Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches


mexican independence
5 templates

hispanic heritage month
21 templates

10 templates

49 templates

indigenous canada
47 templates

39 templates
Brain Presentation templates
The brain is the chief organ of the nervous system. thanks to it, we can perform all our daily actions, from the simplest ones like eating or talking, to the most fun ones, like discovering these google slides and powerpoint templates about the brain itself..
- Calendar & Weather
- Infographics
- Marketing Plan
- Project Proposal
- Social Media
- Thesis Defense
- Black & White
- Craft & Notebook
- Floral & Plants
- Illustration
- Interactive & Animated
- Professional
- Instagram Post
- Instagram Stories

It seems that you like this template!

Register for free and start downloading now
Brain surgery.
Brain surgery can treat many conditions. Explain some details about this medical procedure with this abstract template and include the results of your research.

Brain Infographics
This presentation contains many brain infographics. They are great to express ideas, metaphorically speaking. You can add steps, express the sections of a brainstorming session… They are great in different areas in which creativity is key, such as education, business, education of health. You’ll find tables, arrows, icons and flat...

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access
Brain Tumors Clinical Case
Are you in oncology? This brain tumor clinical case template has the simple design that serious medical topics require. Use it to convey information clearly. With its simple typography and elegant design with a grid background and windows that simulate those of a web browser, this presentation manages to work...

Pastel Watercolor Mental Health Clinic
Sometimes we are more concerned about physical health than mental health, when we should be aware that being both inside and out is essential to our overall well-being. Fortunately, there are medical centers, such as mental health clinics, full of psychology professionals who are in charge of treating our mental...

Neurology Healthcare Center
Neurology is one of the most fascinating branches of medicine, and we still know very little about the amazing organ that is the brain. If you have a medical center specializing in neurology we encourage you to make it known with this fun wave template with doodle style. Its light...

Child's vs Adult's Brain Plasticity - Thesis Defense
Research works and dissertations are created anew every year, and it's great because human knowledge keeps growing thanks to them. How about making a thesis on brain plasticity and how it differs between children and adults? If you want to try something different for your thesis defense, download this template....

Computed Tomography Breakthrough
Experience the avant-garde of technology with a computed tomography breakthrough. Present a breakthrough with this vivid infographics of soft colors and cool illustrations of computed tomography. Its easy-to-navigate functionality lets you explore new frontiers in diagnostics. Make this breakthrough an integral part of your healthcare solution and navigate the future...

Brain Teasers for High School
Do you want to test the ingenuity of your high school students? In this editable template you will find different examples of brain teasers, with which you can get inspired and add your own. As for the design, it contains maze-like shapes on the backgrounds, using different flashy colors that...

Nervous System Breakthrough
Presenting breakthroughs in the nervous system just got cooler! With this amazing presentation template, you can showcase your research with a vintage vibe. Its design style is all sepia, even the illustrations, so it evokes the feeling of finding an old doctor's notebook- like you've unlocked a fascinating secret! This...

Learn More About the Nervous System
Discover the fascinating world of the nervous system with this creative template. With calming colors and engaging visuals, you'll be able to explore the different components of the nervous system in a fun and informative way. Plus, you'll get an in-depth look at the neurons, neurotransmitters, and the effects of...

Cerebellar Disorders
Download the Cerebellar Disorders presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Taking care of yourself and of those around you is key! By learning about various illnesses and how they are spread, people can get a better understanding of them and make informed decisions about eating, exercise, and seeking medical attention....

Brain Glioblastoma Clinical Case
One of the most dangerous types of cancer that can affect the brain is glioblastoma, and there's still some uncertainties surrounding this (for example, it's not known what causes glioblastoma). If you have a clinical case about this, you can use this template to explain it in detail and show...

Create your presentation Create personalized presentation content
Writing tone, number of slides, cerebrovascular accident recovery breakthrough.
Download the "Cerebrovascular Accident Recovery Breakthrough" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Treating diseases involve a lot of prior research and clinical trials. But whenever there’s a new discovery, a revolutionary finding that opens the door to new treatments, vaccines or ways to prevent illnesses, it’s great news. Should there...

Cranioencephalic Trauma Case Report
Download the "Cranioencephalic Trauma Case Report" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. A clinical case is more than just a set of symptoms and a diagnosis. It is a unique story of a patient, their experiences, and their journey towards healing. Each case is an opportunity for healthcare professionals to...

Traumatic Brain Injury Clinical Case
Medical presentations tend to be a bit too serious—of course, injuries and the like are not a matter of laughter. However, you can turn your slideshows a bit more dynamic and enjoyable for all kinds of audiences. With this new template, you can talk about a clinical case on traumatic...

Infectious Disease: Meningitis
Download the "Infectious Disease: Meningitis" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Taking care of yourself and of those around you is key! By learning about various illnesses and how they are spread, people can get a better understanding of them and make informed decisions about eating, exercise, and seeking medical...

Laterality and Learning Difficulties
Left-handed, right-handed, ambidextrous, cross laterality... all this can have an influence on the ways of learning. For example, the students with more learning difficulties are left-handed. Do you want to continue learning and teaching about this topic? Teacher Sandra Medina has provided us with some very interesting content on laterality...

Stroke (CVA) Disease
Download the Stroke (CVA) Disease presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Taking care of yourself and of those around you is key! By learning about various illnesses and how they are spread, people can get a better understanding of them and make informed decisions about eating, exercise, and seeking medical...
- Page 1 of 10
Register for free and start editing online

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
The Human Brain: Anatomy, and Functions,
Published by Lydia Daniel Modified over 9 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "The Human Brain: Anatomy, and Functions,"— Presentation transcript:
The Brain is a highly organized ORGAN that contains approximately 100 billion neurons and has a MASS of 1.4 Kilograms. The Brain is Protected by a BONY.

NERVOUS SYSTEM MCGONIGLE Intro to Psychology. Nervous System Made up of the spinal cord and the brain Neurons : Nerve cell – the neurons transmit.

Chapter 7 The Nervous System

The Nervous System.

Overview The Nervous System. The nervous system of the human is the most highly organized system of the body. The overall function of the nervous system.

And Brain Organization
Major Brain Structures and Functions Made by Ms. Collins Unscrupulously used by Mr. McNalis.

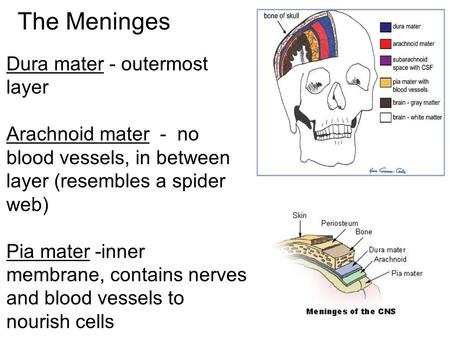
The Meninges Dura mater - outermost layer Arachnoid mater - no blood vessels, in between layer (resembles a spider web) Pia mater -inner membrane, contains.
Nervous System Outline

Principles of Health Science There are two main divisions of the nervous system: The Central Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System Divisions.

Chapter 7:6 The Nervous System.

Anatomy & Physiology Nervous System.
The Human Brain: Anatomy, Functions, and Injury. Main Menu Brain Anatomy Brain Functions Injury Mechanisms.
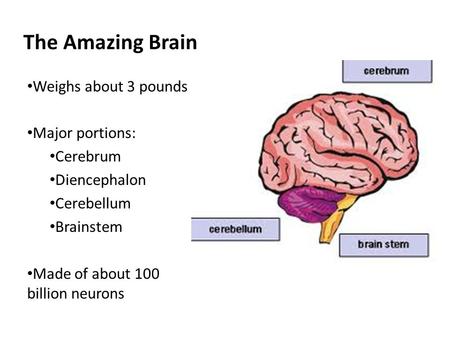
The Amazing Brain Weighs about 3 pounds Major portions: Cerebrum
600 mya = sponges have different tissues 550 mya = flatworm with “eyespots’ 500 mya = first fish 360 mya = reptiles w/lower brains 65 mya =

ANATOMY NERVOUS SYSTEM OVERVIEW. Nervous System The nervous system of the human is the most highly organized system of the body. The overall function.

Unit 1D: The Central Nervous System
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

- Types of Bones
- Axial Skeleton
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Skeletal Pathologies
- Muscle Tissue Types
- Muscle Attachments & Actions
- Muscle Contractions
- Muscular Pathologies
- Functions of Blood
- Blood Vessels
- Circulation
- Circulatory Pathologies
- Respiratory Functions
- Upper Respiratory System
- Lower Respiratory System
- Respiratory Pathologies
- Oral Cavity
- Alimentary Canal
- Accessory Organs
- Absorption & Elimination
- Digestive Pathologies
- Lymphatic Structures
- Immune System
- Urinary System Structures
- Urine Formation
- Urine Storage & Elimination
- Urinary Pathologies
- Female Reproductive System
- Male Reproductive System
- Reproductive Process
- Endocrine Glands
The Human Brain: Anatomy and Function
© 2024 Visible Body

The brain directs our body’s internal functions. It also integrates sensory impulses and information to form perceptions, thoughts, and memories. The brain gives us self-awareness and the ability to speak and move in the world. Its four major regions make this possible: The cerebrum , with its cerebral cortex, gives us conscious control of our actions. The diencephalon mediates sensations, manages emotions, and commands whole internal systems. The cerebellum adjusts body movements, speech coordination, and balance, while the brain stem relays signals from the spinal cord and directs basic internal functions and reflexes.
1. The Seat of Consciousness: High Intellectual Functions Occur in the Cerebrum
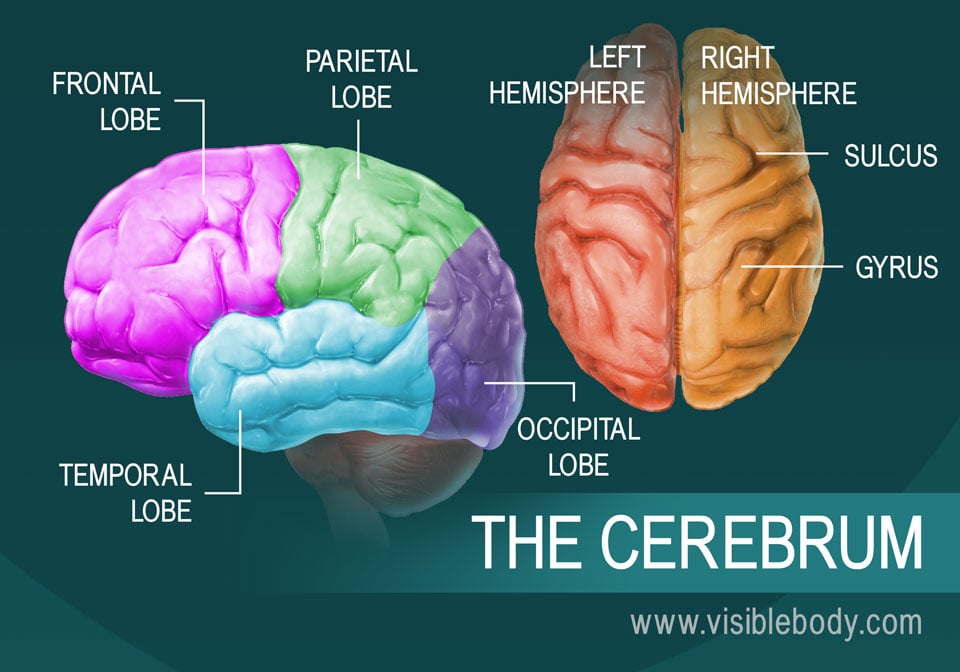
The cerebrum is the largest brain structure and part of the forebrain (or prosencephalon). Its prominent outer portion, the cerebral cortex, not only processes sensory and motor information but enables consciousness, our ability to consider ourselves and the outside world. It is what most people think of when they hear the term “grey matter.” The cortex tissue consists mainly of neuron cell bodies, and its folds and fissures (known as gyri and sulci) give the cerebrum its trademark rumpled surface. The cerebral cortex has a left and a right hemisphere. Each hemisphere can be divided into four lobes: the frontal lobe, temporal lobe, occipital lobe, and parietal lobe. The lobes are functional segments. They specialize in various areas of thought and memory, of planning and decision making, and of speech and sense perception.
2. The Cerebellum Fine-Tunes Body Movements and Maintains Balance
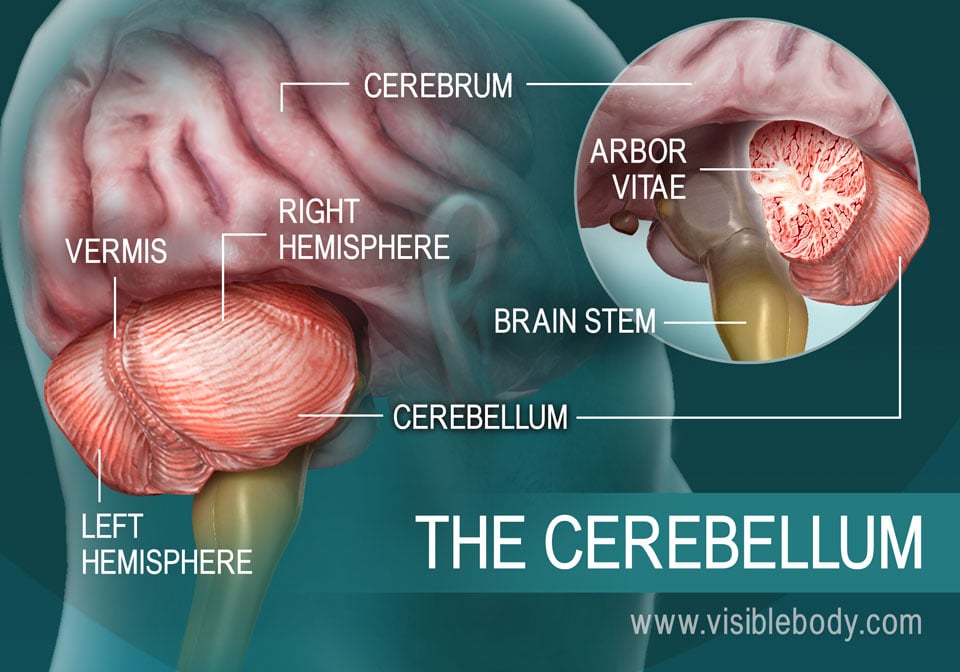
The cerebellum is the second largest part of the brain. It sits below the posterior (occipital) lobes of the cerebrum and behind the brain stem, as part of the hindbrain. Like the cerebrum, the cerebellum has left and right hemispheres. A middle region, the vermis, connects them. Within the interior tissue rises a central white stem, called the arbor vitae because it spreads branches and sub-branches through the hemispheres. The primary function of the cerebellum is to maintain posture and balance. When we jump to the side, reach forward, or turn suddenly, it subconsciously evaluates each movement. The cerebellum then sends signals to the cerebrum, indicating muscle movements that will adjust our position to keep us steady.
3. The Brain Stem Relays Signals Between the Brain and Spinal Cord and Manages Basic Involuntary Functions
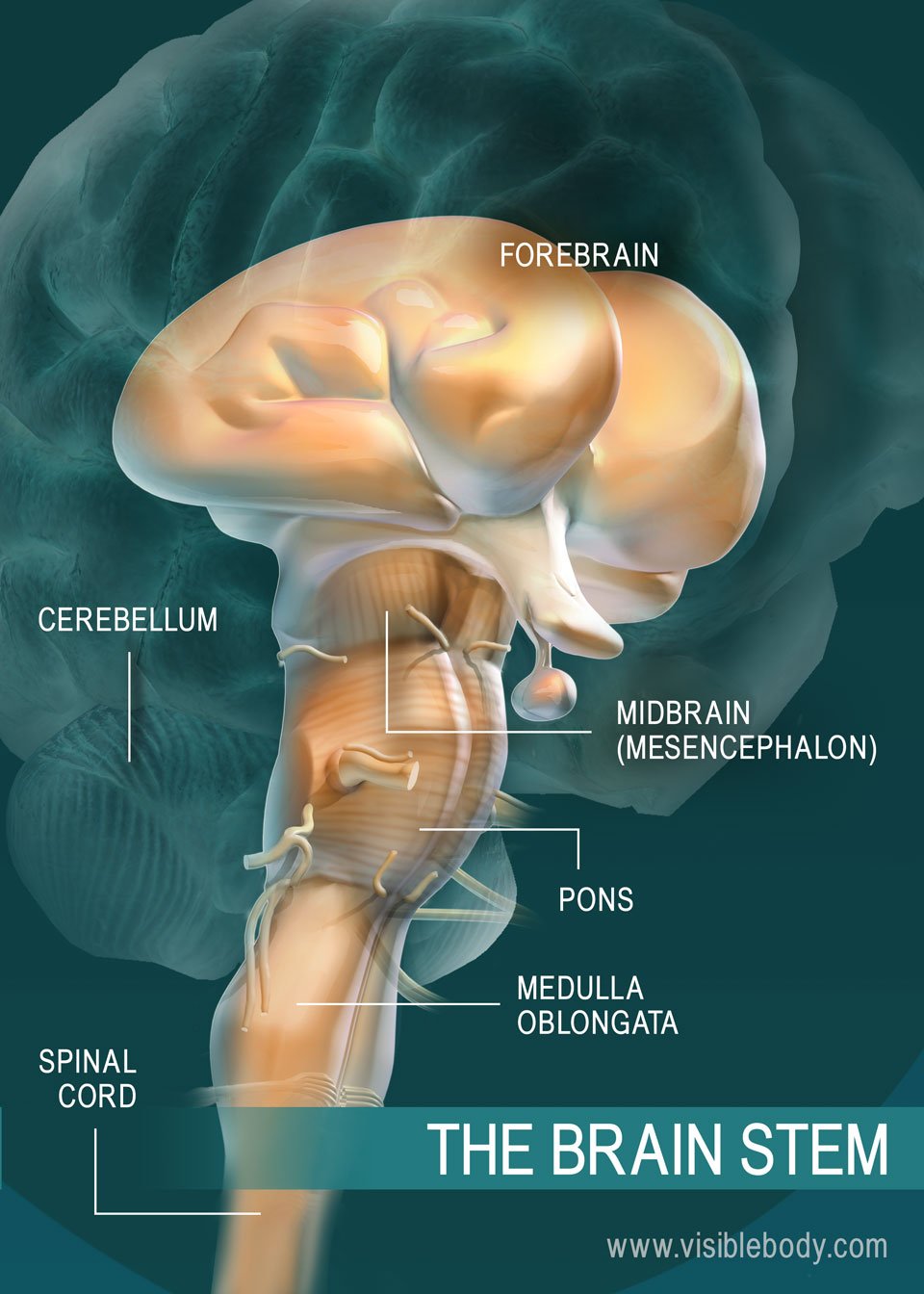
The brain stem connects the spinal cord to the higher-thinking centers of the brain. It consists of three structures: the medulla oblongata , the pons , and the midbrain . The medulla oblongata is continuous with the spinal cord and connects to the pons above. Both the medulla and the pons are considered part of the hindbrain. The midbrain, or mesencephalon, connects the pons to the diencephalon and forebrain. Besides relaying sensory and motor signals, the structures of the brain stem direct involuntary functions. The pons helps control breathing rhythms. The medulla handles respiration, digestion, and circulation, and reflexes such as swallowing, coughing, and sneezing. The midbrain contributes to motor control, vision, and hearing, as well as vision- and hearing-related reflexes.
4. A Sorting Station: The Thalamus Mediates Sensory Data and Relays Signals to the Conscious Brain
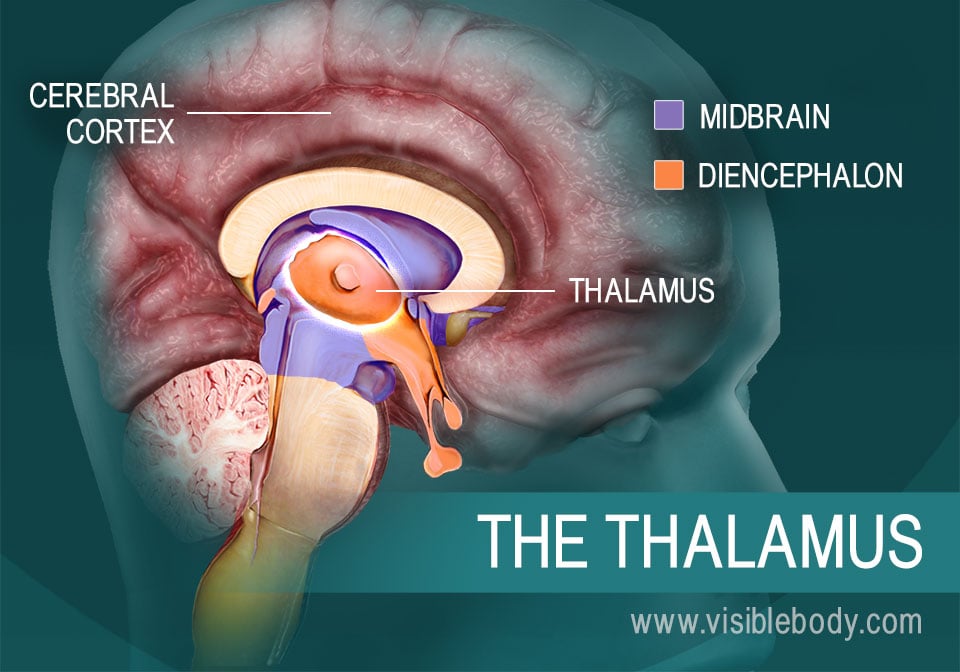
The diencephalon is a region of the forebrain, connected to both the midbrain (part of the brain stem) and the cerebrum. The thalamus forms most of the diencephalon. It consists of two symmetrical egg-shaped masses, with neurons that radiate out through the cerebral cortex. Sensory data floods into the thalamus from the brain stem, along with emotional, visceral, and other information from different areas of the brain. The thalamus relays these messages to the appropriate areas of the cerebral cortex. It determines which signals require conscious awareness, and which should be available for learning and memory.
5. The Hypothalamus Manages Sensory Impulses, Controls Emotions, and Regulates Internal Functions
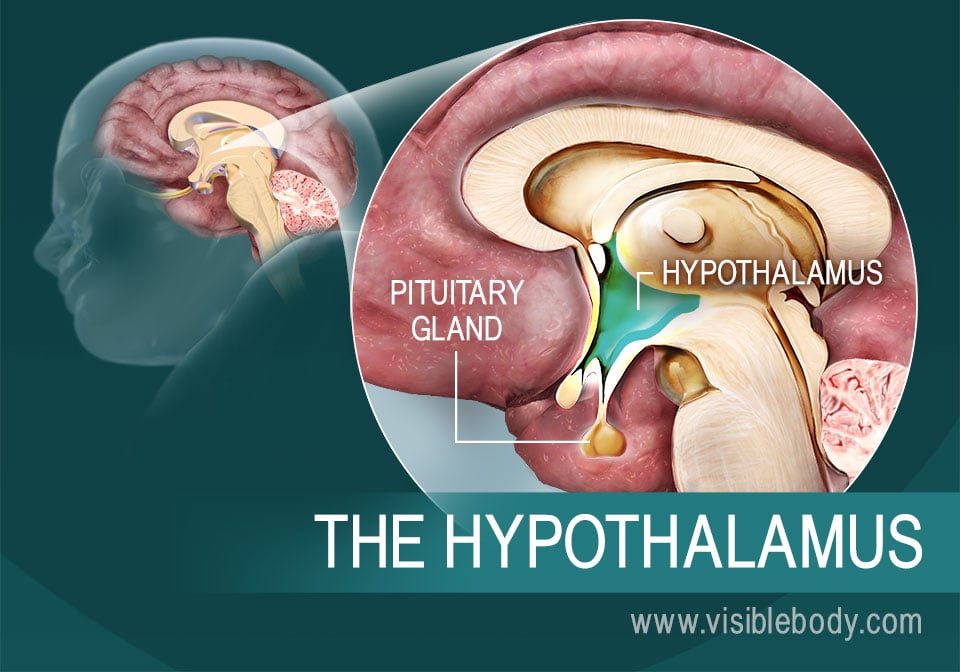
The hypothalamus is part of the diencephalon, a region of the forebrain that connects to the midbrain and the cerebrum. The hypothalamus helps to process sensory impulses of smell, taste, and vision. It manages emotions such as pain and pleasure, aggression and amusement. The hypothalamus is also our visceral control center, regulating the endocrine system and internal functions that sustain the body day to day. It translates nervous system signals into activating or inhibiting hormones that it sends to the pituitary gland. These hormones can activate or inhibit the release of pituitary hormones that target specific glands and tissues in the body. Meanwhile, the hypothalamus manages the autonomic nervous system, devoted to involuntary internal functions. It signals sleep cycles and other circadian rhythms, regulates food consumption, and monitors and adjusts body chemistry and temperature.
Download Brain Lab Manual
External Sources
An article in Science Daily on a research study about REM sleep and the pons , a part of the brain stem.
“ A Neurosurgeon’s Overview of the Brain’s Anatomy ” from the American Association of Neurological Surgeons.
Visible Body Web Suite provides in-depth coverage of each body system in a guided, visually stunning presentation.
Related Articles
Nervous System Overview
Cells that Form the Nervous System
Sight, Sound, Smell, Taste, and Touch

For students
For instructors
Get our awesome anatomy emails!
When you select "Subscribe" you will start receiving our email newsletter. Use the links at the bottom of any email to manage the type of emails you receive or to unsubscribe. See our privacy policy for additional details.
- User Agreement
- Permissions

Brain Basics: Know Your Brain

The brain is the most complex part of the human body. This three-pound organ is the seat of intelligence, interpreter of the senses, initiator of body movement, and controller of behavior. Lying in its bony shell and washed by protective fluid, the brain is the source of all the qualities that define our humanity. It is the crown jewel of the human body.
This fact sheet is a basic introduction to the human brain. It can help you understand how the healthy brain works, how to keep your brain healthy, and what happens when the brain doesn't work like it should.
The Structure of the Brain

The brain is like a group of experts. All the parts of the brain work together, but each part has its own special responsibilities. The brain can be divided into three basic units: the forebrain , the midbrain , and the hindbrain .
The hindbrain includes the upper part of the spinal cord, the brain stem, and a wrinkled ball of tissue called the cerebellum . The hindbrain controls the body’s vital functions such as respiration and heart rate.
The cerebellum coordinates movement and is involved in learned movements. When you play the piano or hit a tennis ball, you are activating the cerebellum.
The uppermost part of the brainstem is the midbrain, which controls some reflex actions and is part of the circuit involved in the control of eye movements and other voluntary movements. The forebrain is the largest and most highly developed part of the human brain: it consists primarily of the cerebrum and the structures hidden beneath it ( see " The Inner Brain").

When people see pictures of the brain it is usually the cerebrum that they notice. The cerebrum sits at the topmost part of the brain and is the source of conscious thoughts and actions. It holds your memories and allows you to plan, imagine, and think. It allows you to recognize friends, read, and play games.
The cerebrum is split into two halves (hemispheres) by a deep fissure. The two cerebral hemispheres communicate with each other through a thick tract of nerve fibers that lies at the base of this fissure, called the corpus callosum. Although the two hemispheres seem to be mirror images of each other, they are different. For instance, the ability to form words seems to lie primarily in the left hemisphere, while the right hemisphere seems to control many abstract reasoning skills.
For some as-yet-unknown reason, nearly all of the signals from the brain to the body and vice versa cross over on their way to and from the brain. This means that the right cerebral hemisphere primarily controls the left side of the body, and the left hemisphere primarily controls the right side. When one side of the brain is damaged, the opposite side of the body is affected. For example, a stroke in the right hemisphere of the brain can leave the left arm and leg paralyzed.
The Cerebral Cortex
Coating the surface of the cerebrum and the cerebellum is a vital layer of tissue the thickness of a stack of two or three dimes. It is called the cortex, from the Latin word for bark. Most of the actual information processing in the brain takes place in the cerebral cortex. When people talk about "gray matter" in the brain, they are talking about the cortex. The cortex is gray because nerves in this area lack the insulation that makes most other parts of the brain appear to be white. The folds in the brain add to its surface area and therefore increase the amount of gray matter and the volume of information that can be processed.
The Geography of Thought

Each cerebral hemisphere can be divided into sections, or lobes, each of which specializes in different functions. To understand each lobe and its specialty, we will take a tour of the cerebral hemispheres.
Frontal lobes

The two frontal lobes lie directly behind the forehead. When you plan a schedule, imagine the future, or use reasoned arguments, these two lobes do much of the work. One of the ways the frontal lobes seem to do these things is by acting as short-term storage sites, allowing one idea to be kept in mind while other ideas are considered.
Motor cortex

In the back portion of each frontal lobe is a motor cortex , which helps plan, control, and execute voluntary movement, like moving your arm or kicking a ball.
Parietal lobes

When you enjoy a good meal—the taste, smell, and texture of the food—two sections behind the frontal lobes called the parietal lobes are at work. The parietal lobes also support reading and arithmetic.
Somatosensory cortex

The forward parts of these lobes, just behind the motor areas, is the somatosensory cortex . These areas receive information about temperature, taste, touch, and movement from the rest of the body.
Occipital lobes

As you look at the words and pictures on this page, two areas at the back of the brain are at work. These lobes, called the occipital lobes , process images from the eyes and link that information with images stored in memory. Damage to the occipital lobes can cause blindness.
Temporal lobes

The last lobes on our tour of the cerebral hemispheres are the temporal lobes , which lie in front of the visual areas and nest under the parietal and frontal lobes. Whether you appreciate symphonies or rock music, your brain responds through the activity of these lobes. At the top of each temporal lobe is an area responsible for receiving information from the ears. The underside of each temporal lobe plays a crucial role in forming and retrieving memories, including those associated with music. Other parts of this lobe integrate memories and sensations of taste, sound, sight, and touch.
The Inner Brain
Deep within the brain, hidden from view, lie structures that are the gatekeepers between the spinal cord and the cerebral hemispheres. These structures not only determine our emotional state, but they also modify our perceptions and responses and allow us to initiate movements that without thinking about them. Like the lobes in the cerebral hemispheres, the structures described below come in pairs: each is duplicated in the opposite half of the brain.

The hypothalamus , about the size of a pearl, directs a multitude of important functions. It wakes you up in the morning and gets the adrenaline flowing during a test or job interview. The hypothalamus is also an important emotional center, controlling the chemicals that make you feel exhilarated, angry, or unhappy. Near the hypothalamus lies the thalamus , a major clearinghouse for information going to and from the spinal cord and the cerebrum.
An arching tract of nerve cells leads from the hypothalamus and the thalamus to the hippocampus . This tiny nub acts as a memory indexer—sending memories out to the appropriate part of the cerebral hemisphere for long-term storage and retrieving them when necessary. The basal ganglia (not shown) are clusters of nerve cells surrounding the thalamus. They are responsible for initiating and integrating movements. Parkinson’s disease, which results in tremors, rigidity, and a stiff, shuffling walk, affects the nerve cells in the basal ganglia.
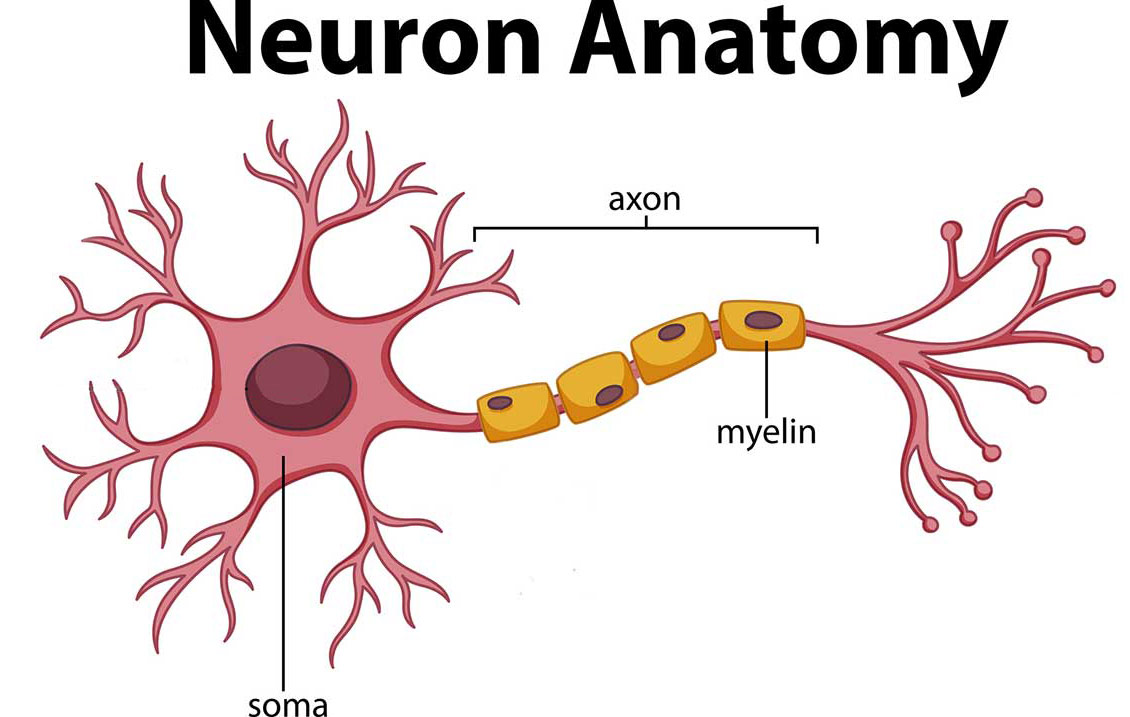
The brain and the rest of the nervous system are composed of many different types of cells, but the primary functional unit is a cell called the neuron. All sensations, movements, thoughts, memories, and feelings are the result of signals that pass through neurons. Neurons consist of three parts: the cell body , dendrites , and the axon .

The cell body contains the nucleus, where most of the molecules that the neuron needs to survive and function are manufactured. Dendrites extend out from the cell body like the branches of a tree and receive messages from other nerve cells. Signals then pass from the dendrites through the cell body and travel away from the cell body down an axon to another neuron, a muscle cell, or cells in some other organ.
The neuron is usually surrounded by many support cells. Some types of cells wrap around the axon to form an insulating myelin sheath . Myelin is a fatty molecule which provides insulation for the axon and helps nerve signals travel faster and farther. Axons may be very short, such as those that carry signals from one cell in the cortex to another cell less than a hair’s width away. Other axons may be very long, such as those that carry messages from the brain all the way down the spinal cord.
The Synapse

Scientists have learned a great deal about neurons by studying the synapse—the place where a signal passes from the neuron to another cell. When the signal reaches the end of the axon it stimulates the release of tiny sacs called vesicles. These vesicles release chemicals known as neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. The neurotransmitters cross the synapse and attach to receptors on the neighboring cell. These receptors can change the properties of the receiving cell. If the receiving cell is also a neuron, the signal can continue the transmission to the next cell.
Some Key Neurotransmitters At Work
Neurotransmitters are chemicals that brain cells use to talk to each other. Some neurotransmitters make cells more active (called excitatory ) while others block or dampen a cell's activity (called inhibitory ).
- Acetylcholine is an excitatory neurotransmitter. It governs muscle contractions and causes glands to secrete hormones. Alzheimer’s disease , which initially affects memory formation, is associated with a shortage of acetylcholine.
- Glutamate is a major excitatory neurotransmitter. Too much glutamate can kill or damage neurons and has been linked to disorders including Parkinson's disease , stroke , seizures, and increased sensitivity to pain .
- GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps control muscle activity and is an important part of the visual system. Drugs that increase GABA levels in the brain are used to treat epileptic seizures and tremors in patients with Huntington’s disease .
- Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that constricts blood vessels and brings on sleep. It is also involved in temperature regulation. Low levels of serotonin may cause sleep problems and depression, while too much serotonin can lead to seizures.
- Dopamine can be excitatory or inhibitory and is involved in mood and the control of complex movements. The loss of dopamine activity in some portions of the brain leads to the muscular rigidity of Parkinson’s disease . Many medications used to treat mental health disorders and conditions work by modifying the action of dopamine in the brain.
Neurological Disorders
The brain is one of the hardest working organs in the body. When the brain is healthy it functions quickly and automatically. But when problems occur, the results can be devastating. NINDS supports research on hundreds of neurological disorders. Knowing more about the brain can lead to the development of new treatments for diseases and disorders of the nervous system and improve many areas of human health.
A quick note about our cookies
We use cookies so we can give you the best website experience possible and to provide us with anonymous data so we can improve our marketing efforts. Read our cookie policy and privacy policy.
Login to your account
New here? Sign up in seconds!
Use social account

Or login with an email
Create an account
Already have an account? Login here
Or sign up with an email

We’re uploading new templates every week
We’d like to send you infrequent emails with brief updates to let you know of the latest free templates. Is that okay?

Reset your Password
Please enter the email you registered with and we will send you a link to reset your password!
Check your email!
We’ve just sent you a link to . Please follow instructions from our email.
- Most Popular Templates
- Corporate & Business Models
- Data (Tables, Graphs & Charts)
- Organization & Planning
- Text Slides
- Our Presentation Services
Get your own design team
Tailored packages for corporates & teams
The Human Brain Presentation Template

Number of slides: 10
The human brain is arguably one of the most complex entities in the entire universe. Even though it sits right behind our eyes, we know only a fraction of what this incredible machine is capable of. Recent advancements in science, medicine and technology have offered us a slight understanding of our brain. And to help your brain focus on the important tasks, this amazing slide deck comes with the Left-Brain Right-Brain slide, the Brain Understanding Timeline and the Brain Processes Matrix to give your audience an introduction into this wonderful biological structure.
- About this template
- How to edit
- Custom Design Services
Human Brain Presentation Template for Free
Left-brain right-brain slide.
The differences between the left brain and right brain have been a topic brought up very often in personality tests and pop culture, but the science is very real. The analytical and creative sides, even though these terms are overly-simplistic to describe the process, perform different functions of the mind that together make you the whole person that you are.
Brain Understanding Timeline
Ancient Egyptians did not think a lot of the brain. They would just scoop it out through the nostrils and discard of it. Thankfully, now we know better, and this process has been ongoing for hundreds of years. Who knows how many hundreds more until we fully understand this complex machine.
Brain Processes Matrix
Different processes are handled in various areas of the brain. This matrix can help you explain how the amygdala differs from the frontal lobe. It can visually represent the distributions of tasks throughout the brain.
Learn about yourself
Discovering more about the brain will help you understand yourself better
Don’t try to understand it all
Not even the most advanced in their field know everything about the brain
Brain Research
The brain is capable of doing incredible things, share your findings with the world!
FIND OUT MORE ABOUT OUR CUSTOM DESIGN SERVICES
Todd Speranzo
VP of Marketing at Avella
"24Slides helps us get PowerPoints on-brand, and improve overall design in a timeframe that is often “overnight”. Leveraging the time zone change and their deep understanding of PowerPoint, our Marketing team has a partner in 24Slides that allows us to focus purely on slide content, leaving all of the design work to 24Slides."
Gretchen Ponts
Strata Research
"The key to the success with working with 24Slides has been the designers’ ability to revamp basic information on a slide into a dynamic yet clean and clear visual presentation coupled with the speed in which they do so. We do not work in an environment where time is on our side and the visual presentation is everything. In those regards, 24Slides has been invaluable."
"After training and testing, 24Slides quickly learnt how to implement our CVI, deliver at a high quality and provide a dedicated design team that always tries to accommodate our wishes in terms of design and deadlines."
What's included in Keynote Template?
I want this template customized class="mobile-none"for my needs!
69 beautifully designed slides 67 icons included PowerPoint and Keynote ready 16:9 full HD class="mobile-none"resolution
Check out other similar templates
Science Icon Template Pack

General PowerPoint Icons Template
Dark themed 30 Slide Template Pack

Generic Mobile Pack Templates
Brain Anatomy and Function
Mar 09, 2019
510 likes | 1.06k Views
Brain Anatomy and Function. Anatomy of the Brain. Separated into right and left halves by the Interhemispheric Fissure. The Central Sulcus runs down & forward The Lateral Fissure runs backward & up. Frontal and Temporal Lobes. Thought Voluntary movement Speech motor
Share Presentation
- brain function
- brain anatomy
- glucose metabolism
- normal brain anatomy
- brain glucose metabolism normal

Presentation Transcript
Anatomy of the Brain • Separated into right and left halves by the Interhemispheric Fissure • The Central Sulcus • runs down & forward • The Lateral Fissure runs backward & up
Frontal and Temporal Lobes • Thought • Voluntary movement • Speech motor • Covers 1/3rd of area of the brain Frontal Temporal • Memory • Auditory function
Parietal and Occipital Lobes • Sensation • Touch • Pressure • Pain • Temperature • Texture • Position/spatial orientation Parietal Occipital • Vision • Visual processes • Reading
Medulla Oblongata, Cerebellum, and Pons • Large Muscle Coordination • Balance • Walking, Writing Medulla Oblongata Cerebellum • Respiration • Heart rate • Continuous with the spinal cord (2.5 cm) Pons • Relay between the cerebral hemispheres and the cerebellum
Basal Ganglia and Thalamus “The Brakes” • Modifies movement on a minute-to-minute basis • Inhibits Movement • Coordination • Cortical relay
Limbic System • Attention • Sensory gateway • Memory processing • Rage • Aggression • Sexuality • Appetite/Thirst
The Nerve Cell Synaptic junction
Neurotransmitters • Serotonin – major – emotions, judgment, eating and sleep disorders (associated with frontotemporal disorder) • Glutamate/GABA - Widespread, anxiety, sleep, (Valium targets this) • Dopamine – memory, mood, movement, Parkinson's Disease, psychiatric problems • Endorphins – relief of pain, (Morphine targets this) Lichtman, J., et al Washington University 2002
Normal functions Emotions Judgment Sleep Imbalances Depression Suicidal behavior Anxiety Impulsive behavior Eating disorders Serotonin Glutamate/GABA • Normal functions • Involved in most facets of brain function • Imbalances • Memory disturbances • Sleep disturbances • Anxiety
Normal functions Mood Movement Memory Imbalances Movement disorders Schizophrenia Addiction Dopamine Endorphins • Normal functions • Relieve pain • Induce euphoria
Normal Aging Brain • Brain weight and volume decrease • Grooves widen • Surface smoothes • Neurofibrillary tangles increase • Understanding normal variation is key to interpretation
Brain Glucose Metabolism –Normal • Normal brain tissue actively metabolizes glucose and its analogue (F-18 FDG) • Glucose metabolism provides 95% of the energy required for brain function • FDG is irreversibly trapped within brain cells in proportion to its use because it cannot be broken down or stored unlike glucose
FDG-PET Normal Brain Metabolism
FDG-PET Abnormal Brain Imaging • Dementia • Memory loss • Cognitive Decline • Epilepsy • Localization of a seizure focus • Tumor Assessment • Radiation Necrosis vs Tumor • Grade • Objective Imaging Diagnosis of Movement Disorders • Huntington’s Disease • Parkinson’s Disease
Dementia Diagnosis:Current Methods • History and physical examination • Neurologist (Sens. = 50-80%) • Neuropsychologist / Neuropsychiatrist • Neuropsychological testing • MRI / CT • Blood testing • Functional Neuroimaging (SPECT/ PET/MR) • Sens.=80-90%
Summary • Normal Brain Anatomy • Normal Brain Function • Current PET Brain Applications: • Diagnosis of Dementia • Seizure Localization • Tumor Assessment • Objective Imaging Diagnosis of Movement Disorders (not CMS approved)
Contributors • Rebecca Trunnell Hyman • Coordinator of PET Services • Clinical PET of West County - Creve Coeur, MO • Kevin L. Berger, M.D. • Assistant Professor of Radiology • Director of PET Imaging • Michigan State University – East Lansing, MI
- More by User

Brain Death Anatomy and Physiology
Brain Death Anatomy and Physiology. Joel S. Cohen, M.D. Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology Albert Einstein College of Medicine. Historical Perspective. Prior to the advent of mechanical respiration, death was defined as the cessation of circulation and breathing .
1.03k views • 42 slides
Muscle Function and Anatomy
Muscle Function and Anatomy. Chapter 2. Muscle Architecture. Muscle Architecture. Sections Deepest section contains two proteins Myosin (thick) Actin (thin) Myosin is surrounded by actin. Muscle Architecture. Myofibrils Bundles of actin and myosin. Muscle Architecture. Muscle fiber
846 views • 27 slides

Brain Pathology Review and Anatomy
Brain Pathology Review and Anatomy. Week 2. BRAIN ANATOMY REVIEW. Pathology Review. Anterior of corpus callosum Anterior horn of of LT lateral ventricle Caudate nucleus Thalamus Third ventricle Pineal gland Posterior horn of LT lateral ventricle. Anterior corpus callosum
819 views • 53 slides

Overview of Brain Anatomy and function
Overview of Brain Anatomy and function . Wei-Ching Lee, M.D. INTRODUCTION. Lobes Frontal Parietal Temporal Occipital Brainstem. Anatomy. Anatomy. Homunculus Man. Circle of Willis. Gold: ACA Pink: MCA Blue: PCA. Frontal Lobe. Conscientiousness Judgments
566 views • 36 slides

Neural Anatomy and Function
Neural Anatomy and Function. NERVOUS SYSTEMS. Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM p. 33. Brain Cerebral Cortex/Cerebrum Motor cortex Basal Ganglia/Diencephalon – sensory input Cerebellum – motor control Brain stem – sensory input Spinal Cord.
673 views • 43 slides

Vestibular Function and Anatomy
. System of balanceMembranous and bony labyrinth embedded in petrous bone5 distinct end organs3 semicircular canals: superior, lateral, posterior2 otolith organs: utricle and saccule. . Semicircular canals sense angular accelerationOtolithic organs (utricle and saccule) sense linear acceleration.
982 views • 43 slides

. System of balanceMembranous and bony labyrinth embedded in petrous bone5 distinct end organs3 semicircular canals: superior, lateral, posterior2 otolith organs: utricle and saccule. . Semicircular canals sense angular accelerationOtolithic organs (utricle and saccule) sense linear acceleratio
594 views • 43 slides
Brain Structure and Function
Brain Structure and Function. Overview. Lobes of the brain (Forebrain) Midbrain/Hindbrain Protection and Blood supply Structure and Function of a neuron Synaptic Transmission Neurotransmitters. The brain. Most complex organ of the body Only weighs 1,300 grams
1.23k views • 29 slides
Brain Structure and Function. “If the human brain were so simple that we could understand it, we would be so simple that we couldn’t” -Emerson Pugh, The Biological Origin of Human Values (1977). The Brain. Brainstem responsible for automatic survival functions Medulla
408 views • 16 slides


Brain Anatomy
Brain Anatomy. Brain. Divided into Forebrain, Midbrain, Hindbrain, Spinal cord. Cerebrum. Largest part Forebrain/Midbrain Left and right sides Parts control senses ( eg . parital lobe = sight ). Cerebral Cortex. Sheet of tissue covering the outermost layer of the cerebrum
2.72k views • 23 slides

Brain Function
Brain Function. By Anna Paul and Natalie Maes. The Three Parts of the Brain. The adult brain is composed of three major divisions: the Cerebrum, Cerebellum and the Brainstem. The Cerebrum . Making up most of (80-85%) of the brain are the right and left hemispheres of the cerebrum.
373 views • 13 slides

Plants: Anatomy, Growth and Function
Plants: Anatomy, Growth and Function. 12.5: Transport in Vascular Plants. Overview of transport in plants. Water and minerals transported in phloem Sugars transported in phloem. Transport of water and minerals.
455 views • 29 slides
Brain Structure and Function. “If the human brain were so simple that we could understand it, we would be so simple that we couldn’t” -Emerson Pugh, The Biological Origin of Human Values (1977). Phineas Gage. September 13 th , 1848 Phineas 25 years old
658 views • 44 slides

Plant Anatomy, Growth and Function
Plant Anatomy, Growth and Function. Candice, Sarah, Stratton, Megan. Unit Plan. Major Unit Concepts. Structure of plants Plants as resources Plants organs and Function Transport in plants Plants growth and development Reproduction in Plants Succession and Sustainability.
335 views • 8 slides

Plants: Anatomy, Growth and Function. 12.5: Transport in Vascular Plants. Overview of transport in plants. Water and minerals transported in xylem Sugars transported in phloem. Transport of water and minerals.
467 views • 28 slides
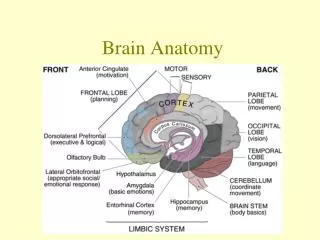
Brain Anatomy. Meninges - 3 layers. Dura Mater Superficial Fuses brain to skull Arachnoid Reduces friction Filled with CSF; shock absorber Pia Mater Very Vascular; needs a lot of oxygen due to high metabolic rate of neurons. Cerebrum Diencephalon Midbrain Pons Medulla Oblongata
1.58k views • 30 slides
Brain Anatomy Neurotransmission & Brain Neurotransmitters
Brain Anatomy Neurotransmission & Brain Neurotransmitters. Brain Structures. Cerebral Hemisphere - 1/2 of Cerebrum. Cerebral Cortex. Cerebral Cortex (Grey Matter). The cerebrum’s surface—the cerebral cortex—is convoluted into hundreds of folds.
1.14k views • 41 slides

Anatomy of Brain
Anatomy of Brain. Dr. Rima Pathak. Gross Anatomy. Main Sulci & Gyri. Central. Cingulate. Parieto Occipital. Precentral gyrus. Premotor area 6. Postcentral gyrus. Cingulate. Superior frontal gyrus. Thalamus. Caudate. Infundibular stalk. Pineal gland. Mid brain. 4 th ventricle.
1.37k views • 78 slides
Have you ever wondered how much simpler life would be if you could just find a way to increase your brain power?
84 views • 7 slides
Brain Structure and Function. LET II. Evolution of the Human Brain. The ancestors of modern man had a brain weighing only about a pound, which is roughly a third of the weight of our current brain. Most of this increased weight is because of a much larger cerebral cortex. The Triune Brain.
198 views • 14 slides

PLANTS: Anatomy, Growth and Function
PLANTS: Anatomy, Growth and Function. Plant Characteristics. Plants need energy, nutrients, water, gas exchange protection from herbivores and disease and to reproduce. Photosynthesis: Carbon dioxide + water + sunlight -> glucose + oxygen
82 views • 6 slides
Home PowerPoint Templates Brain
Brain PowerPoint Templates & Slide Designs for Presentations
Use our Brain PowerPoint & Google Slides Templates in your next presentation to illustrate intelligence, creative ideas, or work with anatomical illustrations. Access a large selection of templates depicting brain and head graphics in typical formats: head with cogwheels to express thought processes, mind maps, brain concepts, open head diagrams filled with ideas (icons), etc.
These illustrations and diagrams seamlessly adapt to your presentation requirements, ensuring a cohesive visual experience. They are crafted with fully editable PowerPoint elements and offer compatibility with Google Slides and Apple Keynote. Power up your presentations with these brain PPT slides today!

Understanding the Teen Brain PowerPoint Template

Neuroscience PowerPoint Template

Brain Slide Template for PowerPoint

Nervous System PowerPoint Template

Statistical Bias PowerPoint Templates

Brain Artificial Intelligence PowerPoint Template

6 Step Brain Machinery Circular Diagram for PowerPoint

Smart Head Design for PowerPoint

Group Thinking Phenomenon PowerPoint Template

Artificial Intelligence PowerPoint Template

Kid Head Silhouette Illustration PowerPoint Template

Human Head Puzzle PowerPoint Template
Presenters often use the picture of the brain as a metaphor for intelligence. It can also be used to prepare presentations on brainstorming ideas.
Working with brain presentation templates will save you the stress of creating a brain slide from scratch – you can easily download any templates and edit them to suit your presentation preference. For example, our Brain Slide Template for PowerPoint presents a customizable brain diagram characterized by distinct lobes and sections, cleverly illustrated with shadow effects and PowerPoint shapes. The curves of the brain are delineated by dark lines, accompanied by four label lines pinpointing crucial brain divisions: the forebrain (comprising the occipital lobe and cerebrum), midbrain, and brain stem.
In this section, you can download brain illustrations, shapes, and brain slides with pictures of the brain.
What is a Brain Presentation?
A Brain Presentation is a PowerPoint presentation focusing on topics related to the human brain. Such presentations cover brain anatomy, cognitive processes, mental health, neurological disorders, learning theories, and more. These presentations can be educational, informative, or persuasive, depending on the context and audience.
What is the Purpose of a Brain Slide Template?
These templates are intended to visually depict and explain concepts related to the brain, neuroscience, cognitive functions, or related topics in presentations. It provides a consistent and engaging framework to communicate complex ideas, making it easier for your audience to understand and remember the information you presented.
Can I Personalize the Brain PowerPoint Template to Suit my Presentation Needs?
Yes. Our brain PowerPoint template is designed to be fully customizable. You can easily modify text, images, colors, and fonts to align with your content and preferences. Click on the placeholders and replace them with your information.
Can I use this Template for my Classroom Presentation?
Certainly! Our brain PowerPoint template is well-suited for educational purposes. Whether you are teaching students about brain anatomy, cognitive processes, or neuroscience principles, this template provides a visually engaging format.
Download Unlimited Content
Our annual unlimited plan let you download unlimited content from slidemodel. save hours of manual work and use awesome slide designs in your next presentation..
Masks Strongly Recommended but Not Required in Maryland
Respiratory viruses continue to circulate in Maryland, so masking remains strongly recommended when you visit Johns Hopkins Medicine clinical locations in Maryland. To protect your loved one, please do not visit if you are sick or have a COVID-19 positive test result. Get more resources on masking and COVID-19 precautions .
- Vaccines
- Masking Guidelines
- Visitor Guidelines
Brain Anatomy and How the Brain Works
What is the brain.
The brain is a complex organ that controls thought, memory, emotion, touch, motor skills, vision, breathing, temperature, hunger and every process that regulates our body. Together, the brain and spinal cord that extends from it make up the central nervous system, or CNS.
What is the brain made of?
Weighing about 3 pounds in the average adult, the brain is about 60% fat. The remaining 40% is a combination of water, protein, carbohydrates and salts. The brain itself is a not a muscle. It contains blood vessels and nerves, including neurons and glial cells.
What is the gray matter and white matter?
Gray and white matter are two different regions of the central nervous system. In the brain, gray matter refers to the darker, outer portion, while white matter describes the lighter, inner section underneath. In the spinal cord, this order is reversed: The white matter is on the outside, and the gray matter sits within.
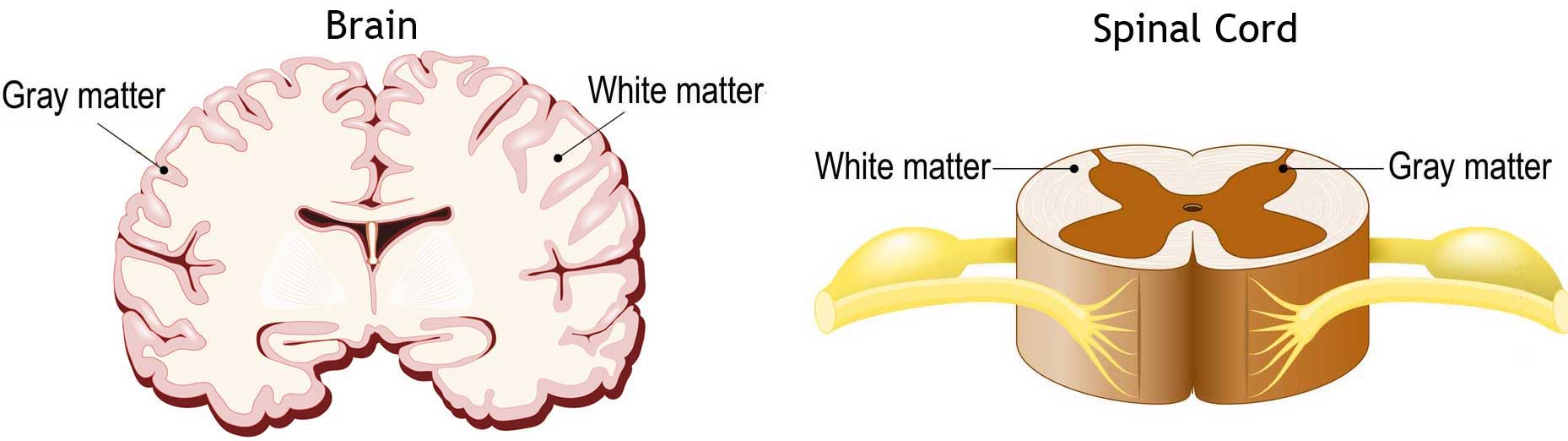
Gray matter is primarily composed of neuron somas (the round central cell bodies), and white matter is mostly made of axons (the long stems that connects neurons together) wrapped in myelin (a protective coating). The different composition of neuron parts is why the two appear as separate shades on certain scans.
Each region serves a different role. Gray matter is primarily responsible for processing and interpreting information, while white matter transmits that information to other parts of the nervous system.
How does the brain work?
The brain sends and receives chemical and electrical signals throughout the body. Different signals control different processes, and your brain interprets each. Some make you feel tired, for example, while others make you feel pain.
Some messages are kept within the brain, while others are relayed through the spine and across the body’s vast network of nerves to distant extremities. To do this, the central nervous system relies on billions of neurons (nerve cells).
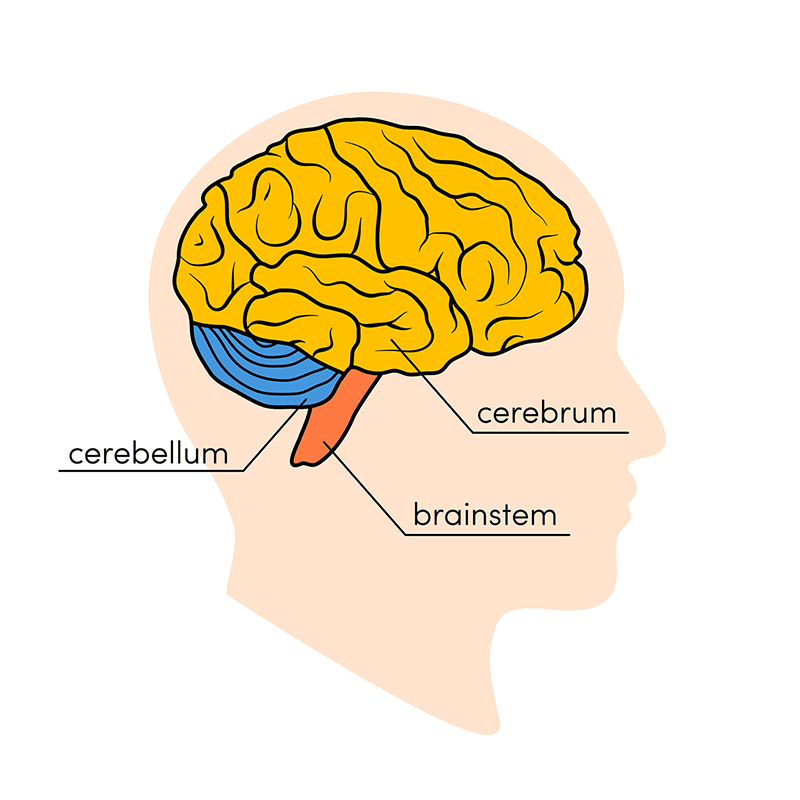
Main Parts of the Brain and Their Functions
At a high level, the brain can be divided into the cerebrum, brainstem and cerebellum.
The cerebrum (front of brain) comprises gray matter (the cerebral cortex) and white matter at its center. The largest part of the brain, the cerebrum initiates and coordinates movement and regulates temperature. Other areas of the cerebrum enable speech, judgment, thinking and reasoning, problem-solving, emotions and learning. Other functions relate to vision, hearing, touch and other senses.
Cerebral Cortex
Cortex is Latin for “bark,” and describes the outer gray matter covering of the cerebrum. The cortex has a large surface area due to its folds, and comprises about half of the brain’s weight.
The cerebral cortex is divided into two halves, or hemispheres. It is covered with ridges (gyri) and folds (sulci). The two halves join at a large, deep sulcus (the interhemispheric fissure, AKA the medial longitudinal fissure) that runs from the front of the head to the back. The right hemisphere controls the left side of the body, and the left half controls the right side of the body. The two halves communicate with one another through a large, C-shaped structure of white matter and nerve pathways called the corpus callosum. The corpus callosum is in the center of the cerebrum.
The brainstem (middle of brain) connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. The brainstem includes the midbrain, the pons and the medulla.
- Midbrain. The midbrain (or mesencephalon) is a very complex structure with a range of different neuron clusters (nuclei and colliculi), neural pathways and other structures. These features facilitate various functions, from hearing and movement to calculating responses and environmental changes. The midbrain also contains the substantia nigra, an area affected by Parkinson’s disease that is rich in dopamine neurons and part of the basal ganglia, which enables movement and coordination.
- Pons. The pons is the origin for four of the 12 cranial nerves, which enable a range of activities such as tear production, chewing, blinking, focusing vision, balance, hearing and facial expression. Named for the Latin word for “bridge,” the pons is the connection between the midbrain and the medulla.
- Medulla. At the bottom of the brainstem, the medulla is where the brain meets the spinal cord. The medulla is essential to survival. Functions of the medulla regulate many bodily activities, including heart rhythm, breathing, blood flow, and oxygen and carbon dioxide levels. The medulla produces reflexive activities such as sneezing, vomiting, coughing and swallowing.
The spinal cord extends from the bottom of the medulla and through a large opening in the bottom of the skull. Supported by the vertebrae, the spinal cord carries messages to and from the brain and the rest of the body.
The cerebellum (“little brain”) is a fist-sized portion of the brain located at the back of the head, below the temporal and occipital lobes and above the brainstem. Like the cerebral cortex, it has two hemispheres. The outer portion contains neurons, and the inner area communicates with the cerebral cortex. Its function is to coordinate voluntary muscle movements and to maintain posture, balance and equilibrium. New studies are exploring the cerebellum’s roles in thought, emotions and social behavior, as well as its possible involvement in addiction, autism and schizophrenia.
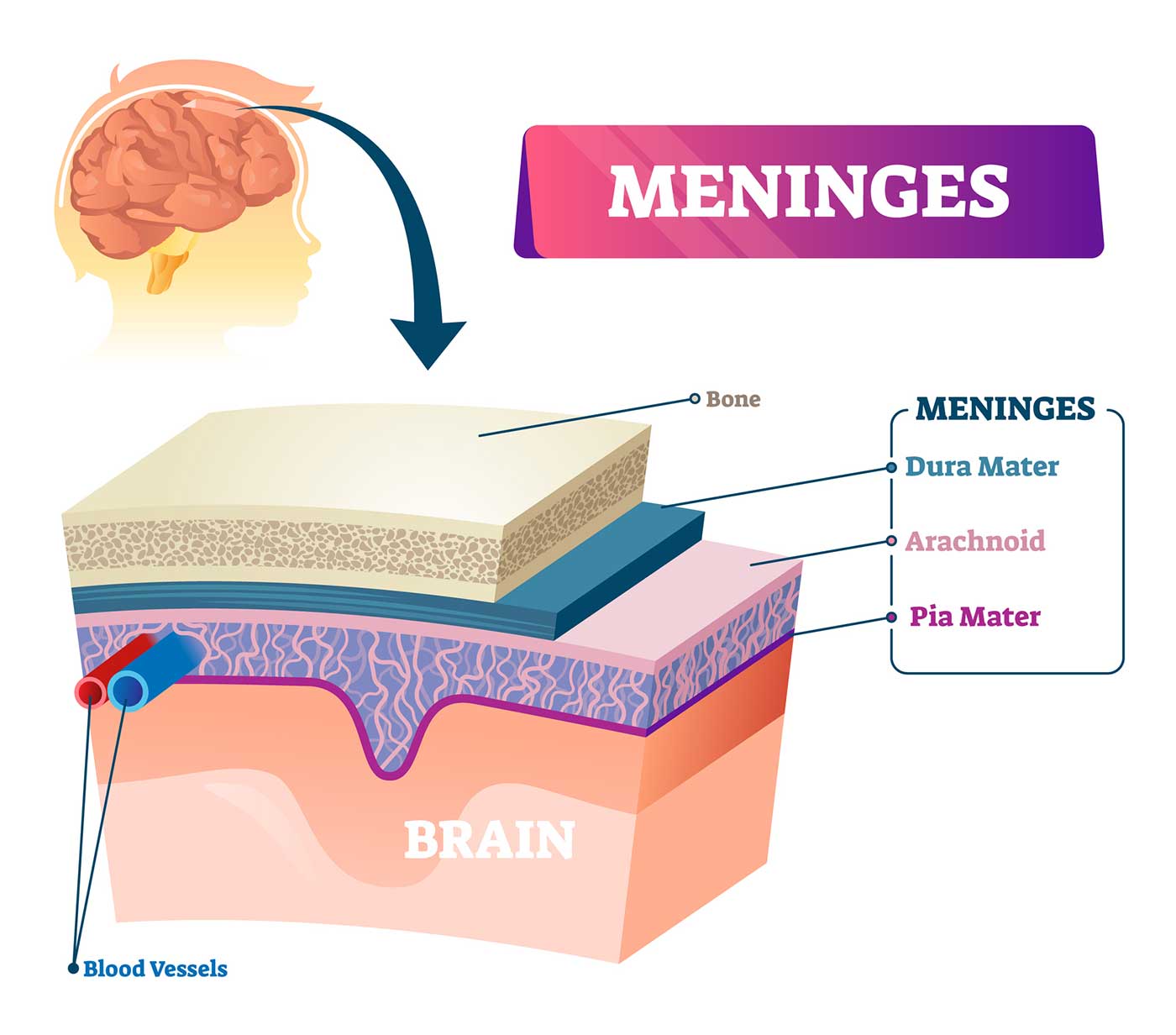
Brain Coverings: Meninges
Three layers of protective covering called meninges surround the brain and the spinal cord.
- The outermost layer, the dura mater , is thick and tough. It includes two layers: The periosteal layer of the dura mater lines the inner dome of the skull (cranium) and the meningeal layer is below that. Spaces between the layers allow for the passage of veins and arteries that supply blood flow to the brain.
- The arachnoid mater is a thin, weblike layer of connective tissue that does not contain nerves or blood vessels. Below the arachnoid mater is the cerebrospinal fluid, or CSF. This fluid cushions the entire central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and continually circulates around these structures to remove impurities.
- The pia mater is a thin membrane that hugs the surface of the brain and follows its contours. The pia mater is rich with veins and arteries.
Lobes of the Brain and What They Control
Each brain hemisphere (parts of the cerebrum) has four sections, called lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital. Each lobe controls specific functions.
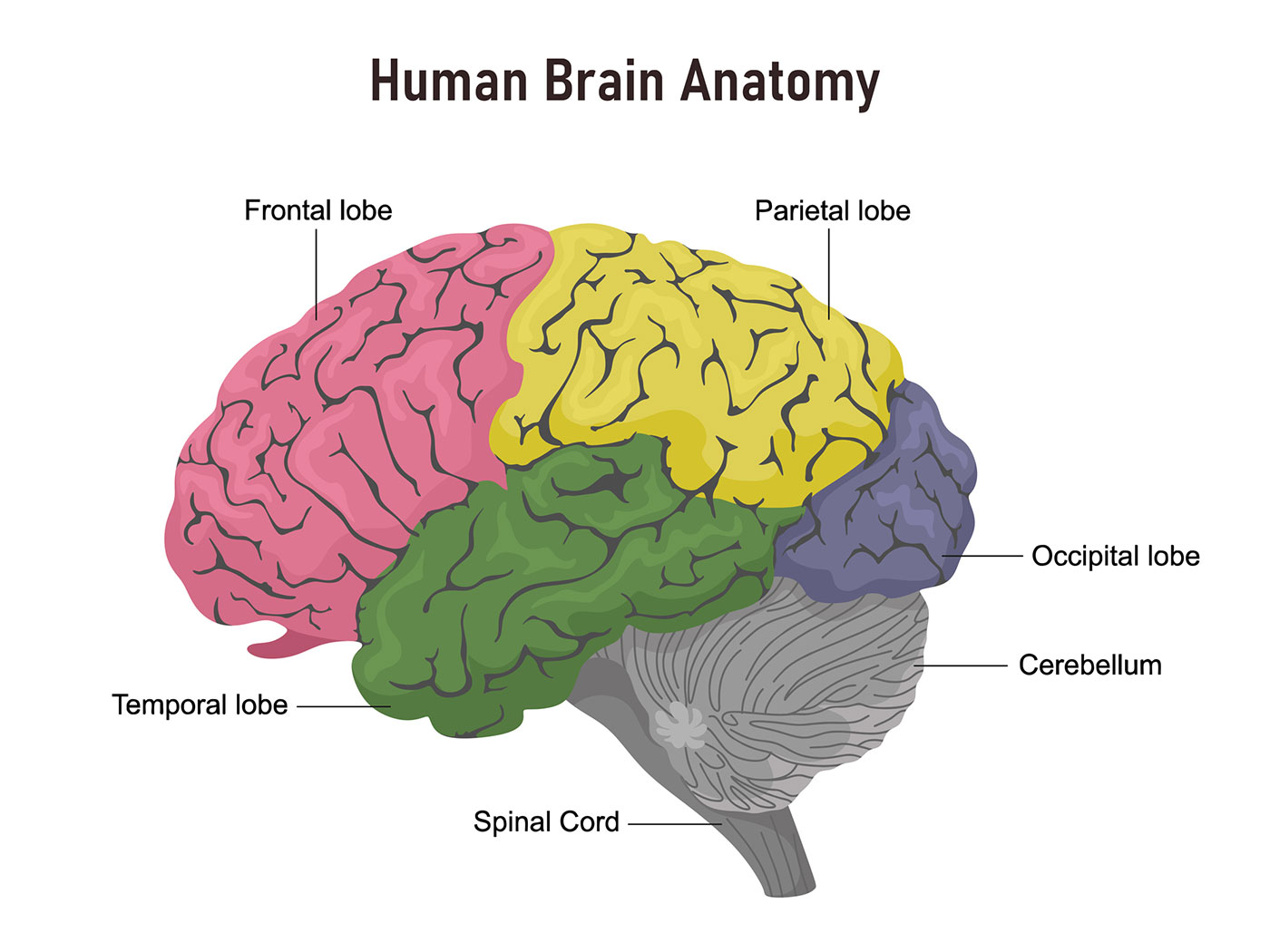
- Frontal lobe. The largest lobe of the brain, located in the front of the head, the frontal lobe is involved in personality characteristics, decision-making and movement. Recognition of smell usually involves parts of the frontal lobe. The frontal lobe contains Broca’s area, which is associated with speech ability.
- Parietal lobe. The middle part of the brain, the parietal lobe helps a person identify objects and understand spatial relationships (where one’s body is compared with objects around the person). The parietal lobe is also involved in interpreting pain and touch in the body. The parietal lobe houses Wernicke’s area, which helps the brain understand spoken language.
- Occipital lobe. The occipital lobe is the back part of the brain that is involved with vision.
- Temporal lobe. The sides of the brain, temporal lobes are involved in short-term memory, speech, musical rhythm and some degree of smell recognition.
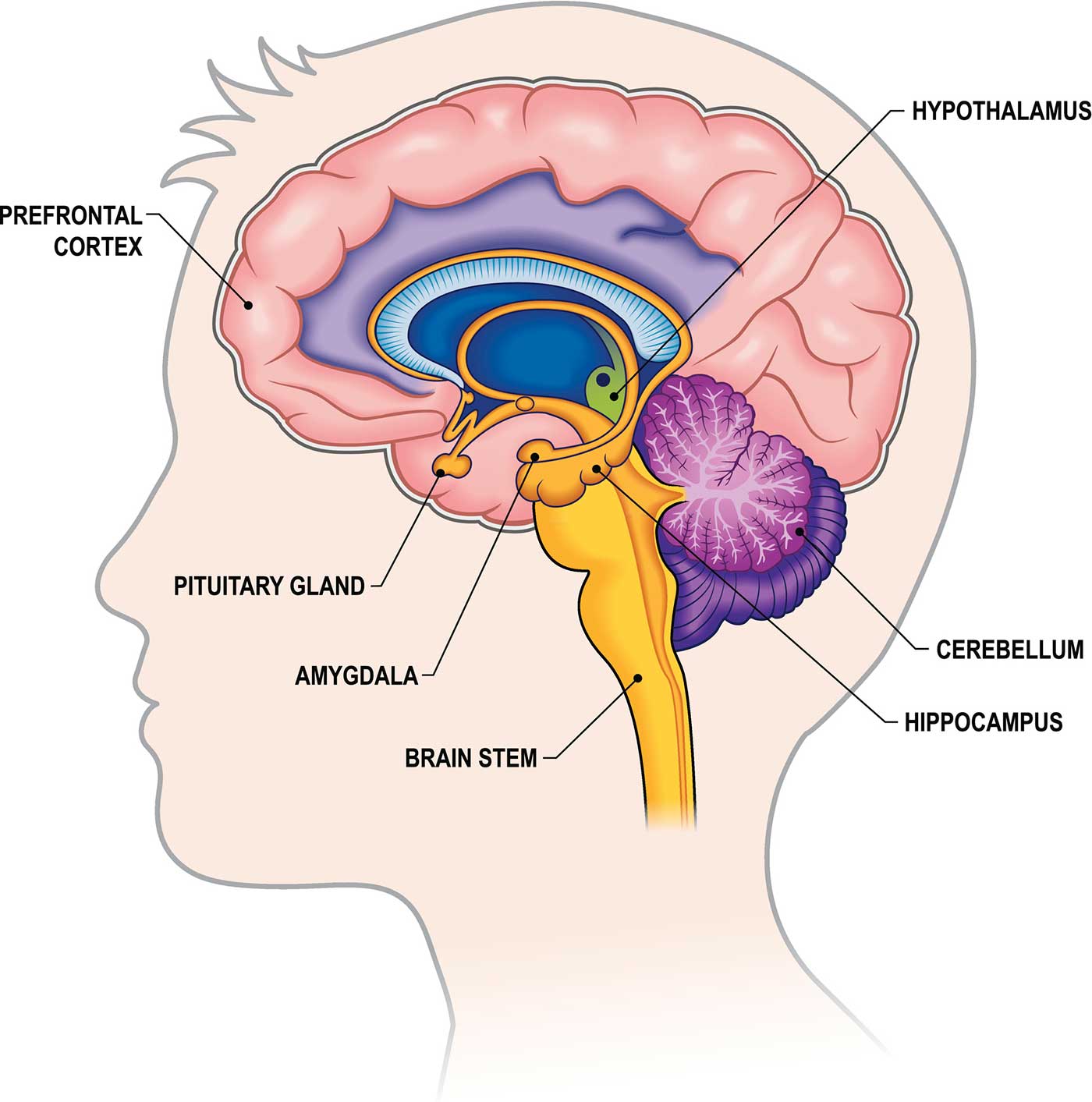
Deeper Structures Within the Brain
Pituitary gland.
Sometimes called the “master gland,” the pituitary gland is a pea-sized structure found deep in the brain behind the bridge of the nose. The pituitary gland governs the function of other glands in the body, regulating the flow of hormones from the thyroid, adrenals, ovaries and testicles. It receives chemical signals from the hypothalamus through its stalk and blood supply.
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus is located above the pituitary gland and sends it chemical messages that control its function. It regulates body temperature, synchronizes sleep patterns, controls hunger and thirst and also plays a role in some aspects of memory and emotion.
Small, almond-shaped structures, an amygdala is located under each half (hemisphere) of the brain. Included in the limbic system, the amygdalae regulate emotion and memory and are associated with the brain’s reward system, stress, and the “fight or flight” response when someone perceives a threat.
Hippocampus
A curved seahorse-shaped organ on the underside of each temporal lobe, the hippocampus is part of a larger structure called the hippocampal formation. It supports memory, learning, navigation and perception of space. It receives information from the cerebral cortex and may play a role in Alzheimer’s disease.
Pineal Gland
The pineal gland is located deep in the brain and attached by a stalk to the top of the third ventricle. The pineal gland responds to light and dark and secretes melatonin, which regulates circadian rhythms and the sleep-wake cycle.
Ventricles and Cerebrospinal Fluid
Deep in the brain are four open areas with passageways between them. They also open into the central spinal canal and the area beneath arachnoid layer of the meninges.
The ventricles manufacture cerebrospinal fluid , or CSF, a watery fluid that circulates in and around the ventricles and the spinal cord, and between the meninges. CSF surrounds and cushions the spinal cord and brain, washes out waste and impurities, and delivers nutrients.
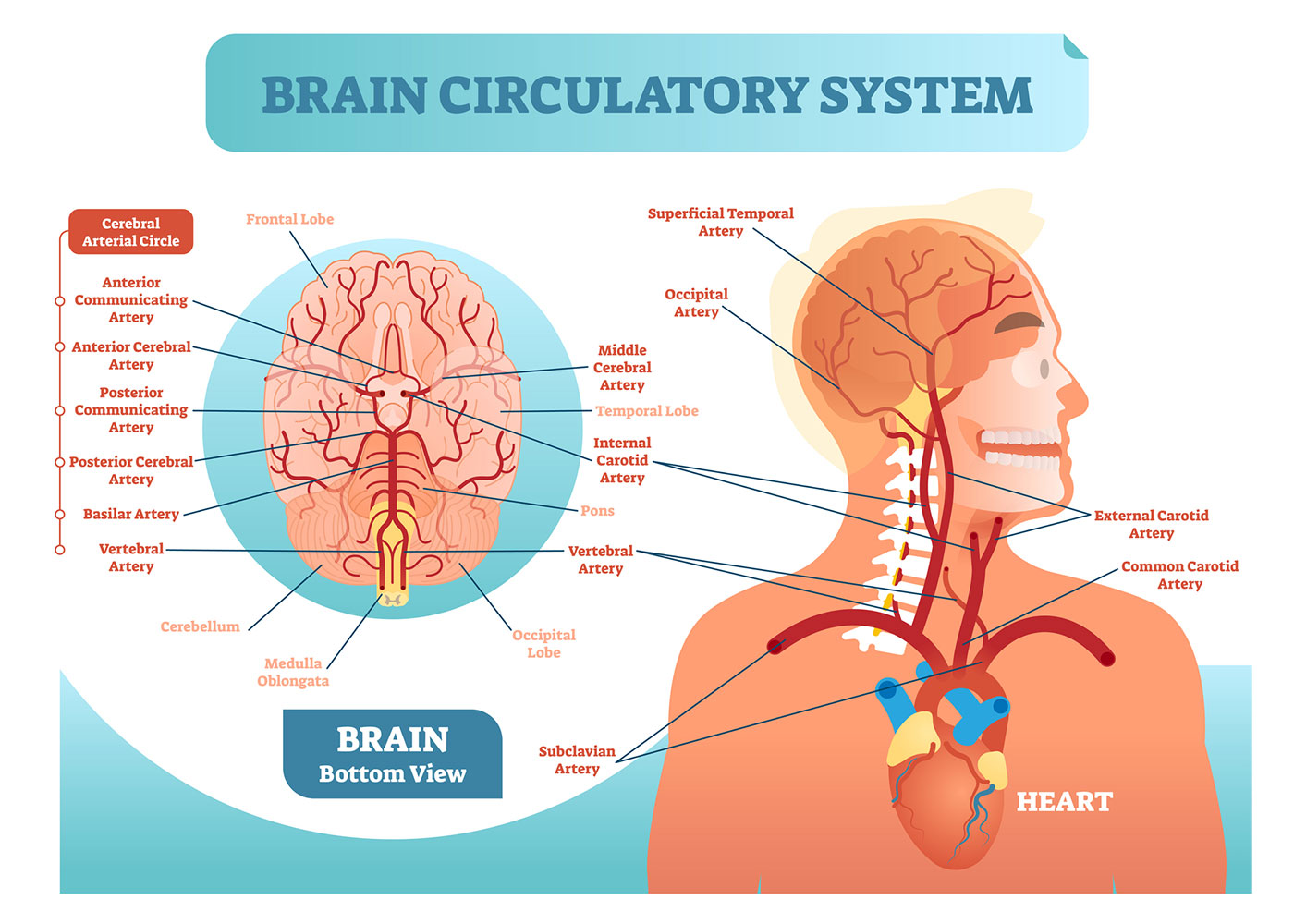
Blood Supply to the Brain
Two sets of blood vessels supply blood and oxygen to the brain: the vertebral arteries and the carotid arteries.
The external carotid arteries extend up the sides of your neck, and are where you can feel your pulse when you touch the area with your fingertips. The internal carotid arteries branch into the skull and circulate blood to the front part of the brain.
The vertebral arteries follow the spinal column into the skull, where they join together at the brainstem and form the basilar artery , which supplies blood to the rear portions of the brain.
The circle of Willis , a loop of blood vessels near the bottom of the brain that connects major arteries, circulates blood from the front of the brain to the back and helps the arterial systems communicate with one another.
Cranial Nerves
Inside the cranium (the dome of the skull), there are 12 nerves, called cranial nerves:
- Cranial nerve 1: The first is the olfactory nerve, which allows for your sense of smell.
- Cranial nerve 2: The optic nerve governs eyesight.
- Cranial nerve 3: The oculomotor nerve controls pupil response and other motions of the eye, and branches out from the area in the brainstem where the midbrain meets the pons.
- Cranial nerve 4: The trochlear nerve controls muscles in the eye. It emerges from the back of the midbrain part of the brainstem.
- Cranial nerve 5: The trigeminal nerve is the largest and most complex of the cranial nerves, with both sensory and motor function. It originates from the pons and conveys sensation from the scalp, teeth, jaw, sinuses, parts of the mouth and face to the brain, allows the function of chewing muscles, and much more.
- Cranial nerve 6: The abducens nerve innervates some of the muscles in the eye.
- Cranial nerve 7: The facial nerve supports face movement, taste, glandular and other functions.
- Cranial nerve 8: The vestibulocochlear nerve facilitates balance and hearing.
- Cranial nerve 9: The glossopharyngeal nerve allows taste, ear and throat movement, and has many more functions.
- Cranial nerve 10: The vagus nerve allows sensation around the ear and the digestive system and controls motor activity in the heart, throat and digestive system.
- Cranial nerve 11: The accessory nerve innervates specific muscles in the head, neck and shoulder.
- Cranial nerve 12: The hypoglossal nerve supplies motor activity to the tongue.
The first two nerves originate in the cerebrum, and the remaining 10 cranial nerves emerge from the brainstem, which has three parts: the midbrain, the pons and the medulla.
Find a Treatment Center
- Neurology and Neurosurgery
Find Additional Treatment Centers at:
- Howard County Medical Center
- Sibley Memorial Hospital
- Suburban Hospital
Request an Appointment

Stiff Person Syndrome: Gay's Story
Neurological Disorder: Hailey's Story
Related Topics
- Brain, Nerves and Spine
Pete’s PowerPoint Station
- Science Index
- Math/Maths Index
- Language Arts/Literature Index
- Social Studies Index
- Holidays Index
- Art, Music, and Many More, A-Z
- Meteorology
- Four Seasons
- Pre-Algebra
- Trigonometry
- Pre-Calculus & Calculus
- Language Arts
- Punctuation
- Social Studies
- World Religions
- US Government
- Criminal Justice
- Famous People
- American History
- World History
- Ancient History
- The Middle Ages
- Architecture
- All Topics, A–Z
- Privacy & Cookie Policy
- Presentations
The Human Brain
Free Presentations in PowerPoint format
Methods for Studying Brain Behavior
Study of Normal Brain Development
Studying Brain Function and Development
Studying the Brain – Implications for Educators
Anatomy of Mild to Moderate Brain Injury
Anatomy of the Brain
Anatomic Landmarks in the Brain
Brain Evolution
Anatomy of the Human Brain
Parts of the Human Brain
Gross Anatomy of the Brain
Brain Power
Brain Anatomy
See Also: Human Body Systems , The Human Body , The Nervous System
Free Brain Games & Activities for Kids
Brain Games
Brain Games – Neuroscience for Kids
FLASH Human Body Presentations
For Teachers
Lots of Lessons – Human Body
Free Video Clips
Free Online Science Games for Kids
Free Clipart for Science

- Customer Help
- X (Twitter)

Human Brain Anatomy PPT Illustration Free Download
Additional information.
| License | Free |
|---|---|
| Aspect ratio | 16:9, 4:3 |
| Versions | for Google Slides (PPTX), for Keynote (KEY), for PowerPoint (PPTX) |
| Support language | English |
Ever wondered what’s going on inside that noggin of yours? The brain, a marvel of nature, is the epicenter of our thoughts, emotions, and bodily functions. Let’s dive deep into its intricate anatomy.
The brain isn’t just a lump of gray matter; it’s an intricate network of billions of neurons, working in harmony to make you, well, you. Imagine it as the world’s most advanced supercomputer, but instead of circuits and wires, it’s made of cells and neurotransmitters.
Major Parts of the Brain Anatomy – Free Download PPT Slide
When preparing a powerpoint presentation on the intricate details of brain anatomy, it’s essential to understand the structure and physiology of the central nervous system. This presentation will guide viewers through the various parts of the brain, ensuring a comprehensive understanding.
The Cerebrum: The Largest Part of the Brain
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, housing over 100 billion neurons. It’s divided into two hemispheres: left and right, connected by the corpus callosum. This part of the brain is responsible for higher cognitive functions and voluntary activities. Imagine it as the CEO of a company, overseeing everything.
Lobes of the Cerebrum
- Frontal Lobe: This lobe manages skills like reasoning, planning, and problem-solving. It’s also home to the Broca’s area, which is crucial for speech production.
- Parietal Lobe: Responsible for processing sensory information, such as touch and temperature. Its surface area is marked by sulci and gyri, increasing the cortex’s capacity to house neuron cell bodies.
- Temporal Lobe: This is the brain’s auditory area, serving as a memory bank and processing sounds.
- Occipital Lobe: The primary visual processing center, akin to the graphics card of a computer. It interprets images from the optic nerves.
The Cerebellum: The Brain’s Coordinator
The cerebellum, part of the hindbrain, is essential for muscle co-ordination and maintaining posture and balance. With its white matter tracts resembling a tree, it connects to the brainstem and ensures smooth movements.
The Brainstem: The Bridge to the Spinal Cord
The brainstem is a crucial structure, connecting the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord. It’s divided into three main parts:
- Midbrain: This section controls reflex movements of the eyes and head.
- Pons: Located below the midbrain, the pons plays a role in controlling breathing and relaying signals between different parts of the brain. Ever wondered about the function of the pons? It’s also involved in functions like swallow, cough, and sneeze.
- Medulla Oblongata: This part controls vital functions like heart rate and blood pressure. It’s also the point where the brainstem connects to the spinal cord.
Additional Resources
For those interested in diving deeper, there are pdf files, google slides, and PPT presentations available for download. These resources include detailed diagrams, images, and specific functions of each brain part. Whether you’re preparing for a class or just curious, these resources are invaluable.
Related Content: Viewers also liked our segments on the thalamus, hypothalamus, and the cerebral cortex. The cortex contains layers, with the outermost layer being crucial for sensory perception and voluntary motor functions. Don’t miss our recently uploaded content on the peripheral nervous system, cranial nerves, and the brain’s blood supply.
There are no reviews yet.
You must be logged in to post a review.
Related products


Brain Template
What do you think of this template.

Product details
The brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind and soul. Intelligence, creativity, emotion, and memory are a few of the many things governed by the brain. Protected within the skull, the brain is composed of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem. The brain receives information through our five senses: sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing – often many at one time. It assembles the messages in a way that has meaning for us, and can store that information in our memory. The brain controls our thoughts, memory and speech, movement of the arms and legs, and the function of many organs within our body. The central nervous system (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is composed of spinal nerves that branch from the spinal cord and cranial nerves that branch from the brain. The brain has three main parts: the cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem. Cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is composed of right and left hemispheres. It performs higher functions like interpreting touch, vision and hearing, as well as speech, reasoning, emotions, learning, and fine control of movement. Cerebellum is located under the cerebrum. Its function is to coordinate muscle movements, maintain posture, and balance. Brainstem acts as a relay center connecting the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord. It many automatic functions such as breathing, heart rate, body temperature, wake and sleep cycles, digestion, sneezing, coughing, vomiting, and swallowing. The cerebrum is divided into two halves: the right and left hemispheres. They are joined by a bundle of fibers called the corpus callosum that transmits messages from one side to the other. Each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body. If a stroke occurs on the right side of the brain, your left arm or leg may be weak or paralyzed. Not all functions of the hemispheres are shared. In general, the left hemisphere controls speech, comprehension, arithmetic, and writing. The right hemisphere controls creativity, spatial ability, artistic, and musical skills. The left hemisphere is dominant in hand use and language in about 92% of people.
Brain Diagrams Templates consists of four slides that have beautiful infographics and a modern style. The first slide is a brain infographic divided into six main parts – cerebrum, cerebellum, medulla oblongata, pons, mesencephalon, thalamus. This slide will primarily be useful to medical professionals and teachers of medical universities. You will be able to use this slide when preparing training courses. Doctors can also prepare their brain studies using this slide. The third slide allows you to display information on the left and right hemispheres of the brain in detail. This slide will be useful in preparing a general biology course for high school students. Also, startups can use this slide when preparing an analytical report on how the brain perceives a new product or technology. The next two slides can be helpful in preparing a course on leadership, memory optimization, or rapid reading. All slides in this template are editable and can be used with any of your other presentations.
Related Products

Team Charter Canvas

New Hire Orientation

Health and Fitness

Agile Project Plan

Escalation Matrix

Business Strategy
Kotter's Change Model

Target Operating Model

Exit Strategy

Customer Journey Map Template
You dont have access, please change your membership plan., great you're all signed up..., verify your account.
PowerSlides.com will email you template files that you've chosen to dowload.
Please make sure you've provided a valid email address! Sometimes, our emails can end up in your Promotions/Spam folder.
Simply, verify your account by clicking on the link in your email.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Brain Presentation templates The brain is the chief organ of the nervous system. Thanks to it, we can perform all our daily actions, from the simplest ones like eating or talking, to the most fun ones, like discovering these Google Slides and PowerPoint templates about the brain itself. ...
Emotions are an extremely complex brain function. The emotional core of the brain is the limbic system. This is where senses and awareness are first processed in the brain. Mood and personality are mediated through the prefrontal cortex. This part of the brain is the center of higher cognitive and emotional functions.
An article in Science Daily on a research study about REM sleep and the pons, a part of the brain stem. "A Neurosurgeon's Overview of the Brain's Anatomy" from the American Association of Neurological Surgeons. Visible Body Web Suite provides in-depth coverage of each body system in a guided, visually stunning presentation.
Early case studies helped us localize some brain functions like the fact that damage to one side of the brain affected the other side of the body, or that damage to the brain could alter personality. Doctors have proven that stimulating parts of the brain can lead to uncontrolled giggling or hearing voices. 5 Tools of Discovery Brain Imaging ...
The brain is like a group of experts. All the parts of the brain work together, but each part has its own special responsibilities. The brain can be divided into three basic units: the forebrain, the midbrain, and the hindbrain.. The hindbrain includes the upper part of the spinal cord, the brain stem, and a wrinkled ball of tissue called the cerebellum.
Free Canva presentation template. Perfect for educators, this adorable green slideshow template on the brain will captivate your students' attention. With cute, illustrative designs, it simplifies complex concepts, making lessons both engaging and informative. Ideal for biology classes, neuroscience topics, and educational workshops, this ...
The Human Brain Presentation Template. The human brain is arguably one of the most complex entities in the entire universe. Even though it sits right behind our eyes, we know only a fraction of what this incredible machine is capable of. Recent advancements in science, medicine and technology have offered us a slight understanding of our brain.
Presentation Transcript. Brain Anatomy and Function. Anatomy of the Brain • Separated into right and left halves by the Interhemispheric Fissure • The Central Sulcus • runs down & forward • The Lateral Fissure runs backward & up. Frontal and Temporal Lobes • Thought • Voluntary movement • Speech motor • Covers 1/3rd of area of ...
A Brain Presentation is a PowerPoint presentation focusing on topics related to the human brain. Such presentations cover brain anatomy, cognitive processes, mental health, neurological disorders, learning theories, and more. These presentations can be educational, informative, or persuasive, depending on the context and audience. ...
The cerebellum ("little brain") is a fist-sized portion of the brain located at the back of the head, below the temporal and occipital lobes and above the brainstem. Like the cerebral cortex, it has two hemispheres. The outer portion contains neurons, and the inner area communicates with the cerebral cortex.
Free Presentations in PowerPoint format. The Human Brain. Methods for Studying Brain Behavior. Study of Normal Brain Development. Studying Brain Function and Development. Studying the Brain - Implications for Educators. Anatomy of Mild to Moderate Brain Injury. Anatomy of the Brain. Anatomic Landmarks in the Brain.
PowerPoint: Click the link to open the presentation in view mode, then download and save the file. Once you have downloaded the PPT, you will be able to enable editing. Please note, PowerPoint and Google Slides have different functionalities, so the resources may have some differences. Twinkl USA 3rd-5th Fourth Grade Science Life Science Human ...
The PowerPoint presentation (PPT, 4.3MB) helps people learn how to reduce the risks related to brain health. This presentation addresses normal aging of the brain, threats to brain health, and healthy aging for the body and brain. A two-page handout (PDF, 1.7MB) for the consumer audience covers the basics of brain health.
This presentation will guide viewers through the various parts of the brain, ensuring a comprehensive understanding. The Cerebrum: The Largest Part of the Brain. The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, housing over 100 billion neurons. It's divided into two hemispheres: left and right, connected by the corpus callosum.
Brain Diagrams Templates consists of four slides that have beautiful infographics and a modern style. The first slide is a brain infographic divided into six main parts - cerebrum, cerebellum, medulla oblongata, pons, mesencephalon, thalamus. This slide will primarily be useful to medical professionals and teachers of medical universities.