- How to Order
Speech Writing
Introduction Speech

Introduction Speech- Tips & Examples
10 min read

People also read
The 10 Key Steps for Perfect Speech Writing
Understanding Speech Format - Simple Steps for Outlining
How to Start A Speech - 13 Interesting Ideas & Examples
20+ Outstanding Speech Examples for Your Help
Common Types of Speeches that Every Speechwriter Should Know
Good Impromptu Speech Topics for Students
Entertaining Speech Topics for Your Next Debate
Understanding Special Occasion Speech: Types, Steps, Examples and Tips
How to Write A Good Acceptance Speech?
Writing A Presentation Speech In English: Tips And Examples
Commemorative Speech - Writing Guide, Outline & Examples
Farewell Speech | Writing Tips & Examples
How to Write an Extemporaneous Speech? A Step-by-Step Guide
A Graduation Speech Writing Guide with Examples
Introduction speeches are all around us. Whenever we meet a new group of people in formal settings, we have to introduce ourselves. That’s what an introduction speech is all about.
When you're facing a formal audience, your ability to deliver a compelling introductory speech can make a lot of difference. With the correct approach, you can build credibility and connections.
In this blog, we'll take you through the steps to craft an impactful introduction speech. You’ll also get examples and valuable tips to ensure you leave a lasting impression.
So, let's dive in!
- 1. What is an Introduction Speech?
- 2. How to Write an Introduction Speech?
- 3. Introduction Speech Outline
- 4. Introduction Speech Example
- 5. Introduction Speech Ideas
- 6. 7 Tips for Delivering the Best Introduction Speech
What is an Introduction Speech?
An introduction speech, or introductory address, is a brief presentation at the beginning of an event or public speaking engagement. Its primary purpose is to establish a connection with the audience and to introduce yourself or the main speaker.
This type of speech is commonly used in a variety of situations, including:
- Public Speaking: When you step onto a stage to address a large crowd, you start with an introduction to establish your presence and engage the audience.
- Networking Events: When meeting new people in professional or social settings, an effective introduction speech can help you make a memorable first impression.
- Formal Gatherings: From weddings to conferences, introductions set the tone for the event and create a warm and welcoming atmosphere.
In other words, an introduction speech is simply a way to introduce yourself to a crowd of people.
How to Write an Introduction Speech?
Before you can just go and deliver your speech, you need to prepare for it. Writing a speech helps you organize your ideas and prepare your speech effectively.
Here is how to introduce yourself in a speech.
- Know Your Audience
Understanding your audience is crucial. Consider their interests, backgrounds, and expectations to tailor your introduction accordingly.
For instance, the audience members could be your colleagues, new classmates, or various guests depending on the occasion. Understanding your audience will help you decide what they are expecting from you as a speaker.
- Opening the Speech with a Hook
The best speech introduction starts with a hook or opening line that grabs your audience's attention. This could be a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or a thought-provoking question about yourself or the occasion.
- Introduce Yourself
Introduce yourself to the audience. State your name, occupation, or other details relevant to the occasion. You should have mentioned the reason for your speech clearly. It will build your credibility and give the readers reasons to stay with you and read your speech.
- Keep It Concise
So how long is an introduction speech?
Introduction speeches should be brief and to the point. Aim for around 1-2 minutes in most cases. Avoid overloading the introduction with excessive details.
- Highlight Key Points
Mention the most important information that establishes the speaker's credibility or your own qualifications. Write down any relevant achievements, expertise, or credentials to include in your speech. Encourage the audience to connect with you using relatable anecdotes or common interests.
- Rehearse and Edit
Practice your introduction speech to ensure it flows smoothly and stays within the time frame. Edit out any unnecessary information, ensuring it's concise and impactful.
- Tailor for the Occasion
Adjust the tone and content of your introduction speech to match the formality and purpose of the event. What works for a business conference may not be suitable for a casual gathering.
Introduction Speech Outline
To assist you in creating a structured and effective introduction speech, here's a simple speech format that you can follow:
|
Here is an example outline for a self-introduction speech.
Outline for Self-Introduction Speech
Introduction Speech Example
So if you are wondering what to say in an introduction speech we have you covered! We have compiled introduction speech examples to help you understand how to put your ideas into practice for different scenarios.
Introduction Speech Writing Sample
Short Introduction Speech Sample
Self Introduction Speech for College Students
Introduction Speech about Yourself
Student Presentation Introduction Speech Script
Teacher Introduction Speech
New Employee Self Introduction Speech
Introduction Speech for Chief Guest
Moreover, here is a video example of a self-introduction speech. Watch it to understand how you should deliver your speech:
Want to read examples for other kinds of speeches? Find the best speeches at our blog about speech examples !
What Are Some Famous Introduction Speeches?
Here are the best introduction speeches for students to get inspired:
- Malala Yousafzai's Nobel Peace Prize Acceptance Speech (2014) : Malala's speech upon receiving the Nobel Peace Prize introduced her advocacy for girls' education and youth empowerment globally.
- Elon Musk's Presentation on SpaceX Interplanetary Transport System (2016) : Elon Musk introduced SpaceX's ambitious plans for interplanetary travel, outlining a vision for the future of space exploration.
- Michelle Obama's Democratic National Convention Speech (2008) : Michelle Obama's speech introduced her as a potential First Lady, sharing personal stories and values that resonated with the audience.
- J.K. Rowling's Harvard Commencement Speech (2008) : Rowling's speech introduced themes of failure, imagination, and resilience, drawing from her personal journey as an author and philanthropist.
Introduction Speech Ideas
So now that you’ve understood what an introduction speech is, you may want to write one of your own. So what should you talk about?
The following are some sample introduction speech topics and ideas that can provide an engaging start to a presentation, meeting, or social gathering.
- Personal Story: Share a brief personal story or experience that has shaped you.
- Professional Background: Highlight your career achievements and expertise.
- Hobby or Passion: Discuss a hobby or passion you're enthusiastic about.
- Volunteer Work: Talk about your involvement in volunteer work or community service.
- Travel Adventures: Share anecdotes from your travel adventures.
- Books or Literature: Provide an introduction related to a favorite book, author, or literary work.
- Achievements and Milestones: Highlight significant achievements and milestones in your life or career.
- Cultural Heritage: Explore your cultural heritage and its influence on your identity.
- Social or Environmental Cause: Discuss your dedication to a particular social or environmental cause.
- Future Aspirations: Share your future goals and aspirations.
You can deliver engaging speeches on all kinds of topics. Here is a list of entertaining speech topics to get inspiration.
7 Tips for Delivering the Best Introduction Speech
Now that you know how to write an effective introduction speech, let's focus on the delivery. The way you present your introduction is just as important as the content itself. Here are some valuable tips to ensure you deliver a better introduction speech:
Tip# 1: Maintain Eye Contact
Make eye contact with the audience to establish a connection. This shows confidence and engages your listeners.
Tip# 2: Use Appropriate Body Language
Your body language should convey confidence and warmth. Stand or sit up straight, use open gestures, and avoid fidgeting.
Tip# 3: Mind Your Pace
Speak at a moderate pace, avoiding rapid speech. A well-paced speech is easier to follow and more engaging.
Tip# 4: Avoid Filler Words
Minimize the use of filler words such as "um," "uh," and "like." They can be distracting and detract from your message.
Tip# 5: Be Enthusiastic
Convey enthusiasm about the topic or the speaker. Your energy can be contagious and inspire the audience's interest.
Tip# 6: Practice, Practice, Practice
Rehearse your speech multiple times. Practice in front of a mirror, record yourself or seek feedback from others.
Tip# 7: Be Mindful of Time
Stay within the allocated time for your introduction. Going too long can make your speech too boring for the audience.
Mistakes to Avoid in an Introduction Speech
When crafting and delivering an introduction speech, it's important to avoid common pitfalls that can reduce its impact. Here are some mistakes to watch out for:
- Rambling On: Avoid making the introduction too long. Keep it short and sweet to set the stage without stealing the spotlight.
- Lack of Preparation: Not preparing enough can lead to awkward pauses or losing your train of thought. Practice your speech to feel more confident.
- Using Jargon or Complex Language: Steer clear of technical jargon or complicated language that might confuse the audience. Keep it simple and clear.
- Being Too Generic: A bland introduction can set a dull tone. Make your speech specific to the event and the speaker to keep it engaging.
- Using Inappropriate Humor: Be careful with humor. Avoid jokes that could offend or alienate the audience.
- Overloading with Background Information: Providing too much background information can overwhelm the audience. Offer just enough to give context without bogging down the introduction.
To Conclude,
An introduction speech is more than just a formality. It's an opportunity to engage, inspire, and connect with your audience in a meaningful way.
With the help of this blog, you're well-equipped to shine in various contexts. So, step onto that stage, speak confidently, and captivate your audience from the very first word.
Moreover, you’re not alone in your journey to becoming a confident introducer. If you ever need assistance in preparing your speech, let the experts help you out.
MyPerfectWords.com offers a custom essay service with experienced professionals who can craft tailored introductions, ensuring your speech makes a lasting impact.
Don't hesitate; hire our professional speech writing service to deliver top-quality speeches at your deadline!
Frequently Asked Questions
How long should a speech introduction be.
A speech introduction should be concise, typically lasting about 1 to 2 minutes. It should set the stage, capture the audience's attention, and provide a clear direction for the rest of the speech.
What Is the Best Speech Introduction Greeting?
The best greeting for a speech introduction depends on the formality of the event. Some examples include:
- Formal: "Good morning/afternoon/evening, distinguished guests."
- Semi-formal: "Hello everyone, thank you for being here today."
- Informal: "Hi everyone, thanks for coming."
What Word to Start a Speech?
Starting a speech with an engaging word or phrase can capture the audience's attention. Here are a few speech starting lines:
- "Imagine..." to prompt the audience to visualize something.
- "Today..." to ground the speech in the present moment.
- "Have you ever..." to ask a thought-provoking question.
- "In our lives..." to make a personal connection.
- "Picture this..." to create a vivid mental image.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

15 Powerful Speech Opening Lines (And How to Create Your Own)
Hrideep barot.
- Public Speaking , Speech Writing

Powerful speech opening lines set the tone and mood of your speech. It’s what grips the audience to want to know more about the rest of your talk.
The first few seconds are critical. It’s when you have maximum attention of the audience. And you must capitalize on that!
Instead of starting off with something plain and obvious such as a ‘Thank you’ or ‘Good Morning’, there’s so much more you can do for a powerful speech opening (here’s a great article we wrote a while ago on how you should NOT start your speech ).
To help you with this, I’ve compiled some of my favourite openings from various speakers. These speakers have gone on to deliver TED talks , win international Toastmaster competitions or are just noteworthy people who have mastered the art of communication.
After each speaker’s opening line, I have added how you can include their style of opening into your own speech. Understanding how these great speakers do it will certainly give you an idea to create your own speech opening line which will grip the audience from the outset!
Alright! Let’s dive into the 15 powerful speech openings…
Note: Want to take your communications skills to the next level? Book a complimentary consultation with one of our expert communication coaches. We’ll look under the hood of your hurdles and pick two to three growth opportunities so you can speak with impact!
1. Ric Elias
Opening: “Imagine a big explosion as you climb through 3,000 ft. Imagine a plane full of smoke. Imagine an engine going clack, clack, clack. It sounds scary. Well I had a unique seat that day. I was sitting in 1D.”
How to use the power of imagination to open your speech?
Putting your audience in a state of imagination can work extremely well to captivate them for the remainder of your talk.
It really helps to bring your audience in a certain mood that preps them for what’s about to come next. Speakers have used this with high effectiveness by transporting their audience into an imaginary land to help prove their point.
When Ric Elias opened his speech, the detail he used (3000 ft, sound of the engine going clack-clack-clack) made me feel that I too was in the plane. He was trying to make the audience experience what he was feeling – and, at least in my opinion, he did.
When using the imagination opening for speeches, the key is – detail. While we want the audience to wander into imagination, we want them to wander off to the image that we want to create for them. So, detail out your scenario if you’re going to use this technique.
Make your audience feel like they too are in the same circumstance as you were when you were in that particular situation.
2. Barack Obama
Opening: “You can’t say it, but you know it’s true.”
3. Seth MacFarlane
Opening: “There’s nowhere I would rather be on a day like this than around all this electoral equipment.” (It was raining)
How to use humour to open your speech?
When you use humour in a manner that suits your personality, it can set you up for a great speech. Why? Because getting a laugh in the first 30 seconds or so is a great way to quickly get the audience to like you.
And when they like you, they are much more likely to listen to and believe in your ideas.
Obama effortlessly uses his opening line to entice laughter among the audience. He brilliantly used the setting (the context of Trump becoming President) and said a line that completely matched his style of speaking.
Saying a joke without really saying a joke and getting people to laugh requires you to be completely comfortable in your own skin. And that’s not easy for many people (me being one of them).
If the joke doesn’t land as expected, it could lead to a rocky start.
Keep in mind the following when attempting to deliver a funny introduction:
- Know your audience: Make sure your audience gets the context of the joke (if it’s an inside joke among the members you’re speaking to, that’s even better!). You can read this article we wrote where we give you tips on how you can actually get to know your audience better to ensure maximum impact with your speech openings
- The joke should suit your natural personality. Don’t make it look forced or it won’t elicit the desired response
- Test the opening out on a few people who match your real audience. Analyze their response and tweak the joke accordingly if necessary
- Starting your speech with humour means your setting the tone of your speech. It would make sense to have a few more jokes sprinkled around the rest of the speech as well as the audience might be expecting the same from you
4. Mohammed Qahtani
Opening: Puts a cigarette on his lips, lights a lighter, stops just before lighting the cigarette. Looks at audience, “What?”
5. Darren Tay
Opening: Puts a white pair of briefs over his pants.
How to use props to begin your speech?
The reason props work so well in a talk is because in most cases the audience is not expecting anything more than just talking. So when a speaker pulls out an object that is unusual, everyone’s attention goes right to it.
It makes you wonder why that prop is being used in this particular speech.
The key word here is unusual . To grip the audience’s attention at the beginning of the speech, the prop being used should be something that the audience would never expect. Otherwise, it just becomes something that is common. And common = boring!
What Mohammed Qahtani and Darren Tay did superbly well in their talks was that they used props that nobody expected them to.
By pulling out a cigarette and lighter or a white pair of underwear, the audience can’t help but be gripped by what the speaker is about to do next. And that makes for a powerful speech opening.
6. Simon Sinek
Opening: “How do you explain when things don’t go as we assume? Or better, how do you explain when others are able to achieve things that seem to defy all of the assumptions?”
7. Julian Treasure
Opening: “The human voice. It’s the instrument we all play. It’s the most powerful sound in the world. Probably the only one that can start a war or say “I love you.” And yet many people have the experience that when they speak people don’t listen to them. Why is that? How can we speak powerfully to make change in the world?”
How to use questions to open a speech?
I use this method often. Starting off with a question is the simplest way to start your speech in a manner that immediately engages the audience.
But we should keep our questions compelling as opposed to something that is fairly obvious.
I’ve heard many speakers start their speeches with questions like “How many of us want to be successful?”
No one is going to say ‘no’ to that and frankly, I just feel silly raising my hand at such questions.
Simon Sinek and Jullian Treasure used questions in a manner that really made the audience think and make them curious to find out what the answer to that question is.
What Jullian Treasure did even better was the use of a few statements which built up to his question. This made the question even more compelling and set the theme for what the rest of his talk would be about.
So think of what question you can ask in your speech that will:
- Set the theme for the remainder of your speech
- Not be something that is fairly obvious
- Be compelling enough so that the audience will actually want to know what the answer to that question will be
8. Aaron Beverley
Opening: Long pause (after an absurdly long introduction of a 57-word speech title). “Be honest. You enjoyed that, didn’t you?”
How to use silence for speech openings?
The reason this speech opening stands out is because of the fact that the title itself is 57 words long. The audience was already hilariously intrigued by what was going to come next.
But what’s so gripping here is the way Aaron holds the crowd’s suspense by…doing nothing. For about 10 to 12 seconds he did nothing but stand and look at the audience. Everyone quietened down. He then broke this silence by a humorous remark that brought the audience laughing down again.
When going on to open your speech, besides focusing on building a killer opening sentence, how about just being silent?
It’s important to keep in mind that the point of having a strong opening is so that the audience’s attention is all on you and are intrigued enough to want to listen to the rest of your speech.
Silence is a great way to do that. When you get on the stage, just pause for a few seconds (about 3 to 5 seconds) and just look at the crowd. Let the audience and yourself settle in to the fact that the spotlight is now on you.
I can’t put my finger on it, but there is something about starting the speech off with a pure pause that just makes the beginning so much more powerful. It adds credibility to you as a speaker as well, making you look more comfortable and confident on stage.
If you want to know more about the power of pausing in public speaking , check out this post we wrote. It will give you a deeper insight into the importance of pausing and how you can harness it for your own speeches. You can also check out this video to know more about Pausing for Public Speaking:
9. Dan Pink
Opening: “I need to make a confession at the outset here. Little over 20 years ago, I did something that I regret. Something that I’m not particularly proud of. Something that in many ways I wish no one would ever know but that here I feel kind of obliged to reveal.”
10. Kelly McGonigal
Opening: “I have a confession to make. But first I want you to make a little confession to me.”
How to use a build-up to open your speech?
When there are so many amazing ways to start a speech and grip an audience from the outset, why would you ever choose to begin your speech with a ‘Good morning?’.
That’s what I love about build-ups. They set the mood for something awesome that’s about to come in that the audience will feel like they just have to know about.
Instead of starting a speech as it is, see if you can add some build-up to your beginning itself. For instance, in Kelly McGonigal’s speech, she could have started off with the question of stress itself (which she eventually moves on to in her speech). It’s not a bad way to start the speech.
But by adding the statement of “I have a confession to make” and then not revealing the confession for a little bit, the audience is gripped to know what she’s about to do next and find out what indeed is her confession.
11. Tim Urban
Opening: “So in college, I was a government major. Which means that I had to write a lot of papers. Now when a normal student writes a paper, they might spread the work out a little like this.”
12. Scott Dinsmore
Opening: “8 years ago, I got the worst career advice of my life.”
How to use storytelling as a speech opening?
“The most powerful person in the world is the storyteller.” Steve Jobs
Storytelling is the foundation of good speeches. Starting your speech with a story is a great way to grip the audience’s attention. It makes them yearn to want to know how the rest of the story is going to pan out.
Tim Urban starts off his speech with a story dating back to his college days. His use of slides is masterful and something we all can learn from. But while his story sounds simple, it does the job of intriguing the audience to want to know more.
As soon as I heard the opening lines, I thought to myself “If normal students write their paper in a certain manner, how does Tim write his papers?”
Combine such a simple yet intriguing opening with comedic slides, and you’ve got yourself a pretty gripping speech.
Scott Dismore’s statement has a similar impact. However, just a side note, Scott Dismore actually started his speech with “Wow, what an honour.”
I would advise to not start your talk with something such as that. It’s way too common and does not do the job an opening must, which is to grip your audience and set the tone for what’s coming.
13. Larry Smith
Opening: “I want to discuss with you this afternoon why you’re going to fail to have a great career.”
14. Jane McGonigal
Opening: “You will live 7.5 minutes longer than you would have otherwise, just because you watched this talk.”
How to use provocative statements to start your speech?
Making a provocative statement creates a keen desire among the audience to want to know more about what you have to say. It immediately brings everyone into attention.
Larry Smith did just that by making his opening statement surprising, lightly humorous, and above all – fearful. These elements lead to an opening statement which creates so much curiosity among the audience that they need to know how your speech pans out.
This one time, I remember seeing a speaker start a speech with, “Last week, my best friend committed suicide.” The entire crowd was gripped. Everyone could feel the tension in the room.
They were just waiting for the speaker to continue to know where this speech will go.
That’s what a hard-hitting statement does, it intrigues your audience so much that they can’t wait to hear more! Just a tip, if you do start off with a provocative, hard-hitting statement, make sure you pause for a moment after saying it.
Silence after an impactful statement will allow your message to really sink in with the audience.
Related article: 5 Ways to Grab Your Audience’s Attention When You’re Losing it!
15. Ramona J Smith
Opening: In a boxing stance, “Life would sometimes feel like a fight. The punches, jabs and hooks will come in the form of challenges, obstacles and failures. Yet if you stay in the ring and learn from those past fights, at the end of each round, you’ll be still standing.”
How to use your full body to grip the audience at the beginning of your speech?
In a talk, the audience is expecting you to do just that – talk. But when you enter the stage and start putting your full body into use in a way that the audience does not expect, it grabs their attention.
Body language is critical when it comes to public speaking. Hand gestures, stage movement, facial expressions are all things that need to be paid attention to while you’re speaking on stage. But that’s not I’m talking about here.
Here, I’m referring to a unique use of the body that grips the audience, like how Ramona did. By using her body to get into a boxing stance, imitating punches, jabs and hooks with her arms while talking – that’s what got the audience’s attention.
The reason I say this is so powerful is because if you take Ramona’s speech and remove the body usage from her opening, the entire magic of the opening falls flat.
While the content is definitely strong, without those movements, she would not have captured the audience’s attention as beautifully as she did with the use of her body.
So if you have a speech opening that seems slightly dull, see if you can add some body movement to it.
If your speech starts with a story of someone running, actually act out the running. If your speech starts with a story of someone reading, actually act out the reading.
It will make your speech opening that much more impactful.
Related article: 5 Body Language Tips to Command the Stage
Level up your public speaking in 15 minutes!
Get the exclusive Masterclass video delivered to your inbox to see immediate speaking results.
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
Final Words
So there it is! 15 speech openings from some of my favourite speeches. Hopefully, these will act as a guide for you to create your own opening which is super impactful and sets you off on the path to becoming a powerful public speaker!
But remember, while a speech opening is super important, it’s just part of an overall structure.
If you’re serious about not just creating a great speech opening but to improve your public speaking at an overall level, I would highly recommend you to check out this course: Acumen Presents: Chris Anderson on Public Speaking on Udemy. Not only does it have specific lectures on starting and ending a speech, but it also offers an in-depth guide into all the nuances of public speaking.
Being the founder of TED Talks, Chris Anderson provides numerous examples of the best TED speakers to give us a very practical way of overcoming stage fear and delivering a speech that people will remember. His course has helped me personally and I would definitely recommend it to anyone looking to learn public speaking.
No one is ever “done” learning public speaking. It’s a continuous process and you can always get better. Keep learning, keep conquering and keep being awesome!
Lastly, if you want to know how you should NOT open your speech, we’ve got a video for you:
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

How to Brag Like a Pro as a Speaker

Less is More! Tips to Avoid Overwhelming Your Audience

What does it mean to Resonate with the Audience- Agreement, Acceptance, Approval

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved

Self-introduction for Students [With Sample Intros]
- Published on Dec 25, 2017
- shares
You would want to make a good impression on your friends when you introduce yourself on the first day in class at your school or college – or at some other gathering. Wouldn’t you?
A small note before we dive into thick of things: Self-introductions can be context-driven, implying that because of unique situation you’re in, you may have to customize some part of the introduction. So, feel free to add or subtract to what’s covered here.
What to include in self-introduction?
Is there a format (for the introduction) to follow? The organizer, for example, may ask to include your name, place you come from, and your hobbies in the introduction.
If there is a format, follow it, but feel free to venture into areas that aren’t included in the format if they provide a more complete picture of yours.
You may include following in your introduction:
1. The start
You can start with the obvious – your name.
But that’s a common start. You can be bit innovative by starting with an attention-grabber. Watch the beginning of this video on marketing to get a feel of what I’m saying (watch the first 15 seconds):
Neil didn’t start with his name. He started with things that will grab people’s attention immediately and came to his name later on.
You can follow the same strategy to stand out among your classmates, most of whom would be following the standard ‘name first’ approach. You can start with a unique experience or a peculiar fact about your city or your uncommon hobby. The first sample intro (later in the post) follows this strategy.
More resources on conversations and introductions:
- How to introduce yourself in different settings?
- How to say ‘thank you’?
- How to respond when someone asks ‘how are you’?
2. Where are you from?
Mention the city you come from. You may add a sentence or two about the city as well if there is something interesting to talk about. Maybe the city is known for historic monuments. Maybe it’s known for natural resources.
And if you’ve lived in multiple cities, you may briefly mention the names and, as mentioned above, a sentence or two on the most interesting of them.
3. Where did you last attend the school?
If you recently moved to a new school (or college) and are introducing yourself there, you can briefly talk about your last school. Are there any interesting facts about your last school? If yes, mention them. Maybe it was established a long, long time ago. Maybe it has produced few famous alumni.
If you’re continuing in the same school, you may mention how many years you’ve been studying there.
4. Interests, hobbies, and achievements
What are your interests and hobbies?
Playing a sport? Traveling? Hiking? Reading? Kite flying? Or something unusual, say bull fighting?
Go into details if you’ve pursued the hobby with serious interest. For example, if you’re into reading, mention what genres you read, your favorite books, your favorite author, and how reading has affected you.
Don’t forget to mention your participation in extracurricular activities in school, if you did. Don’t forget to mention any significant achievements you’ve had?
5. Which stream/department/subject have you enrolled in?
You can briefly talk about which subjects (math, science, arts, commerce, biology, and so on) you’ve picked or you intend to pick in future. Optionally, you may also mention why you made the choice you have. Was it because you love it? Was it because it’ll help you achieve your career goals?
If you’re a college student, you can mention the department you’ve enrolled in. Are you in Arts, Commerce, Mechanical Engineering, Science, or Economics?
This doesn’t apply though if you’re introducing yourself to students who’re all from the same stream/department/subject.
6. Do you’ve clarity on interests/goals you want to pursue in future?
If you’re in K-12, you may not have seriously evaluated what career path you want to follow, and that’s fine. But if you’ve certain career aspiration and if you want to talk about it, you can. Some want to become engineer. Some, astronaut. Some, doctor. Some, model. Speak out what you aspire to become.
Most college students though have more concrete idea on post-college career. If you’ve decided the career path you want to pursue after college, you can share it with your classmates. You never know few of your classmates harboring same career aspirations may just approach you to be friends. You may also mention professional clubs you want to join to hone your skills.
Participate in a short survey
If you’re a learner or teacher of English language, you can help improve website’s content for the visitors through a short survey.
7. Where can you help others?
If you’ve a strength others in your class can benefit from, feel free to share it. For example, if you’re good in dancing, you can offer to teach the ropes to anyone interested. If you’re strong in a particular subject that is part of your syllabus, you can offer to help others in that subject.
If people know of your strengths, they’ll readily approach you when they need help. This is an easy way to make friends in college. And if you think helping others may be a time waster, you should remember that you too may need help in areas where others are stronger.
This is also a good stage – by offering help – to finish your intro. (See the first sample intro.)
Should I talk about my family?
Avoid it unless the format of the intro requires you to talk about your family as well. You need not go into what your parents do and which class your siblings study in.
Should I mention my last year’s grades?
You shouldn’t unless specifically asked to or others are mentioning it. Top grades can lend a snobbish air to your intro, even if you’re otherwise. Students may make an impression that you’re flaunting your grades, even if you aren’t.
Remember, the primary goal of your intro is to make friends, find people with shared interests.
Four do’s and don’ts when introducing yourself
1. listen to other intros.
Listen to intros that come before yours. If you can refer to someone else’s point or two seamlessly in your intro, you’ll impress people around.
2. Practice, but don’t cram
People often go blank on some of the points or get nervous when they stand up to speak. The best long-term way to overcome this is exposure to such speaking experiences . But in the immediate term, practice what you want to say few times (don’t cram though) to increase your odds of speaking with confidence.
3. Appear confident even if you’re not
After the presentations by executives and entrepreneurs (presumably confident speakers) as part of an executive program at Harvard University, Carmine Gallo , one of the judges, asked them how their presentations went. He heard following comments:
“I was so nervous. I was shaking.”
“I forgot what to say about a slide.”
“I stumbled over my words.”
“I totally lost my place.”
But, no one in the audience spotted those mistakes.
This phenomenon is called spotlight effect , which in nutshell means that people overestimate how much others are noticing their actions and appearance.
What’s the lesson?
If you’re nervous or you make few mistakes, don’t let them rattle you. Most won’t even notice them. Caroline Goyder captures this sentiment aptly in her book Find Your Voice: The Secret to Talking with Confidence in Any Situation :
When you dive into contribution [speaking], and move beyond the anxious competing, you realize that all the worry was such a waste of time. No one is ever judging you as harshly as you judge yourself. Because the truth is that most people are thinking about themselves.
But if you let nervousness and mistakes overpower you, you may make a mistake or display body language that will be noticed by all. And once you’re through the first few lines in your intro, your nerves will start easing.
So, stay composed and carry on. Many in the audience in fact wouldn’t even be listening to most introductions, as they would be busy silently rehearsing their own lines.
4. Make eye contact and be enthusiastic
Make eye contact with other students while speaking. Don’t fix your eyes on a familiar section of the audience. Move your eyes around. And, last but important, your voice and body language should show enthusiasm.
Here are few sample self-introductions for you to get a hang of how they’re done:
Sample self-introductions
Introduction 1
I once spent an entire night in a dense forest with a friend. Well, this act was not to show off how brave I was, but it was forced on me… by my foolishness. During a trek in [name of the region], I and a friend got too adventurous and strayed from our regular route despite instructions to the contrary by our trek guide. We got lost. We survived somehow (that’s a story for another day), but I haven’t given up on my adventure streak and love for outdoors.
Friends, I’m [your first name] and I love outdoors. I’ve been to treks in Himalayas on multiple occasions. These outdoor expeditions have also forced me to learn basic cooking. Well, I don’t boast of cooking dishes you’ll relish, but yes when you’re dying of hunger in the middle of night, you can count on me. I also love cycling long distances – 20+ kilometers in a stretch – and I can manage singing which some may find intolerable.
I’m from [name of the city]. It’s not a big place, but it somehow exists on the map. I’m really excited to be here. I look forward to having some fun, making friends, and building myself up for college. If you’re organizing any outdoor event in future, you can always count on me for help.
Thanks for giving me this opportunity to introduce myself.
Introduction 2
My name is [your first name]. I’m from [name of the city] where I finished my schooling last year from [name of the school]. Is there anyone here from my city? (Changes tack to engage with the audience.) OK, few.
I like watching movies, at least once a month. I play basketball on weekends and chess whenever I get time. I’m into reading thriller novels as well, Dan Brown being my favorite novelist.
I’m happy to step into college life, which provides more freedom and where, finally, I don’t have to come in a uniform. Post-college, I aspire to work in consulting industry.
I’m particularly strong in Excel worksheets and creating well-designed banners and documents. If anyone requires support in these areas, I’ll be glad to help. I look forward to meeting each one of you in the coming days.
Thanks. Have a great day.

Anil is the person behind this website. He writes on most aspects of English Language Skills. More about him here:
15 Comments
This really helped me… Thank you so so much.
Thank u….this is quite helpful to overcome my nervousness and get into action..Cheers🙂
Man, I was so nervous about my interview for school admission. But after reading this, I felt comfortable. Thanks, this was a great explanation.
It helped me a lot. Thank you so much. It was like I was the center of attraction. Thank you again.
Thanx…. It really helped on my first day of college.
Dude, this is another level. Thanks a lot.
Thanks a lot. It was useful. Now, I should be able to introduce my self without nerves 👌👍🙂🙂
Thank you. Now I get some ideas for self intro and thank you for your brief explanation.
I was a little nervous about my varsity first introduction and my confidence increased after watching it.
Intro 2 was like fire…. It helped me a lot, thanx!!
Thanks, dude!!!! I am a school-level student and the introduction part really helped me.
I have a virtual introduction meeting with my seniors in college. I am so nervous about it. This piece is so helpful. Thanks.
Excellent. I like this a lot. I searched for this type of introduction on many websites, but this post is so interesting and good enough to impress my teacher and classmates.
My name is Yeabkal Solomon. I’m a first year student at Arba minch University. It helped me when I was gave my oral presentation.
I was very scared. I was really scared. Thank you very much for helping with the interview. It was very helpful for me
Comments are closed.
Speech introductions
The introduction and conclusion of a speech are essential. The audience will remember the main ideas even if the middle of the speech is a mess or nerves overtake the speaker. So if nothing else, get these parts down!
Introduction
The introduction gives the audience a reason to listen to the remainder of the speech. A good introduction needs to get the audience’s attention, state the topic, make the topic relatable, establish credibility, and preview the main points. Introductions should be the last part of the speech written, as they set expectations and need to match the content.
Attention getters
The first few sentences of a speech are designed to catch and maintain the audience’s attention. Attention getters give the audience a reason to listen to the rest of the speech. Your attention getter helps the audience understand and reflect on your topic.
- Speaker walks up to stage with notes stuck to hands with jelly.
- Did you know there is a right way to make a peanut butter and jelly sandwich?
- Rob Gronkowski once said, “Usually, about 2 hours before a game, I stuff in a nice peanut butter and jelly [sandwich] with chocolate milk.”
- A little boy walks in from a long day at school, telling his mom that he is starving. His mom is confused because she knows she sent him to school with a full lunch. As she opens his lunch box, she sees his peanut butter and jelly, with the grape jelly smeared on the side of the bag. She realizes there has to be a better way to make a PB&J.
- Bring in a clear sandwich bag with jelly seeping through the bread of a peanut butter and jelly sandwich.
Logical orientation
Once the audience is invested in the speech, logical orientation tells the audience how the speaker will approach and develop the topic.
- Peanut butter on both sides of the bread with jelly in the middle is the best way to make a PB&J.
- PB&Js have developed a bad reputation, because of the jelly making the bread soggy and hands sticky.
Psychological orientation
Like the logical orientation of a speech, the psychological orientation is also going to provide the audience with a map for how and why the topic is being presented.
- Most of us remember our moms – dads too – packing a peanut butter and jelly sandwich in our lunches. We also remember how the jelly did not just stay in the sandwich, but became a new stain on our shirts and the glue that held all the playground dirt to our hands.
- We can end this torture for future generations by making sure all parents are aware of the best way to make a PB&J.
- I have eaten numerous PB&Js myself, but my real authority on the topic comes from being a mom of two boys and the maker of many PB&Js.
Both the logical and psychological orientations give the audience a road map for the speech ahead as well as cues for what to listen to. This will help the audience transition from the introduction to the main points of the speech.
Beebe, S. A., & Beebe, S. J. (2012). A concise public speaking handbook . Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
Lucas, S. (2012). The art of public speaking . New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Sprague, J. & Stuart, D. (2013). The speaker's compact handbook, 4th ed . Portland: Ringgold, Inc.
Vrooman, S. S. (2013). The zombie guide to public speaking: Why most presentations fail, and what you can do to avoid joining the horde . Place of publication not identified: CreateSpace.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
8 Effective Introductions and Powerful Conclusions
Learning objectives.
- Identify the functions of introductions and conclusions.
- Understand the key parts of an introduction and a conclusion.
- Explore techniques to create your own effective introductions and conclusions.

Introductions and conclusions can be challenging. One of the most common complaints novice public speakers have is that they simply don’t know how to start or end a speech. It may feel natural to start crafting a speech at the beginning, but it can be difficult to craft an introduction for something which doesn’t yet exist. Many times, creative and effective ideas for how to begin a speech will come to speakers as they go through the process of researching and organizing ideas. Similarly, a conclusion needs to be well considered and leave audience members with a sense of satisfaction.
In this chapter, we will explore why introductions and conclusions are important, and we will identify various ways speakers can create impactful beginnings and endings. There is not a “right” way to start or end a speech, but we can provide some helpful guidelines that will make your introductions and conclusions much easier for you as a speaker and more effective for your audience.
The Importance of an Introduction

The introduction of a speech is incredibly important because it needs to establish the topic and purpose, set up the reason your audience should listen to you and set a precedent for the rest of the speech. Imagine the first day of a semester long class. You will have a different perception of the course if the teacher is excited, creative and clear about what is to come then if the teacher recites to you what the class is about and is confused or disorganized about the rest of the semester. The same thing goes for a speech. The introduction is an important opportunity for the speaker to gain the interest and trust of the audience.
Overall, an effective introduction serves five functions. Let’s examine each of these.
Gain Audience Attention and Interest
The first major purpose of an introduction is to gain your audience’s attention and get them interested in what you have to say. While your audience may know you, this is your speeches’ first impression! One common incorrect assumption beginning speakers make that people will naturally listen because the speaker is speaking. While many audiences may be polite and not talk while you’re speaking, actually getting them to listen and care about what you are saying is a completely different challenge. Think to a time when you’ve tuned out a speaker because you were not interested in what they had to say or how they were saying it. However, I’m sure you can also think of a time someone engaged you in a topic you wouldn’t have thought was interesting, but because of how they presented it or their energy about the subject, you were fascinated. As the speaker, you have the ability to engage the audience right away.
State the Purpose of Your Speech
The second major function of an introduction is to reveal the purpose of your speech to your audience. Have you ever sat through a speech wondering what the basic point was? Have you ever come away after a speech and had no idea what the speaker was talking about? An introduction is critical for explaining the topic to the audience and justifying why they should care about it. The speaker needs to have an in-depth understanding of the specific focus of their topic and the goals they have for their speech. Robert Cavett, the founder of the National Speaker’s Association, used the analogy of a preacher giving a sermon when he noted, “When it’s foggy in the pulpit, it’s cloudy in the pews.” The specific purpose is the one idea you want your audience to remember when you are finished with your speech. Your specific purpose is the rudder that guides your research, organization, and development of main points. The more clearly focused your purpose is, the easier it will be both for you to develop your speech and your audience to understand your core point. To make sure you are developing a specific purpose, you should be able to complete the sentence: “I want my audience to understand…” Notice that your specific speech purpose is phrased in terms of expected audience responses, not in terms of your own perspective.
Establish Credibility
One of the most researched areas within the field of communication has been Aristotle’s concept of ethos or credibility. First, and foremost, the idea of credibility relates directly to audience perception. You may be the most competent, caring, and trustworthy speaker in the world on a given topic, but if your audience does not perceive you as credible, then your expertise and passion will not matter to them. As public speakers, we need to communicate to our audiences why we are credible speakers on a given topic. James C. McCroskey and Jason J. Teven have conducted extensive research on credibility and have determined that an individual’s credibility is composed of three factors: competence, trustworthiness, and caring/goodwill (McCroskey & Teven, 1999). Competence is the degree to which a speaker is perceived to be knowledgeable or expert in a given subject by an audience member.
The second factor of credibility noted by McCroskey and Teven is trustworthiness or the degree to which an audience member perceives a speaker as honest. Nothing will turn an audience against a speaker faster than if the audience believes the speaker is lying. When the audience does not perceive a speaker as trustworthy, the information coming out of the speaker’s mouth is automatically perceived as deceitful.
Finally, caring/goodwill is the last factor of credibility noted by McCroskey and Teven. Caring/goodwill refers to the degree to which an audience member perceives a speaker as caring about the audience member. As indicated by Wrench, McCroskey, and Richmond, “If a receiver does not believe that a source has the best intentions in mind for the receiver, the receiver will not see the source as credible. Simply put, we are going to listen to people who we think truly care for us and are looking out for our welfare” (Wrench, McCroskey & Richmond, 2008). As a speaker, then, you need to establish that your information is being presented because you care about your audience and are not just trying to manipulate them. We should note that research has indicated that caring/goodwill is the most important factor of credibility. This understanding means that if an audience believes that a speaker truly cares about the audience’s best interests, the audience may overlook some competence and trust issues.
Credibility relates directly to audience perception. You may be the most competent, caring, and trustworthy speaker in the world on a given topic, but if your audience does not perceive you as credible, then your expertise and passion will not matter to them.
Trustworthiness is the degree to which an audience member perceives a speaker as honest.
Caring/goodwill is the degree to which an audience member perceives a speaker as caring about the audience member.
Provide Reasons to Listen
The fourth major function of an introduction is to establish a connection between the speaker and the audience, and one of the most effective means of establishing a connection with your audience is to provide them with reasons why they should listen to your speech. The idea of establishing a connection is an extension of the notion of caring/goodwill. In the chapters on Language and Speech Delivery, we’ll spend a lot more time talking about how you can establish a good relationship with your audience. This relationship starts the moment you step to the front of the room to start speaking.
Instead of assuming the audience will make their own connections to your material, you should explicitly state how your information might be useful to your audience. Tell them directly how they might use your information themselves. It is not enough for you alone to be interested in your topic. You need to build a bridge to the audience by explicitly connecting your topic to their possible needs.
Preview Main Ideas
The last major function of an introduction is to preview the main ideas that your speech will discuss. A preview establishes the direction your speech will take. We sometimes call this process signposting because you’re establishing signs for audience members to look for while you’re speaking. In the most basic speech format, speakers generally have three to five major points they plan on making. During the preview, a speaker outlines what these points will be, which demonstrates to the audience that the speaker is organized.
A study by Baker found that individuals who were unorganized while speaking were perceived as less credible than those individuals who were organized (Baker, 1965). Having a solid preview of the information contained within one’s speech and then following that preview will help a speaker’s credibility. It also helps your audience keep track of where you are if they momentarily daydream or get distracted.
Putting Together a Strong Introduction

Now that we have an understanding of the functions of an introduction, let’s explore the details of putting one together. As with all aspects of a speech, these may change based on your audience, circumstance, and topic. But this will give you a basic understanding of the important parts of an intro, what they do, and how they work together.
Attention Getting Device
An attention-getter is the device a speaker uses at the beginning of a speech to capture an audience’s interest and make them interested in the speech’s topic. Typically, there are four things to consider in choosing a specific attention-getting device:
- Topic and purpose of the speech
- Appropriateness or relevance to the audience
First, when selecting an attention-getting device is considering your speech topic and purpose. Ideally, your attention-getting device should have a relevant connection to your speech. Imagine if a speaker pulled condoms out of his pocket, yelled “Free sex!” and threw the condoms at the audience. This act might gain everyone’s attention, but would probably not be a great way to begin a speech about the economy. Thinking about your topic because the interest you want to create needs to be specific to your subject. More specifically, you want to consider the basic purpose of your speech. When selecting an attention getter, you want to make sure that you select one that corresponds with your basic purpose. If your goal is to entertain an audience, starting a speech with a quotation about how many people are dying in Africa each day from malnutrition may not be the best way to get your audience’s attention. Remember, one of the goals of an introduction is to prepare your audience for your speech . If your attention-getter differs drastically in tone from the rest of your speech the disjointedness may cause your audience to become confused or tune you out completely.
Possible Attention Getters
These will help you start brainstorming ideas for how to begin your speech. While not a complete list, these are some of the most common forms of attention-getters:
- Reference to Current Events
- Historical Reference
- Startling Fact
- Rhetorical Question
- Hypothetical Situation
- Demonstration
- Personal Reference
- Reference to Audience
- Reference to Occasion
Second, when selecting an attention-getting device, you want to make sure you are being appropriate and relevant to your specific audience. Different audiences will have different backgrounds and knowledge, so you should keep your audience in mind when determining how to get their attention. For example, if you’re giving a speech on family units to a group of individuals over the age of sixty-five, starting your speech with a reference to the television show Gossip Girl may not be the best idea because the television show may not be relevant to that audience.
Finally, the last consideration involves the speech occasion. Different occasions will necessitate different tones or particular styles or manners of speaking. For example, giving a eulogy at a funeral will have a very different feel than a business presentation. This understanding doesn’t mean certain situations are always the same, but rather taking into account the details of your circumstances will help you craft an effective beginning to your speech. When selecting an attention-getter, you want to make sure that the attention-getter sets the tone for the speech and situation.
Tones are particular styles or manners of speaking determined by the speech’s occasion.
Link to Topic
The link to the topic occurs when a speaker demonstrates how an attention-getting device relates to the topic of a speech. This presentation of the relationship works to transition your audience from the attention getter to the larger issue you are discussing. Often the attention-getter and the link to the topic are very clear. But other times, there may need to be a more obvious connection between how you began your attention-getting device and the specific subject you are discussing. You may have an amazing attention-getter, but if you can’t connect it to the main topic and purpose of your speech, it will not be as effective.
Significance
Once you have linked an attention-getter to the topic of your speech, you need to explain to your audience why your topic is important and why they should care about what you have to say. Sometimes you can include the significance of your topic in the same sentence as your link to the topic, but other times you may need to spell out in one or two sentences why your specific topic is important to this audience.
Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a short, declarative sentence that states the purpose, intent, or main idea of a speech. A strong, clear thesis statement is very valuable within an introduction because it lays out the basic goal of the entire speech. We strongly believe that it is worthwhile to invest some time in framing and writing a good thesis statement. You may even want to write a version of your thesis statement before you even begin conducting research for your speech in order to guide you. While you may end up rewriting your thesis statement later, having a clear idea of your purpose, intent, or main idea before you start searching for research will help you focus on the most appropriate material.
Preview of Speech
The final part of an introduction contains a preview of the major points to be covered by your speech. I’m sure we’ve all seen signs that have three cities listed on them with the mileage to reach each city. This mileage sign is an indication of what is to come. A preview works the same way. A preview foreshadows what the main body points will be in the speech. For example, to preview a speech on bullying in the workplace, one could say, “To understand the nature of bullying in the modern workplace, I will first define what workplace bullying is and the types of bullying, I will then discuss the common characteristics of both workplace bullies and their targets, and lastly, I will explore some possible solutions to workplace bullying.” In this case, each of the phrases mentioned in the preview would be a single distinct point made in the speech itself. In other words, the first major body point in this speech would examine what workplace bullying is and the types of bullying; the second major body point in this speech would discuss the characteristics of both workplace bullies and their targets; and lastly, the third body point in this speech would explore some possible solutions to workplace bullying.
Putting it all together
The importance of introductions often leads speakers to work on them first, attending to every detail. While it is good to have some ideas and notes about the intro, specifically the thesis statement, it is often best to wait until the majority of the speech is crafted before really digging into the crafting of the introduction. This timeline may not seem intuitive, but remember, the intro is meant to introduce your speech and set up what is to come. It is difficult to introduce something that you haven’t made yet. This is why working on your main points first can help lead to an even stronger introduction.
Why Conclusions Matter
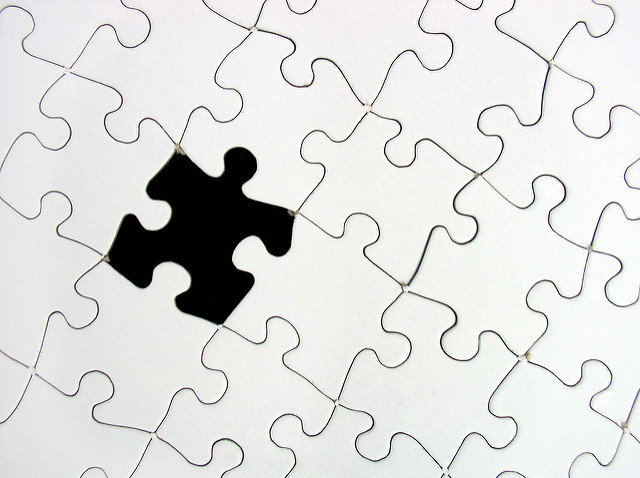
Willi Heidelbach – Puzzle2 – CC BY 2.0.
As public speaking professors and authors, we have seen many students give otherwise good speeches that seem to fall apart at the end. We’ve seen students end their three main points by saying things such as “OK, I’m done”; “Thank God that’s over!”; or “Thanks. Now what? Do I just sit down?” It’s understandable to feel relief at the end of a speech, but remember that as a speaker, your conclusion is the last chance you have to drive home your ideas. When a speaker opts to end the speech with an ineffective conclusion, or no conclusion at all, the speech loses the energy that’s been created, and the audience is left confused and disappointed. Instead of falling prey to emotional exhaustion, remind yourself to keep your energy up as you approach the end of your speech, and plan ahead so that your conclusion will be an effective one.
Of course, a good conclusion will not rescue a poorly prepared speech. Thinking again of the chapters in a novel, if one bypasses all the content in the middle, the ending often isn’t very meaningful or helpful. So to take advantage of the advice in this chapter, you need to keep in mind the importance of developing a speech with an effective introduction and an effective body. If you have these elements, you will have the foundation you need to be able to conclude effectively. Just as a good introduction helps bring an audience member into the world of your speech, and a good speech body holds the audience in that world, a good conclusion helps bring that audience member back to the reality outside of your speech.
In this section, we’re going to examine the functions fulfilled by the conclusion of a speech. A strong conclusion serves to signal the end of the speech and helps your listeners remember your speech.
Signals the End
The first thing a good conclusion can do is to signal the end of a speech. You may be thinking that showing an audience that you’re about to stop speaking is a “no brainer,” but many speakers don’t prepare their audience for the end. When a speaker just suddenly stops speaking, the audience is left confused and disappointed. Instead, we want to make sure that audiences are left knowledgeable and satisfied with our speeches. In the next section, we’ll explain in great detail about how to ensure that you signal the end of your speech in a manner that is both effective and powerful.
Aids Audience’s Memory of Your Speech
The second reason for a good conclusion stems out of some research reported by the German psychologist Hermann Ebbinghaus back in 1885 in his book Memory: A Contribution to Experimental Psychology (Ebbinghaus, 1885). Ebbinghaus proposed that humans remember information in a linear fashion, which he called the serial position effect. He found an individual’s ability to remember information in a list (e.g. a grocery list, a chores list, or a to-do list) depends on the location of an item on the list. Specifically, he found that items toward the top of the list and items toward the bottom of the list tended to have the highest recall rates. The serial position effect finds that information at the beginning of a list (primacy) and information at the end of the list (recency) are easier to recall than information in the middle of the list.
So what does this have to do with conclusions? A lot! Ray Ehrensberger wanted to test Ebbinghaus’ serial position effect in public speaking. Ehrensberger created an experiment that rearranged the ordering of a speech to determine the recall of information (Ehrensberger, 1945). Ehrensberger’s study reaffirmed the importance of primacy and recency when listening to speeches. In fact, Ehrensberger found that the information delivered during the conclusion (recency) had the highest level of recall overall.
Steps of a Conclusion

Matthew Culnane – Steps – CC BY-SA 2.0.
In the previous sections, we discussed the importance a conclusion has on a speech. In this section, we’re going to examine the three steps to building an effective conclusion.
Restatement of the Thesis
Restating a thesis statement is the first step to a powerful conclusion. As we explained earlier, a thesis statement is a short, declarative sentence that states the purpose, intent, or main idea of a speech. When we restate the thesis statement at the conclusion of our speech, we’re attempting to reemphasize what the overarching main idea of the speech has been. Suppose your thesis statement was, “I will analyze Barack Obama’s use of lyricism in his July 2008 speech, ‘A World That Stands as One.’” You could restate the thesis in this fashion at the conclusion of your speech: “In the past few minutes, I have analyzed Barack Obama’s use of lyricism in his July 2008 speech, ‘A World That Stands as One.’” Notice the shift in tense. The statement has gone from the future tense (this is what I will speak about) to the past tense (this is what I have spoken about). Restating the thesis in your conclusion reminds the audience of the main purpose or goal of your speech, helping them remember it better.
Review of Main Points
After restating the speech’s thesis, the second step in a powerful conclusion is to review the main points from your speech. One of the biggest differences between written and oral communication is the necessity of repetition in oral communication. When we preview our main points in the introduction, effectively discuss and make transitions to our main points during the body of the speech, and review the main points in the conclusion, we increase the likelihood that the audience will retain our main points after the speech is over.
In the introduction of a speech, we deliver a preview of our main body points, and in the conclusion, we deliver a review . Let’s look at a sample preview:
In order to understand the field of gender and communication, I will first differentiate between the terms biological sex and gender. I will then explain the history of gender research in communication. Lastly, I will examine a series of important findings related to gender and communication.
In this preview, we have three clear main points. Let’s see how we can review them at the conclusion of our speech:
Today, we have differentiated between the terms biological sex and gender, examined the history of gender research in communication, and analyzed a series of research findings on the topic.
In the past few minutes, I have explained the difference between the terms “biological sex” and “gender,” discussed the rise of gender research in the field of communication, and examined a series of groundbreaking studies in the field.
Notice that both of these conclusions review the main points initially set forth. Both variations are equally effective reviews of the main points, but you might like the linguistic turn of one over the other. Remember, while there is a lot of science to help us understand public speaking, there’s also a lot of art as well. You are always encouraged to choose the wording that you think will be most effective for your audience.
Concluding Device
The final part of a powerful conclusion is the concluding device. A concluding device is a final thought you want your audience members to have when you stop speaking. It also provides a definitive sense of closure to your speech. One of the authors of this text often makes an analogy between a gymnastics dismount and the concluding device in a speech. Just as a gymnast dismounting the parallel bars or balance beam wants to stick the landing and avoid taking two or three steps, a speaker wants to “stick” the ending of the presentation by ending with a concluding device instead of with, “Well, umm, I guess I’m done.” Miller observed that speakers tend to use one of ten concluding devices when ending a speech (Miller, 1946). The rest of this section is going to examine these ten concluding devices and one additional device that we have added.
Conclude with a Challenge
The first way that Miller found that some speakers end their speeches is with a challenge. A challenge is a call to engage in some activity that requires a special effort. In a speech on the necessity of fund-raising, a speaker could conclude by challenging the audience to raise 10 percent more than their original projections. In a speech on eating more vegetables, you could challenge your audience to increase their current intake of vegetables by two portions daily. In both of these challenges, audience members are being asked to go out of their way to do something different that involves effort on their part.
Conclude with a Quotation
A second way you can conclude a speech is by reciting a quotation relevant to the speech topic. When using a quotation, you need to think about whether your goal is to end on a persuasive note or an informative note. Some quotations will have a clear call to action, while other quotations summarize or provoke thought. For example, let’s say you are delivering an informative speech about dissident writers in the former Soviet Union. You could end by citing this quotation from Alexander Solzhenitsyn: “A great writer is, so to speak, a second government in his country. And for that reason, no regime has ever loved great writers” (Solzhenitsyn, 1964). Notice that this quotation underscores the idea of writers as dissidents, but it doesn’t ask listeners to put forth the effort to engage in any specific thought process or behavior. If, on the other hand, you were delivering a persuasive speech urging your audience to participate in a very risky political demonstration, you might use this quotation from Martin Luther King Jr.: “If a man hasn’t discovered something that he will die for, he isn’t fit to live” (King, 1963). In this case, the quotation leaves the audience with the message that great risks are worth taking, that they make our lives worthwhile, and that the right thing to do is to go ahead and take that great risk.
Conclude with a Summary
When a speaker ends with a summary, they are simply elongating the review of the main points. While this may not be the most exciting concluding device, it can be useful for information that was highly technical or complex or for speeches lasting longer than thirty minutes. Typically, for short speeches (like those in your class), this summary device should be avoided.
Conclude by Visualizing the Future
The purpose of a conclusion that refers to the future is to help your audience imagine the future you believe can occur. If you are giving a speech on the development of video games for learning, you could conclude by depicting the classroom of the future where video games are perceived as true learning tools and how those tools could be utilized. More often, speakers use visualization of the future to depict how society would be, or how individual listeners’ lives would be different if the speaker’s persuasive attempt worked. For example, if a speaker proposes that a solution to illiteracy is hiring more reading specialists in public schools, the speaker could ask her or his audience to imagine a world without illiteracy. In this use of visualization, the goal is to persuade people to adopt the speaker’s point of view. By showing that the speaker’s vision of the future is a positive one, the conclusion should help to persuade the audience to help create this future.
Conclude with an Appeal for Action
Probably the most common persuasive concluding device is the appeal for action or the call to action. In essence, the appeal for action occurs when a speaker asks their audience to engage in a specific behavior or change in thinking. When a speaker concludes by asking the audience “to do” or “to think” in a specific manner, the speaker wants to see an actual change. Whether the speaker appeals for people to eat more fruit, buy a car, vote for a candidate, oppose the death penalty, or sing more in the shower, the speaker is asking the audience to engage in action.
One specific type of appeal for action is the immediate call to action. Whereas some appeals ask for people to engage in behavior in the future, an immediate call to action asks people to engage in behavior right now. If a speaker wants to see a new traffic light placed at a dangerous intersection, he or she may conclude by asking all the audience members to sign a digital petition right then and there, using a computer the speaker has made available ( http://www.petitiononline.com ). Here are some more examples of immediate calls to action:
- In a speech on eating more vegetables, pass out raw veggies and dip at the conclusion of the speech.
- In a speech on petitioning a lawmaker for a new law, provide audience members with a prewritten e-mail they can send to the lawmaker.
- In a speech on the importance of using hand sanitizer, hand out little bottles of hand sanitizer and show audience members how to correctly apply the sanitizer.
- In a speech asking for donations for a charity, send a box around the room asking for donations.
These are just a handful of different examples we’ve seen students use in our classrooms to elicit an immediate change in behavior. These immediate calls to action may not lead to long-term change, but they can be very effective at increasing the likelihood that an audience will change behavior in the short term.
Conclude by Inspiration
By definition, the word inspire means to affect or connect with someone emotionally. Both affect and arouse have strong emotional connotations. The ultimate goal of an inspiration concluding device is similar to an “appeal for action,” but the ultimate goal is more lofty or ambiguous. The goal is to stir someone’s emotions in a specific manner. Maybe a speaker is giving an informative speech about the prevalence of domestic violence in our society today. That speaker could end the speech by reading Paulette Kelly’s powerful poem “I Got Flowers Today.” “I Got Flowers Today” is a poem that evokes strong emotions because it’s about an abuse victim who received flowers from her abuser every time she was victimized. The poem ends by saying, “I got flowers today… Today was a special day. It was the day of my funeral. Last night he killed me” (Kelly, 1994).
Conclude with Advice
The next concluding device is one that should be used primarily by speakers who are recognized as expert authorities on a given subject. Advice is a speaker’s opinion about what should or should not be done. The problem with opinions is that everyone has one, and one person’s opinion is not necessarily any more correct than another’s. There needs to be a really good reason for your opinion. Your advice should matter to your audience. If, for example, you are an expert in nuclear physics, you might conclude a speech on energy by giving advice about the benefits of nuclear energy.
Conclude by Proposing a Solution
Another way a speaker can conclude a speech powerfully is to offer a solution to the problem discussed within a speech. For example, perhaps a speaker has been discussing the problems associated with the disappearance of art education in the United States. The speaker could then propose a solution for creating more community-based art experiences for school children as a way to fill this gap. Although this can be a compelling conclusion, a speaker must ask themselves whether the solution should be discussed in more depth as a stand-alone main point within the body of the speech so that audience concerns about the proposed solution may be addressed.
Conclude with a Question
Another way you can end a speech is to ask a rhetorical question that forces the audience to ponder an idea. Maybe you are giving a speech on the importance of the environment, so you end the speech by saying, “Think about your children’s future. What kind of world do you want them raised in? A world that is clean, vibrant, and beautiful—or one that is filled with smog, pollution, filth, and disease?” Notice that you aren’t asking the audience to verbally or nonverbally answer the question. The goal of this question is to force the audience into thinking about what kind of world they want for their children.
Conclude with a Reference to Audience
The last concluding device discussed by Miller (1946) was a reference to one’s audience. This concluding device is when a speaker attempts to answer the audience question, “What’s in it for me?” The goal of this concluding device is to spell out the direct benefits a behavior or thought change has for audience members. For example, a speaker talking about stress reduction techniques could conclude by listing all the physical health benefits stress reduction offers (e.g. improved reflexes, improved immune system, improved hearing, reduction in blood pressure). In this case, the speaker is spelling out why audience members should care. They’re telling the audience what’s in it for them!
Connect to your Introduction
Finally, one tactic a speaker often uses is to link the introduction of the speech to the conclusion. For example, if you began your speech with a quotation, your conclusion may refer back to that person’s words in respect to what your audience has learned throughout your speech. While not always necessary, linking back to your introduction can provide a feeling of coming full circle for your audience. The repetitive nature can also help aid in remembering your speech and topic. However, you don’t want to just repeat. Instead, you want to utilize similar aspects of your attention getter to illustrate growth or movement from the beginning of your speech to the end.
A concluding device is a final thought you want your audience members to have when you stop speaking.
A challenge is a call to engage in some activity that requires special effort.
An appeal for action occurs when a speaker asks their audience to engage in a specific behavior or change in thinking.
An immediate call to action asks people to engage in behavior right now.
Inspire means to affect or connect with someone emotionally.
Advice is a speaker’s opinion about what should or should not be done.
Informative versus Persuasive Conclusions
As you read through the ten possible ways to conclude a speech, hopefully, you noticed that some of the methods are more appropriate for persuasive speeches and others are more appropriate for informative speeches. To help you choose appropriate conclusions for informative, persuasive, or entertaining speeches, we’ve created a table to help you quickly identify suitable concluding devices.
Your Speech Purpose and Concluding Devices
| Types of Concluding Devices | General Purposes of Speeches | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Challenge | x | ||
| Quotation | x | x | |
| Summary | x | x | |
| Visualizing the Future | x | x | |
| Appeal | x | ||
| Inspirational | x | x | |
| Advice | x | ||
| Proposal of Solution | x | ||
| Question | x | x | |
| Reference to Audience | x | ||
Ebbinghaus, H. (1885). Memory: A contribution to experimental psychology [Online version]. Retrieved from http://psychclassics.yorku.ca/Ebbinghaus/index.htm .
Ehrensberger, R. (1945). An experimental study of the relative effectiveness of certain forms of emphasis in public speaking. Speech Monographs, 12 , 94–111. doi: 10.1080/03637754509390108.
Kelly, P. (1994). I got flowers today. In C. J. Palmer & J. Palmer, Fire from within . Painted Post, NY: Creative Arts & Science Enterprises.
King, M. L. (1963, June 23). Speech in Detroit. Cited in Bartlett, J., & Kaplan, J. (Eds.), Bartlett’s familiar quotations (6th ed.). Boston, MA: Little, Brown & Co., p. 760.
Miller, E. (1946). Speech introductions and conclusions. Quarterly Journal of Speech, 32 , 181–183.
Solzhenitsyn, A. (1964). The first circle. New York: Harper & Row. Cited in Bartlett, J., & Kaplan, J. (Eds.), Bartlett’s familiar quotations (6th ed.). Boston, MA: Little, Brown & Co., p. 746.
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2017 by Josh Miller; Marnie Lawler-Mcdonough; Megan Orcholski; Kristin Woodward; Lisa Roth; and Emily Mueller is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- Blogging Aloud
- About me/contact
- How to write an introduction speech
Introduction speech for a guest speaker
How to write a good introduction speech step by step
By: Susan Dugdale
If you've been asked to give the introduction speech for a guest speaker you're in the right place.
Everything you need to prepare it is here. Follow the steps and you'll have an introductory speech you'll be proud to deliver.
What you'll find on this page:
- an overview of the purpose of an introduction speech for a guest speaker
- the content you're expected to cover
- an organizational pattern or template to follow
- an example introduction speech
- 6 important tips to use to ensure your speech is a success

The function of an introduction speech
Let's start with the purpose of the speech. When you understand what the speech is supposed to achieve you'll find it much easier to write.

The job of an introduction speech is to:
- introduce your guest speaker,
- give them a warm welcome,
- and create ready-and-motivated-to-listen anticipation in the audience.
Essentially you are the warm-up act. Your task is to focus and unite the audience members, to get them ready for what is to come.
Return to Top
To prepare your introduction speech you'll need:
- the guest speaker's name and, if they have one, their title. For example; Judge, Sir, The Right Honorable... Do make sure you can say their name properly and easily! If you're in doubt get the correct pronunciation from your guest speaker and practice. Also ask if they have personal pronoun preferences. Eg: they/them, she/her, he/him...
- the guest speaker's biography or the credentials of the speaker Sometimes you'll be given what the guest speaker wants said about themselves. If that isn't provided select events, achievements and qualifications to support establishing him/her as an authority within the context of the occasion. And do check that your guest is happy with what you are preparing to say about them.
- attention getters or a surprise to delight the audience, something that is not commonly known, and something revealing the personality or humanity of the person.

How to organize your material
- Build excitement or interest by adding one piece of information after another.
- Make the speaker's name and their speech title, the climax and end of your speech.
To show you how it's done I've put together an...
Introduction speech example
Let's put the speech in context to help you make sense of it.
The setting for this fictitious introduction speech is a conference for an organization called " Women in Leadership" . The audience are primarily women drawn together through an interest in leadership roles.

At the end of the speech, the speaker will lead the clapping as Rose Stephenson, the keynote speaker being introduced, takes center stage.
Now here's the introduction speech text.
Now here's the introduction speech text
" She's been a stalwart member of "Women in Leadership" for the last ten years. Over that time she's served in every office: secretary, treasurer, chairperson, chief fundraiser, education officer... to name just a few, and in some roles several times over.
Her passionate dedication to promoting public speaking as an important component of empowerment is inspiring. We estimate that she has personally mentored at least 100 new speakers and has set an extraordinary "yes, you can" example for many more. We see her as capable, confident and fluent: never at a loss for words. But what you probably don't know is that this women once stuttered, stammered and blushed.
Yes, she was often temporarily paralyzed, struck dumb by the mere thought of standing in front of an audience to speak.
How she got from awkward tongue tied silence to becoming an eloquent front line spokesperson is the story she will share with us tonight.
Ladies, without further ado, it's with great pleasure, I give you... Rose Stephenson on "Speaking To Lead!"
Say the speech out loud! Use it as a template!
Try saying it out loud to get the flow of it.
If you like it, use it as a model for the introduction speech you need to write.
6 tips to make your introduction speech successful
1. consider tone and language use.
Is what you've prepared appropriate for the occasion, audience and your guest speaker? Have you avoided using a string of clichés?
2. Check the length of your speech

Pertinent and pithy: a short speech is what you want. One to two minutes should be enough.
Test it out loud with a timer and trim if necessary.
My example speech is 171 words long. That will take approximately 1 minute 30 seconds to say depending on the speaker's rate of speech.
For more on: the number of words per minute in a speech . (This page has estimations for the number of words per minute spoken at a slow, medium and fast rate for speeches from 1 - 10 minutes long.)
3. Resist exaggerating or "puffing up" the speaker's achievements
First impressions count. You don't want to talk about your guest in a way that may embarrass and cause the audience to question their right to be there.
4. Always check your facts
Beware the horror of getting your facts muddled and, if you wish to mention something that may be sensitive, ask permission before you announce it in front of an audience.
5. Remember you are not the main speaker, or the star of the show

You've done a good job when you cover just enough to make the coming speech eagerly anticipated.
Please do not stray into telling the audience what the guest speaker's speech will cover in detail. That's terribly unfair on the speaker!
6. Rehearse your speech
Practice out loud until you are confidently fluent and able to convey the pleasure or enthusiasm the audience needs to get them in the right frame of mind.
For more: how to rehearse a speech well
For more: how to use your voice expressively
Other related pages you may find useful:
- How to give a self-introduction speech (with an example of a brief speech to introduce yourself to fellow workshop participants)
- How to write a welcome speech (with an example of a short welcome speech to open an event)
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.3 Putting It Together: Steps to Complete Your Introduction
Learning objectives.
- Clearly identify why an audience should listen to a speaker.
- Discuss how you can build your credibility during a speech.
- Understand how to write a clear thesis statement.
- Design an effective preview of your speech’s content for your audience.
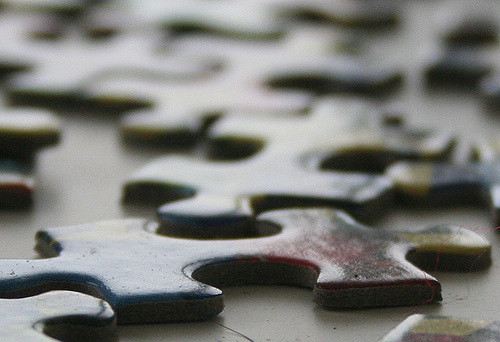
Erin Brown-John – puzzle – CC BY-NC 2.0.
Once you have captured your audience’s attention, it’s important to make the rest of your introduction interesting, and use it to lay out the rest of the speech. In this section, we are going to explore the five remaining parts of an effective introduction: linking to your topic, reasons to listen, stating credibility, thesis statement, and preview.
Link to Topic
After the attention-getter, the second major part of an introduction is called the link to topic. The link to topic is the shortest part of an introduction and occurs when a speaker demonstrates how an attention-getting device relates to the topic of a speech. Often the attention-getter and the link to topic are very clear. For example, if you look at the attention-getting device example under historical reference above, you’ll see that the first sentence brings up the history of the Vietnam War and then shows us how that war can help us understand the Iraq War. In this case, the attention-getter clearly flows directly to the topic. However, some attention-getters need further explanation to get to the topic of the speech. For example, both of the anecdote examples (the girl falling into the manhole while texting and the boy and the filberts) need further explanation to connect clearly to the speech topic (i.e., problems of multitasking in today’s society).
Let’s look at the first anecdote example to demonstrate how we could go from the attention-getter to the topic.
In July 2009, a high school girl named Alexa Longueira was walking along a main boulevard near her home on Staten Island, New York, typing in a message on her cell phone. Not paying attention to the world around her, she took a step and fell right into an open manhole. This anecdote illustrates the problem that many people are facing in today’s world. We are so wired into our technology that we forget to see what’s going on around us—like a big hole in front of us.
In this example, the third sentence here explains that the attention-getter was an anecdote that illustrates a real issue. The fourth sentence then introduces the actual topic of the speech.
Let’s now examine how we can make the transition from the parable or fable attention-getter to the topic:
The ancient Greek writer Aesop told a fable about a boy who put his hand into a pitcher of filberts. The boy grabbed as many of the delicious nuts as he possibly could. But when he tried to pull them out, his hand wouldn’t fit through the neck of the pitcher because he was grasping so many filberts. Instead of dropping some of them so that his hand would fit, he burst into tears and cried about his predicament. The moral of the story? “Don’t try to do too much at once.” In today’s world, many of us are us are just like the boy putting his hand into the pitcher. We are constantly trying to grab so much or do so much that it prevents us from accomplishing our goals. I would like to show you three simple techniques to manage your time so that you don’t try to pull too many filberts from your pitcher.
In this example, we added three new sentences to the attention-getter to connect it to the speech topic.
Reasons to Listen
Once you have linked an attention-getter to the topic of your speech, you need to explain to your audience why your topic is important. We call this the “why should I care?” part of your speech because it tells your audience why the topic is directly important to them. Sometimes you can include the significance of your topic in the same sentence as your link to the topic, but other times you may need to spell out in one or two sentences why your specific topic is important.
People in today’s world are very busy, and they do not like their time wasted. Nothing is worse than having to sit through a speech that has nothing to do with you. Imagine sitting through a speech about a new software package you don’t own and you will never hear of again. How would you react to the speaker? Most of us would be pretty annoyed at having had our time wasted in this way. Obviously, this particular speaker didn’t do a great job of analyzing her or his audience if the audience isn’t going to use the software package—but even when speaking on a topic that is highly relevant to the audience, speakers often totally forget to explain how and why it is important.
Appearing Credible
The next part of a speech is not so much a specific “part” as an important characteristic that needs to be pervasive throughout your introduction and your entire speech. As a speaker, you want to be seen as credible (competent, trustworthy, and caring/having goodwill). As mentioned earlier in this chapter, credibility is ultimately a perception that is made by your audience. While your audience determines whether they perceive you as competent, trustworthy, and caring/having goodwill, there are some strategies you can employ to make yourself appear more credible.
First, to make yourself appear competent, you can either clearly explain to your audience why you are competent about a given subject or demonstrate your competence by showing that you have thoroughly researched a topic by including relevant references within your introduction. The first method of demonstrating competence—saying it directly—is only effective if you are actually a competent person on a given subject. If you are an undergraduate student and you are delivering a speech about the importance of string theory in physics, unless you are a prodigy of some kind, you are probably not a recognized expert on the subject. Conversely, if your number one hobby in life is collecting memorabilia about the Three Stooges, then you may be an expert about the Three Stooges. However, you would need to explain to your audience your passion for collecting Three Stooges memorabilia and how this has made you an expert on the topic.
If, on the other hand, you are not actually a recognized expert on a topic, you need to demonstrate that you have done your homework to become more knowledgeable than your audience about your topic. The easiest way to demonstrate your competence is through the use of appropriate references from leading thinkers and researchers on your topic. When you demonstrate to your audience that you have done your homework, they are more likely to view you as competent.
The second characteristic of credibility, trustworthiness, is a little more complicated than competence, for it ultimately relies on audience perceptions. One way to increase the likelihood that a speaker will be perceived as trustworthy is to use reputable sources. If you’re quoting Dr. John Smith, you need to explain who Dr. John Smith is so your audience will see the quotation as being more trustworthy. As speakers we can easily manipulate our sources into appearing more credible than they actually are, which would be unethical. When you are honest about your sources with your audience, they will trust you and your information more so than when you are ambiguous. The worst thing you can do is to out-and-out lie about information during your speech. Not only is lying highly unethical, but if you are caught lying, your audience will deem you untrustworthy and perceive everything you are saying as untrustworthy. Many speakers have attempted to lie to an audience because it will serve their own purposes or even because they believe their message is in their audience’s best interest, but lying is one of the fastest ways to turn off an audience and get them to distrust both the speaker and the message.
The third characteristic of credibility to establish during the introduction is the sense of caring/goodwill. While some unethical speakers can attempt to manipulate an audience’s perception that the speaker cares, ethical speakers truly do care about their audiences and have their audience’s best interests in mind while speaking. Often speakers must speak in front of audiences that may be hostile toward the speaker’s message. In these cases, it is very important for the speaker to explain that he or she really does believe her or his message is in the audience’s best interest. One way to show that you have your audience’s best interests in mind is to acknowledge disagreement from the start:
Today I’m going to talk about why I believe we should enforce stricter immigration laws in the United States. I realize that many of you will disagree with me on this topic. I used to believe that open immigration was a necessity for the United States to survive and thrive, but after researching this topic, I’ve changed my mind. While I may not change all of your minds today, I do ask that you listen with an open mind, set your personal feelings on this topic aside, and judge my arguments on their merits.
While clearly not all audience members will be open or receptive to opening their minds and listening to your arguments, by establishing that there is known disagreement, you are telling the audience that you understand their possible views and are not trying to attack their intellect or their opinions.
Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a short, declarative sentence that states the purpose, intent, or main idea of a speech. A strong, clear thesis statement is very valuable within an introduction because it lays out the basic goal of the entire speech. We strongly believe that it is worthwhile to invest some time in framing and writing a good thesis statement. You may even want to write your thesis statement before you even begin conducting research for your speech. While you may end up rewriting your thesis statement later, having a clear idea of your purpose, intent, or main idea before you start searching for research will help you focus on the most appropriate material. To help us understand thesis statements, we will first explore their basic functions and then discuss how to write a thesis statement.
Basic Functions of a Thesis Statement
A thesis statement helps your audience by letting them know “in a nutshell” what you are going to talk about. With a good thesis statement you will fulfill four basic functions: you express your specific purpose, provide a way to organize your main points, make your research more effective, and enhance your delivery.
Express Your Specific Purpose
To orient your audience, you need to be as clear as possible about your meaning. A strong thesis will prepare your audience effectively for the points that will follow. Here are two examples:
- “Today, I want to discuss academic cheating.” (weak example)
- “Today, I will clarify exactly what plagiarism is and give examples of its different types so that you can see how it leads to a loss of creative learning interaction.” (strong example)
The weak statement will probably give the impression that you have no clear position about your topic because you haven’t said what that position is. Additionally, the term “academic cheating” can refer to many behaviors—acquiring test questions ahead of time, copying answers, changing grades, or allowing others to do your coursework—so the specific topic of the speech is still not clear to the audience.
The strong statement not only specifies plagiarism but also states your specific concern (loss of creative learning interaction).
Provide a Way to Organize Your Main Points
A thesis statement should appear, almost verbatim, toward the end of the introduction to a speech. A thesis statement helps the audience get ready to listen to the arrangement of points that follow. Many speakers say that if they can create a strong thesis sentence, the rest of the speech tends to develop with relative ease. On the other hand, when the thesis statement is not very clear, creating a speech is an uphill battle.
When your thesis statement is sufficiently clear and decisive, you will know where you stand about your topic and where you intend to go with your speech. Having a clear thesis statement is especially important if you know a great deal about your topic or you have strong feelings about it. If this is the case for you, you need to know exactly what you are planning on talking about in order to fit within specified time limitations. Knowing where you are and where you are going is the entire point in establishing a thesis statement; it makes your speech much easier to prepare and to present.
Let’s say you have a fairly strong thesis statement, and that you’ve already brainstormed a list of information that you know about the topic. Chances are your list is too long and has no focus. Using your thesis statement, you can select only the information that (1) is directly related to the thesis and (2) can be arranged in a sequence that will make sense to the audience and will support the thesis. In essence, a strong thesis statement helps you keep useful information and weed out less useful information.
Make Your Research More Effective
If you begin your research with only a general topic in mind, you run the risk of spending hours reading mountains of excellent literature about your topic. However, mountains of literature do not always make coherent speeches. You may have little or no idea of how to tie your research all together, or even whether you should tie it together. If, on the other hand, you conduct your research with a clear thesis statement in mind, you will be better able to zero in only on material that directly relates to your chosen thesis statement. Let’s look at an example that illustrates this point:
Many traffic accidents involve drivers older than fifty-five.
While this statement may be true, you could find industrial, medical, insurance literature that can drone on ad infinitum about the details of all such accidents in just one year. Instead, focusing your thesis statement will help you narrow the scope of information you will be searching for while gathering information. Here’s an example of a more focused thesis statement:
Three factors contribute to most accidents involving drivers over fifty-five years of age: failing eyesight, slower reflexes, and rapidly changing traffic conditions.
This framing is somewhat better. This thesis statement at least provides three possible main points and some keywords for your electronic catalog search. However, if you want your audience to understand the context of older people at the wheel, consider something like:
Mature drivers over fifty-five years of age must cope with more challenging driving conditions than existed only one generation ago: more traffic moving at higher speeds, the increased imperative for quick driving decisions, and rapidly changing ramp and cloverleaf systems. Because of these challenges, I want my audience to believe that drivers over the age of sixty-five should be required to pass a driving test every five years.
This framing of the thesis provides some interesting choices. First, several terms need to be defined, and these definitions might function surprisingly well in setting the tone of the speech. Your definitions of words like “generation,” “quick driving decisions,” and “cloverleaf systems” could jolt your audience out of assumptions they have taken for granted as truth.
Second, the framing of the thesis provides you with a way to describe the specific changes as they have occurred between, say, 1970 and 2010. How much, and in what ways, have the volume and speed of traffic changed? Why are quick decisions more critical now? What is a “cloverleaf,” and how does any driver deal cognitively with exiting in the direction seemingly opposite to the desired one? Questions like this, suggested by your own thesis statement, can lead to a strong, memorable speech.
Enhance Your Delivery
When your thesis is not clear to you, your listeners will be even more clueless than you are—but if you have a good clear thesis statement, your speech becomes clear to your listeners. When you stand in front of your audience presenting your introduction, you can vocally emphasize the essence of your speech, expressed as your thesis statement. Many speakers pause for a half second, lower their vocal pitch slightly, slow down a little, and deliberately present the thesis statement, the one sentence that encapsulates its purpose. When this is done effectively, the purpose, intent, or main idea of a speech is driven home for an audience.
How to Write a Thesis Statement
Now that we’ve looked at why a thesis statement is crucial in a speech, let’s switch gears and talk about how we go about writing a solid thesis statement. A thesis statement is related to the general and specific purposes of a speech as we discussed them in Chapter 6 “Finding a Purpose and Selecting a Topic” .
Choose Your Topic
The first step in writing a good thesis statement was originally discussed in Chapter 6 “Finding a Purpose and Selecting a Topic” when we discussed how to find topics. Once you have a general topic, you are ready to go to the second step of creating a thesis statement.
Narrow Your Topic
One of the hardest parts of writing a thesis statement is narrowing a speech from a broad topic to one that can be easily covered during a five- to ten-minute speech. While five to ten minutes may sound like a long time to new public speakers, the time flies by very quickly when you are speaking. You can easily run out of time if your topic is too broad. To ascertain if your topic is narrow enough for a specific time frame, ask yourself three questions.
First, is your thesis statement narrow or is it a broad overgeneralization of a topic? An overgeneralization occurs when we classify everyone in a specific group as having a specific characteristic. For example, a speaker’s thesis statement that “all members of the National Council of La Raza are militant” is an overgeneralization of all members of the organization. Furthermore, a speaker would have to correctly demonstrate that all members of the organization are militant for the thesis statement to be proven, which is a very difficult task since the National Council of La Raza consists of millions of Hispanic Americans. A more appropriate thesis related to this topic could be, “Since the creation of the National Council of La Raza [NCLR] in 1968, the NCLR has become increasingly militant in addressing the causes of Hispanics in the United States.”
The second question to ask yourself when narrowing a topic is whether your speech’s topic is one clear topic or multiple topics. A strong thesis statement consists of only a single topic. The following is an example of a thesis statement that contains too many topics: “Medical marijuana, prostitution, and gay marriage should all be legalized in the United States.” Not only are all three fairly broad, but you also have three completely unrelated topics thrown into a single thesis statement. Instead of a thesis statement that has multiple topics, limit yourself to only one topic. Here’s an example of a thesis statement examining only one topic: “Today we’re going to examine the legalization and regulation of the oldest profession in the state of Nevada.” In this case, we’re focusing our topic to how one state has handled the legalization and regulation of prostitution.
The last question a speaker should ask when making sure a topic is sufficiently narrow is whether the topic has direction. If your basic topic is too broad, you will never have a solid thesis statement or a coherent speech. For example, if you start off with the topic “Barack Obama is a role model for everyone,” what do you mean by this statement? Do you think President Obama is a role model because of his dedication to civic service? Do you think he’s a role model because he’s a good basketball player? Do you think he’s a good role model because he’s an excellent public speaker? When your topic is too broad, almost anything can become part of the topic. This ultimately leads to a lack of direction and coherence within the speech itself. To make a cleaner topic, a speaker needs to narrow her or his topic to one specific area. For example, you may want to examine why President Obama is a good speaker.
Put Your Topic into a Sentence
Once you’ve narrowed your topic to something that is reasonably manageable given the constraints placed on your speech, you can then formalize that topic as a complete sentence. For example, you could turn the topic of President Obama’s public speaking skills into the following sentence: “Because of his unique sense of lyricism and his well-developed presentational skills, President Barack Obama is a modern symbol of the power of public speaking.” Once you have a clear topic sentence, you can start tweaking the thesis statement to help set up the purpose of your speech.
Add Your Argument, Viewpoint, or Opinion
This function only applies if you are giving a speech to persuade. If your topic is informative, your job is to make sure that the thesis statement is nonargumentative and focuses on facts. For example, in the preceding thesis statement we have a couple of opinion-oriented terms that should be avoided for informative speeches: “unique sense,” “well-developed,” and “power.” All three of these terms are laced with an individual’s opinion, which is fine for a persuasive speech but not for an informative speech. For informative speeches, the goal of a thesis statement is to explain what the speech will be informing the audience about, not attempting to add the speaker’s opinion about the speech’s topic. For an informative speech, you could rewrite the thesis statement to read, “This speech is going to analyze Barack Obama’s use of lyricism in his speech, ‘A World That Stands as One,’ delivered July 2008 in Berlin.”
On the other hand, if your topic is persuasive, you want to make sure that your argument, viewpoint, or opinion is clearly indicated within the thesis statement. If you are going to argue that Barack Obama is a great speaker, then you should set up this argument within your thesis statement.
Use the Thesis Checklist
Once you have written a first draft of your thesis statement, you’re probably going to end up revising your thesis statement a number of times prior to delivering your actual speech. A thesis statement is something that is constantly tweaked until the speech is given. As your speech develops, often your thesis will need to be rewritten to whatever direction the speech itself has taken. We often start with a speech going in one direction, and find out through our research that we should have gone in a different direction. When you think you finally have a thesis statement that is good to go for your speech, take a second and make sure it adheres to the criteria shown in Table 9.1 “Thesis Checklist”
Table 9.1 Thesis Checklist
| Instructions: For each of the following questions, check either “yes” or “no.” | Yes | No | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Does your thesis clearly reflect the topic of your speech? | ||
| 2. | Can you adequately cover the topic indicated in your thesis within the time you have for your speech? | ||
| 3. | Is your thesis statement simple? | ||
| 4. | Is your thesis statement direct? | ||
| 5. | Does your thesis statement gain an audience’s interest? | ||
| 6. | Is your thesis statement easy to understand? | ||
| 7. | Does your thesis statement introduce a clear argument? | ||
| 8. | Does your thesis statement clearly indicate what your audience should do, how your audience should think, or how your audience should feel? | ||
| Scoring: For a strong thesis statement, all your answers should have been “yes.” | |||
Preview of Speech
The final part of an introduction contains a preview of the major points to be covered within your speech. I’m sure we’ve all seen signs that have three cities listed on them with the mileage to reach each city. This mileage sign is an indication of what is to come. A preview works the same way. A preview foreshadows what the main body points will be in the speech. For example, to preview a speech on bullying in the workplace, one could say, “To understand the nature of bullying in the modern workplace, I will first define what workplace bullying is and the types of bullying, I will then discuss the common characteristics of both workplace bullies and their targets, and lastly, I will explore some possible solutions to workplace bullying.” In this case, each of the phrases mentioned in the preview would be a single distinct point made in the speech itself. In other words, the first major body point in this speech would examine what workplace bullying is and the types of bullying; the second major body point in this speech would discuss the common characteristics of both workplace bullies and their targets; and lastly, the third body point in this speech would explore some possible solutions to workplace bullying.
Key Takeaways
- Linking the attention-getter to the speech topic is essential so that you maintain audience attention and so that the relevance of the attention-getter is clear to your audience.
- Establishing how your speech topic is relevant and important shows the audience why they should listen to your speech.
- To be an effective speaker, you should convey all three components of credibility, competence, trustworthiness, and caring/goodwill, by the content and delivery of your introduction.
- A clear thesis statement is essential to provide structure for a speaker and clarity for an audience.
- An effective preview identifies the specific main points that will be present in the speech body.
- Make a list of the attention-getting devices you might use to give a speech on the importance of recycling. Which do you think would be most effective? Why?
- Create a thesis statement for a speech related to the topic of collegiate athletics. Make sure that your thesis statement is narrow enough to be adequately covered in a five- to six-minute speech.
- Discuss with a partner three possible body points you could utilize for the speech on the topic of volunteerism.
- Fill out the introduction worksheet to help work through your introduction for your next speech. Please make sure that you answer all the questions clearly and concisely.
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Introduction Speech Examples That Increase Speaker Credibility

You may be called upon to introduce yourself in a speech or introduce a speaker, a guest, an employee, a product, or a concept. Your job is to grab the audience’s attention so that they are ready to receive the main message. Here are some introduction speech examples to help you.
Table of Contents
What Is A Speech Of Introduction?
In public speaking, a speech of introduction introduces someone to the audience members. It can also be a self-introduction speech wherein the speaker does the introduction.
Whether the speaker will deliver an informative speech, persuasive speech, or any type of speech, the speech of introduction aims to help establish the speaker’s background. Who are they? What do they do? What makes them credible to talk about the topic they will discuss?
How Do I Start A Speech To Introduce Someone?
If your job is to introduce someone before their speech or presentation, the first fundamental thing to remember is to keep things short and sweet. Your goal is to set the tone and entice the crowd to listen to the rest of the speech the speaker will deliver.
When writing such a speech, you must bear in mind the following:
- You must grab the audience’s attention. Though it depends on the setting and theme of the occasion, the general rule is to have an upbeat opening that will help you grab the audience’s attention. You can begin with a simple “Good morning/Good evening, ladies and gentlemen”; then state the purpose of your speech — introducing the topic, the purpose of the speech, and the guest speaker.
- You must effectively establish the speaker’s qualifications. Introduction speeches are considered commemorative speeches in the sense that they celebrate the achievements and milestones of someone. In your speech, you must concisely provide an overview of the qualifications, expertise, and relevant accomplishments of the individual you’re introducing. This is a way to establish credibility and entice the audience to listen attentively.
- You must make the speaker welcome. As someone tasked to introduce the speaker, you serve as the bridge that helps connect them with the audience. However, your goal isn’t just to prepare the audience for the speech. You must make the speaker also feel welcome with an enthusiastic tone and body language. If you have personal anecdotes or connections to share, you can do so — briefly and with the utmost authenticity.

What Is A Welcome Speech, And Can It Be Used to Introduce Someone?
A welcome speech or address is a type of speech that sets the mood for a specific event.
While it can serve as an excellent introduction to the guest speaker, it’s also an opportune time to emphasize what the event is all about and acknowledge the organization or individual behind the occasion. An excellent welcome speech can also preview what the attendees can expect — apart from the remarks by the speaker.
How Do You Introduce Yourself In Speech Examples?
In speech writing and public speaking, knowing how to introduce the speaker properly is essential. In some instances, speakers briefly introduce themselves before their speech proper. They can also incorporate it into their speech opening.
In any self-introduction speech example (check out this TED Talks compilation of intros), you will observe that there are common ingredients behind an effective self-introduction speech.
This speech must help the audience get to know you, showcase your qualification (without sounding boastful), establish connections with and create value for your listeners, and introduce your speech topics and main points. This portion aims to give your audience a reason to stick with you and hear the rest of your speech. Also, note that first impressions last, so you must ensure your intro is impactful and engaging.

See the examples below to give you an idea of how to introduce yourself while still having effective attention-getters (e.g., a rhetorical question, an anecdote, a statistic, or a bold statement).
- “Good morning/afternoon/evening. I’m X, and I’m here to talk about Y. To begin, I’d like to share a story…”
- “Have you heard about X? I’m Y, and today, I’ll share with you my thoughts about…”
- “What if overcoming your biggest fear doesn’t have to be as hard as you thought it would be? My name is X. And I’m a testament to how….”
- “Hi, I’m X, and I wanted to know: How many of you have experienced Y?”
- “Did you know that X? My name is Y, and I was asked to discuss…”
What Are Introduction Speech Examples For?
When you look for speech examples for a short introduction of speech or a self-introductory speech, you’ll find that this type of speech has a great variety.
You can use it to introduce a public speaker and a guest. In a business setting, you can also use an introduction speech to introduce an employee or present a product. Even in academe or civilian environments (e.g., you’re a high school public teacher or a personal development coach), you can count on an introduction speech to introduce a concept.
Here’s a template you can follow.
A public speaker or a guest
- Attention-getter
- State your role
- Introduce the speaker/guest
- Note the speaker/guest’s credibility and contributions
- State the topic
- A personal connection, story, or experience
- What can the audience expect/ how can the speaker provide value
- Transition to the speaker

An employee
- Introduce the employee
- Highlight their tenure/experience, achievements, skills, and qualities
- State what the employee will be discussing
- State the significance of the employee’s work/impact on the audience
- Transition to the employee
A product or a concept
- Attention-getter
- State the purpose of your speech
- Introduce the product or concept
- Share its significance
- Share its benefits
- Showcase the key features
- Do a demonstration
- Explain the potential impact
- Cite supporting facts
- Deliver a strong call to action
- Transition to the next phase or proportion of the event

No matter who or what you’re introducing in your speech, the key is to create a concise yet comprehensive one. Your speech must prepare the audience and make the speaker feel welcome. While remaining factual and genuine, you must write and deliver this piece in a way that generates interest and sets an excellent tone for the speech proper — and the rest of the event.
Recent Posts
Active Listening Absorbs The Whole Message, Not Just The Words
Active listening goes beyond hearing the words someone is saying to you and understanding the message they are conveying. Many only hear a small percentage of what is being said as they are...
Counteracting Fear Of Public Speaking With Coaching And Therapy
Nearly 75% of people experience the social phobia of fear of public speaking. The result may be nervousness before speaking or a full-blown panic attack. Practicing public speaking may lessen the...
Written Samples
3 self introduction speech samples that will impress.
A self-introduction speech is a personal narrative shared in front of an audience, whether it’s colleagues at a professional event, fellow members at a club, or a class at an educational institution.
The purpose is to provide insight into your personal and professional background, interests, and goals, all while engaging and often inspiring your audience.
Self Introduction Speech Samples
Here, we present three distinct self-introduction speech samples, each crafted to suit different personalities and occasions, complete with fictional details for relatability and impact.
Ladies and gentlemen, distinguished guests, and members of the audience, I extend my warmest greetings to all of you. It is both a pleasure and a privilege to stand here before you today, tasked with the delightful challenge of introducing myself. I am [Your Name], and I come before you as a tapestry of my experiences, beliefs, and aspirations. This introduction is not merely a recount of my personal and professional milestones but rather a glimpse into the journey that has shaped me into the individual I stand before you today.
Introduction
My story begins in a small town, infused with dreams and surrounded by a community that values hard work and perseverance. Born into a family that prized education and curiosity, I was always encouraged to explore the world around me with a keen eye and an open heart. This nurturing environment was the crucible that forged my early values and aspirations.
Educational and Professional Journey
As a child, I was fascinated by the stories of great individuals who had changed the world through their contributions to science, art, and leadership. Inspired by their journeys, I embarked on my own path of discovery and learning. I pursued my education with a fervor, delving into subjects that sparked my interest and challenged my understanding. My academic journey took me from the hallowed halls of [University/College Name] where I majored in [Your Major], to the challenging projects and roles I undertook in my professional career.
Throughout my career, I have sought to embody the principles of innovation, integrity, and impact. My professional path has been diverse, leading me through various roles in [Industry/Field], from [Specific Roles] to [Leadership Positions]. Each position offered its unique set of challenges and learning opportunities, contributing to a rich tapestry of experiences that I carry with me.
Personal Philosophy and Aspirations
Beyond my professional life, I am a person driven by a set of core values and beliefs. I believe in the power of continuous learning, the importance of empathy and compassion, and the relentless pursuit of excellence. My experiences have taught me the importance of adaptability and resilience—qualities that have been my companions through the highs and lows of my journey.
As I stand before you today, I am not just a summation of my experiences and achievements but also a product of the dreams, challenges, and support that have accompanied me along the way. My aspirations for the future are fueled by a desire to contribute meaningfully to my field and community, to inspire others as I have been inspired, and to continue growing both personally and professionally.
Contribution and Community Engagement
Part of my narrative is the unwavering commitment to giving back to the community that has given me so much. I am actively involved in [Charitable Work/Volunteering/Community Service], where I [describe specific activities]. These endeavors are not just extracurricular activities; they are integral to who I am. They allow me to connect with individuals from diverse backgrounds, learn from their experiences, and contribute to making a positive impact.
Vision for the Future
Looking ahead, I see a horizon filled with possibilities. I am committed to pursuing excellence in everything I do, to learning and growing from each new challenge, and to making a difference in the lives of others. My journey is ongoing, and each day is a new chapter waiting to be written.
In conclusion, as I stand here and share my story with you, I am reminded of the countless individuals who have been part of my journey—mentors, family, friends, and colleagues—who have shaped me into the person I am today. My story, like everyone’s, is a work in progress, and I look forward to the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead. Thank you for allowing me the honor of introducing myself today. I am excited about the possibilities of what we can achieve together and am looking forward to the journey ahead.
Esteemed audience, colleagues, and friends, I am profoundly grateful for the opportunity to stand before you today and share a bit about my life’s journey, my passions, and the path that has brought me to this moment. My name is [Your Name], and as I unfold my story, you’ll find that it is one of ambition, discovery, and a continuous quest for making a meaningful difference in the world.
My journey began in the vibrant streets of [Hometown], a place teeming with culture and history, shaping my perspective and igniting a curiosity about the world from a young age. Raised in a family where education and hard work were as natural as breathing, I was inspired early on to aim high and dream big.
Academic Pursuits and Early Career
I ventured into academics with an insatiable appetite for learning, which led me to pursue a degree in [Your Field] from [University/College Name]. My university years were a whirlwind of learning, exploration, and self-discovery, filled with late-night study sessions, stimulating discussions, and meaningful friendships that have lasted a lifetime.
After graduation, I embarked on a professional journey that has been equally exhilarating and challenging. My career began as a [Your Initial Job], where I learned the ropes of [Industry/Field] and quickly realized that my passion lay in [Specific Aspect of Your Field]. This revelation steered my career trajectory towards [Advanced Roles/Positions], where I have had the privilege of working on [Describe Specific Projects or Initiatives].
Personal Philosophy and Core Values
Throughout my life, I’ve adhered to a philosophy of [Your Personal Philosophy], which has guided both my personal and professional decisions. I believe in [List Core Values], principles that have not only shaped my career but also my approach to everyday life. These values have been my north star, helping me navigate through life’s complexities with integrity and purpose.
My aspirations are driven by a commitment to excellence and a desire to impact positively on the people and communities around me. Whether through my professional work, volunteering, or mentorship, I strive to leave a lasting imprint that inspires others to pursue their passions and make a difference.
Achievements and Contributions
Over the years, I have been fortunate to achieve [Mention Awards/Accolades] and contribute to [Mention Projects/Community Initiatives]. These milestones, while personally fulfilling, are not the end goals but rather the markers of a journey that is continuously evolving. I take great pride in my [Specific Contributions] and am always looking for new ways to leverage my skills and experiences for the greater good.
As I look to the future, I am filled with excitement for the potential to grow, learn, and contribute even more significantly. My journey is far from complete, and each day offers new opportunities to expand my horizons and embark on new adventures. I am particularly passionate about [Future Goals/Aspirations], and I am actively seeking ways to make these ambitions a reality.
In sharing my story with you today, I hope to have provided not just an account of my personal and professional history but also a sense of the values and motivations that drive me. I am incredibly excited about the opportunity to [Mention Any Upcoming Projects or Collaborations], and I look forward to engaging with each of you, learning from your experiences, and contributing to our shared goals. Thank you for the privilege of your time and attention, and I am eager to see where our collective efforts lead us.
Sample 3 (Humorous)
Hello and good [morning/afternoon/evening], esteemed guests, dear colleagues, and anyone who might have wandered in thinking this was a different event! My name is [Your Name], and I am here to introduce myself, which is fortunate because I happen to know a lot about the subject.
My journey began in a small, quirky town known as [Hometown]. It’s one of those places where everyone knows your business, whether you want them to or not, and where the local llama parade is considered high entertainment. I grew up in a family that could either be described as ‘colorful’ or ‘why are all the neighbors whispering about us?’
Early Years and Education
As a young sprout, I was as curious as a cat with a WiFi connection, always poking my nose into books, experiments, and occasionally, electrical sockets. I took to education like a duck to water, or perhaps like a duck to quantum physics, given my tendency to overcomplicate my science fair projects.
I ventured forth to [University/College Name], where I majored in [Your Major] and minored in trying to find parking. College was a blur of caffeine-fueled study sessions, existential ponderings over cafeteria food, and learning that, yes, you can indeed use a pizza box as a makeshift desk.
Career Path and Achievements
Professionally speaking, I’ve dabbled in [Industry/Field], starting as a [Initial Job]. I learned early on that ‘entry-level’ is code for ‘We’ll pay you with experience and leftover birthday cake.’ I’ve since climbed the ranks, working on projects ranging from [Important Work] to ‘Are you sure this is legal?’ My career’s been a roller coaster, which is to say thrilling, occasionally terrifying, and with a higher than average chance of losing your lunch.
Personal Philosophy and Misadventures
My personal philosophy is simple: ‘Why not?’ It’s led me to some incredible experiences, like [Anecdote] and some dubious decisions, like that time I [Humorous Misadventure]. I believe in living life with enthusiasm, curiosity, and a generous sprinkling of reckless optimism.
In terms of contributions, I’ve been involved in [Community Work/Volunteering], where I’ve honed my skills in [Skill] and discovered that yes, you can indeed fix that with duct tape. I’m proud of my [Achievement], though I’m equally proud of my record for [Quirky Personal Record].
Looking Ahead with a Wink
As for the future, I’m excited about [Upcoming Projects/Goals]. I approach new challenges with a blend of determination, strategic thinking, and an emergency stash of chocolate. I’m on a quest to [Future Ambition], and while I may not know exactly what twists and turns lie ahead, I guarantee it won’t be boring.
In wrapping up this wild ride of an introduction, I hope I’ve given you a taste of who I am: a blend of [Your Characteristics] with a penchant for [Your Quirk]. I look forward to the adventures we’ll have, the projects we’ll tackle, and the inevitable bloopers along the way. Thank you for your time, your laughter, and the opportunity to be a part of this incredible [Event/Organization]. Let the journey begin!
My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics
Self Introduction Speech [Topics + Outline Sample]

Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class.

This page deals with self introduction speech topics for classroom or other public speaking events an opportunities in life for a good first impression.
In this article:
Sample Introduction Speech Topics
Sample self introduction speech outline.
Another short manner for introducing yourself is the elevator speech, meant for business purposes.
The key question for successful and effective presenting yourself to others in both occasions is: how much and what information do you want the audience to know about you?
Due to the fact you have to write your talk around one theme, I recommend to develop one aspect of your life. That aspect will tell who you are and what you are about. Some people call this type a one-point preliminary, because it is based on one speaking idea.
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
Look at the sample self introduction speech topics and pick out the aspects of your personal life you want to share with the audience. Approach the list below with the who, the what, the whereabouts, for sure the why, the how and when questions. That is an effective way to outline your first thoughts.
- What activity has played or plays an important part in your life? Tell the story and distract the message.
- What is your main personal goal?
- What do you like very much? Your hobby?
- What do you hate or dislike? Your aversions?
- Do you have developed a very special skill?
- What is your lifestyle?
- Can you come up with a turning point or milestone in you life?
- What is your hobby or interest in your spare time?
- What is a pet peeve or another very familiar topic you like to talk about, to do or to discuss?
- Where you are from? Do your roots reveal something about yourself that is new for the audience? That always works in a small nice text for introducing your biggest personal features.
- Is there an object or prop that means a lot to you?
- What distinguishes you from other individuals in class?
Now that you have picked out a central thesis, use this example profiler I have created:
Grab their attention . Immediately bring in your central message and come to the point.
Give some background information . Tell why it is important to you, why you are doing it, why you want to tell them, etcetera.
Now work out your item of discussion in a few sentences. Draw the contours, make it personal.
Give an example .
In conclusion, offer a memorable answer in your self-introduction speech on the question the listeners probably will have when they listen to your public speaking efforts: what’s in it for me? Tell how this aspect of your life makes who you are and what you are. It will be the perfect ending of your spoken presentation.
113 Extemporaneous Speech Topics
147 Unique Speech Topics [Persuasive, Informative]
2 thoughts on “Self Introduction Speech [Topics + Outline Sample]”
i think that talking about some people that have influenced you the most really gives good base to your speech and it helps you by writing about things that you are familiar with so if you write about what has inspired you and what you care about you can easily write about anything.
Domestic violence
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class

Speech Writing Outline and Format for Students
Learning how to write a speech is a skill most students will need help refining. Guide your students through the speech writing process with the outline and descriptions below. All of the major components of a speech are included and explained in a format students can understand and apply. Once students understand the step-by-step method for crafting a successful speech, they will feel more confident speaking in front of an audience.
I. Introduction
The beginning of a speech is called the introduction. The introduction is important because it sets the tone for the entire presentation. The introduction can be broken into two parts: the attention grabber and the preview.
A. Attention Grabber: Capturing the attention of the audience is the first thing the speaker says or does. In order to do this, the speaker might tell a humorous story, ask a rhetorical question, describe a hypothetical situation, or share an interesting fact.
B. Preview: The second part of the introduction is when the speaker introduces himself or herself and the topic of the speech. The main points of the speech can also be presented at this time.
II. Body
After the introduction, the speaker transitions to the body of the speech. This is where the speaker will spend the most amount of time. The goal of the body of the speech is to clearly explain the topic.
A. Main Points: To clearly explain the topic, the body of the speech is broken down into main points. The number of main points will vary from speech to speech. Regardless of the number, it is important to keep the main points organized in a purposeful way. Also, clear transitions between main points (and throughout the speech) are critical. Without them, the audience will have trouble following along.
1. Supporting Details: Each main point needs supporting material to help the audience understand and remember that point. Examples, explanations, visual aids, and props can be used as supporting material.
III. Conclusion
The conclusion puts the finishing touches on the speech. It lets the audience know that the speech is about to end. Like the introduction, the conclusion can be broken into two parts: the review and the final statement.
A. Review: During the first part of the conclusion, the speaker restates the topic of the speech and each main point.
B. Final Statement: The speech ends with a strong final statement. The final statement addresses the topic one last time in a powerful and meaningful way. The purpose of the final statement is to round out the speech and provide the audience with a strong signal that the presentation is complete.
Click here to download everything you need to teach your students how to write an organized speech. The comprehensive lesson includes “How to Write a Speech” informational text, comprehension questions, example speech, speech outline template, speech writing rubric, and a list of 40 student-friendly speech topics.
Speech Writing Lesson Bundle
“This was an excellent way to begin the year in my speech class. It was very informative for students, had a fun appearance, and was easy to follow. I know I will use this every semester! Thank you!” -Kim O.
Students LOVE this microphone!
This wireless Bluetooth microphone is perfect for student presentations, read alouds, speeches, and so much more! The microphone has 27 colorful LED lights that flicker in rhythm with the voice. You can also use this wireless microphone as a portable Bluetooth speaker. It’s available in a bunch of different colors, and it comes with a nice storage case.
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ Over 18,000 ratings on Amazon!
“The kids loved this! I think it encouraged them to try to talk more!”
This post contains affiliate links. Click here to read my affiliate policy .

Self-Introduction Speech Examples & Tips to Help You Be Confident & Calm
Here's how you can nail your self-introduction speech, without the sweaty palms! Go from nervous to natural with these tips.
It's time! The moment for your self-introduction speech is upon you. Are your palms sweating just at the thought? There are two secrets to making it easier to give an introduction speech about yourself: practice and preparation.
And with those two things already on your to-do list, we took care of some of the lifting for you with these self-introduction speech examples. Plus plenty of tips to help you not only get through it but get through it and feel good about it after. Yes, it is possible. And you're on your way!
Easy Self-introduction Speeches for School
It's the first day of school or of the semester. Perhaps you've found yourself in a new classroom halfway through the academic year. No fear, these intros will ease you into things and hook you a few new friends and classroom groupmates, too.
- Student Council Speech Ideas & Tips to Help You Win
- Editorial Writing Examples & Tips to Share Your Opinion
- 47 Fun & Relaxing Things to Do When You Want to Unwind
Self-Introduction for Elementary or Middle School Kids
For the younger kiddos, these intros are all about who they are and what makes them happy.
- "Hi, everybody! My name is [Your Name], and I'm super excited to be in this class with all of you. I'm [Your Age] years old. I live with my family, and we have a dog named [Dog's Name] who likes to eat all my homework. I really love dinosaurs, especially the T-Rex because he's big but has tiny arms, just like my baby brother when he tries to reach for cookies on the high shelf. In my free time, I love building rocket ships from Legos. One day, I hope to become an astronaut and find aliens -- friendly ones, of course!"
- "Good morning, everyone! I'm [Your Name], and I'm really excited to be part of this class. I am [Your Age] years old. At home, I'm the queen/king of board games, although my cat [Cat's Name] often tries to join in and messes up the pieces. My favorite food is pizza, because who can say no to pizza? And when I grow up, I want to be a detective because I love solving mysteries, like where my missing socks go in the dryer. I'm looking forward to learning and having fun with all of you this year!"
Self-Introduction Speech for High Schoolers
Give new classmates an in or let people know that you're just like them so you can make friends once you find the cafeteria.
- "Hey everyone, I'm [Your Name]. I'm new here, so please go easy on me if I can't find my way to the cafeteria. A few facts about me: I love music and play the guitar -- it's like a six-stringed stress buster for me. I'm a total sci-fi geek. If you need someone to debate Star Wars vs. Star Trek, I'm your person! And I have a secret ambition: to try every ice cream flavor in the world. Looking forward to getting to know all of you."
Self-Introduction Speech for College Kids
A quip about your major is a great way to start, but you can also loop in anything you love (or avoid) on your campus too, even if it's the steps by the library that seem to go on for eternity.
- "Hello everyone! My name is [Your Name] and I'm majoring in [Your Major]. When I'm not elbow-deep in textbooks or caffeine, I love exploring the city, one coffee shop at a time. Yes, I'm a self-confessed coffee addict and my dream is to find the perfect cup of coffee. I also enjoy [Another Hobby], because what's life without a little variety, right? Excited to be on this journey with you all!"
Job Interview Self-Introduction Speech
There's nothing like the dreaded "tell us about yourself" comment at an interview. The good news? You won't have any more nightmares because this intro is the perfect way to ease into the answer.
- "Good morning/afternoon! I'm [Your Name], and it's a pleasure to meet you. I graduated from [Your University] with a degree in [Your Major], and since then, I've gained [Number of Years of Experience] years of experience in the [Your Field] field. During my previous role at [Your Previous Company], I was responsible for [Key Responsibility] and I [Describe a Key Achievement or Impact You Made]. What I particularly enjoyed about that role was the opportunity to [Something You Enjoyed that Relates to the New Job]. In my free time, I enjoy [Briefly Mention a Hobby], which helps me to [Explain How It Applies to the New Role]. For example, [Concrete Example of How Hobby Relates to Job]. I'm excited about the possibility of bringing my unique experience and passion for [Mention Something About the Company or Role] to this position. Thank you for this opportunity to interview."
- Wedding Reception Introductions for Every Type of Couple
Work Self-Introduction Speeches
Make a smooth, witty, and warm self-introduction when you land the job or want to kick off an introduction with ease.
Introduction for a New Job
You're the new kid on the block at the office, you have enough to learn, here's an easy intro on your first day before jumping in.
- "Hello team, I'm [Your Name]. I'm thrilled to be joining the [Company Name] family as your new [Your Job Title]. I come with a background in [Relevant Skills or Experience], and most recently, I was at [Previous Company] where I [Describe a Key Achievement or Project]. Outside work, I love [A Personal Interest or Hobby]. I look forward to collaborating with all of you and contributing to our shared success."
Introduction for a Presentation or Meeting
Before you launch into the important information, take a moment to let people know who you are, why you're giving this presentation, and why you're qualified to do it. After all, you've done all the hard work, allow your accolades to shine.
- "Good morning/afternoon everyone, for those who don't know me yet, I'm [Your Name], the [Your Job Title] here at [Company Name]. I oversee [Briefly Describe Your Responsibilities]. I've been with [Company Name] for [Duration at the Company], and before that, I worked at [Previous Company]. Today, I'm excited to discuss [Topic of Presentation or Meeting]. Although if you want to chat after, I also love [Hobby]."
Introduction for a Networking Event
You'll be introducing yourself a lot at networking, so now is the time to make yourself pop and be memorable.
- "Hello, I'm [Your Name], currently serving as a [Your Job Title] at [Company Name]. I've been in the [Your Industry] industry for [Number of Years], specializing in [Your Specialty]. When I'm not [Job-Related Activity], I like to [Personal Interest or Hobby]. I'm eager to meet like-minded professionals and see how we can help each other grow in our careers."
Introducing Yourself at a Funeral
Whether you're delivering a eulogy, poem, or making a brief introduction of yourself to other family and friends, you can rely on this intro to make things a little easier.
- "Good morning/afternoon, everyone. My name is [Your Name], and I had the honor of being [Deceased's Name]'s [Your Relation to the Deceased, e.g., friend, colleague, neighbor]. We shared many [memories/experiences] together, and I am here to pay my respects and celebrate the remarkable life they led. Their [specific quality or memory] has always stuck with me, and it is something I will carry in their memory."
How to Introduce Yourself at a Party
It's party time! Keep the intro laid back and casual.
- "Hi! I'm [Your Name]. I may know some of you from [How You Know Some People at the Party]. I'm [a brief sentence about yourself, e.g., your job, where you're from]. I'm a bit of a [Hobby] enthusiast, so if you ever want to chat about [Topic Related to Hobby], I'm all ears."
Examples of How to Introduce Yourself to a New Group
You're the newbie, and there's nothing wrong with that. Start your clean slate with a short and sweet intro.
- "Hello, everyone! My name is [Your Name]. I'm thrilled to be joining this group! I have always been passionate about [Your Hobby]. It all started when [A Short Story About How You Got Started With This Hobby]. Over the years, my love for it has only grown, and I've spent countless hours [Describe Something You Do Related to The Hobby].
- Apart from this, I'm [Something About Your Job or Other Interests]. In my day-to-day life, I'm a [Your Profession], which can be pretty demanding, but [Your Hobby] has always been my perfect stress-buster.
- I joined this group because I wanted to meet people who share this passion, learn from your experiences, and hopefully contribute with some of my own insights. I'm really excited to be a part of this community and can't wait to get to know all of you better!"
10 Tips for Writing and Making a Self-Introduction Speech
Here are some tips to keep in mind while writing and giving your self-introduction speech. The most important tip, however, is to do what feels natural and flows easily.
- Know Your Audience : Tailor your introduction to the context and the audience. A self-introduction at a professional event will be very different from one at a casual party.
- Start Strong: Grab the audience's attention from the beginning. You can start with an interesting fact about yourself, a short story, or a joke if the setting is informal.
- Keep It Brief: Your introduction should be concise and to the point. Stick to key details about who you are, what you do, and perhaps one or two interesting facts or hobbies.
- Be Authentic : Genuine introductions are the most memorable. Be honest about who you are and don't be afraid to show some personality.
- Highlight Key Moments : Especially in a professional setting, it can be helpful to highlight a few key experiences or achievements that have defined your career or personal life.
- End on a Positive Note: Conclude your introduction on a positive or forward-looking note. You could express excitement about the event or meeting, or share a hope or goal for the future.
- Practice, Practice, Practice : Rehearse your introduction speech so you can deliver it confidently and naturally. This will help reduce any nerves and ensure you come across as polished and professional.
- Be Engaging : Use body language to engage your audience. Make eye contact, smile, and use gestures where appropriate.
- Relate It to the Purpose of the Event : If there's a specific reason for your introduction (like starting a new job, or joining a club), make sure to mention your relationship to the event or group and your expectations or goals.
- Provide A Personal Touch : Share a little about your personal life (like a hobby or interest) to make your introduction more unique and memorable.
- 15 Powerful Attention Getters for Any Type of Speech
Remember, the goal is to introduce yourself effectively, not to tell your entire life story. Keep it brief, engaging, and genuine .
Introducing Yourself With Ease
Sit yourself in front of the mirror, and run through your lines like an actor for a play, and in no time at all, the words will flow and you'll find a natural cadence. You may even surprise yourself with how easily your introductions flows once you take the stage. Don't be surprised if people ask how you were so calm and cool.
Unsupported browser
This site was designed for modern browsers and tested with Internet Explorer version 10 and later.
It may not look or work correctly on your browser.
- Presentations
- Public Speaking
9 Good Attention Getters for Speech Introductions
The idea of a presentation is relaying a message. To make that happen you need your audience's attention! This is why you need to start your speech strong with an attention-grabbing speech introduction.

If you feel a little bit lost in the matter, fear not! This tutorial is here to help you out. We'll go over:
- how to write a speech introduction
- what makes a speech introduction good
- good attention getters for speeches
- awesome speech introduction examples so you can open with a bang
Having the right tools can help you produce a riveting introduction and an even better presentation. Turn to Envato Elements , the ultimate subscription service to find premium digital assets.
Whether you're in need of presentation templates , logo stings , infographics , and more, you can get it all for a low monthly fee!
Jump to content in this section:
- Play a Video
- Put Together Visually-Appealing Slides
- Tell a Story
- Encourage Audience Participation
- Start with Compelling Hard Data
- Be Aware of Your Non-Verbal Communication
- Break the Ice with Powerful Quotes
- Show and Tell With Props
- State Importance
A Good Speech Introduction: What, Why, and How
First, let's go over the basics.
But what makes a speech introduction good? An effective opener serves a few purposes:
- Start connecting with and engaging the audience.
- Outline the subject to be discussed.
- Let the audience know what to expect from the presentation.
- Establish your credibility and the topic's relevance.
Moreover, the introduction sets the tone for the rest of the presentation. It's in those first minutes when the audience will decide if this is worth paying attention to. O ne main purpose of a speech introduction is to get your audience's attention.
Wondering how to write a speech introduction? The simplest way to begin is to answer the basic questions:
- What are you talking about (review main ideas)?
- Who are you and why are you qualified to talk about it?
- Why is the topic important?
As you start answering those questions, there are a few things to consider. When preparing a speech introduction you should usually think about:
- Your audience. Who are you talking to and how can you tailor to them?
- The way you present those answers. Is there a hook you could use? Is there a particularly interesting piece of information? How can you pique your audience's interest?
Finally, a good introduction isn't just about the information you share. To make a good impression with your introduction, you should:
- Edit, edit, edit. Add ideas, move them around, and delete a few until you find the right flow.
- Rehearse, rehearse, rehearse. Go over the introduction a few times and even rehearse it in front of other people so you can perfect it.
All these pointers will set the foundation on which to build a great introduction to your speech.
If you followed the steps above, that means you’ve worked hard on your presentation. You've spent time and energy gathering information, structuring precisely, and creating engrossing slides.
Keep your audience’s attention away from their phones. Follow these effective attention getters for speeches and presentations:
1. Play a Video
We're highly visual beings. Moving images can catch our eyes and attention easily. For this reason, one of the best ways to introduce your speech is to play a video.
This way you'll add voices to your presentation and assist in illustrating the subject you're about to present. Plus, it will give you a chance to take a deep breath before you begin.
To make the process of creating a video for your presentation easier, you can turn to premium assets. For instance, video templates , stock video , logo stings and royalty-free music can allow you to explore your creativity and come up with a fascinating audiovisual product.
If it is, it could have the opposite effect of what you're trying to achieve.
Are you unsure of how to embed videos to your PowerPoint presentations? Here you go:

2. Put Together Visually Appealing Slides
Expanding on the tip above, make sure you have powerful visuals in your presentation slides, especially in the title slide. A p rofessional, clean, and appealing title slide will pull people in.
To make your presentation slides a success , employ the tools at your disposal. Use high-quality photos and readable, concise text.
Add interesting design elements, like a logo, shapes and the use of color. Increase the slide's appeal and present your message better.

You don't have to stress about your presentation's look and feel if you don't want to. Save time and energy and focus on the content with premium presentation templates from Envato Elements.
Work with professionally designed and easily customizable templates to make creating a presentation a breeze.
You can even learn to convert PPT to Google Slides to use the presentation software you feel most comfortable with. Take a look at this quick tutorial:

3. Tell a Story
Even today, our brains are constantly seeking for and creating narratives to understand the world around us better. Why wouldn’t you want to work with this to your advantage?
Introduce your subject with a story. It can be a personal story, a historical passage, a made-up narrative, a well-known story, and even a joke. Regardless, people will be more likely to remember it than a list of facts. Stories engage emotions, which facilitates connection.
Of course, you will need to find a way to tie the story to your presentation. As a speech introduction example, if you're talking about how to reach a goal, the popular story of the tortoise and the hare can be useful.
Just don't get carried away with the story! Word it well so you don't get lost on details and divert too far from the point you're trying to make.
4. Encourage Audience Participation
Do you want to make sure people are paying attention?
Ask them to participate from the get-go! "Show of hands", asking questions, and inserting your audience into "what ifs," "imagine thats," and hypothetical situations will get them involved with your presentation.
As a speech introduction example, a presentation about dehydration can benefit from asking the audience if they've already drank their eight glasses of water that day.
Keep this section short and sweet, so you can move on to your actual presentation. Additionally, avoid questions or situations that invite too much audience participation. They could result in the audience forgetting the main idea.

5. Start With Compelling Hard Data
Shock the audience with compelling hard data: numbers, statistics, and percentages.
Enthralling tidbits of hard data will bring abstract concepts to the real world, which can make them easier to digest. Plus, they'll be memorable and attention-grabbing.
Infographics , maps, timelines, graphics, and charts will give the eyes something to focus on and help the audience visualize your ideas more clearly.
For example, if you're looking for investors, open your speech by telling them the growth percentage of the area you work on. Or if you're talking about the environment you could work with graphic elements to create an infographic like the ones below:
Learn to make great infographics easily in PowerPoint and Google Slides with these tutorials:
6. Be Aware of Your Non-Verbal Communication
We’ve all sat through classes or presentations from people who were too nervous, unprepared, or simply weren’t great speakers. Those were masterclasses on what not to do if you want to get people interested in your presentation.
And a big way of doing that is through your non-verbal communication and body language.
Non-verbal communication refers to your voice (its volume, tone, and rhythm), eye contact, how you move around the space, hand gestures, facial expressions, how you stand, and more. You should be aware and in control of these aspects as you give your speech.
To improve your body language, record yourself going through your presentation. This way, you'll see what you look like and how you sound. With that information, you can find areas you can work on. Turning to friends and family and listening to their feedback can also be incredibly helpful.
Finally, you may want to read this tutorial to learn more about the subject and how to master your body language:
.jpg)
7. Break the Ice With Powerful Quotes
“To be or not to be.” “Be the change you want to see in the world.” “Imagine all the people…” “E equals MC square.”
These are powerful quotes that anybody could identify with. And they can be a great ice breaker.
Harness the power of these sayings and use them to start your presentation. If you’re working with a popular saying, you’ll get the added advantage that people will know it by heart and will probably finish the quote with you. This means you'll increase engagement.
Find ways to link those quotes to your subject so you can get into it in a seamless way. Cliché quotes that don't make sense in the context will only lead to confusion and a disconnected audience.
Need help putting together a great quote presentation slide? We've got you covered:

8. Show and Tell With Props
Think back to Steve Jobs and the times he unveiled a new Apple device. He didn't just sit on his hands and gave a long, detailed description on how it looked, what it did, and how it worked. He grabbed the iPhone and showed the audience.
This goes to show the advantages of using props that relate to your presentation. They'll make complicated subjects easier to understand. An external element can also make the presentation more fun and entertaining.
As a speech introduction example, if you're in finance, illustrate the concepts you'll be going over with a piggy bank and coins. This adds something special to your speech, which will keep all eyes on you.
Here's another example. In the image below, a doctor employs a mannequin and a volunteer for a CPR demonstration:

9. State Importance
Finally, this is a tip we mentioned before but it bears repeating. Start by answering the main question: why should your audience pay attention? Are you trying to solve a problem? Do you have a request?
On that subject, be sure to answer the question, “ who? ” Not only, why is the presentation important, but why should they listen to you? What makes you an expert on it? This gives you and your presentation some validity.
It's a simple tip, but if you do it right, you can engage your audience.
Take Your Presentations to the Next Level With Envato Elements
Need presentation templates, infographics, videos or music to take your presentation to the next level? Look no further than Envato Elements .
Envato Elements has a unique and unbeatable offer. For a low monthly fee, you get access to thousands of premium digital assets. This means you can download as many presentation attention getters as you want!
And here are just a few examples of the type of professional and premium digital items from Envato Elements. These can take your presentation to the next level:
1. Modern Editable Infographics vol. 2

One of the best ways to get people interested in what you want to say is by sharing informative graphics. Instead of telling them what they want to know, show it to them with a premium infographic template like this one! Here are its features:
- AI and PDF file types
- 2 color themes
- fully editable charts and data
- vector objects
- fonts and help guide included
2. Bowman - Creative Keynote

If you're presenting a project or business that's in the creative sphere, you need to show that through your slides. Letting your personality shine through will help you reach the audience effectively. For instance, this template has interesting shapes, colors, elements, and features that help it stand out:
- 40 multipurpose slides
- 16:9 HD widescreen slide format
- based on Master Slides
- fully editable text, images, colors, shapes
3. Corporate Piano Royalty-Free Song
Some chill, subdued music can add to your presentation without overwhelming the audience. A royalty-free song like this one can even make any videos or logo stings you may have more powerful.
This main track comes in MP3 and is 2:24 long. It doesn't have any vocals that could interfere with your speech and can be looped as many times as you want.
4. Logo Reveal

If what you want to do is mesmerize your audience, make sure to do it with your logo! Share who you are in an impactful way with a logo reveal template like this one. You can easily customize it in After Effects, and you don't need any plugins to do it.
5. MURO - PowerPoint Minimal Template

Finally, here's another premium example of the power that can come from having the right presentation template by your side. In this case, we're looking at a minimal, modern, smart slide deck. Muro has:
- over 115 unique slides
- 16x9 full HD format
- over 500 vector line icons
- easily and quickly editable in PowerPoint
Enchant Your Audience!
We went through a bunch of good attention fetters for speech introductions, A speech introduction can be tough to get right. It has to capture the attention of the audience and make them want to hear more.
Hopefully, you’ll be a step closer to success with this tutorial and the ideas we shared:
- and speech introduction examples
Be sure to mix the tips up and play around with them to find the attention getters for speech introductions that work best for you.


- Undergraduate Students
- Doctoral Students
- Master’s Students
- Engineering Master’s Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Parents & Families
- Asian / Pacific Islander
- Black/African American
- First Generation/Low Income
- Hispanic/Latinx
- International
- Native American/Indigenous
- Neurodiverse
- Student Athletes
- Students with Disabilities
- Undocumented
- What is a Career Community?
- Business, Finance & Consulting
- Data, Technology & Engineering
- Discovery & Exploration
- Education, Government, Nonprofit & Policy
- Energy, Environment & Sustainability
- Entertainment, Media & Arts
- Healthcare & Biomedical Sciences
- Innovation, Entrepreneurship & Design
- Know Yourself
- Explore Options
- Focus & Prepare
- Take Action
- Evaluate & Refine
- Featured Opportunities
- Career Readiness Resources
- Personalize Your Hub
- For Employers
How to Craft an Engineer Elevator Pitch with Examples
- Share This: Share How to Craft an Engineer Elevator Pitch with Examples on Facebook Share How to Craft an Engineer Elevator Pitch with Examples on LinkedIn Share How to Craft an Engineer Elevator Pitch with Examples on X
By Brooklyn Kiosow, Melissa Epifano

An elevator pitch or elevator speech is a succinct way to explain one’s goals and skills and why they stand out from the crowd and opens up a conversation with a focused, interested audience.
It’s often used at the beginning of a job interview, as a base for cover letters, as an introduction at career fairs or at a networking event, or even when
happening upon an old friend that mentions an appealing job opening at their company.
While they might sound simple on the surface, elevator pitches aren’t so easy to perfect. You want to pitch yourself in a unique but concise way, and there are a few things you should always try to include in your pitch.
Once you have an elevator pitch memorized, you’ll be able to work it into a conversation with ease and keep potential employers interested. A well constructed elevator pitch becomes a handy tool and spoken cover letter at a job interview, networking event, career fair, or as a value proposition or unique selling point if you start your own business.
Below, we’ve compiled a list of everything that makes a successful engineering elevator pitch as well as a template you can follow to get started.
The post How to Craft an Engineer Elevator Pitch with Examples appeared first on Thomasnet .

- GW Mission Statement
- GW Leadership
- GW Board of Trustees

Office of the President
- About President Granberg
- Past Presidents
- Speeches & Events
- F Street House
- Name Change Requests
- Contact the Office

Convocation 2024 Address
Convocation Address (as delivered)
August 24, 2024
President Ellen M. Granberg
19th President of the George Washington University

Thank you, Provost Bracey.
Hello, and good morning, everyone! Class of 2028… welcome to the George Washington University!
You've already had a week packed with activities coordinated by our fantastic New Student Orientation team. Has it been fun?
I have really enjoyed the time I’ve spent meeting you and your families, listening to Dr. Eboo Patel’s words of wisdom at the orientation kick-off, cheering for GW at the Buff and Blue Pep Rally, and hanging out together at the National Mall. I hope you are already starting to have some of your own “only-at-GW” moments as you’ve gotten to know our campus and city.
As Provost Bracey noted, today, we are gathering to mark the beginning of your academic experience at GW. At universities around the country, a student’s academic journey is marked by two points where you gather together as a full class. The first, the one we are holding today, is called Convocation, and the second will be your Commencement on the National Mall.
GW students are some of the most intellectually and socially engaged on the planet, and your academic experience is part of what will give you the skills you need to take all of that energy and channel it into greatness. It is an amazing privilege and an amazing opportunity, and the next four years of your life will be like no other.
And what a time to begin!
As you embark on your college experience here in Washington, D.C., our nation is gearing up for an important and consequential presidential election. Every four years, this process ignites the innate passion for politics and civic engagement that defines our university, and our campuses come alive with the spirit of democracy. From canvassing and campaigning to providing expert commentary, engaging in debate, and voting—our faculty, students, and staff are involved in every aspect of this critical process.
I shared this in my welcome message earlier this week, but it bears repeating today: our location here in the heart of the nation's capital isn't just a point on a map—it's an open invitation to participate in history. I can’t imagine a more exciting time or place to begin your college journey.
Today also marks another important GW tradition—our annual Day of Service. This is one of your very first opportunities to work together as a class and have a tangible impact throughout our local communities. This dedication to service is an integral part of GW's legacy of impact, and I look forward to joining you for today's activities.
Finally, today's Convocation also marks your entrance into the GW community— a remarkable group of local, national, and global leaders and changemakers.
Over 120 members of Congress, 79 ambassadors, 2 U.S. Secretaries of State, 2 U.S. Attorney Generals, and countless journalists, judges, CEOs, athletes, and entertainers have started their careers at a GW Convocation sitting in the very seats you occupy now. And like them, you are embarking on your own unique and exciting journey to change the world.
Now, I know some of you might be thinking, "I just got here, and I'm just trying to figure this campus out."
Well, I am here today to tell you that at GW, we're experts in turning "just" into "just watch me." Every day on this campus, you will run head-first into an opportunity to engage with your passions, challenge your assumptions, and discover what truly matters to you.
I encourage you to join a club or student organization, participate in an intramural sport, attend events you may not usually have thought to attend, and engage with people who think differently than you.
If you're interested in cutting-edge research in fields like sustainability or artificial intelligence or humanitarian development, go knock on a professor's door—trust me, they'll be excited to chat with you. For those passionate about social justice and community service, our extensive community partnerships provide countless avenues to make a real difference.
These are just a few of the ways to get involved, but countless Only-at-GW opportunities await you in the years ahead.
And here's the best part about joining the GW community: you don't have to figure this all out alone.
Our faculty aren't just leaders in their fields; they're dedicated mentors committed to your success. Get to know them—visit their office hours, engage in class discussions, and ask questions.
Equally important are our staff members, who work every day to support you at every point of your GW journey.
Of course, one of the most valuable resources you have at GW is seated all around you.
Your classmates come from all 50 states and over 100 countries and represent one of the most talented classes to ever arrive at GW. They bring unique experiences and viewpoints that will challenge and enrich your own. I urge you to get to know your fellow students—not just those in your dorm or major, but those studying in different fields with different interests.
As our future leaders, one of the most critical skills I hope you take away from your time at GW is the ability to engage constructively despite differences, work across disciplines, and learn important lessons from a wide range of perspectives.
I will warn you—the next four years won't always be easy. We'll ask you to step out of your comfort zone and to grapple with problems that might seem insurmountable. But that's precisely why we all chose to come to GW. You're here to learn, grow, push boundaries, and become the kind of leader our world needs.
Class of 2028, your journey begins today, and I can't wait to see where it takes you.
On behalf of the entire GW community, welcome to the George Washington University!
Now, let’s get ready for a fantastic Day of Service!

Speech for Students
Speech generator for students.
As much as you’ve always excelled in academics, delivering a speech has never been your forte. You just don’t possess the speech skills that some people have. But now you’ve been informed that you’re the class Valedictorian and that you’ll be delivering a simple speech on your graduation day. It can’t be that bad, can it?
Well, you don’t actually have to be the best speech writer to create a good speech. There are various aspects to a good speech in pdf , whether it’s the power brought by your choice of words or you’re ability to stand and deliver a speech.
Student Council Speech

Size: 211 KB
Short Speech for Students
Size: 13 KB
Student Farewell Speech

Size: 389 KB
How Is a Student Speech Different from a Regular Speech?
Students are often asked to deliver a speech in front of the class or even the entire student body. This could be to present, inform, or inspire an audience. A student’s speech is usually meant to be straightforward and simple. They aren’t meant to be complex and they follow the standard structure of speech outline templates.
Why Have Student Speeches?
Students are often encouraged to exercise their freedom of speech. It promotes communication and interaction between individuals. This allows them to express their thoughts and protest against actions properly. A speech can help develop a student’s logical reasoning, and it allows them to ponder on various topics and provide insights on what they have learned. It’s also a way for students to continuously gain confidence in themselves. You may also see presentation speech examples & samples.
Furthermore, a student’s speech is often addressed to fellow students and other members of the academe. With this in mind, it allows the speaker to connect with the audience and build a relationship through the speech being delivered. For instance, in an introduction speech , students can be creative with their way of delivering. This is to give meaning and purpose to the speech instead of it seeming as a lecture.
Student Award Example

Size: 35 KB
Graduation Speech

Size: 136 KB
Inspirational Student Example

Size: 85 KB
How to Conclude a Student Speech
Student speeches vary in type. Some can be inspiring, such as a graduation speech , while others are simply informative. But creating these types of speeches can be tough. You deliver the speech to a group that you encounter on a daily basis, the type of individuals whose attention span is said to be about 10 to 15 minutes long.
There are various speech examples that tell you how to start a speech but there isn’t much attention given on how to end it. It’s important to keep in mind that your last words will linger in the minds of your listeners making it your last opportunity to leave an impact. Here are a few ways for you to do so:
- Tell a brief story . It should illustrate the main points of your speech.
- Summarize key points . This is to remind your audience of the purpose of your speech. There might have been points that your listeners zoned out on, so it’s good to give them a brief run through of what was covered. You may also like steps in speech composition .
- A call to action . Presenting a challenge to an audience will always leave them thinking. Motivate them with encouraging words and a strong energy.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a speech for students on achieving academic success
Help me write a speech for students on the power of perseverance

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Example: "Good afternoon, everyone.". 2. Self-Introduction (if introducing yourself) State your name and your role or position. Example: "My name is [Your Name], and I am [your position, e.g., 'the new marketing manager'].". 3. Purpose of the Speech. Explain why you are speaking and the context of the event.
Write down any relevant achievements, expertise, or credentials to include in your speech. Encourage the audience to connect with you using relatable anecdotes or common interests. Rehearse and Edit. Practice your introduction speech to ensure it flows smoothly and stays within the time frame.
Opening your speech in silence can help enhance your speech in two ways. First, it will give the audience some time to settle in, post which you can expect to grab their dedicated attention. And secondly, silence would give you some time to understand the room and calm your pre-stage anxiousness. 6.
Analyze their response and tweak the joke accordingly if necessary. Starting your speech with humour means your setting the tone of your speech. It would make sense to have a few more jokes sprinkled around the rest of the speech as well as the audience might be expecting the same from you. 4. Mohammed Qahtani.
9. It's in the news. Take headlines from what's trending in media you know the audience will be familiar with and see. Using those that relate to your speech topic as the opening of your speech is a good way to grab the attention of the audience. It shows how relevant and up-to-the-minute the topic is. For example:
Here are few sample self-introductions for you to get a hang of how they're done: Sample self-introductions. Introduction 1. I once spent an entire night in a dense forest with a friend. Well, this act was not to show off how brave I was, but it was forced on me… by my foolishness.
1664 N. Virginia Street, Reno, NV 89557. William N. Pennington Student Achievement Center, Mailstop: 0213. [email protected]. (775) 784-6030. Get tips for creating a great introduction to your speech from the Writing & Speaking Center at the University of Nevada, Reno.
The introduction of a speech is incredibly important because it needs to establish the topic and purpose, set up the reason your audience should listen to you and set a precedent for the rest of the speech. ... These are just a handful of different examples we've seen students use in our classrooms to elicit an immediate change in behavior ...
Each part has an individual purpose and contributes to setting the stage for the rest of the speech. The first step is to show the students a completed intro that contains all four components. Read the intro to the students or have them read it on their own. Example Intro: For as long as I can remember, I have been helping in the kitchen.
2. Check the length of your speech. Pertinent and pithy: a short speech is what you want. One to two minutes should be enough. Test it out loud with a timer and trim if necessary. My example speech is 171 words long. That will take approximately 1 minute 30 seconds to say depending on the speaker's rate of speech.
However, some attention-getters need further explanation to get to the topic of the speech. For example, both of the anecdote examples (the girl falling into the manhole while texting and the boy and the filberts) need further explanation to connect clearly to the speech topic (i.e., problems of multitasking in today's society).
Step 1: Understand Your Audience. Before diving into crafting your speech introduction, take the time to observe your audience. Consider their interests, knowledge level, and preferences. Tailor your introduction to resonate with them, making it relatable and engaging. Understanding your audience will allow you to choose the right tone ...
See the examples below to give you an idea of how to introduce yourself while still having effective attention-getters (e.g., a rhetorical question, an anecdote, a statistic, or a bold statement). "Good morning/afternoon/evening. I'm X, and I'm here to talk about Y. To begin, I'd like to share a story…".
Here's a guide on how to prepare for your self-introduction speech: 1. Understand Your Audience. Audience Analysis: Consider the interests, expectations, and the level of formality of your audience. Context of the Introduction: Tailor your speech according to the occasion, whether it's a professional setting, a classroom, or a social gathering.
10 Lines on Student Introduction Speech. Good morning everyone. Being a student means embodying discipline and culture and presenting oneself as the same. My name is Ajay, and I was born in Himachal Pradesh and raised in Kanpur. I am a tenth-standard student at Little Flower Montessori English Medium High School.
Sample 1. Ladies and gentlemen, distinguished guests, and members of the audience, I extend my warmest greetings to all of you. It is both a pleasure and a privilege to stand here before you today, tasked with the delightful challenge of introducing myself. I am [Your Name], and I come before you as a tapestry of my experiences, beliefs, and ...
Sample Introduction Speech Topics. Look at the sample self introduction speech topics and pick out the aspects of your personal life you want to share with the audience. Approach the list below with the who, the what, the whereabouts, for sure the why, the how and when questions. That is an effective way to outline your first thoughts.
It lets the audience know that the speech is about to end. Like the introduction, the conclusion can be broken into two parts: the review and the final statement. A. Review: During the first part of the conclusion, the speaker restates the topic of the speech and each main point. B. Final Statement: The speech ends with a strong final statement.
Practice, Practice, Practice: Rehearse your introduction speech so you can deliver it confidently and naturally. This will help reduce any nerves and ensure you come across as polished and professional. Be Engaging: Use body language to engage your audience. Make eye contact, smile, and use gestures where appropriate.
Introduction Speech for New Students at a University. "Hello and a warm welcome to all the new faces joining us today! My name is Jordan Lee, and as the President of the Student Council, it's my honor and pleasure to introduce you to our beloved university. Today marks not just the beginning of your academic journey here but also the start ...
9 Good Attention Getters for Speech Introductions. If you followed the steps above, that means you've worked hard on your presentation. You've spent time and energy gathering information, structuring precisely, and creating engrossing slides. Keep your audience's attention away from their phones.
An elevator pitch or elevator speech is a succinct way to explain one's goals and skills and why they stand out from the crowd and opens up a conversation with a focused, interested audience. It's often used at the beginning of a job interview, as a base for cover letters, as an introduction at career fairs or at a networking event, or even ...
Defining the Word Speech. When you hear the word speech, often than not, the first few things that may come to mind are talking in front of a lot of people. Explaining a topic while people are listening or saying something in front of a crowd. You're not wrong.
GW students are some of the most intellectually and socially engaged on the planet, and your academic experience is part of what will give you the skills you need to take all of that energy and channel it into greatness. It is an amazing privilege and an amazing opportunity, and the next four years of your life will be like no other.
Furthermore, a student's speech is often addressed to fellow students and other members of the academe. With this in mind, it allows the speaker to connect with the audience and build a relationship through the speech being delivered. For instance, in an introduction speech, students can be creative with their way of delivering. This is to ...