to see that none of them are writing anything down.
This is where sharing a handout can be helpful. You can create something that has all of those important nuggets of information in one place so that they can take it with them and refer back to it.
Or, you can take things a step further and encourage more diligent note-taking by creating some sort of worksheet or template that they can fill in as you move through your presentation.
4. Create a diagram
Let’s say that your presentation needs to thoroughly explain a somewhat-complex process , such as the details and different steps of your recruitment and hiring process. That can be a lot for your audience to take in and attempt to visualize on their own.
Fortunately, you can make it far more digestible by distilling the process down into a simple diagram that they can reference — something straightforward with bubbles and arrows. Processes are sequential, so they lend themselves well to a visual representation that quite literally maps out the flow of things. And, having that to display not only makes the process easier to understand, but also far easier for you to explain.

Read more: Make your own quiz in minutes with Poll Everywhere Competitions
5. Highlight an interesting quote, statistic, or point
Naturally, there are certain things that you want to emphasize throughout your presentation — whether it’s an impactful statistic or a pull quote.
Don’t back yourself into a corner by becoming convinced that your presentation aids need to be completely visual. Rest assured, some text is allowed.
Call attention to that shocking statistic by putting it on its own slide in large font. Or, if there’s a certain quote, word, or theme you want your attendees to keep in mind as you move through your presentation, write it on the whiteboard up front.
Tactics like these do exactly what your visual aids are supposed to do: Highlight the most important pieces of your presentation.
6. Show a brief video
Remember those school days when the teacher would announce that you were going to watch a movie and everyone was suddenly overcome with excitement?
Chances are, your presentation attendees feel some of that same giddiness when you show them a video as part of your presentation.
Doing so changes up the flow of your presentation, and helps recapture audience attention. Plus, a video gives you the flexibility to be more creative with how you present information — since you aren’t only limited to what you can use and do directly in the front of that conference room.
Presentation aids like the ones above can help make your information that much more memorable and your presentation far more engaging.
But, while these visuals are important, always remember that eye contact still matters. These aids aren’t for you to stare at — they’re for your audience. So, despite what visuals you implement in your presentation, always remember to make eye contact and interact with your attendees. Trust me, that will be the most helpful tactic of all.
Related articles

Effective presentations: How visual aids reinforce your message

1. Instantly turn complexity into simplicity
- show change processes
- point out a problem
- explain the processes used in the presentation
- create enthusiasm for a product launch
- introduce people
- communicate corporate values
- present experience reports

2. Diagrams to support facts
- Building up the diagrams piece by piece adds to the suspense and gets you thinking along with it.
- Diagrams over time help us put the facts in a chronological context.
- Contrasting diagrams adds context by focusing on the impact of the information.

3. Using memes as a way to lighten the mood
- They make the audience feel close to them.
- They produce the same reaction in everyone
- They lighten the mood
- They bring the lecture back into focus.
- They set the stage for the next few points.
- They show us a common issue that we all face.

4. Before and after pictures for direct reactions
- what the company logo looked like before and now,
- how website views have changed since change X,
- how much better the sales figures are since point Y was changed in the ad,
- how bureaucratic a process was yesterday and how digital and automated it is today.
5. Let the text speak for itself
Conclusion: visual aids deepen the message of every presentation, see related articles.

How reducing complexity helps us understand the world

Tips for keeping the audience engaged in video presentations

5 tips for creating explainer videos that wow your audience
Get started with simpleshow today.
Module 15: Creating and Using Presentation Aids
Why use visual aids, learning objectives.
Identify how visual aids can enhance a presentation.
Visuals can spark interest , build emotional connections , clarify your words, explain abstract ideas , help draw conclusions , or increase understanding . For instance, a speaker may show a stacks of books to represent the amount of data storage in a speech about the evolution of computers, or demonstrate the proper use of ear plugs by distributing ear plugs, showing how to insert them, and then blasting an air horn in a speech about preventing hearing loss in order to make the value of ear protection more memorable and concrete. Done well—simple, visible, relevant, memorable, and audience-focused—visual aids can have a profound impact on your audience and your overall message.
Visual aids can be an important part of conveying your message effectively since people learn far more by hearing and seeing than through hearing or seeing alone. [1] The brain processes verbal and visual information separately. By helping the audience build visual and verbal memories, they are more likely to be able to remember the information at a later time. [2] If you can find a visual aid to complement what you are saying, you will help your audience understand the information you are presenting and remember your message. For example, a speaker might show the proper and improper ways to bow when being introduced in Japan while at the same time talking about the movements and also displaying a slide with the appropriate angles and postures for bowing. By using multiple modes in concert with each other, the message is strengthened by the pairing of words, images, and movement.

This picture of a guinea pig has nothing at all to do with the content of this page. It’s cute, but it’s just a distraction. Visuals should always be relevant to your message.
Not just any visual will do, however. Each visual should be relevant to your message, convey an important point, be clearly understandable, and be visible by your entire audience. Visuals should be used to make concepts easier to understand and to reinforce your message. They should illustrate important points that are otherwise hard to understand. [3] [4] [5]
Use visuals for speeches about processes, products, or demonstrations of how to do something, such as a diagram of how email is delivered in a speech about computer security. Use visuals when you need to explain things you cannot see because they are hidden or abstract, like a model of your internal organs in a speech about gastric bypass surgery. Use them when you need to grab your audience’s attention or stir their emotions. A speaker could use a photo of a starving child and a bag of rice that represents the daily calorie intake of a poor child in a speech about food insecurity to create a visceral reaction in the audience. As they say, a picture is worth a thousand words, so use images to tell a story or create a visual metaphor. Visual metaphors are useful when trying to evoke an emotion, such as showing an image of someone running or diving into a pool when you want to evoke action on the part of your audience. The images convey the message to “get going” or “dive in.” When talking about numbers or statistics, use visuals to provide context, comparison, and to help your audience understand the meaning of data. Done well, graphs can help make patterns or trends in the data much more comprehensible to your audience. [6]
- Vasile, Albert J.. Speak with Confidence: A Practical Guide. United Kingdom, Allyn and Bacon, 2004. ↵
- Malamed, Connie. Visual Language for Designers: Principles for Creating Graphics that People Understand. United States, Rockport Publishers, 2011. ↵
- Detz, Joan. It's Not What You Say, It's How You Say It: Ready-to-Use Advice for Presentations, Speeches, and Other Speaking Occasions, Large and Small. United States, St. Martin's Publishing Group, 2000. ↵
- Palmer, Erik. Well Spoken: Teaching Speaking to All Students. United States, Stenhouse Publishers, 2011. ↵
- Young, Kathryn Sue, and Travis, Howard Paul. Oral Communication: Skills, Choices, and Consequences. United States, Waveland Press, 2008. ↵
- Tufte, Edward R.. Visual and Statistical Thinking: Displays of Evidence for Making Decisions . Graphics Press, 1997. ↵
- Why use visual aids?. Authored by : Sheila Kasperek. Provided by : Mansfield University, Mansfield, PA. Project : Public Speaking Project. License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Used by permission
- Guinea Pig. Located at : https://www.pickpik.com/piggy-guinea-pig-pet-animals-pets-home-159250 . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn how to use visual aids effectively and create a perfect picture of what you want your audience to see in your presentations. Explore the benefits, types, and examples of visual aids, such as videos, demonstrations, roleplays, props, and slides.
Learn how to use presentation aids such as visual aids, audio and video clips, handouts, demonstrations and more to engage your audience and deliver your message. Find out why and how to use different types of presentation aids for in-person or virtual presentations.
Learn how to use pictures, drawings, charts, diagrams, maps, handouts, audio, video, and presentation programs as visual aids in your presentations. See examples of each type and tips on how to choose the best one for your purpose.
Learn how to create engaging visual presentations with Venngage's graphic design tips, templates and tools. Discover the best practices, types and examples of visual presentations for different purposes and audiences.
Learn what presentation aids are, how they differ from visual aids, and why they are important for effective communication. Explore various types of presentation aids, such as slideshows, charts, graphs, and multimedia, and see examples and templates.
Learn how to use visual aids such as PowerPoint, whiteboards, handouts and video clips to enhance your presentations and training sessions. Find out how to prepare, choose and tailor your visual aids to suit your audience and purpose.
Learn how to use visual aids to improve your presentation skills and engage your audience. Discover 10 examples of visual aids, from videos and props to slides and roleplays, with tips and benefits for each.
Are your meetings and presentations lacking that wow factor? In this video, I'll walk you through the power of VISUAL AIDs (Visual, Interactive, Simple, Atte...
Learn how to use visual aids effectively in presentations and avoid common pitfalls. Find out about different types of visual aids, such as slides, whiteboards, flip charts, videos and handouts, and see examples and tips.
Learn how to choose and use visual aids that are relevant, clear, concise, and consistent with your presentation objectives. Find tips for planning, designing, and delivering visual aids that enhance your message and impact your audience.
Apple® founder Steve Jobs was known widely for his great presentations. His unveiling of the iPhone® in 2007 is considered to have been one of his best presentations ever, and, if you were one of the millions who watched it online, you'll know why. The presentation was engaging, and passionate. Jobs was particularly well known for building his presentations around powerful visual aids.
Learn how to use visual aids to enhance your presentations and communicate your message more effectively. Explore various types of visual aids, such as charts, diagrams, videos, and infographics, and see examples of effective visual aids for different purposes.
Learn how to use presentation aids, such as images, graphs, diagrams, maps, audio and video, to enhance your speech and engage your audience. Find out the benefits, tips and examples of different types of presentation aids for various purposes and contexts.
Learn how to use visual aids effectively to enhance comprehension, attention and memorability in your presentations. Find out the benefits, tips and examples of different types of visual aids, such as graphs, infographics and images.
Learn how visual aids can help you capture and keep your audience's attention, make complex ideas easier to understand, build emotional bridges, improve retention, and stay on track. This article also provides tips and tools for creating effective presentations with Microsoft 365.
1. Visual Aids. Visual communication relies on vision and is primarily presented or expressed with two-dimensional images. Visuals with accompanying text have a greater power to inform, educate, or persuade a person or audience than text alone. One way to make your presentation vivid and memorable is through visual aids.
Learn how presentation aids can improve audience understanding, retention, and interest in public speaking. See examples of diagrams, images, and slides that clarify, emphasize, and organize your message.
Learn why visual aids are important for capturing attention, clarifying message, building emotional connection, and reinforcing key points in presentations. Find out how to use images, charts, graphs, and other tools effectively and avoid common pitfalls.
Learn the most important rule for visual presentations: less is more. Find out how to use the fewest number of slides, images, words and colors to convey your idea clearly and avoid distracting your audience.
Learn how to use slides effectively in your presentations with this video from Management Courses. Find out the purpose, content, format and design of visual aids, and get tips and exercises to ...
Learn how to use demonstrations, charts, graphs, handouts, diagrams, quotes, and videos to enhance your presentation. These visual aids can help you educate your audience, simplify complex information, and engage them with your content.
Learn how to use videos, diagrams, memes, pictures, and text to make your presentations more engaging and memorable. Visual aids can support facts, show change, lighten the mood, and create enthusiasm for your audience.
Learn how visual aids can enhance a presentation by sparking interest, building emotional connections, clarifying words, explaining abstract ideas, and increasing understanding. Find out what makes a visual aid simple, visible, relevant, memorable, and audience-focused.