HTML Projects for Beginners: 10 Easy Starter Ideas
Updated: August 01, 2024
Published: December 11, 2023
Are you eager to level up your HTML skills? Embarking on HTML projects for beginners is an excellent way to start. As someone who once stood where you are now, I can confidently say that the journey from HTML novice to proficiency is both thrilling and immensely rewarding. It's not just about learning a language; it’s about creating and bringing your ideas to life.

In my early days of exploring web development, HTML was the cornerstone that laid the foundation for my career. Now, with several years of experience in web development and a passion for being a resource for beginners, I understand the importance of starting with practical, easy-to-follow projects.
In this blog, I'm excited to share with you a curated list of HTML projects that are perfect for beginners. These projects are designed not only to increase your understanding of HTML but also to spark your creativity and enthusiasm for web development.
![basic assignment for html Download Now: 25 HTML & CSS Hacks [Free Guide]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/848be230-f06a-420e-9a24-82b45fe61632.png)

Table of Contents
- Understanding the Basics
- Project 1: Personal Portfolio Page
- Project 2: Simple Blog Layout
- Project 3: Landing Page
- Project 4: eCommerce Page
- Project 5: Recipe Page
- Project 6: Technical Documentation
- Project 7: Small Business Homepage
- Project 8: Simple Survey Form
- Project 9: Event Invitation Page
- Project 10: Parallax Website
The Road Ahead in Web Development

Free Guide: 25 HTML & CSS Coding Hacks
Tangible tips and coding templates from experts to help you code better and faster.
- Coding to Convention
- Being Browser-Friendly
- Minimizing Bugs
- Optimizing Performance
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Understanding the Basics: What is HTML?
Before I dive into the exciting world of HTML projects, I want to share why grasping the basics of HTML is crucial. HTML , which stands for HyperText Markup Language, is the foundational building block of the web. It’s not a programming language, but a markup language that I use to define the structure and layout of a web page through various elements and tags.
To me, HTML is like creating a framework for web content, similar to how an architect designs a building's blueprint. You would use tags to mark up text, insert images, create links, and lay out web pages in a format that browsers can understand and display. These tags , the basic units of HTML, help differentiate between headings, paragraphs, lists, and other content types, giving the web its versatile and user-friendly nature.

Every web developer starts somewhere, and for many, including myself, that starting point is HTML. It's a language that empowers me to create, experiment, and develop various digital experiences . So, as we embark on these beginner projects, remember that you're not just learning a new skill. You are stepping into a world full of endless possibilities and opportunities.
10 HTML Projects for Beginners: Your Journey Starts Here
As a web developer passionate about teaching, I‘m thrilled to guide you through this series. This section is crafted to progressively enhance your skills, offering a blend of creativity and learning. I’ve seen firsthand how these projects can transform beginners into confident creators, and I‘m excited to see the unique and innovative web experiences you’ll bring to life. Let's embark on this adventure together, turning code into compelling digital stories!
Project 1: Creating a Personal Portfolio Page
One of the best ways to start your HTML journey is by creating a personal portfolio page. This project allows you to introduce yourself to the world of web development while learning the basics of HTML. It’s not just about coding; it’s about telling your story through the web.
The objective here is to craft a web page that effectively portrays your personal and professional persona. This includes detailing your biography, showcasing your skills, and possibly even including a portfolio of work or projects you've completed. This page will be a cornerstone in establishing your online presence and can evolve as you progress in your career.
See the Pen HTML Project 1 by HubSpot ( @hubspot ) on CodePen .
- Showcase and Evolve : I'm selecting projects that best represent my abilities, and I plan to continually update my portfolio as I develop new skills.
- Simplicity and Clarity : My focus is on creating a clear, user-friendly layout that makes navigating my story and achievements effortless for visitors.
Project 2: Building a Simple Blog Layout
After creating a personal portfolio, the next step in your HTML journey is to build a simple blog layout. This project will introduce you to more complex structures and how to organize content effectively on a webpage.
The goal of this project is to create a basic blog layout that includes a header, a main content area for blog posts, and a footer. This layout serves as the foundation for any blog, providing a clear structure for presenting articles or posts.
See the Pen HTML Project 2 by HubSpot ( @hubspot ) on CodePen .
- Consistency is Key : In designing the blog, I'm focusing on maintaining a consistent style throughout the page to ensure a cohesive look.
- Content First : My layout will prioritize readability and easy navigation, making the content the star of the show.
Project 3: Designing a Landing Page
For the third project, let's shift gears and focus on creating a landing page. A landing page is a pivotal element in web design, often serving as the first point of contact between a business or individual and their audience. This project will help you learn how to design an effective and visually appealing landing page.
The objective is to create a single-page layout that introduces a product, service, or individual, with a focus on encouraging visitor engagement, such as signing up for a newsletter, downloading a guide, or learning more about a service.
See the Pen HTML Project 3 by HubSpot ( @hubspot ) on CodePen .
- Clear Call to Action : I'm ensuring that my landing page has a clear and compelling call to action (CTA) that stands out and guides visitors towards the desired engagement.
- Visual Appeal and Simplicity : My focus is on combining visual appeal with simplicity, making sure the design is not only attractive but also easy to navigate and understand.
Project 4: Crafting an eCommerce Page
Creating an eCommerce page is an excellent project for web developers looking to dive into the world of online retail. This project focuses on designing a web page that showcases products, includes product descriptions, prices, and a shopping cart.
The aim is to build a user-friendly and visually appealing eCommerce page that displays products effectively, providing customers with essential information and a seamless shopping experience. The page should include product images, descriptions, prices, and add-to-cart buttons.
See the Pen HTML Project 4 by HubSpot ( @hubspot ) on CodePen .
- Clarity and Accessibility : In designing the eCommerce page, my priority is to ensure that information is clear and accessible, making the shopping process straightforward for customers.
- Engaging Product Presentation : I'll focus on presenting each product attractively, with high-quality images and concise, informative descriptions that entice and inform.

Project 5: Developing a Recipe Page
One of the best ways to enhance your HTML and CSS skills is by creating a recipe page. This project is not only about structuring content but also about making it visually appealing. A recipe page is a delightful way to combine your love for cooking with web development, allowing you to share your favorite recipes in a creative and engaging format.
The aim of this project is to design a web page that effectively displays a recipe, making it easy and enjoyable to read. This includes organizing the recipe into clear sections such as ingredients and instructions, and styling the page to make it visually appealing. The recipe page you create can serve as a template for future culinary postings or a personal collection of your favorite recipes.
See the Pen HTML Project 5 by HubSpot ( @hubspot ) on CodePen .
- Clarity and Simplicity : My focus is on presenting the recipe in an organized manner, ensuring that the ingredients and instructions are easy to distinguish and follow.
- Engaging Visuals : I plan to use appealing images and a thoughtful layout, making the page not just informative but also a delight to the eyes.

50 Free Coding Templates
Free code snippet templates for HTML, CSS, and JavaScript -- Plus access to GitHub.
- Navigation Menus & Breadcrumbs Templates
- Button Transition Templates
- CSS Effects Templates
Project 6: Creating a Technical Documentation
Implementing a responsive navigation menu is a crucial skill in web development, enhancing user experience on various devices. This project focuses on creating a navigation menu that adjusts to different screen sizes, ensuring your website is accessible and user-friendly across all devices.
The goal is to create a navigation menu that adapts to different screen sizes. This includes a traditional horizontal menu for larger screens and a collapsible " hamburger " menu for smaller screens. Understanding responsive design principles and how to apply them using HTML and CSS is key in this project.
See the Pen HTML Project 6 by HubSpot ( @hubspot ) on CodePen .
- Flexibility is Key : I'm focusing on building a navigation menu that's flexible and adapts smoothly across various devices.
- Simplicity in Design : Keeping the design simple and intuitive is crucial, especially for the mobile version, to ensure ease of navigation.
Project 7: Building a Small Business Homepage
Creating a homepage for a small business is a fantastic project for applying web development skills in a real-world context. This project involves designing a welcoming and informative landing page for a small business, focusing on user engagement and business promotion.
The aim is to create a homepage that effectively represents a small business, providing key information such as services offered, business hours, location, and contact details. The design should be professional, inviting, and aligned with the business's branding.
See the Pen HTML Project 7 by HubSpot ( @hubspot ) on CodePen .
- Clarity and Accessibility : My priority is ensuring that key information is presented clearly and is easily accessible to visitors.
- Brand Consistency : I plan to incorporate design elements that are in line with the business's branding, creating a cohesive and professional online presence.
Project 8: Setting Up a Simple Survey Form
Creating a simple survey form is a valuable project for practicing form handling in HTML and CSS. It's a fundamental skill in web development, essential for gathering user feedback, conducting research, or learning more about your audience.
The objective of this project is to create a user-friendly survey form that collects various types of information from users. The form will include different types of input fields, such as text boxes, radio buttons, checkboxes, and a submit button. The focus is on creating a clear, accessible, and easy-to-use form layout.
See the Pen HTML Project 8 by HubSpot ( @hubspot ) on CodePen .
- Simplicity in Design : I'm aiming for a design that's straightforward and intuitive, ensuring that filling out the form is hassle-free for users.
- Responsive Layout : Ensuring the form is responsive and accessible on different devices is a key consideration in its design.
Project 9: Creating an Event Invitation Page
Designing an event invitation page is a fantastic way to combine creativity with technical skills. This project involves creating a web page that serves as an online invitation for an event, such as a conference, workshop, or party.
The aim is to create a visually appealing and informative event invitation page. This page should include details about the event like the date, time, venue, and a brief description. The focus is on using HTML and CSS to present this information in an engaging and organized manner.
See the Pen HTML Project 9 by HubSpot ( @hubspot ) on CodePen .
- Visual Impact : I'm aiming for a design that captures the essence of the event, making the page immediately engaging.
- Clear Information Hierarchy : Organizing the event details in a clear and logical manner is crucial for effective communication.
Project 10: Building a Parallax Website
Creating a parallax website involves implementing a visual effect where background images move slower than foreground images, creating an illusion of depth and immersion. It's a popular technique for modern, interactive web design.
The objective of this project is to create a website with a parallax scrolling effect. This will be achieved using HTML and CSS, specifically focusing on background image positioning and scroll behavior. The key is to create a visually engaging and dynamic user experience.
See the Pen HTML Project 10 by HubSpot ( @hubspot ) on CodePen .
- Balance in Motion : While implementing parallax effects, I'll ensure the motion is smooth and not overwhelming, to maintain a pleasant user experience.
- Optimized Performance : I'll be mindful of optimizing images and code to ensure the parallax effect doesn't hinder the site's performance.
As we reach the end of our journey through various web development projects, it's clear that the field of web development is constantly evolving, presenting both challenges and opportunities. From creating basic HTML pages to designing dynamic, interactive websites, the skills acquired are just the beginning of a much broader and exciting landscape.
Embracing New Technologies: The future of web development is tied to the ongoing advancements in technologies. Frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.js are changing how we build interactive user interfaces. Meanwhile, advancements in CSS, like Flexbox and Grid, have revolutionized layout design, making it more efficient and responsive.
Focus on User Experience: As technology progresses, the emphasis on user experience (UX) will become even more crucial. The success of a website increasingly depends on how well it engages users, provides value, and creates meaningful interactions. Web developers must continuously learn about the latest UX trends and apply them to their work.
The Rise of Mobile-First Development: With the increasing use of smartphones for internet access, mobile-first design is no longer an option but a necessity. This approach involves designing websites for smaller screens first and then scaling up to larger screens, ensuring a seamless experience across all devices.
Web Accessibility and Inclusivity: Making the web accessible to everyone, including people with disabilities, is a growing focus. This includes following best practices and guidelines for web accessibility, ensuring that websites are usable by everyone, regardless of their abilities or disabilities.
Performance and Optimization: As users become more demanding about performance, optimizing websites for speed and efficiency will continue to be a priority. This includes minimizing load times, optimizing images and assets, and writing efficient code.
Emerging Trends: The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in web development is on the rise, offering new ways to personalize user experiences and automate tasks. Additionally, the development of Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) is blurring the lines between web and mobile apps, offering offline capabilities and improved performance.
Continuous Learning: The only constant in web development is change. Continuous learning and adaptation are key to staying relevant in this field. Whether it's learning new programming languages, frameworks, or design principles, the ability to evolve with the industry is critical for any web developer.
As you continue on your path in web development, remember that each project is a step towards mastering this ever-changing discipline. Embrace the challenges, stay curious, and keep building, for the road ahead in web development is as exciting as it is limitless.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![basic assignment for html How to Make an HTML Text Box [Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/html-text-box.webp)
How to Make an HTML Text Box [Examples]

HTML Comments: How to Write Them and Why I Think You Should Use Them

The Ultimate Guide to HTML for Beginners: How to Write, Learn & Use It

How to Add & Change Background Color in HTML

4 Steps to Add a Clickable Telephone Link in HTML
![basic assignment for html How to Create an HTML Dropdown Menu [+ Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/html-dropdown.jpg)
How to Create an HTML Dropdown Menu [+ Examples]
![basic assignment for html Onchange Event in HTML: How to Use It [+Examples]](https://knowledge.hubspot.com/hubfs/onchange.webp)
Onchange Event in HTML: How to Use It [+Examples]

HTML Dialog: How to Create a Dialog Box in HTML
How to Create a Landing Page in HTML & CSS [+ 15 Templates]

HTML Audio Tag: How to Add Audio to Your Website
CMS Hub is flexible for marketers, powerful for developers, and gives customers a personalized, secure experience
32 HTML And CSS Projects For Beginners (With Source Code)

updated Apr 17, 2024
If you want to feel confident in your front-end web developer skills, the easiest solution is to start building your own HTML and CSS projects from scratch.
As with any other skill, practicing on simple, realistic projects helps you build your skills and confidence step-by-step.
But if you are new to HTML and CSS, you may be wondering:
Where can I find ideas for beginner-level HTML and CSS projects?
Even if you are just starting out with HTML and CSS, there are some fun and easy projects you can create.
Whether you are new to learning web development or have some experience under your belt, this guide is the perfect place to start improving your skills.
In this article, I’ll walk you through 32 fun HTML and CSS coding projects that are easy to follow. We will start with beginner-level projects and then move on to more demanding ones.
If you want to become a professional front-end developer, the projects below will help you expand your portfolio.
When it’s time to apply for your first entry-level job, you can showcase your skills to potential employers with a portfolio packed with real-life project examples.
Let’s get started!
Please note: This post contains affiliate links to products I use and recommend. I may receive a small commission if you purchase through one of my links, at no additional cost to you. Thank you for your support!
What are HTML and CSS?
HTML and CSS are the most fundamental languages for front-end web development.
Learning them will allow you to:
- Build stunning websites
- Start a coding blog
- Make money freelancing
Let’s take a quick look at both of them next:
What is HTML?
HTML or HyperText Markup Language is the standard markup language for all web pages worldwide.
It’s not a “typical” programming language – like Python or Java – since it doesn’t contain any programming logic. HTML can’t perform data manipulations or calculations, for example.
Instead, HTML allows you to create and format the fundamental structure and content of a web page.
You will use HTML to create:
- Page layouts (header, body, footer, sidebar)
- Paragraphs and headings
- Input fields
- Checkboxes and radio buttons
- Embedded media
Thus, HTML only allows you to determine the structure of a web page and place individual content elements within it.
For more details, check out my post on what HTML is and how it works .
You can’t format the look and feel of your web page with HTML, though.
Your HTML web page will look dull and boring. Sort of like this:

The example above is the first web page every built for the WWW , by the way.
This is how websites used to look in the ’90s. But we’ve come a long way since then – luckily.
To make your HTML content visually appealing and professional-looking, you need another language: CSS. Let’s look at that next.
What is CSS?
CSS or Cascading Style Sheets is a style sheet language that allows you to adjust the design and feel of your HTML content.
Thus, you can turn your pure-HTML pages into stunning, modern websites with CSS. And it’s super easy to learn, too!
Here’s how it works:
CSS allows you to target individual HTML elements and apply different styling rules to them.
For example, here’s a CSS rule that targets H2 headings, their font-size property, and sets it to a value of 24px:
You can use CSS to adjust:
- Backgrounds
- Fonts and text styling
- Spacings (paddings, margins)
- CSS animations
- Responsiveness (media queries)
If you want to create stunning websites and become a front-end web developer, CSS is one of the first tools you must learn and master.
For more details, check out my post on what CSS is and how it works .

Why build HTML and CSS projects?
Practicing on realistic, hands-on projects is the best way to learn how to create something useful and meaningful with HTML and CSS.
The more projects you build, the more confident you will feel in your skills.
To build a web page from scratch , you need a basic understanding of how HTML works. You should be comfortable with writing the necessary HTML code to create a page without copying a boilerplate or following a tutorial.
Thus, if you want to become a front-end web developer , building HTML and CSS projects will teach you how to use these two languages in real life.
Therefore, practising your skills with the projects in this article will give you a competitive edge against anyone who’s simply following tutorials and copy-pasting other people’s code.
Finally, building HTML and CSS projects helps you build a professional portfolio of real-world projects.
When it’s time to start applying for your first job, you will have 10 to 20 cool projects to showcase your skills to potential employers. Not bad!
32 HTML and CSS projects: Table of contents
Here’s an overview of the HTML and CSS projects we’ll go through:
Beginner project: CSS radio buttons
Beginner project: css toggle buttons, beginner project: hamburger menu, beginner project: pure css sidebar toggle menu, beginner project: animated css menu, beginner project: custom checkboxes, beginner project: pure css select dropdown, beginner project: modal/popup without javascript, beginner project: animated gradient ghost button, beginner project: css image slider, basic html & css website layout, tribute page, survey page with html forms, sign-up page / log-in page, job application form page, landing page, product landing page, interactive navigation bar, responsive website header, restaurant menu, restaurant website, parallax website, custom 404 error page, personal portfolio website, blog post layout.
- Photography website
Music store website
Discussion forum website.
- Event or conference website
Technical documentation website
Online recipe book, website clone.
Share this post with others!

This quick project is a great example of what you can do with pure CSS to style radio buttons or checkboxes:
See the Pen CSS radio buttons by Angela Velasquez ( @AngelaVelasquez ) on CodePen .
☝️ back to top ☝️
This HTML and CSS project teaches you how to create custom CSS toggle buttons from scratch:
See the Pen Pure CSS Toggle Buttons | ON-OFF Switches by Himalaya Singh ( @himalayasingh ) on CodePen .
Every website needs a menu, right?
This hamburger menu is beautiful and clean, and you can build it with just HTML and CSS:
See the Pen Pure CSS Hamburger fold-out menu by Erik Terwan ( @erikterwan ) on CodePen .
Placing your website navigation inside a sidebar toggle is an easy way to clean up the overall look and feel of your design.
Here’s a modern-looking solution to a pure-CSS sidebar toggle menu:
See the Pen PURE CSS SIDEBAR TOGGLE MENU by Jelena Jovanovic ( @plavookac ) on CodePen .
If you want to build a more dynamic, interactive website navigation, try this animated CSS menu:
See the Pen Animate menu CSS by Joël Lesenne ( @joellesenne ) on CodePen .
Styling your checkboxes to match the overall design is an easy way to elevate the look and feel of your website.
Here’s an easy HTML and CSS practice project to achieve that:
See the Pen Pure CSS custom checkboxes by Glen Cheney ( @Vestride ) on CodePen .
Standard select dropdowns often look dull and boring. Here’s a quick CSS project to learn how to create beautiful select dropdowns easily:
See the Pen Pure CSS Select by Raúl Barrera ( @raubaca ) on CodePen .
Modals and popups often use JavaScript, but here’s a pure HTML and CSS solution to creating dynamic, interactive modals and popups:
See the Pen Pure css popup box by Prakash ( @imprakash ) on CodePen .
Ghost buttons can look great if they fit the overall look and feel of your website.
Here’s an easy project to practice creating stunning, dynamic ghost buttons for your next website project:
See the Pen Animated Gradient Ghost Button Concept by Arsen Zbidniakov ( @ARS ) on CodePen .
This image slider with navigation buttons and dots is a fantastic HTML and CSS project to practice your front-end web development skills:
See the Pen CSS image slider w/ next/prev btns & nav dots by Avi Kohn ( @AMKohn ) on CodePen .
Now, before you start building full-scale web pages with HTML and CSS, you want to set up your basic HTML and CSS website layout first.
The idea is to divide your page into logical HTML sections. That way, you can start filling those sections with the right elements and content faster.
For example, you can break up the body of your page into multiple parts:
- Header: <header>
- Navigation: <nav>
- Content: <article>
- Sidebar: <aside>
- Footer: <footer>

Depending on your project, you can fill the article area with a blog post, photos, or other content you need to present.
This layout project will serve as a starting point for all your future HTML and CSS projects, so don’t skip it.
Having a template like this will speed up your next projects, because you won’t have to start from scratch.
Here are two tutorials that will walk you through the steps of creating a basic website layout using HTML and CSS:
- https://www.w3schools.com/html/html_layout.asp
- https://www.w3schools.com/css/css_website_layout.asp
Building a tribute page is fantastic HTML and CSS practice for beginners.
What should your tribute page be about?
Anything you like!
Build a tribute page about something you love spending time with.
Here are a few examples:
- a person you like
- your favorite food
- a travel destination
- your home town
My first HTML-only tribute page was for beetroots. Yes, beetroots. I mean, why not?

HTML and CSS concepts you will practice:
- HTML page structure
- basic HTML elements: headings, paragraphs, lists
- embedding images with HTML
- CSS fundamentals: fonts and colors
- CSS paddings, margins, and borders
Here’s a helpful tutorial for building a HTML and CSS tribute page .
Whether you want to become a full-time web developer or a freelance web designer, you will use HTML forms in almost every project.
Forms allow you to build:
- Contact forms
- Login forms
- Sign up forms
- Survey forms
Building a survey page allows you to practice HTML input tags, form layouts, radio buttons, checkboxes, and more.
Pick any topic you like and come up with 10 pieces of information you want to collect from respondents.
Perhaps an employee evaluation form? Or a customer satisfaction form?
- form elements: input fields, dropdowns, radio buttons, labels
- styling for forms and buttons
Here’s an example survey form project for inspiration:
See the Pen Good Vibes Form by Laurence ( @laurencenairne ) on CodePen .
Let’s practice those HTML forms a bit more, shall we?
For this project, you will build a sign-up or log-in page with the necessary input fields for a username and a password.
Because we can create a user profile on almost every website, forms are absolutely essential for allowing people to set their usernames and passwords.
Your forms will collect inputs from users and a separate back-end program will know how to store and process that data.
Creating a clean and clear sign-up page can be surprisingly difficult. The more you learn about HTML and CSS, the more content you want to create to showcase your skills. But the thing is: a sign-up page needs to be as clean and easy-to-use as possible.
Thus, the biggest challenge with this project is to keep it simple, clear, and light.
Here’s an example project to get started with:
See the Pen Learn HTML Forms by Building a Registration Form by Noel ( @WaterNic10 ) on CodePen .
For more inspiration, check out these 50+ sign-up forms built with HTML and CSS .
Using a HTML form is the best way to collect information from job applicants.
You can also generate and format a job description at the top of the page.
Then, create a simple job application form below to collect at least 10 pieces of information.
Use these HTML elements, for example:
- Text fields
- Email fields
- Radio buttons
Here’s an example job application page you can build with HTML and CSS:
See the Pen Simple Job Application Form Example by Getform ( @getform ) on CodePen .
One of your first HTML and CSS projects should be a simple landing page.
Your landing page can focus on a local business, an event, or a product launch, for example.
Landing pages play an important role for new businesses, marketing campaigns, and product launches. As a front-end developer, you will be asked to create them for clients.
For this project, create a simple HTML file and style it with CSS. Be sure to include a headline, some text about the company or its services, and a call-to-action (CTA) button.
Make sure that your landing page is clean and clear and that it’s easy to read.
If you build a landing page for a new product, highlight the product’s key benefits and features.
To get started, follow this freeCodeCamp tutorial to build a simple landing page . You will need JavaScript for a few features. If you are not familiar with JavaScript, leave those features out for now and come back to them later.
For more inspiration, check out these HTML landing page templates .

A product landing page is a page that you build to promote a specific product or service.
For example, if you want to sell your ebook about how to use CSS to build an animated website, then you would create a product landing page for it.
Your product landing page can be very simple to start with. When your skills improve, add some complexity depending on what kind of information you need to present.
One of the most iconic product landing pages is the iPhone product page by Apple, for example:

Of course, the iPhone landing page is technically complex, so you won’t build it as your first project. But still, it’s a good place to find inspiration and new ideas.
The best way to design your first product landing page is to create a simple wireframe first. Sketch your page layout on paper before you start building it.
Wireframes help you maintain a clear overview of your HTML sections and elements.
To get started, browse through these product landing page examples for some inspiration .
Building an interactive navigation bar will teach you how to create an animated menu with dropdowns using HTML and CSS.
This is another great project for beginners, because it will teach you how to create menus using HTML and CSS. You’ll also learn how to style them with different colors, fonts, and effects.
You’ll also learn how to use anchors and pseudo-classes to create the menu navigation, as well as how to create the dropdown menus from scratch.
If you aren’t familiar with CSS media queries yet, building a responsive navigation bar is a smart way to learn and practice them.
CSS media queries allow you to create a responsive navigation menu that changes its size and layout depending on screen width.
To get started, check out this tutorial on how to build an interactive navigation bar with HTML and CSS .
One of the best ways to practice your HTML and CSS skills is to create custom website headers. This is a great project to add to your portfolio website, as it will show off your skills and help you attract new clients.
There are a number of different ways that you can create a stylish and responsive website header. One option is to use a premade CSS framework such as Bootstrap or Foundation. Alternatively, you can create your own custom styles by hand.
No matter which option you choose, be sure to make your header mobile-friendly by using media queries. This will ensure that your header looks great on all devices, regardless of their screen size or resolution.
To get started, check out this simple example for a responsive HTML and CSS header .
If you’re looking to get into web development, one of the best HTML and CSS projects you can build is a simple restaurant menu.
Align the different foods and drinks using a CSS layout grid.
Add prices, images, and other elements you need to give it a professional, clean look and feel.
Choose a suitable color palette, fonts, and stock photos.
You can also add photos or a gallery for individual dishes. If you want to add an image slider, you can create one with HTML and CSS, too.
Here’s an example of a very simple restaurant menu project:
See the Pen Simple CSS restaurant menu by Viszked Tamas Andras ( @ViszkY ) on CodePen .
Once you’ve built your restaurant menu with, it’s time to tackle a more complex HTML and CSS project.
Building a real-life restaurant website is a fun way to practice a ton of HTML and CSS topics.
Not only will you learn the basics of creating a beautiful, professional web page, but you also get a chance to practice responsive web design, too.
And if you’re looking to land your first front-end web developer job, having a well-designed business website in your portfolio will help you stand out from the crowd.

Make sure your website matches the restaurant’s menu and target clientele. A fine-dining place on Manhattan will have a different website than a simple (but delicious!) diner in rural Wisconsin.
Here are a few key details to include on your restaurant website:
- Clear navigation bar
- Restaurant details
- Menu for food and drinks
- Location and directions
- Contact details
- Upcoming events
To get started, check out this free tutorial on how to build a restaurant website with HTML and CSS .
To build a parallax website, you will include fixed background images that stay in place when you scroll down the page.
Although the parallax look isn’t as popular or modern as it was a few years back, web designers still use the effect a lot.
The easiest way to build a parallax HTML and CSS project is to start with a fixed background image for the entire page.
After that, you can experiment with parallax effects for individual sections.
Create 3-5 sections for your page, fill them with content, and set a fixed background image for 1-2 sections of your choice.
Word of warning: Don’t overdo it. Parallax effects can be distracting, so only use them as a subtle accent where suitable.
Here’s an example project with HTML and CSS source code:
See the Pen CSS-Only Parallax Effect by Yago Estévez ( @yagoestevez ) on CodePen .
404 error pages are usually boring and generic, right?
But when a visitor can’t find what they’re searching for, you don’t want them to leave your website.
Instead, you should build a custom 404 error page that’s helpful and valuable, and even fun and entertaining.
A great 404 page can make users smile and – more importantly – help them find what they are looking for. Your visitors will appreciate your effort, trust me.
For some inspiration, check out these custom 404 page examples .
Any web developer will tell you that having a strong portfolio is essential to landing your first job.
Your portfolio is a chance to show off your skills and demonstrate your expertise in front-end web development.
And while there are many ways to create a portfolio website, building one from scratch using HTML and CSS will give you tons of valuable practice.
Your first version can be a single-page portfolio. As your skills improve, continue adding new pages, content, and features. Make this your pet project!
Remember to let your personality shine through, too. It will help you stand out from the crowd of other developers who are vying for the same jobs.
Introduce yourself and share a few details about your experience and future plans.
Employers and clients want to see how you can help them solve problems. Thus, present your services and emphasize the solutions you can deliver with your skills.
Add your CV and share a link to your GitHub account to showcase your most relevant work samples.
Make sure to embed a few key projects directly on your portfolio website, too.
Finally, let your visitors know how to get in touch with you easily. If you want, you can add links to your social media accounts, too.
In this project, you’ll create a simple blog post page using HTML and CSS.
You’ll need to design the layout of the page, add a title, a featured image, and of course add some content to your dummy blog post.
You can also add a sidebar with a few helpful links and widgets, like:
- An author bio with a photo
- Links to social media profiles
- List of most recent blog posts
- List of blog post categories
Once your HTML structure and content are in place, it’s time to style everything with CSS.
Photography website with a gallery
If you’re a photographer or just enjoy taking pictures, then this project is for you.
Build a simple photo gallery website using HTML and CSS to practice your web design skills.
Start with the basic HTML structure of the page, and figure out a cool layout grid for the photos. You will need to embed the photos and style everything beautiful with CSS.
My tip: Use CSS Flexbox and media queries to create a responsive galleries that look great on all devices.
Here’s a full tutorial for building a gallery website with HTML and CSS:
If you love music, why not practice your HTML and CSS skills by building a music store web page?
Before you start, make a thorough plan about your website structure. What’s the purpose of your music store? What genres will you cover?
Pick a suitable color palette, choose your fonts, and any background images you want to use.
My tip: If you feature album cover images, keep your colors and fonts as clean and simple as possible. You don’t want to overpower the album covers with a busy web page with tons of different colors and mismatching fonts.
Create a user-friendly menu and navigation inside the header. Fill the footer with helpful links for your store, career page, contact details, and newsletter form, for example.
Building a music store website with HTML and CSS is a great opportunity to practice your skills while you are still learning.
Start with very basic features, and add new ones as your skills improve. For example, you can add media queries to make your website responsive.
A forum is a great way to create a community around a topic or interest, and it’s also a great way to practice your coding skills.
In this project, you’ll create a simple forum website using HTML and CSS.
You’ll need to design the layout of the site, add categories and forums, and set up some initial content.
Of course, you should start with creating the basic layout and structure with HTML first. You will need a navigation bar, at least one sidebar, and an area for the main content.
To make your discussion forum website more interesting, add new content and remember to interlink related threads to make the site feel more realistic.
Event or conference web page
Creating a web page for an event is a fun HTML and CSS project for beginners.
You can either pick a real event and build a better landing page than the real one, or come up with an imaginary conference, for example.
Make sure to include these elements:
- Register button
- Venue details
- Dates and schedule
- Speakers and key people
- Directions (how to get there)
- Accommodation details
Divide the landing page into sections, and create a header and a footer with menus and quick links.
Come up with a suitable color palette, pick your fonts, and keep your design clean and clear.
Every programming language, software, device and gadget has a technical documentation for helpful information and support.
Creating a technical documentation website with just HTML and CSS allows you to build a multi-page site with hierarchies, links, and breadcrumbs.
The main idea is to create a multi-page website where you have a sidebar menu on the left, and the content on the right.
The left-hand side contains a vertical menu with all the topics your documentation covers.
The right-hand side presents the description and all the details for each individual topic.
For simplicity, start with the homepage and 2–3 subpages first. Come up with a clean layout and make sure your links are working properly.
Then, start expanding the website with additional sub-pages, content, and elements.
- HTML hyperlinks and buttons
Creating an online recipe book as an HTML and CSS project requires a similar setup than the previous project example.
You will need to create a homepage that serves as a directory for all your recipes. Then, create a separate subpage for each recipe.
If you want to challenge yourself, add recipe categories and create separate directory pages for each of them.
- embedding recipe photos
One of the best ways to practice HTML and CSS is to clone an existing web page from scratch.
Use your browser’s inspecting tools to get an idea of how the page is built.
As with any HTML and CSS project, start by creating the basic page template with:
Then, divide your page into sections, rows, and columns.
Finally, fill your page with individual elements like headings, paragraphs, and images.
Once the HTML content is in place, use CSS to style your page.
Start with something simple, like the PayPal login page.
Then move on to more demanding cloning projects, such as a news website. Try the BBC homepage, for example.
Where to learn HTML and CSS?
There are no prerequisites required for you to learn HTML and CSS.
Both languages are easy to learn for beginners, and you can start building real-life projects almost right away.
Here are a few courses to check out if you want to learn HTML and CSS online at your own pace:
1: Build Responsive Real World Websites with HTML5 and CSS3

Build Responsive Real World Websites with HTML5 and CSS3 was my first online web development course focused 100% on HTML and CSS.
You don’t need any coding or web development experience for this course. But if you have watched some online tutorials but you’re not sure how to create a full-scale website by yourself, you are going to love it.
2: The Complete Web Developer Course 2.0

The Complete Web Developer Course 2.0 changed my life back when I started learning web development.
This course takes you from zero to knowing the basics of all fundamental, popular web development tools. You’ll learn:
- HTML and CSS
- JavaScript and jQuery
- and much more
3: Modern HTML & CSS From The Beginning (Including Sass)

I’m a big fan of Brad Traversy, and I really can’t recommend his Modern HTML & CSS From The Beginning course enough.
Even if you have never built a website with HTML and CSS before, this course will teach you all the basics you need to know.
4: The Complete 2023 Web Development Bootcamp

One of my most recent favorites, The Complete 2023 Web Development Bootcamp by Dr. Angela Yu is one of the best web development courses for beginners I’ve come across.
If you’re not quite sure what area or language to specialize in, this course is the perfect place to try a handful of tools and programming languages on a budget.
5: Learn HTML (Codecademy)

Learn HTML is a free beginner-level course that walks you through the fundamentals with interactive online lessons.
Codecademy also offers a plethora of other web development courses. Check out their full course catalog here .
6: Responsive Web Design (freeCodeCamp)

The Responsive Web Design certification on FreeCodeCamp is great for learning all the basics of web development from scratch for free.
You start with HTML and CSS to get the hang of front-end web dev fundamentals. Then, you start learning new tools and technologies to add to your toolkit, one by one.
Also, check out these roundups with helpful web development courses:
- 27 Best Web Development Courses (Free and Paid)
- 20+ Web Development Books for Beginners
- 120+ Free Places to Learn to Code (With No Experience)
- 100+ Web Development Tools and Resources
Final thoughts: HTML and CSS project ideas for beginners
There you go!
When it comes to learning HTML and CSS, practice really makes perfect. I hope you found a few inspirational ideas here to start building your next project right away.
Learning HTML and CSS may seem intimidating at first, but when you break it down into small, less-intimidating projects, it’s really not as hard as you might think.
HTML and CSS are easy to learn. You can use them to create really cool, fun projects – even if you are new to coding.
Try these beginner-level HTML and CSS project ideas to improve your front-end web development skills starting now. Do your best to build them without following tutorials.
Remember to add your projects to your portfolio website, too.
It’s possible to learn how to code on your own, and it’s possible to land your first developer job without any formal education or traditional CS degree.
It all boils down to knowing how to apply your skills by building an awesome portfolio of projects like the ones above.
So, which project will you build first? Let me know in the comments below!
Once you feel comfortable with HTML and CSS, it’s time to start learning and practising JavaScript .
To get started, check out my guide with 20+ fun JavaScript projects ideas for beginners . I’ll see you there!
Share this post with others:
About mikke.

Hi, I’m Mikke! I’m a blogger, freelance web developer, and online business nerd. Join me here on MikkeGoes.com to learn how to code for free , build a professional portfolio website , launch a tech side hustle , and make money coding . When I’m not blogging, you will find me sipping strong coffee and biking around town in Berlin. Learn how I taught myself tech skills and became a web dev entrepreneur here . And come say hi on Twitter !
Leave a reply:
Download 15 tips for learning how to code:.
GET THE TIPS NOW
Sign up now to get my free guide to teach yourself how to code from scratch. If you are interested in learning tech skills, these tips are perfect for getting started faster.


10 HTML and CSS Code Challenges for Beginners

- Share article on Twitter
- Share article on Facebook
- Share article on LinkedIn
HTML and CSS form the foundation of modern web development . HTML defines how a web page is structured, and CSS defines its style. While both languages are relatively easy to learn, once you know the basics, you’ll still need to sharpen your skills with practice.
Code challenges are a great way to sharpen your programming skills and combine them in different ways. Here are 10 HTML and CSS code challenges that’ll help you take your skills to the next level. To get started, just pick a challenge, open up a workspace , and start coding.
Note that while these challenges are designed for beginners, you’ll still need to have a basic understanding of HTML and CSS. If you need a refresher, use the courses below:
1. Create a tribute page
Choose a historical figure who’s meaningful to you and create a webpage dedicated to them. The webpage should include:
- A title or heading with the person’s name
- An image of the person
- A caption for the image
- A timeline of the person’s life in the form of a list
This can be completed with only HTML, but use CSS to give it some style.
2. Create a Wikipedia page
Wikipedia is one of the backbones of the internet, and it has a relatively simple layout. Create a Wikipedia page on the topic of your choice. It should include:
- A title or heading
- A table of contents with links to sections within the page
- Superscript number links that link to the corresponding number in the reference section
- An ordered list of references
3. Create an HTML and CSS-only search results page
Create a mock Google search results page. It should include:
- The Google logo
- A search bar at the top
- A list of search results with clickable links
Here’s an example of what it might look like.
4. Create a survey form
HTML forms are an important part of many websites. Create a form for a survey on the topic of your choice.
Include a variety of answer options, including text fields, dropdowns, radio buttons, checkboxes, and a submit button. Don’t forget to add a title, and consider using CSS to improve the look of your form. Here’s an example .
5. Create a parallax website
A parallax website has a fixed image in the background that stays in place while you scroll through other parts of the page. It’s a popular effect in web design and gives an elegant look and feel to a page.
Design a parallax webpage. Divide the page into three or four sections. Set three or four background images and align text to each section. You’ll use margins , padding , and background positioning to create the effect. Here’s an example of a parallax website.
6. Create a product landing page
Many websites are designed to showcase and sell products. A product landing page needs to be attractive, informative, and easy to read to appeal to consumers. Your product landing page should include:
- A picture of the product
- A header and footer
- Multiple sections
Consider the color scheme and ensure that elements don’t overlap each other.
7. Create a restaurant website
A restaurant website is similar to a product landing page in that it should showcase the restaurant and menu items appealingly. It’s more complex, though, with images of different foods and drinks. First, create a responsive restaurant website using a viewport and media queries.
8. Create a chessboard
This challenge teaches you how to create and format a table . You’ll also need to learn how to insert UNICODE characters.
Create a chessboard. The board should be alternating colors and an eight-by-eight grid. Here are the UNICODE characters you’ll need for the pieces.
- White King: ♔
- White Queen: ♕
- White Rook: ♖
- White Bishop: ♗
- White Knight: ♘
- White Pawn: ♙
- Black King: ♚
- Black Queen: ♛
- Black Rook: ♜
- Black Bishop: ♝
- Back Knight: ♞
- Black Pawn: ♟
9. Create an event or conference website
This challenge continues the theme of building attractive web pages. This one will include a registration button that links to a registration form. You’ll also need details and images of the speaker or performer and venue. Describe the event and include multiple sections along with a header and footer. Consider the color scheme and use fonts that are readable and reflect the theme of the event.
10. Create a portfolio website
Take what you’ve learned throughout the other challenges and create a portfolio website. The website should reflect your skills.
Include a page with your resume, work samples, a photo, and a top menu with links to an about page, contact page, and any other pages you’d like to include. In the footer, include your contact information and links to your relevant social media accounts.
Building your HTML and CSS skills
Code challenges are just one way to build your HTML and CSS skills. You can also brush up with courses like Learn HTML , Learn CSS , and Learn Intermediate CSS . These courses build on one another, though you can always jump into an intermediate class if you already have a good base knowledge of CSS.
Skill Paths are another great way to learn specific skills. Our Learn How to Build Websites Skill Path walks you through HTML and CSS, along with responsive design and accessibility . You’ll end the class with a polished website that you can use in your portfolio. We also have a standalone course on responsive design .
If you feel confident in your HTML and CSS skills, it may be time to learn another language. Our course on JavaScript builds on HTML and CSS to help you make websites even more responsive and dynamic. Once you learn JavaScript, we offer a course on Building Interactive JavaScript Websites that brings all those skills together.
Whether you’re looking to break into a new career, build your technical skills, or just code for fun, we’re here to help every step of the way. Check out our blog post about how to choose the best Codecademy plan for you to learn about our structured courses, professional certifications, interview prep resources, career services, and more.
Related courses
Learn intermediate css, subscribe for news, tips, and more, related articles.

How We’re Harnessing GPT-4o in Our Courses
Our new AI Learning Assistant is powered by GPT-4o.

What Is JavaScript Used For?
JavaScript is a powerful programming language with a wide range of applications. Learn about its uses in web development, game development, VR & more.

7 Most Popular Programming Languages for Game Development
Learn the best languages for game development and why developers choose to use them. Discover how our classes can get you started with game design.

What Is Python Used For?
Python’s versatility makes it a valuable addition to any developer’s tech stack. Here, we explore its advantages and applications in different industries.

What is HTML? Common Uses & Defining Features
HTML lies at the heart of web development and forms the structure of our favorite websites.

How Myspace, Neopets & The Internet of the Aughts Taught Millennials to Code
Nostalgia loading…

Justice For HTML/CSS: How These Languages Built The 2000s Internet & Launched Countless Tech Careers
Programmers are quick to dismiss these foundational languages — here’s why.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to search
- Skip to select language
- Sign up for free
- Português (do Brasil)
Getting started with HTML
- Overview: Introduction to HTML
In this article, we cover the absolute basics of HTML. To get you started, this article defines elements, attributes, and all the other important terms you may have heard. It also explains where these fit into HTML. You will learn how HTML elements are structured, how a typical HTML page is structured, and other important basic language features. Along the way, there will be an opportunity to play with HTML too!
| Prerequisites: | , and basic knowledge of . |
|---|---|
| Objective: | To gain basic familiarity with HTML, and practice writing a few HTML elements. |

What is HTML?
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a markup language that tells web browsers how to structure the web pages you visit. It can be as complicated or as simple as the web developer wants it to be. HTML consists of a series of elements , which you use to enclose, wrap, or mark up different parts of content to make it appear or act in a certain way. The enclosing tags can make content into a hyperlink to connect to another page, italicize words, and so on. For example, consider the following line of text:
If we wanted the text to stand by itself, we could specify that it is a paragraph by enclosing it in a paragraph ( <p> ) element:
Note: Tags in HTML are not case-sensitive. This means they can be written in uppercase or lowercase. For example, a <title> tag could be written as <title> , <TITLE> , <Title> , <TiTlE> , etc., and it will work. However, it is best practice to write all tags in lowercase for consistency and readability.
Anatomy of an HTML element
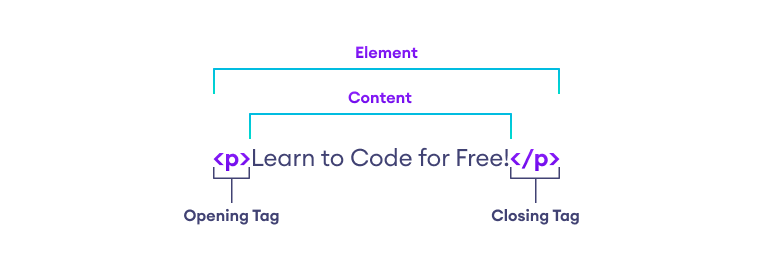
Let's further explore our paragraph element from the previous section:

The anatomy of our element is:
- The opening tag: This consists of the name of the element (in this example, p for paragraph), wrapped in opening and closing angle brackets. This opening tag marks where the element begins or starts to take effect. In this example, it precedes the start of the paragraph text.
- The content: This is the content of the element. In this example, it is the paragraph text.
- The closing tag: This is the same as the opening tag, except that it includes a forward slash before the element name. This marks where the element ends. Failing to include a closing tag is a common beginner error that can produce peculiar results.
The element is the opening tag, followed by content, followed by the closing tag.
Active learning: creating your first HTML element
Edit the line below in the "Editable code" area by wrapping it with the tags <em> and </em>. To open the element , put the opening tag <em> at the start of the line. To close the element , put the closing tag </em> at the end of the line. Doing this should give the line italic text formatting! See your changes update live in the Output area.
If you make a mistake, you can clear your work using the Reset button. If you get really stuck, press the Show solution button to see the answer.
Nesting elements
Elements can be placed within other elements. This is called nesting . If we wanted to state that our cat is very grumpy, we could wrap the word very in a <strong> element, which means that the word is to have strong(er) text formatting:
There is a right and wrong way to do nesting. In the example above, we opened the p element first, then opened the strong element. For proper nesting, we should close the strong element first, before closing the p .
The following is an example of the wrong way to do nesting:
The tags have to open and close in a way that they are inside or outside one another . With the kind of overlap in the example above, the browser has to guess at your intent. This kind of guessing can result in unexpected results.
Void elements
Not all elements follow the pattern of an opening tag, content, and a closing tag. Some elements consist of a single tag, which is typically used to insert/embed something in the document. Such elements are called void elements . For example, the <img> element embeds an image file onto a page:
This would output the following:
Note: In HTML, there is no requirement to add a / at the end of a void element's tag, for example: <img src="images/cat.jpg" alt="cat" /> . However, it is also a valid syntax, and you may do this when you want your HTML to be valid XML.
Elements can also have attributes. Attributes look like this:

Attributes contain extra information about the element that won't appear in the content. In this example, the class attribute is an identifying name used to target the element with style information.
An attribute should have:
- A space between it and the element name. (For an element with more than one attribute, the attributes should be separated by spaces too.)
- The attribute name, followed by an equal sign.
- An attribute value, wrapped with opening and closing quote marks.
Active learning: Adding attributes to an element
The <img> element can take a number of attributes, including:
The src attribute is a required attribute that specifies the location of the image. For example: src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mdn/beginner-html-site/gh-pages/images/firefox-icon.png" .
The alt attribute specifies a text description of the image. For example: alt="The Firefox icon" .
The width attribute specifies the width of the image with the unit being pixels. For example: width="300" .
The height attribute specifies the height of the image with the unit being pixels. For example: height="300" .
Edit the line below in the Input area to turn it into an image.
- Find your favorite image online, right click it, and press Copy Image Link/Address .
- Back in the area below, add the src attribute and fill it with the link from step 1.
- Set the alt attribute.
- Add the width and height attributes.
You will be able to see your changes live in the Output area.
If you make a mistake, you can always reset it using the Reset button. If you get really stuck, press the Show solution button to see the answer.
Boolean attributes
Sometimes you will see attributes written without values. This is entirely acceptable. These are called Boolean attributes. Boolean attributes can only have one value, which is generally the same as the attribute name. For example, consider the disabled attribute, which you can assign to form input elements. (You use this to disable the form input elements so the user can't make entries. The disabled elements typically have a grayed-out appearance.) For example:
As shorthand, it is acceptable to write this as follows:
For reference, the example above also includes a non-disabled form input element. The HTML from the example above produces this result:
Omitting quotes around attribute values
If you look at code for a lot of other sites, you might come across a number of strange markup styles, including attribute values without quotes. This is permitted in certain circumstances, but it can also break your markup in other circumstances. The element in the code snippet below, <a> , is called an anchor. Anchors enclose text and turn them into links. The href attribute specifies the web address the link points to. You can write this basic version below with only the href attribute, like this:
Anchors can also have a title attribute, a description of the linked page. However, as soon as we add the title in the same fashion as the href attribute there are problems:
As written above, the browser misinterprets the markup, mistaking the title attribute for three attributes: a title attribute with the value The , and two Boolean attributes, Mozilla and homepage . Obviously, this is not intended! It will cause errors or unexpected behavior, as you can see in the live example below. Try hovering over the link to view the title text!
Always include the attribute quotes. It avoids such problems, and results in more readable code.
Single or double quotes?
In this article, you will also notice that the attributes are wrapped in double quotes. However, you might see single quotes in some HTML code. This is a matter of style. You can feel free to choose which one you prefer. Both of these lines are equivalent:
Make sure you don't mix single quotes and double quotes. This example (below) shows a kind of mixing of quotes that will go wrong:
However, if you use one type of quote, you can include the other type of quote inside your attribute values:
To use quote marks inside other quote marks of the same type (single quote or double quote), use character references . For example, this will break:
Instead, you need to do this:
Anatomy of an HTML document
Individual HTML elements aren't very useful on their own. Next, let's examine how individual elements combine to form an entire HTML page:
Here we have:
- <!DOCTYPE html> : The doctype. When HTML was young (1991-1992), doctypes were meant to act as links to a set of rules that the HTML page had to follow to be considered good HTML. Doctypes used to look something like this: html <! DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd" > More recently, the doctype is a historical artifact that needs to be included for everything else to work right. <!DOCTYPE html> is the shortest string of characters that counts as a valid doctype. That is all you need to know!
- <html></html> : The <html> element. This element wraps all the content on the page. It is sometimes known as the root element.
- <head></head> : The <head> element. This element acts as a container for everything you want to include on the HTML page, that isn't the content the page will show to viewers. This includes keywords and a page description that would appear in search results, CSS to style content, character set declarations, and more. You will learn more about this in the next article of the series.
- <meta charset="utf-8"> : The <meta> element. This element represents metadata that cannot be represented by other HTML meta-related elements, like <base> , <link> , <script> , <style> or <title> . The charset attribute specifies the character encoding for your document as UTF-8, which includes most characters from the vast majority of human written languages. With this setting, the page can now handle any textual content it might contain. There is no reason not to set this, and it can help avoid some problems later.
- <title></title> : The <title> element. This sets the title of the page, which is the title that appears in the browser tab the page is loaded in. The page title is also used to describe the page when it is bookmarked.
- <body></body> : The <body> element. This contains all the content that displays on the page, including text, images, videos, games, playable audio tracks, or whatever else.
Active learning: Adding some features to an HTML document
If you want to experiment with writing some HTML on your local computer, you can:
- Copy the HTML page example listed above.
- Create a new file in your text editor.
- Paste the code into the new text file.
- Save the file as index.html .
Note: You can also find this basic HTML template on the MDN Learning Area GitHub repo .
You can now open this file in a web browser to see what the rendered code looks like. Edit the code and refresh the browser to see what the result is. Initially, the page looks like this:
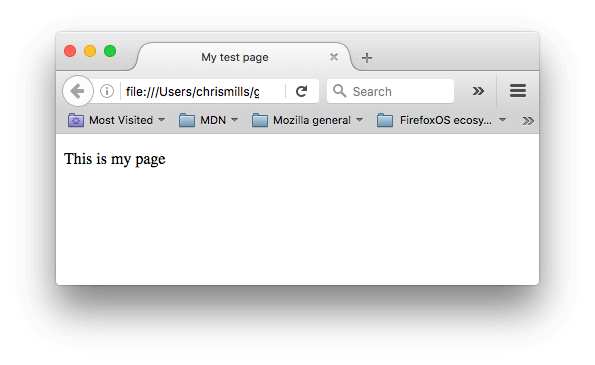
In this exercise, you can edit the code locally on your computer, as described previously, or you can edit it in the sample window below (the editable sample window represents just the contents of the <body> element, in this case). Sharpen your skills by implementing the following tasks:
- Just below the opening tag of the <body> element, add a main title for the document. This should be wrapped inside an <h1> opening tag and </h1> closing tag.
- Edit the paragraph content to include text about a topic that you find interesting.
- Make important words stand out in bold by wrapping them inside a <strong> opening tag and </strong> closing tag.
- Add a link to your paragraph, as explained earlier in the article .
- Add an image to your document. Place it below the paragraph, as explained earlier in the article . Earn bonus points if you manage to link to a different image (either locally on your computer or somewhere else on the web).
Whitespace in HTML
In the examples above, you may have noticed that a lot of whitespace is included in the code. This is optional. These two code snippets are equivalent:
No matter how much whitespace you use inside HTML element content (which can include one or more space characters, but also line breaks), the HTML parser reduces each sequence of whitespace to a single space when rendering the code. So why use so much whitespace? The answer is readability.
It can be easier to understand what is going on in your code if you have it nicely formatted. In our HTML we've got each nested element indented by two spaces more than the one it is sitting inside. It is up to you to choose the style of formatting (how many spaces for each level of indentation, for example), but you should consider formatting it.
Let's have a look at how the browser renders the two paragraphs above with and without whitespace:
Note: Accessing the innerHTML of elements from JavaScript will keep all the whitespace intact. This may return unexpected results if the whitespace is trimmed by the browser.
Character references: including special characters in HTML
In HTML, the characters < , > , " , ' , and & are special characters. They are parts of the HTML syntax itself. So how do you include one of these special characters in your text? For example, if you want to use an ampersand or less-than sign, and not have it interpreted as code.
You do this with character references . These are special codes that represent characters, to be used in these exact circumstances. Each character reference starts with an ampersand (&), and ends with a semicolon (;).
| Literal character | Character reference equivalent |
|---|---|
| < | |
| > | |
| " | |
| ' | |
| & |
The character reference equivalent could be easily remembered because the text it uses can be seen as less than for < , quotation for " and similarly for others. To find more about entity references, see List of XML and HTML character entity references (Wikipedia).
In the example below, there are two paragraphs:
In the live output below, you can see that the first paragraph has gone wrong. The browser interprets the second instance of <p> as starting a new paragraph. The second paragraph looks fine because it has angle brackets with character references.
Note: You don't need to use entity references for any other symbols, as modern browsers will handle the actual symbols just fine as long as your HTML's character encoding is set to UTF-8 .
HTML comments
HTML has a mechanism to write comments in the code. Browsers ignore comments, effectively making comments invisible to the user. The purpose of comments is to allow you to include notes in the code to explain your logic or coding. This is very useful if you return to a code base after being away for long enough that you don't completely remember it. Likewise, comments are invaluable as different people are making changes and updates.
To write an HTML comment, wrap it in the special markers <!-- and --> . For example:
As you can see below, only the first paragraph is displayed in the live output.
You made it to the end of the article! We hope you enjoyed your tour of the basics of HTML.
At this point, you should understand what HTML looks like, and how it works at a basic level. You should also be able to write a few elements and attributes. The subsequent articles of this module go further on some of the topics introduced here, as well as presenting other concepts of the language.
- As you start to learn more about HTML, consider learning the basics of CSS (Cascading Style Sheets). CSS is the language used to style web pages, such as changing fonts or colors or altering the page layout. HTML and CSS work well together, as you will soon discover.
- Applying color to HTML elements using CSS
Popular Tutorials
Learn python interactively, popular examples.
- Introduction
What is HTML?
HTML Basics
- HTML Web Design Basics
- HTML Paragraphs
- HTML Headings
- HTML Comments
- HTML Unordered List
- HTML Ordered List
- HTML Description List
- HTML Line Break
- HTML Pre Tag
- HTML Horizontal Line
HTML Inline
- HTML Block and Inline
- HTML Images
- HTML Italic
- HTML Superscript and Subscript
- HTML Formatting
- HTML Meta Elements
- HTML Favicon
- HTML Form Elements
- HTML Form Action
Semantic HTML
- HTML Semantic HTML
- HTML div Tag
- HTML aside Tag
- HTML section Tag
- HTML footer Tag
- HTML main Tag
- HTML figure and figcaption
- HTML Accessibility
HTML, CSS & JavaScript
- HTML Layout
- HTML Responsive Web Design
- HTML and JavaScript
Graphics & Media
- HTML Canvas
HTML Miscellaneous
- HTML Iframes
- HTML Entities
- HTML Quotations
- HTML File Paths
- HTML Emojis
- HTML Symbols
Web Tutorials
- HTML <main> Tag
Web Design Basics: How HTML, CSS and JavaScript Work?
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a markup language used to structure and organize the content on a web page. It uses various tags to define the different elements on a page, such as headings, paragraphs, and links.
- HTML Hierarchy
HTML elements are hierarchical, which means that they can be nested inside each other to create a tree-like structure of the content on the web page.
This hierarchical structure is called the DOM (Document Object Model), and it is used by the web browser to render the web page. For example,
Browser Output

In this example, the html element is the root element of the hierarchy and contains two child elements: head and body . The head element, in turn, contains a child element called the title , and the body element contains child elements: h1 and p .
Let's see the meaning of the various elements used in the above example.
- <html> : the root element of the DOM, and it contains all of the other elements in the code
- <head> : contains metadata about the web page, such as the title and any linked CSS or JavaScript files
- <title> : contains the title of the web page, which will be displayed in the web browser's title bar or tab
- <body> : contains the main content of the web page, which will be displayed in the web browser's window
- <p> : contains the paragraphs of text on the web page
- <strong> , <em> : child elements of the <p> elements, they are used to mark text as important and emphasized respectively
Note : Only the elements inside the <body> tag renders in the web browser.
- What are HTML elements?
HTML elements consist of several parts, including the opening and closing tags, the content, and the attributes. Here is an explanation of each of these parts:
- The opening tag : This consists of the element name, wrapped in angle brackets. It indicates the start of the element and the point at which the element's effects begin.
- The closing tag : This is the same as the opening tag, but with a forward slash before the element name. It indicates the end of the element and the point at which the element's effects stop.
- The content : This is the content of the element, which can be text, other elements, or a combination of both.
- The element: The opening tag, the closing tag, and the content together make up the element.
- What are HTML Attributes?
HTML elements can have attributes, which provide additional information about the element. They are specified in the opening tag of the element and take the form of name-value pairs. Let's see an example:
The href is an attribute. It provides the link information about the <a> tag. In the above example,
- href - the name of attribute
- https://www.programiz.com - the value of attribute
Note : HTML attributes are mostly optional.
- HTML Syntax
We need to follow a strict syntax guidelines to write valid HTML code. This includes the use of tags, elements, and attributes, as well as the correct use of indentation and white space. Here are some key points about HTML syntax:
1. HTML tags consist of the element name, wrapped in angle brackets. For example, <h1> , <p> , <img> are some HTML tags.
2. HTML elements are created by enclosing the content of the element inside the opening and closing tags of the element. For example,
is an HTML element.
3. HTML attributes are used to provide additional information about HTML elements and are specified in the opening tag of the element. For example,
Here, target is an attribute.
4. HTML code should be well-formed and properly indented, with each element on its own line and each level of hierarchy indented by one level. This makes the code easier to read and understand, and can help to avoid errors. For example,
Table of Contents
Related tutorials.
Programming
- HTML CSS Exercises Home
- ▼HTML Exercises Basic
- Abbreviation
- Define Description
- Description List
- Definition Term
- Noscript Tag
- Order list Tag
- Optgroup Tag
- Paragraph Tag
- parameter Tag
- Preformatted text Tag
- Progress Tag
- Quotation Tag
- Strikethrough Tag
- Subscript Tag
- Summary Tag
- Supperscript Tag
- Table body Tag
- Table data Tag
- Textarea Tag
- Table footer Tag
- Table column head Tag
- Table Header Tag
- Table row Tag
- Underline Tag
- UnOrder list Tag
- Variable Tag
- Word break Tag
- ..More to come..
HTML5 Basic (Tag and attribute) - Exercises, Practice, Solution
Html5 basic (tag and attribute) [exercises with solution].
1. How to comment HTML tags?
2. How to create a hyperlink?[More question on this]
3. How to author an abbreviation or an acronym?
4. What is the correct way to write address in an HTML document?
5. How to create an area inside an image-map?[More question on this]
6. Create an HTML document which uses article element?
7. Create an HTML document which uses aside element?
8. How to embed audio in a HTML document?[More question on this]
9. How to write bold text using HTML tags?
10. How to specify the base URL/target for all relative URLs in a document?
11. How to isolate a part of the text that might be formatted in a different direction from other text outside it?
12. How to override the current text direction?
13. How to define a section that is quoted from another source?
14. How to define the document's body?
15. How to define a single line break?
16. How to define a clickable button?[more question on this]
17. How to draw graphics, on the fly, via scripting?[more question on this]
18. How to define a table caption?
19. How to define the title of an HTML document?
20. How to specify the column properties of each column within a colgroup element?
21. How to define a piece of code?[more question on this]
22. How to specify a list of pre-defined options for input controls?
23. How to define a description/value of a term in a description list?
24. How to semantically delete text from an HTML document?[more question on this]
25. How to define additional details that the user can view or hide?
26. How to represent the defining instance of a term?
27. How to define a dialog box or window with an HTML tag?
28. How to define a section in a document?
29. How to define a definition list?
30. How to define a term or name in a definition list?
31. How to emphasize text in an HTML document?
32. How to define a container for an external (non-HTML) application?
33. How to groups related elements in a form?
34. How to define a caption for a figure element?
35. How to specify self-contained content?
36. How to define a footer for a document or section?
37. How to define an HTML form for user input?
38. How to define an HTML heading?
39. How to define information about the document?
40. How to define a header for a document or section?
41. How to define a thematic change in the content?
42. How to define the root of an HTML document?
43. How to define a part of text in an alternate voice or mood?
44. How to define an inline frame? [more question on this]
45. How to define an image? [more question on this]
46. How to define an input control? [more question on this]
47. How to define a text that has been inserted into a document? [more question on this]
48. How to define a keyboard input?
49. How to define a key-pair generator field (for forms)?[more question on this]
50. How to define a label for an input element?[more question on this]
51. How to define a caption for a fieldset element?
52. How to define a list item?
53. How to define the relationship between a document and other resources? [more question on this]
54. How to specify the main content of a document?
55. How to define a client-side image-map?
56. How to define marked/highlighted text?
57. How to define a list/menu of commands?
58. How to define metadata about an HTML document?[more question on this]
59. How to define a scalar measurement within a known range?[more question on this]
60. How to define navigation links?
61. How to define an alternate content for users that do not support client-side scripts?
62. How to define an embedded object?[more question on this]
63. How to define an ordered list?[more question on this]
64. How to define a group of related options in a drop-down list?[more question on this]
65. How to define an option in a drop-down list?[more question on this]
66. How to define the result of a calculation?[more question on this]
67. How to define a paragraph?
68. How to define a parameter for an object?
69. How to define preformatted text?
70. How to represent the progress of a task?
71. How to define a short quotation?
72. How to define text that is no longer correct?
73. How to define a client-side script?[more question on this]
74. How to define a drop-down list?[more question on this]
75. How to define smaller text?
76. How to define multiple media resources for media elements?[more question on this]
77. How to define a section in a document?
78. How to define important text?
79. How to define style information for a document?[more question on this]
80. How to define subscripted text?
81. How to define a visible heading for a details element?
82. How to define superscripted text?
83. How to define a table?
84. How to group the body content in a table?
85. How to define a cell in a table?
86. How to define a multiline input control text area?
87. How to group the footer content in a table?
88. How to define a header cell in a table?[more question on this]
89. How to group the header content in a table?
90. How to define a title for the document?
91. How to define a row in a table?
92. How to underline a text in an HTML document?
93. How to define an unordered list?
94. How to define a variable?
95. How to define a video or movie?[more question on this]
96. How to define a possible link-break?
See the Pen html css common editor by w3resource ( @w3resource ) on CodePen .
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
Follow us on Facebook and Twitter for latest update.
- Weekly Trends and Language Statistics

- HTML Basics
Basic HTML Exercises about HTML Links, Paragraphs, Layouts, Tags, & Text Formatting
Steps to Create a Webpage in HTML using Notepad
A website is simply a collection of web-pages. A web page or web documents written in HTML (HyperText Markup Language) . These Web pages can be viewed using any web browser and Internet.
Html Language is used to write code and programs to create a webpage. It is easy to create a webpage and you can learn it with few basic steps mentioned below:
HTML Program or page can be created by many HTML or Text Editors. These editors are software that help us writing our code with easy user interface. Today, we will see how to create a html or webpage using Notepad Editor.
Notepad editor is built-in text editor in Windows Computers. You can find similar editors in Mac and Linux Operating system as well.
There are many advanced HTML editor or software are also available. However, we will recommend using default and simple editor like notepad for the beginners. That is always a good way to start learning HTML.
Creating a Simple HTML Page using Notepad Editor
Follow the four steps below to create your first web page with Notepad.
Step 1: Open Notepad (Windows)
Windows 8 or later: Open the Start Screen and Search (Type Notepad)
Windows 7 or previous Windows: Open Start > Programs > Accessories > Notepad
Step 2: Create a New Document
Go to Notepad Menu: File > New
A New blank document will be opened and you can start writing your first HTML Program here.
Step 3: Write Some HTML code or Program
Write some HTML code. If you do not know about HTML Yet, read few chapters in HTML Tutorials Section .
Write your own HTML code or simply copy the following HTML Simple Program into notepad document.
Step 4: Save the HTML Page
Go to Notepad Menu: File > Save (or use short-key CTRL + S)
It will ask you to Save the file on your computer. Give it a name with .html extension and Save it (for example program.html)
Note: HTML page should be saved with .html extension carefully.
Step 5: View the HTML Page using Browser
Web browsers are programs or software that are used to view Webpages/Websites. You can find Internet Explored by default if using Windows Computer machine. You can also download other popular web browsers such as Google Chrome or Firefox. Use any of them.
Now Simply, open the saved HTML file in any browser: Double click on the file or right-click on the file and choose “Open with” option to select other browser.
You HTML File will be opened in web browser and it will show output based on your html program.
Congratulations if you are able to run your first HTML Program.
You can now learn more about HTML Tags and create more HTML web pages. Using these HTML Pages, you can easily create your own website as well.
Program to see difference between paragraphs & normal text with line break
We can write some text in body and it will be displayed in browser. All text will be displayed in single line until it reach browser window border. If you want to add some line break, you can use <br/> tag.
Another option is to use text between paragraph tag. You can use multiple paragraph tags to display multiple text paragraphs.
Different between HTML Paragraph & Regular line break:
Using <br/> tag, it only add a single line break. While using <p> tag it creates a paragraph with extra spacing before and after the paragraph.
Write an HTML program to display hello world.
Description: You need to write an HTML program to display hello world on screen.
Hint : You need to type Hello World inside the body tag.
Write a program to create a webpage to print values 1 to 5
Description: Write a program to create a webpage to print values 1 to 5 on the screen.
Hint: Put values inside the body tag.
Write a program to create a webpage to print your city name in red color.
Description: Write a program to create a webpage to print your city name in red color.
Hint: You need to put the city name inside the body tag and use color attribute to provide the color.
Write a program to print a paragraph with different font and color.
Description: Create a webpage to print a paragraph with 4 – 5 sentences. Each sentence should be in a different font and color.
Hint: Put the paragraph content inside the body tag and paragraph should be enclosed in <p> tag.

- HTML Exercises Categories
- HTML All Exercises & Assignments
- HTML Top Exercises
- HTML Paragraphs

- HTML Lab Assignments
HTML Assignment and HTML Examples for Practice
Text formatting, working with image, working with link, frame set & iframe.
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Auto Racing
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
As recruiting rebounds, the Army will expand basic training to rebuild the force for modern warfare
FILE - Students gather during physical training exercises in the new Army prep course at Fort Jackson in Columbia, S.C. Saturday, Aug. 27, 2022. The Army will expand its basic combat training for newly enlisted soldiers in what its leaders hope reflects a turning point as it prepares to meet the challenges of future wars. The added training will begin in October 2024 and comes as the Army works to reverse several years of dismal recruiting when it failed to meet its enlistment goals. (AP Photo/Sean Rayford, File)
FILE - Students enlisted in the new Army prep course work together in barracks at Fort Jackson in Columbia, S.C., Aug. 26, 2022. The Army will expand its basic combat training for newly enlisted soldiers in what its leaders hope reflects a turning point as it prepares to meet the challenges of future wars. The added training will begin in October 2024 and comes as the Army works to reverse several years of dismal recruiting when it failed to meet its enlistment goals. (AP Photo/Sean Rayford, File)
- Copy Link copied
WASHINGTON (AP) — Buoyed by an increase in recruiting, the Army will expand its basic combat training in what its leaders hope reflects a turning point as it prepares to meet the challenges of future wars.
The added training will begin in October and comes as the Army tries to reverse years of dismal recruiting when it failed to meet its enlistment goals. New units in Oklahoma and Missouri will train as many as 4,000 recruits every year.
Army leaders are optimistic they will hit their target of 55,000 recruits this year and say the influx of new soldiers forced them to increase the number of training sites.
“I am happy to say last year’s recruiting transformation efforts have us on track to make this year’s recruiting mission, with thousands awaiting basic training” in the next year, Army Secretary Christine Wormuth said. Adding the two new locations, she said, is a way to get the soldiers trained and into units quickly, “with further expansion likely next spring if our recruiting numbers keep improving.”
The expanded training is part of a broader effort to restructure the Army so it is better able to fight against a sophisticated adversary such as Russia or China. The U.S. military spent much of the past two decades battling insurgent groups in Iraq and Afghanistan rather than fighting a broader war with another high-tech, more capable nation.
Brig. Gen. Jenn Walkawicz, head of operations for the Army’s Training and Doctrine Command, said there will be two new training companies at Fort Sill in Oklahoma and two at Fort Leonard Wood in Missouri.
Driving the growth is the successful Future Soldier Prep Course , which was created at Fort Jackson, South Carolina, in August 2022 as a new way to bolster enlistments. That program gives lower-performing recruits up to 90 days of academic or fitness instruction to help them meet military standards and move on to basic training.
Created two years ago, the program has been cited as a key reason Army leaders expect that this fall they will reverse several years of recruiting shortfalls. In the budget year that ended Sept. 30, the Army brought in a bit more than 50,000 recruits , falling far short of the publicly stated “stretch goal” of 65,000.
The Army has 151 training companies overall that work with recruits at Fort Jackson and Fort Moore, Georgia, in addition to the 15 training companies assigned to the prep course. Army leaders have expanded the prep course, which is expected to bring in nearly 20,000 recruits this budget year and that total is expected to spike in 2025.
Due to the Army’s recruiting struggles, the number of recruits going through basic training dropped in recent years. As a result, the 15 training units, which total 27 soldiers each, including 16 drill sergeants, were available for the prep course. But as the prep course grows, those units are not available to do basic training.
“We don’t want to mess with that because right now that formula’s working and it’s provided a lot of value for the Army,” Walkawicz said. So, the Army is creating the four new companies and has developed plans for more if needed.
She added that Fort Sill and Fort Leonard Wood have the infrastructure, the barracks and the room to accommodate the new units and could take more if needed. The costs of the program are limited because the Army already had the equipment and rooms required, but there will be maintenance, food, staffing and other costs. Army officials did not provide a total price.
The move to add units is the latest change in what has been a tumultuous time for the Army. Coming out of the Iraq and Afghanistan wars, when the service grew dramatically to fill the nation’s combat needs, the U.S. military began to see recruiting dip.
Unemployment has been low, corporate jobs pay well and offer good benefits, and, according to estimates, just 23% of people age 17 to 24 are physically, mentally and morally qualified to serve without receiving some type of waiver. Moral behavior issues include drug use, gang ties or a criminal record.
Those problems were only amplified as the coronavirus pandemic took hold, preventing recruiters from meting with students in person at schools, fairs and other public events.
In 2022, the Army fell 15,000 short of its enlistment goal of 60,000, and the other services had to dig deep into their pools of delayed entry candidates in order to meet their recruiting numbers. Then in 2023, the Army, Navy and Air Force all missed their recruitment targets. The Marine Corps and the tiny Space Force have consistently hit their goals.
Partly in response to the recruiting shortfalls, Army leaders slashed the size of the force by about 24,000, or almost 5%. They said many of the cuts were in already vacant jobs.
HTML for Beginners – How to Get Started with Web Development Basics

Have you always been interested in learning HTML but didn't know where or how to start? Well, this guide is for you.
In it, we will look at:
- An introduction to HTML
A Brief History of HTML
Why learn html.
- Prerequisites for learning HTML
- A simple HTML page
- How to get started with HTML
Introduction to HTML

HTML is an abbreviation for HyperText Markup Language.
This acronym is composed of two main parts: HyperText and Markup Language.
What does “HyperText” mean?
HyperText refers to the hyperlinks or simply links that an HTML page may contain. A HyperText can contain a link to a website, web content, or a web page.
What is a “Markup language”?
A markup language is a computer language that consists of easily understood keywords, names, or tags that help format the overall view of a page and the data it contains. In other words, it refers to the way tags are used to define the page layout and elements within the page.
Since we now know what HyperText and Markup Language mean, we can also understand what these terms mean when put together.
What is HTML?
HTML or HyperText Markup Language is a markup language used to describe the structure of a web page. It uses a special syntax or notation to organize and give information about the page to the browser.
HTML consists of a series of elements that tell the browser how to display the content. These elements label pieces of content such as "this is a heading", "this is a paragraph", "this is a link", and so on. They usually have opening and closing tags that surround and give meaning to each piece of content.
There are different tag options you can use to wrap text to show whether the text is a heading, a paragraph, or a list. Tags look like <h1> (opening tag) and </h1> (closing tag).
Let's see some other examples:
The first version of HTML was written in 1993; since then, many different versions of HTML have been released, allowing developers to create interactive web pages with animated images, sound, and gimmicks of all kinds.
The most widely used version throughout the 2000's was HTML 4.01, which became an official standard in December 1999.
Another version, XHTML, was a rewrite of HTML as an XML language.
In 2014, HTML5 was released, and it took over from previous versions of HTML. This version includes new elements and capabilities added to the language. These new features allow you to create more powerful and complex websites and web apps, while keeping the code easier to read.
HTML is the foundation of all web pages. Without HTML, you would not be able to organize text or add images or videos to your web pages. HTML is the root of everything you need to know to create great-looking web pages!
As the name suggests, hypertext refers to cross-referencing (or linking) between different related sections or webpages on the world-wide-web.
HyperText mark-up language is a standard mark-up language that allows developers to structure, link, and present webpages on the world-wide-web. So it is important to know the structure and layout of the website that you would like to build.
Prerequisites for Learning HTML
HTML is a relatively easy language and does not require any formal education. So basically, there are no prerequisites for learning it.
HTML is text-based computer coding, and anyone can learn and run it, as long as they understand letters and basic symbols. So, all you need is basic computer knowledge and the ability to work with files.
Of course, any knowledge of other programming languages will enhance your abilities with HTML and web development, but this is not a prerequisite for learning HMTL.
What a Simple HTML Page Looks Like
Alright let's see what's going on here:
Note: In HTML, an opening tag begins a section of page content, and a closing tag ends it.
For example, to markup a section of text as a paragraph, you would open the paragraph with an opening paragraph tag, which is "<p>", and close it with a closing paragraph tag, which is "</p>".
In closing tags, the element is always preceded by a forward slash ("/").
How to Get Started with HTML
There are many different online resources that can help you learn HTML. I recommend the following ones:
- freeCodecamp : an interactive and free learning platform that aims to make learning web development possible for anyone. This platform has well-structured content, good exercises to help you grasp the concept, and a supportive community that can help you in case of any difficulties during the course.
- W3Schools : a learning platform that covers all the aspects of web development. It explains HTML tags in a very understandable and in-depth way, which also makes it easier to learn how to use them well.
Learning some of the basics of HTML may not take much time for some people. But getting really good at HTML, like any skill, definitely takes time. You might be able to grasp the basic HTML tags in a few hours, but make sure to take the time to learn how to properly work with them.
My name is Patrick Cyubahiro, I am a software & web developer, UI/UX designer, technical writer, and Community Builder.
I hope you enjoyed reading this article; and if it was helpful to you, feel free to let me know on Twitter: @ Pat_Cyubahiro or via email: ampatrickcyubahiro[at]gmail.com
Thanks for reading and happy learning!
Community Builder, Software & web developer, UI/IX Designer, Technical Writer.
If you read this far, thank the author to show them you care. Say Thanks
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp's open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
- Work & Careers
- Life & Arts
Universal basic income: the bad idea that never quite dies
To read this article for free register now.
Once registered, you can:
- Read free articles
- Get our Editor's Digest and other newsletters
- Follow topics and set up personalised events
- Access Alphaville: our popular markets and finance blog
- Global news & analysis
- Expert opinion
- Special features
- FirstFT newsletter
- Videos & Podcasts
- Android & iOS app
- FT Edit app
- 10 gift articles per month
Explore more offers.
Standard digital.
- FT Digital Edition
Premium Digital
Print + premium digital, ft professional, weekend print + standard digital, weekend print + premium digital.
Then $75 per month. Complete digital access to quality FT journalism. Cancel anytime during your trial.
- Global news & analysis
- Exclusive FT analysis
- FT App on Android & iOS
- FirstFT: the day's biggest stories
- 20+ curated newsletters
- Follow topics & set alerts with myFT
- FT Videos & Podcasts
- 20 monthly gift articles to share
- Lex: FT's flagship investment column
- 15+ Premium newsletters by leading experts
- FT Digital Edition: our digitised print edition
- Weekday Print Edition
- Videos & Podcasts
- Premium newsletters
- 10 additional gift articles per month
- FT Weekend Print delivery
- Everything in Standard Digital
- Everything in Premium Digital
Today's FT newspaper for easy reading on any device. This does not include ft.com or FT App access.
- 10 monthly gift articles to share
- Everything in Print
- Make and share highlights
- FT Workspace
- Markets data widget
- Subscription Manager
- Workflow integrations
- Occasional readers go free
- Volume discount
Essential digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
Terms & Conditions apply
Explore our full range of subscriptions.
Why the ft.
See why over a million readers pay to read the Financial Times.
- HTML Tutorial
- HTML Exercises
- HTML Attributes
- Global Attributes
- Event Attributes
- HTML Interview Questions
- DOM Audio/Video
- HTML Examples
- Color Picker
- A to Z Guide
- HTML Formatter
HTML Introduction
- HTML Editors
- HTML Basics
- HTML Comments
- HTML Elements
- HTML Headings
- HTML Paragraphs
- HTML Text Formatting
- HTML Quotations
- HTML Colors
- HTML Links Hyperlinks
- HTML Images
- HTML Favicon
- HTML Tables
- HTML Ordered Lists
- HTML Unordered Lists
- HTML Description Lists
- HTML Block and Inline Elements
- HTML Iframes
- HTML File Paths
- HTML Layout
- HTML Computer Code Elements
- HTML5 Semantics
- HTML Entities
- HTML Symbols
- HTML Emojis
- HTML Charsets
- HTML URL Encoding
- HTML Responsive Web Design
HTML Graphics
- SVG Tutorial
HTML Tutorial References
- HTML Tags - A to Z List
- HTML Attributes Complete Reference
- HTML Global Attributes
- HTML5 Complete Reference
- HTML5 MathML Complete Reference
- HTML DOM Complete Reference
- HTML DOM Audio/Video Complete Reference
- SVG Element Complete Reference
- SVG Attribute Complete Reference
- SVG Property Complete Reference
- HTML Canvas Complete Reference
- HTML Exercises, Practice Questions and Solutions
HTML, or HyperText Markup Language , is the standard markup language used to create web pages. It’s a combination of Hypertext, which defines the link between web pages, and Markup language, which is used to define the text document within tags to structure web pages. This language is used to annotate text so that machines can understand and manipulate it accordingly. HTML is human-readable and uses tags to define what manipulation has to be done on the text. This guide will help you understand the workings of HTML and explain it with examples.
Table of Content
What is HTML?
Features of html, html elements and tags, html page structure, web browsers.
- Why learn HTML?
Advantages of HTML
Disadvantages of html.
HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language and it is used to create webpages. It uses HTML tags and attributes to describe the structure and formatting of a web page.
HTML consists of various elements, that are responsible for telling search engines how to display page content. For example, headings, lists, images, links, and more.
HTML Example
- It is easy to learn and easy to use.
- It is platform-independent.
- Images, videos, and audio can be added to a web page.
- Hypertext can be added to the text.
- It is a markup language.
HTML uses predefined tags and elements that instruct the browser on how to display the content. HTML elements include an opening tag, some content, and a closing tag. It’s important to remember to include closing tags. If omitted, the browser applies the effect of the opening tag until the end of the page.
This section will dive into the basic structure of an HTML page, which includes essential building-block elements like doctype declaration, HTML, head, title, and body elements.

The basic structure of an HTML page is shown below. It contains the essential building-block elements (i.e. doctype declaration, HTML, head, title, and body elements) upon which all web pages are created.
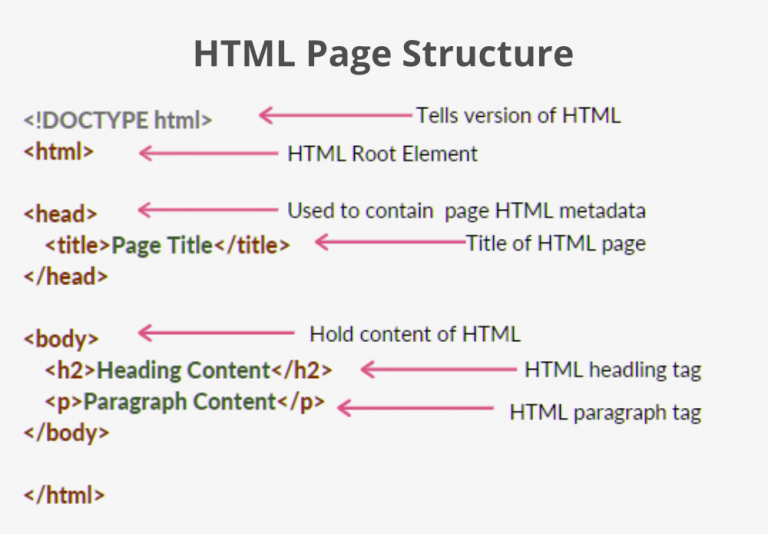
- <!DOCTYPE html> – This is the document type declaration (not technically a tag). It declares a document as being an HTML document. The doctype declaration is not case-sensitive.
- <html> – This is called the HTML root element. All other elements are contained within it.
- <head> – The head tag contains the “behind the scenes” elements for a webpage. Elements within the head aren’t visible on the front end of a webpage. HTML elements used inside the <head> element include:
- <style> – This HTML tag allows us to insert styling into our web pages and make them appealing to look at with the help of CSS.
- <title> – The title is what is displayed on the top of your browser when you visit a website and contains the title of the webpage that you are viewing.
- <base> – It specifies the base URL for all relative URL’s in a document.
- <noscript> – Defines a section of HTML that is inserted when the scripting has been turned off in the user’s browser.
- <script> – This tag is used to add functionality to the website with the help of JavaScript.
- <meta> – This tag encloses the metadata of the website that must be loaded every time the website is visited. For eg:- the metadata charset allows you to use the standard UTF-8 encoding on your website. This in turn allows the users to view your webpage in the language of their choice. It is a self-closing tag.
- <link> – The ‘link’ tag is used to tie together HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. It is self-closing.
- <body> – The body tag is used to enclose all the visible content of a webpage. In other words, the body content is what the browser will show on the front end.
An HTML document can be created using an HTML text editor . Save the text file using the “ .html” or “ .htm” extension. Once saved as an HTML document, the file can be opened as a webpage in the browser.
Note: Basic/built-in text editors are Notepad (Windows) and TextEdit (MacOS) . Other advanced text editors include Sublime Text, Visual Studio Code, Froala , etc.
This example illustrates the basic structure of HTML code.

Unlike other programming languages, HTML does not show output on the compiler.
Web browsers show the results of an HTML code. It reads HTML files and determines how to show content with the help of HTML tags.
Any web browser ( Google, Safari, Mozilla Firefox , etc) can be used to open a . HTML file and view the results.
Why learn HTML?
- It is a simple markup language. Its implementation is easy.
- It is used to create a website.
- Helps in developing fundamentals about web programming.
- Boost professional career.
HTML History
HTML is a markup language used by the browser to manipulate text, images, and other content, in order to display it in the required format. HTML was created by Tim Berners-Lee in 1991 . The first-ever version of HTML was HTML 1.0 , but the first standard version was HTML 2.0 , published in 1995.
Currently, we are using HTML5 , which is the latest and most recent version of HTML.
- HTML is used to build websites.
- It is supported by all browsers.
- It can be integrated with other languages like CSS , JavaScript , etc.
- HTML can only create static web pages. For dynamic web pages, other languages have to be used.
- A large amount of code has to be written to create a simple web page.
- The security feature is not good.
In conclusion, mastering HTML is a fundamental step in your web development journey. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for understanding HTML, from the basics to more advanced topics. Remember, HTML is more than just a markup language – it’s a powerful tool for creating engaging, accessible, and SEO-friendly websites.
To learn more about HTML, visit the HTML Tutorial Page.
Master The Art of Web Development with Full Stack Web Development
Frequently Asked Questions about HTML Introduction
What are the basics of html.
HTML basics include understanding the syntax, elements/tags, attributes, structure and formatting of HTML file.
What are the 5 uses of HTML?
5 key uses of HTML are: Creating web page. Integrating CSS and JavaScript Accessing web content Semantic markup Cross-platform compatibility
What is HTML syntax?
HTML syntax means the set of rules and regulation that defines how HTML code is structured and written.
What is the main concept of HTML?
HTML is a global markup language for web. You can create any a webpage using HTML and any browser can open that HTML file.

Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Web Technologies
- HTML-Basics
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
HTML Tutorial
Html graphics, html examples, html references.
Examples explained
HTML Attributes
Html headings, html paragraphs, html styles.
Advertisement
HTML Text Formatting
Html quotations and citations, html comments, html images, html tables, html block and inline elements, html div element, html classes, html layout, html iframe, html head elements, html scripts, html computercode elements, html form elements, html input types, html input attributes, html canvas graphics, html svg graphics, html geolocation, html local storage, more html examples.

COLOR PICKER

Contact Sales
If you want to use W3Schools services as an educational institution, team or enterprise, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Top Tutorials
Top references, top examples, get certified.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
W3Schools offers free online tutorials, references and exercises in all the major languages of the web. Covering popular subjects like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Python, SQL, Java, and many, many more.
The basic structure of an HTML form involves several key elements: <form> <!-- Your form elements go here --> </form> The <form> tag marks the beginning and end of your form. It acts as a container for various form elements. It commonly houses label, input types, textarea, and button tags.
Project 4: Crafting an eCommerce Page. Creating an eCommerce page is an excellent project for web developers looking to dive into the world of online retail. This project focuses on designing a web page that showcases products, includes product descriptions, prices, and a shopping cart.
In this project, you'll create a simple blog post page using HTML and CSS. You'll need to design the layout of the page, add a title, a featured image, and of course add some content to your dummy blog post. You can also add a sidebar with a few helpful links and widgets, like: An author bio with a photo.
Embark on your HTML learning journey by accessing our online practice portal. Choose exercises suited to your skill level, dive into coding challenges, and receive immediate feedback to reinforce your understanding. Our user-friendly platform makes learning HTML engaging and personalized, allowing you to develop your skills effectively.
HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language. HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages. HTML describes the structure of a Web page. HTML consists of a series of elements. HTML elements tell the browser how to display the content. HTML elements label pieces of content such as "this is a heading", "this is a paragraph", "this is ...
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the code that is used to structure a web page and its content. For example, content could be structured within a set of paragraphs, a list of bulleted points, or using images and data tables. As the title suggests, this article will give you a basic understanding of HTML and its functions.
HTML All Exercises & Assignments - Tutorials ClassIf you are seeking HTML assignment help, you can find a variety of exercises and solutions on this webpage. You can practice HTML basics, tags, attributes, forms, tables, and more. Learn HTML by doing these assignments and improve your web development skills.
Here are 10 HTML and CSS code challenges that'll help you take your skills to the next level. To get started, just pick a challenge, open up a workspace, and start coding. Note that while these challenges are designed for beginners, you'll still need to have a basic understanding of HTML and CSS. If you need a refresher, use the courses below:
HTML, a shorthand for Hyper Text Markup Language, is one of the most fundamental building blocks of the Web. HTML was officially born in 1993 and since then it evolved into its current state, moving from simple text documents to powering rich Web Applications. This handbook is aimed at a vast audience. First, the beginner.
How to create an HTML document. First, let's open Visual Studio Code (or your favorite code editor). In the folder of your choice, create a new file and name it index.html. In the index.html file, type ! (exclamation mark) and press enter.
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a language used for creating webpages which is the fundamental building block of the Web. One thing to remember about HTML is that it is a markup language with no programming constructs. Instead, the language provides us with a structure to build web pages. Using HTML, we can define web page elements such as ...
If you want to experiment with writing some HTML on your local computer, you can: Copy the HTML page example listed above. Create a new file in your text editor. Paste the code into the new text file. Save the file as index.html. Note: You can also find this basic HTML template on the MDN Learning Area GitHub repo.
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a markup language used to structure and organize the content on a web page. HTML Basics (With Examples). HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a markup language used to structure and organize the content on a web page. It uses various tags to define the different elements on a page, such as headings, paragraphs, and links.
HTML5 Basic (Tag and attribute) [exercises with solution] [An editor is available at the bottom of the page to write and execute the scripts.] 1. How to comment HTML tags? 2. How to create a hyperlink?[More question on this] 3. How to author an abbreviation or an acronym? 4. What is the correct way to write address in an HTML document? 5.
Step 4: Save the HTML Page. Go to Notepad Menu: File > Save (or use short-key CTRL + S) It will ask you to Save the file on your computer. Give it a name with .html extension and Save it (for example program.html) Note: HTML page should be saved with .html extension carefully.
With basic knowledge of HTML and CSS, you can give a parallax effect to a website. Using the parallax effect in web designing is really popular and it gives beautiful look and feels to the webpage. Give it a try and divide the whole page into three to four different sections. Set 3-4 background images, align the text for different sections, set ...
HTML Lab Assignments; HTML Assignment and HTML Examples for Practice. UNIT - 1 Text Formatting Assignment 1 Assignment 2 Assignment 3 Assignment 4 Assignment 5- India. ... Basic Form Registration Form Assignment 3 Assignment 4 Doctor Appointment Form Questions Paper . UNIT - 7 Frame set & iFrame
Southwest is under pressure to drum up revenue from an oversupplied U.S. market and an activist investor.
Attorney General Merrick Garland stressed his unhappiness with the Florida-based judge who said his appointment of a special counsel to prosecute Donald Trump was illegal, saying he wouldn't ...
FILE - Students gather during physical training exercises in the new Army prep course at Fort Jackson in Columbia, S.C. Saturday, Aug. 27, 2022. The Army will expand its basic combat training for newly enlisted soldiers in what its leaders hope reflects a turning point as it prepares to meet the challenges of future wars.
W3Schools offers free online tutorials, references and exercises in all the major languages of the web. Covering popular subjects like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Python, SQL, Java, and many, many more.
HTML or HyperText Markup Language is a markup language used to describe the structure of a web page. It uses a special syntax or notation to organize and give information about the page to the browser. HTML consists of a series of elements that tell the browser how to display the content. These elements label pieces of content such as "this is ...
Intel shares fall 20% on plans to cut 15,000 jobs; Former CNN anchor Don Lemon sues Elon Musk and X over cancelled show; Apple revenues rise on strong services business and iPad sales
HTML Page Structure. The basic structure of an HTML page is shown below. It contains the essential building-block elements (i.e. doctype declaration, HTML, head, title, and body elements) upon which all web pages are created. <!DOCTYPE html> - This is the document type declaration (not technically a tag). It declares a document as being an ...
Students enlisted in the new Army prep course work together in barracks at Fort Jackson in Columbia, S.C., Aug. 26, 2022. The Army will expand its basic combat training for newly enlisted soldiers ...
Consumers have reached their breaking point with $6 iced coffees and lemonades at Starbucks.. Starbucks sales dropped 3% globally at stores open for at least a year, including a 2% drop in its ...
Southwest's seat assignment plan came as it faced significant challenges in achieving its growth plans. The airline, which flies only Boeing 737 planes, said in April that it expected only 20 ...
View HTML Source Code: Click CTRL + U in an HTML page, or right-click on the page and select "View Page Source". This will open a new tab containing the HTML source code of the page. Inspect an HTML Element: Right-click on an element (or a blank area), and choose "Inspect" to see what elements are made up of (you will see both the HTML and the ...
W3Schools offers free online tutorials, references and exercises in all the major languages of the web. Covering popular subjects like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Python, SQL, Java, and many, many more.