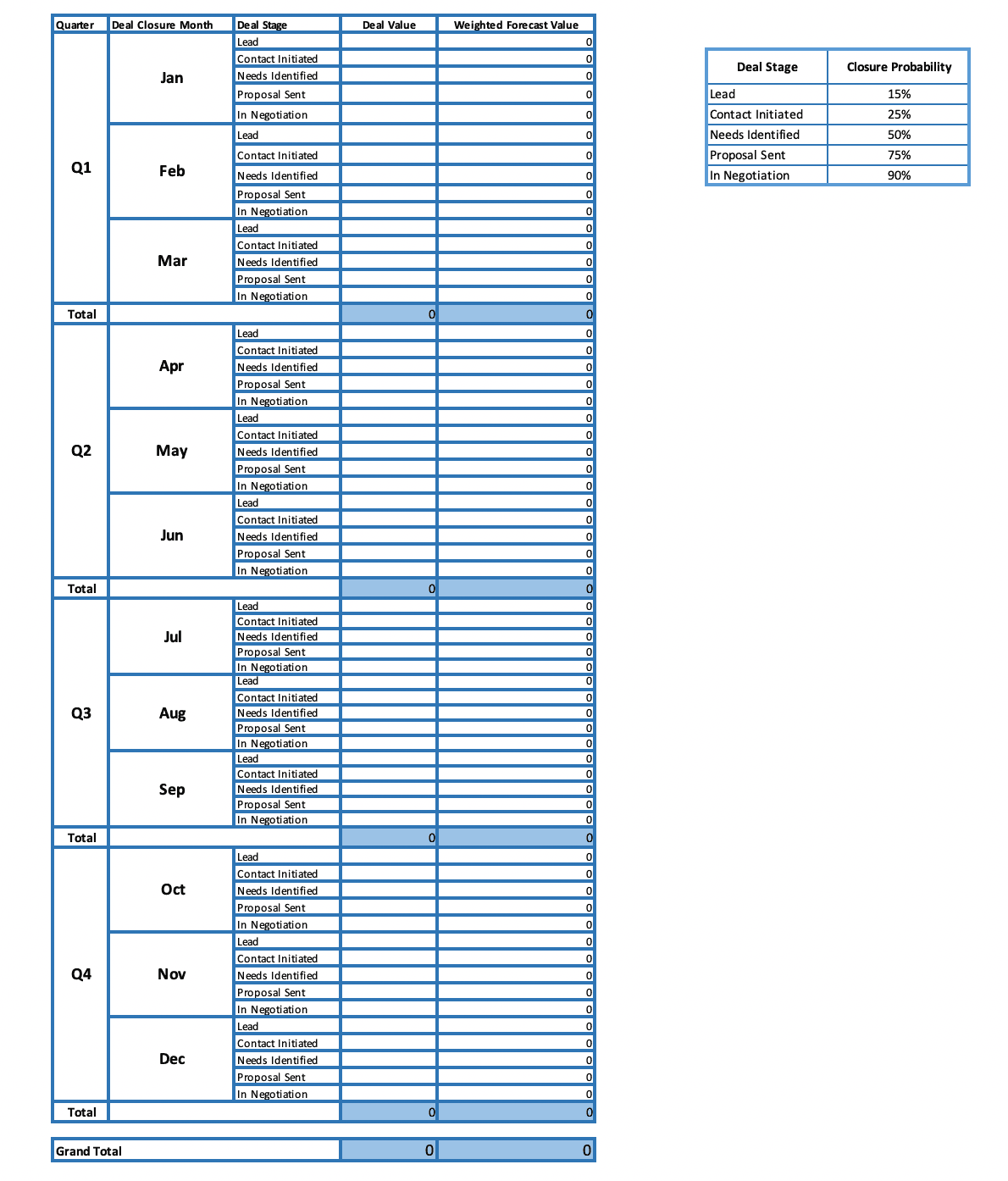
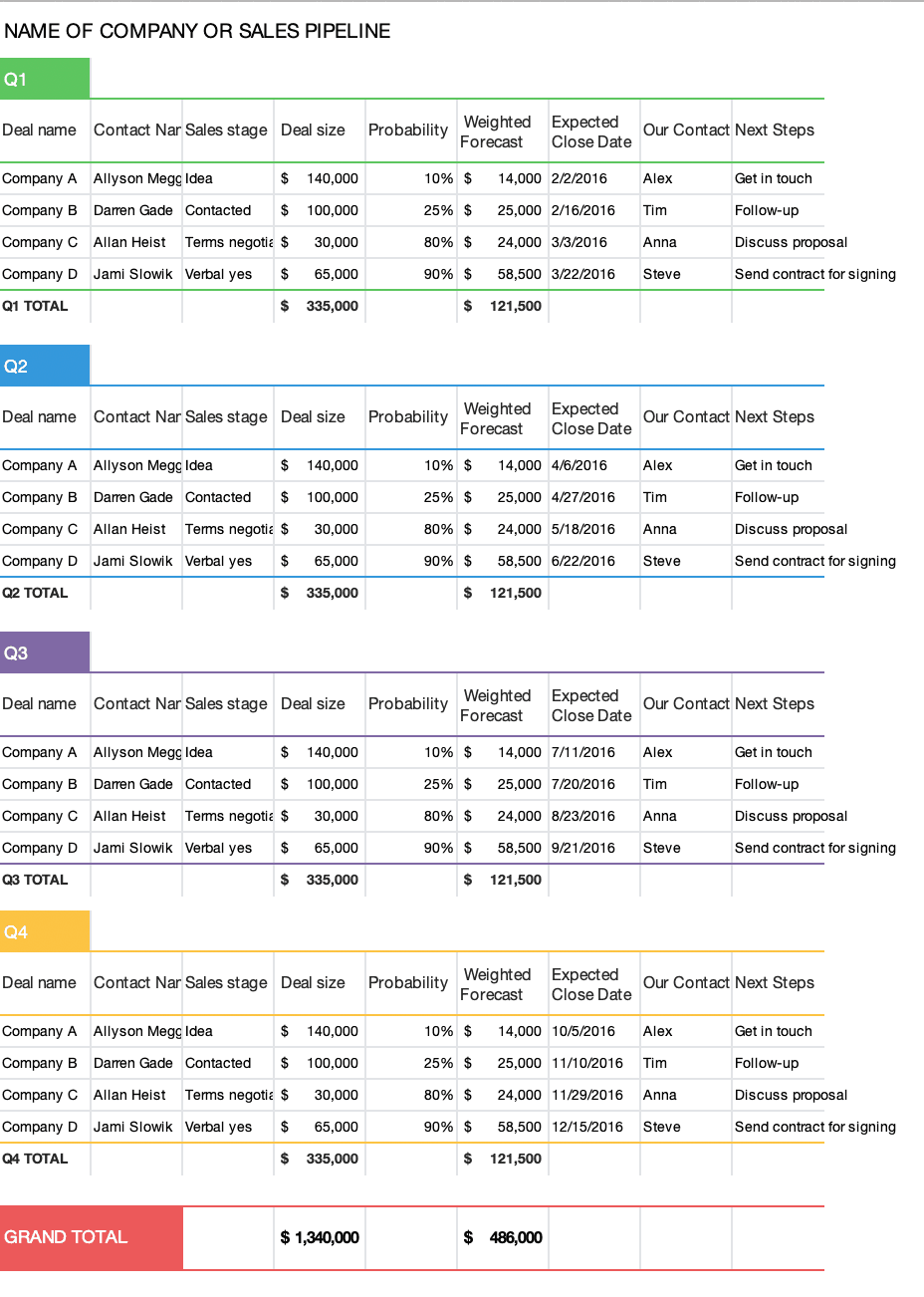
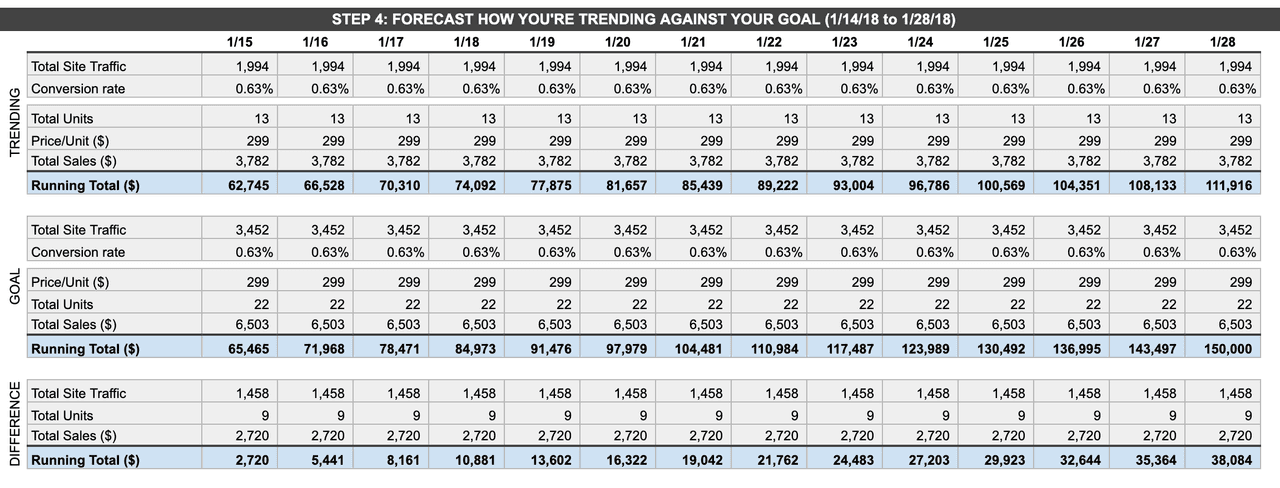
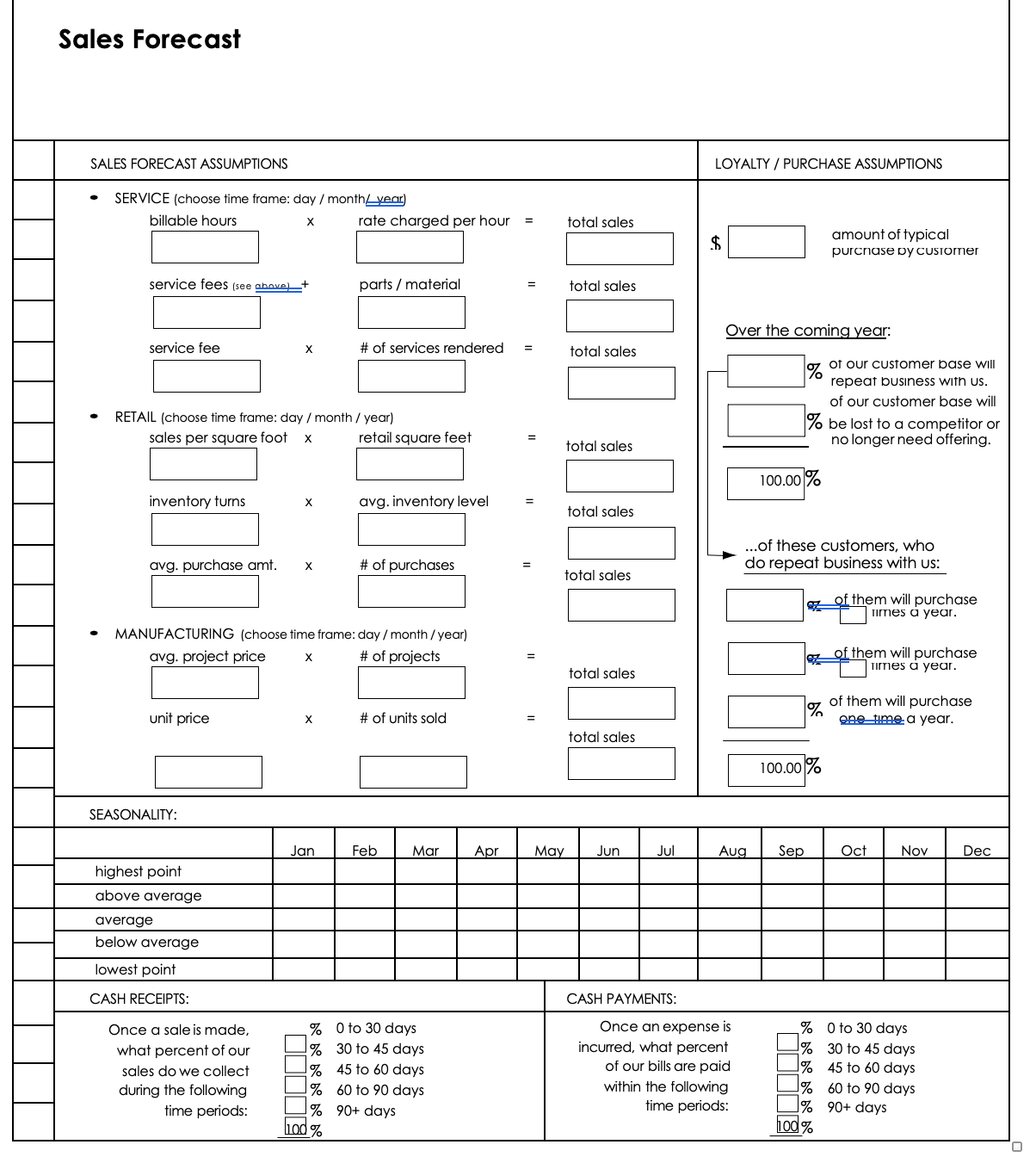
- Product overview
- All features
- Latest feature release
- App integrations
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Capacity planning
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- Permissions
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Project intake
- Resource planning
- Product launches
- View all uses arrow-right icon

- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Business strategy |
- Sales forecasting: How to create a sale ...

Sales forecasting: How to create a sales forecast template (with examples)

A strong sales team is the key to success for most companies. They say a good salesperson can sell sand at the beach, but whether you’re selling products in the Caribbean or Antarctica, it all comes down to strategy. When you’re unsure if your current strategy is working, a sales forecast can help.
What is a sales forecast?
A sales forecast predicts future sales revenue using past business data. Your sales forecast can predict a number of different things, including the number of new sales for an existing product, the new customers you’ll gain, or the memberships you’ll sell in a given time period. These forecasts are then used during project planning to determine how much you should allocate towards new products and services.
Why is sales forecasting important?
Sales forecasting helps you keep a finger on your business’s pulse. It sets the ground rules for a variety of business operations, including your sales strategy and project planning. Once you calculate your sales projections, you can use the results to assess your business health, predict cash flow, and adjust your plans accordingly.
![sales projection in business plan example [inline illustration] the importance of sales forecasting (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/9c03e89a-1145-44c3-be52-f0f8e9d6785c/inline-business-strategy-sales-forecast-template-3-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
An effective sales forecasting plan:
Predicts demand: When you have an idea of how many units you may sell, you can get a head start on production.
Helps you make smart investments: If you have future goals of expanding your business with new locations or products, knowing when you’ll have the income to do so is important.
Contributes to goal setting: Your sales forecast can help you set goals outside of investments as well, like outshining competitors or hiring new team members.
Guides spending: Your sales forecast may be the wake-up call you need to set a budget and use cost control to reduce expenses.
Improves the sales process: You can change your current sales process based on the sales projections you’re unhappy with.
Highlights financial problems: Your sales forecast template will open your eyes to problem areas you may not have noticed otherwise.
Helps with resource management: Do you have the resources you need to fill orders if it’s an accurate sales forecast? Your sales forecast can guide how you allocate and manage resources to hit targets.
When you have an accurate prediction of your future sales, you can use your projections to adjust your current sales process. Leveraging inventory management software can help you implement these adjustments more effectively by providing up-to-date data on stock levels and supply chain performance.
Sales forecasting methods
Sales forecasting is an important part of strategic business planning because it enables sales managers and teams to predict future sales and make informed decisions. But why are there multiple sales forecasting methods? Simply put, businesses vary in size, industry, and market dynamics, so no single methodology suits all.
Choosing the right sales forecasting method is more of an art than a science. It involves:
Analyzing your business size and industry
Assessing the available data and tools
Understanding your sales cycle's complexity
A few telltale signs that you've picked the correct approach include:
Improved accuracy in sales target predictions
Enhanced understanding of market trends
Better alignment with your business goals
Opportunity stage forecasting
Opportunity stage forecasting is a dynamic approach ideal for businesses using CRM systems like Salesforce. It assesses the likelihood of sales closing based on the stages of the sales pipeline. This method is particularly beneficial for sales organizations with a clearly defined sales process.
For example, a software company might use this method to forecast sales by examining the number of prospects in each stage of their funnel, from initial contact to final negotiation.
Pipeline forecasting method
The pipeline forecasting method is similar to opportunity stage forecasting but focuses more on the volume and quality of leads at each pipeline stage. It's particularly useful for businesses that rely heavily on sales forecasting tools and dashboards for decision-making.
A real estate agency could use it by examining the number of properties listed, the stage of negotiations, and the number of closings forecasted in the pipeline.
Length of sales cycle forecasting
Small businesses often prefer the length of sales cycle forecasting. It's straightforward and involves analyzing the duration of past sales cycles to predict future ones. This method is effective for businesses with consistent sales cycle lengths.
A furniture manufacturer, for instance, might use this method by analyzing the average time taken from initial customer contact to closing a sale in the past year.
Intuitive forecasting
Intuitive forecasting relies on the expertise and intuition of sales managers and their teams. It's less about spreadsheets and more about market research and understanding customer behavior. This method is often used with other, more data-driven approaches.
A boutique fashion store, for example, might use this method, relying on the owner's deep understanding of fashion trends and customer preferences.
Historical forecasting
Historical forecasting uses past performance data to predict future sales. This method is advantageous for businesses with ample historical sales data. It's less effective for new markets or rapidly changing industries.
An established book retailer could use historical data from previous years, considering seasonal trends and past marketing campaigns, to forecast next quarter's sales.
Multivariable analysis forecasting
Multivariable analysis forecasting is a more sophisticated method that's ideal for larger sales organizations. It analyzes factors like market trends, economic conditions, and marketing efforts to provide a holistic view of potential sales outcomes.
An automotive company, for example, could analyze factors like economic conditions, competitor activity, and past sales data to forecast future car sales.
How to calculate sales forecast
Sales forecasts determine how much you expect to do in sales for a given time frame. For example, let’s say you expect to sell 100 units in Q1 of fiscal year 2024. To calculate sales forecasts, you’ll use past data to predict future trends.
When you’re first creating a forecast, it’s important to establish benchmarks that determine how much you normally sell of any given product to how many people. Compare historical sales data against sales quotas—i.e., how much you sold vs. how much you expected to sell. This type of analysis can help you set a baseline for what you expect to achieve every week, month, quarter, and so on.
For many companies, this means establishing a formula. The exact inputs will vary based on your products or services, but generally, you can use the following:
Sales forecast = Number of products you expect to sell x The value of each product
For example, if you sell SaaS products, your sales forecast might look something like this:
SaaS FY24 Sales forecast = Number of expected subscribers x Subscription price
Ultimately, the sales forecasting process is a guess—but it’s an educated one. You’ll use the information you already have to create a data-driven forecasting model. How accurate your forecast is depends on your sales team. The sales team uses facts such as their prospects, current market conditions, and their sales pipeline. But they will also use their experience in the field to decide on final numbers for what they think will sell. Because of this, sales leaders are more likely to have better forecasting accuracy than new members of the sales team.
Sales forecast vs. sales goal
Your sales forecast is based on historical data and current market conditions. While you always hope your sales goals are attainable—and you can use data to estimate what your team is capable of—your goals might not line up directly with your forecast. This can be for a number of reasons, including wanting to create stretch goals that push your sales team beyond what they’ve done in the past or big, pie-in-the-sky goals that boost investor confidence.
How to create a sales forecast
There are different sales forecasting methods, and some are simpler than others. With the steps below, you’ll have a basic understanding of how to create a sales forecast template that you can customize to the method of your choice.
![sales projection in business plan example [inline illustration] 5 steps to make a sales forecast template (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/35de7f09-d37d-4c5e-bf88-86af25016c28/inline-business-strategy-sales-forecast-template-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
1. Track your business data
Without details from your past sales, you won’t have anything to base your predictions on. If you don’t have past sales data, you can begin tracking sales now to create a sales forecast in the future. The data you’ll need to track includes:
Number of units sold per month
Revenue of each product by month
Number of units returned or canceled (so you can get an accurate sales calculation)
Other items you can track to make your predictions more accurate include:
Growth percentage
Number of sales representatives
Average sales cycle length
There are different ways to use these data points when forecasting sales. If you want to calculate your sales run rate, which is your projected revenue for the next year, use your revenue from the past month and multiply it by 12. Then, adjust this number based on other relevant data points, like seasonality.
Tip: The best way to track historical data is to use customer relationship management (CRM) software. When you have a CRM strategy in place, you can easily pull data into your sales forecast template and make quick projections.
2. Set your metrics
Before you perform the calculations in your sales forecast template, you need to decide what you’re measuring. The basic questions you should ask are:
What is the product or service you’re selling and forecasting for? Answering this question helps you decide what exactly you’re evaluating. For example, you can investigate future trends for a long-standing product to decide whether it’s worth continuing, or you can predict future sales for a new product.
How far in the future do you want to make projections? You can decide to make projections for as little as six months or as much as five years in the future. The complexity of your sales forecast is up to you.
How much will you sell each product for, and how do you measure your products? Set your product’s metrics, whether they be units, hours, memberships, or something else. That way, you can calculate revenue on a price-per-unit basis.
How long is your sales cycle? Your sales cycle—also called a sales funnel—is how long it takes for you to make the average sale from beginning to end. Sales cycles are often monthly, quarterly, or yearly. Depending on the product you’re selling, your sales cycle may be unique. Steps in the sales cycle typically include:
Lead generation
Lead qualification
Initial contact
Making an offer
Negotiation
Closing the deal
Tip: You can still project customer growth versus revenue even if your company is in its early phases. If you don’t have enough historical data to use for your sales forecast template, you can use data from a company similar to yours in the market.
3. Choose a forecasting method
While there are many forecasting methods to choose from, we’ll concentrate on two straightforward approaches to provide a clear understanding of how sales forecasting can be implemented efficiently. The top-down method starts with the total size of the market and works down, while the bottom-up method starts with your business and expands out.
Top-down method: To use the top-down method, start with the total size of the market—or total addressable market (TAM). Then, estimate how much of the market you think your business can capture. For example, if you’re in a large, oversaturated market, you may only capture 3% of the TAM. If the total addressable market is $1 billion, your projected annual sales would be $30 million.
Bottom-up method: With the bottom-up method, you’ll estimate the total units your company will sell in a sales cycle, then multiply that number by your average cost per unit. You can expand out by adding other variables, like the number of sales reps, department expenses, or website views. The bottom-up forecasting method uses company data to project more specific results.
You’ll need to choose one method to fill in your sales forecast template, but you can also try both methods to compare results.
Tip: The best forecasting method for you may depend on what type of business you’re running. If your company experiences little fluctuation in revenue, then the top-down forecasting method should work well. The top-down model can also work for new businesses that have little business data to work with. Bottom-up forecasting may be better for seasonal businesses or startups looking to make future budget and staffing decisions.
4. Calculate your sales forecast
You’ve already learned a basic way to calculate revenue using the top-down method. Below, you’ll see another way to estimate your projected sales revenue on an annual scale.
Divide your sales revenue for the year so far by the number of months so far to calculate your average monthly sales rate.
Multiply your average monthly sales rate by the number of months left in the year to calculate your projected sales revenue for the rest of the year.
Add your total sales revenue so far to your projected sales revenue for the rest of the year to calculate your annual sales forecast.
A more generalized way to estimate your future sales revenue for the year is to multiply your total sales revenue from the previous year.
Example: Let’s say your company sells a software application for $300 per unit and you sold 500 units from January to March. Your sales revenue so far is $150,000 ($300 per unit x 500 units sold). You’re three months into the calendar year, so your average monthly sales rate is $50,000 ($150,000 / 3 months). That means your projected sales revenue for the rest of the year is $450,000 ($50,000 x 9 months).
5. Adjust for external factors
A sales forecast predicts future revenue by making assumptions about your growth rate based on past success. But your past success is only one component of your growth rate. There are external factors outside of your control that can affect sales growth—and you should consider them if you want to make accurate projections.
Some external factors you can adjust your calculations around include:
Inflation rate: Inflation is how much prices increase over a specific time period, and it usually fluctuates based on a country’s overall economic state. You can take your annual sales forecast and factor in inflation rate to ensure you’re not projecting a higher or lower number of sales than the economy will permit.
The competition: Is your market becoming more competitive as time goes on? For example, are you selling software during a tech boom? If so, assess whether your market share will shrink because of rising competition in the coming year(s).
Market changes: The market can shift as people change their behavior. Your audience may spend an average of six hours per day on their phones in one year. In the next year, mental health awareness may cause phone usage to drop. These changes are hard to predict, so you must stay on top of market news.
Industry changes: Industry changes happen when new products and technologies come on the market and make other products obsolete. One instance of this is the invention of AI technology.
Legislation: Although not as common, changes in legislation can affect the way companies sell their products. For example, vaping was a multi-million dollar industry until laws banned the sale of vape products to people under the age of 21.
Seasonality: Many industries experience seasonality based on how human behavior and human needs change with the seasons. For example, people spend more time inside during the winter, so they may be on their computers more. Retail stores may also experience a jump in sales around Christmas time.
Tip: You can create a comprehensive sales plan to set goals for team members. Aside from revenue targets and training milestones, consider assigning each of these external factors to your team members so they can keep track of essential information. That way, you’ll have your bases covered on anything that may affect future sales growth.
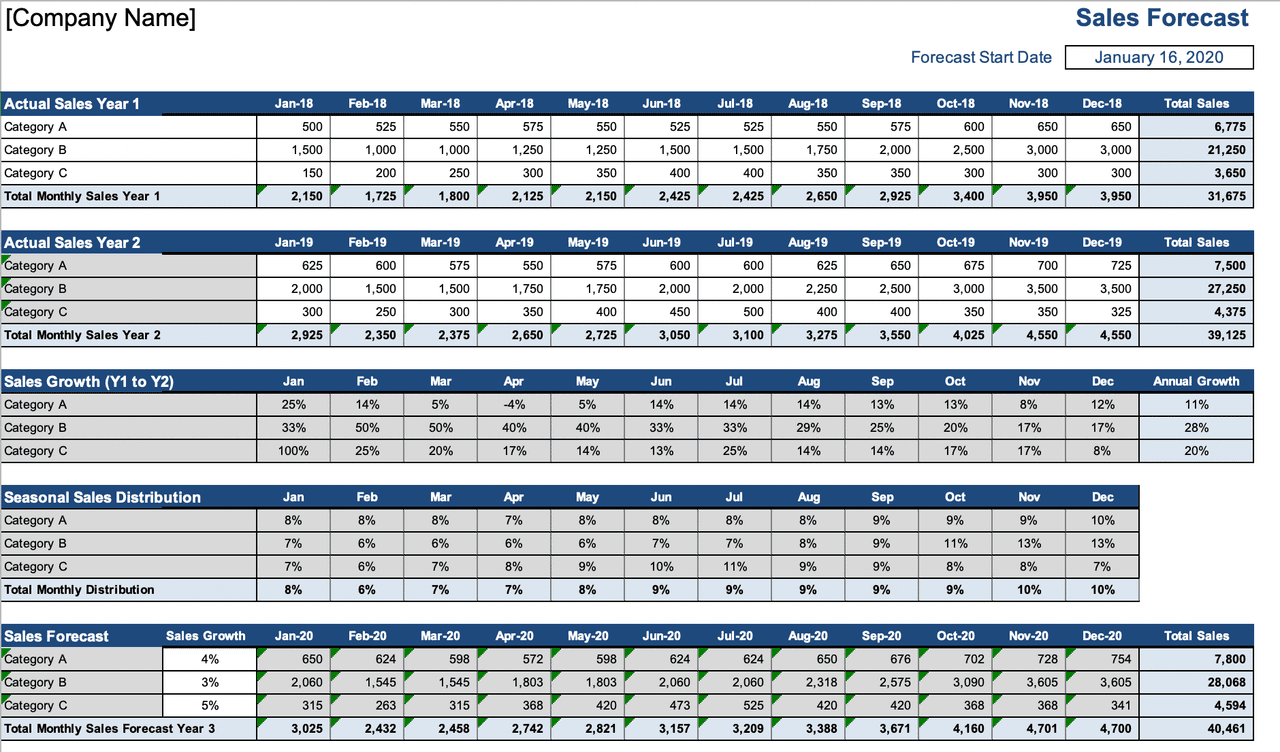
Sales forecast template
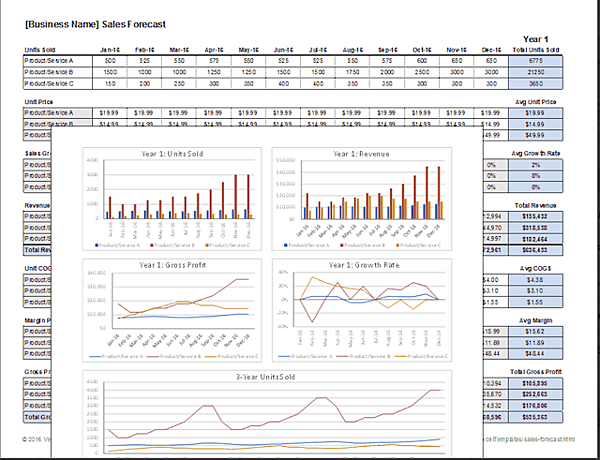
Below you’ll see an example of a software company’s six-month sales forecast template for two products. Product one is a software application, and product two is a software accessory.
In this sales forecast template, the company used past sales data to fill in each month. They projected their sales would increase by 10% each month because of a 5% increase in inflation and because they gained 5% more of the market. They kept their price per unit the same as the previous year.
Putting both products in the same chart can help the company see that their lower-cost product—the software accessory—brings in more revenue than their higher-cost product. The company can then use this insight to create more low-cost products in the future.
Sales forecast examples
Sales forecasting is not a one-size-fits-all process. It varies significantly across industries and business sizes. Understanding this through practical examples can help businesses identify the most suitable forecasting method for their unique needs.
![sales projection in business plan example [inline illustration] 6 month sales forecast (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/1ea5d5bf-2c96-428a-9097-40a76a798573/inline-business-strategy-sales-forecast-template-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Sales forecasting example 1: E-commerce
In the e-commerce sector, where trends can shift rapidly, intuitive forecasting is often useful for making quick, informed decisions.
Scenario: An e-commerce retailer specializing in fashion accessories is planning for the upcoming festive season.
Trend analysis phase: The team spends the first week analyzing customer feedback and current fashion trends on social media, using intuitive forecasting to predict which products will be popular.
Inventory planning phase: Based on these insights, the next three weeks are dedicated to selecting and ordering inventory, focusing on products predicted to be in high demand.
Sales monitoring and adjustment: As the holiday season approaches, the team closely monitors early sales data, ready to adjust their inventory and marketing strategies based on real-time sales performance.
This approach allows the e-commerce retailer to stay agile , adapting quickly to market trends and customer preferences.
Sales forecasting example 2: Software development
For a software development company, especially one working with B2B clients, opportunity stage forecasting can help predict sales and manage the sales pipeline effectively.
Scenario: A software development company is launching a new project management tool.
Lead generation and qualification phase: In the initial month, the sales team focuses on generating leads, qualifying them, and categorizing potential clients based on their progress through the sales pipeline.
Proposal and negotiation phase: For the next two months, the team works on creating tailored proposals for high-potential leads and enters negotiation stages, using opportunity stage forecasting to predict the likelihood of deal closures.
Closure and review: In the final phase, the team aims to close deals, review the accuracy of their initial forecasts, and refine their approach based on the outcomes.
Opportunity stage forecasting enables the software company to efficiently manage its sales pipeline , focusing resources on the most promising leads and improving their chances of successful deal closures.
Pair your sales forecast with a strong sales process
A sales forecast is only one part of the larger sales picture. As your team members acquire leads and close deals, you can track them through the sales pipeline. A solid sales plan is the foundation of future success.
Related resources

Everything you need to know about requirements management
How to streamline compliance management software with Asana

15 creative elevator pitch examples for every scenario

How Asana streamlines strategic planning with work management

- Data Enrichment
- Chrome Extension
- Email Verification
- Technographics
- Email Finder
- Intent Data
- Case Studies
- Affiliate Program
- Help Center
How to Create a Sales Forecast (Examples & Templates)
Every business needs management tools to maximize performance and keep everything running smoothly. A sales forecast is a critical tool that businesses use to measure their progress and check everything is going to plan. Here’s a closer look at why sales forecasts are important and how to create them. We have some great templates for you, too.
What Is a Sales Forecast – And Which Factors Impact It?
Sales forecasts are data-backed predictions about the sales volume a business will experience over a specific period.
A sales forecast is very important because it provides the foundation for almost all other planning activities. Businesses will rely on accurate sales forecasting to better understand how they should plan financially and execute their game plan .
This means that sales forecasts have the potential to make or break a business.
As with anything in life, though, nothing is certain. Sales forecasts can be affected by a range of factors. This means that businesses have to prepare for any and all eventualities.
Here’s a look at some of the factors that can affect sales forecasting:
A lack of sales history
Sales forecasts are often built using historical data. Businesses analyze previous results to extrapolate and create predictions. If a business starts and lacks a good body of historical sales data, it will struggle to create an accurate sales forecast.
The type of business
Each industry has its series of unique challenges and quirks. Those factors are sometimes unpredictable and could affect a business’s revenues. The ad tech industry, for instance, is often rocked by new data privacy regulations.
Outside factors
Some businesses find that everything is moving according to plan before blindsiding by an unpredictable event they cannot control. Consumer earnings may plummet, for instance, and cause people to restrict their spending.
Inside factors
Some businesses are forced to change their pricing or payment structures. This new dynamic can often have unpredictable effects and cause a business to veer off course from what its sales forecast predicted.
Why Should You Establish Sales Forecasts?
Sales forecasting is essential for every business. Here are some of the key reasons.
Perform accurate financial planning
Sales forecasts help the CFO and financial team understand how much cash is going to be coming into a business. This gives businesses a better understanding of how they can use that capital and makes it possible to calculate what profit they can expect over a given period .
Plan sales activities
A sales forecast can help executives with sales planning. Those executives will understand how many salespeople to employ, for instance, and which quotas and targets to attribute to each of those salespeople. This means that an accurate sales forecast can help salespeople to understand and hit their objectives.
Coordinate marketing
A sales forecast will have a big impact on marketing. For instance, the sales forecast might show that sales are waning, and a bigger investment needs to be placed within marketing. It might also show that a particular product or service fails to deliver appropriate amounts of value.
Control inventory
A sales forecast gives businesses a good understanding of how much inventory they will need to purchase and retain. This is an important factor; it helps businesses balance overstocking and running out of materials. This is also true for SaaS businesses needing customer support and success.
Avoid fluctuations in price
An accurate sales forecast helps businesses maintain consistent product and service pricing. A poor sales forecast might mean a business is forced to adjust its pricing unpredictably. This tactic is often the result of panic; without the proper strategy, it jeopardizes a business’s profitability.

How to Forecast Sales – The Best Sales Forecasting Methods
Businesses around the world use a range of sales forecasting techniques. Here’s a closer look at some key methods you could use.
Opportunity Stage Forecasting
What is it?
This sales forecasting technique calculates the likelihood of deals closing throughout a pipeline.
Most businesses use a sales pipeline divided into a series of sections. The likelihood of converting a prospect increases the deeper the prospect moves into the sales process. To get the most from this technique, the team must dig into the current performance of the sales team.
After that analysis, the probabilities might look something like this:
- Sales Accepted lead : 10% probability of closing
- Sales Qualified Lead : 25% probability of closing
- Proposal sent : 40% probability of closing
- Negotiating : 60% probability of closing
- Contract sent : 90% probability of closing
Using these probabilities, you can extrapolate an opportunity stage sales forecast. You’ll want to take the deal’s potential value and multiply that by the win likelihood.
Who should use it
This is a great sales forecasting method if you have access to historical data, lots of leads in your pipeline, and you need a quick estimate. It’s important to understand that this isn’t the most accurate option, given that many random factors affect those probabilities.
Length of Sales Cycle Forecasting
This sales forecasting method finds the average length of your sales cycle. This helps you predict when your deals will likely close and reveal opportunities for your sales team to expedite the sales cycle.
This method is simple. You can find the length of your average sales cycle using the following basic formula:
Total # of days to close deals / # of closed deals
Let’s imagine, for instance, that you find the following:
- Deal 1: 28 days
- Deal 2: 15 days
- Deal 3: 50 days
- Deal 4: 38 days
We closed four deals, and it took 131 days to close them all together. This means that the average length of our sales cycle is 33 days.
Equipped with that information, we can look at our pipeline and estimate how likely we are to close deals based on how old they are. The closer a deal moves toward the average sales cycle length, the more likely it will be closed.
This is a great sales forecasting method for sales managers who want to learn more about the deals spread across their pipeline. For instance, they can use this method to differentiate between different types of groups.
Sales managers might find that the average sales cycle length is much shorter for web leads, for example, when compared to email leads.
Historical Forecasting
Historical forecasting is a very quick and simple sales forecasting technique. The process involves looking back at your previous performance within a certain timeframe and assuming that your future performance will be superior or at least equal.
This is a useful reference because it helps you to get to grips with seasonality and the outside factors that affect your sales. You might find, for instance, that the holidays are a particularly slow time for your business, and looking at historical data can help you to prepare.
With that said, historical forecasting has its issues. It assumes that buyer demand will be constant, which is no longer a given. This could mean you overestimate your sales statistics and use an accurate sales forecast.
This forecasting method is ideal for a business that needs a quick and easy way to project how much it will sell over a given period. That said, historical data should be used as a benchmark instead of the foundation of a sales forecast.
Lead Pipeline Forecasting
This time-consuming sales forecasting method involves reviewing each lead within your pipeline and determining how likely the deal will be closed. That likelihood is determined by exploring factors like the value of the opportunity, the performance of your salespeople, seasonality, and more.
This is a time-consuming method, and it often makes sense for businesses with fewer high-value leads – it wouldn’t necessarily be efficient or make much sense for a SaaS business, for instance.
The big benefit of this method is its accuracy. If you have reliable and rigid data to base your analysis on, you will find that this method can give you a deeper insight into each lead.
This method makes sense for those businesses that have a lower number of leads. Inside salespeople, for instance, will want to get a clearer picture of every lead within their pipeline. This method isn’t appropriate for SaaS businesses that operate according to volume.
Test Market Analysis Forecasting
Businesses often launch exciting new products and services. But it can be difficult to get accurate sales forecasts without historical data . Test Market Analysis forecasting is the process of developing a product or service and introducing it to a test market to forecast sales and get an approximation of future sales.
This limited rollout allows businesses to track the performance of the new offering and monitor things like consumer awareness, repeat purchase patterns, and more. This is a data-gathering exercise, and it feeds businesses with the information they need to create accurate sales forecasts.
This approach is perfect for those businesses that need to perform real-world experiments to gather useful information. A new business can use sales forecasting to use its sales data to predict where future sales can come from. This can limit the cost since it’s an effective way of having a busy sales pipeline. The limited rollout of the product is also useful from a product perspective, given that adjustments can be made according to feedback.
A big issue with this form of forecasting is that one test market may not be like the others. Your data might not reflect the wider reality, so you must make prudent choices that provide you with accurate information.
Multivariable Analysis
As the name suggests, this method calls upon analyzing a range of variables to get the clearest picture possible. This means that if the method is performed well, it can often provide the most accurate forecast.
If you use this technique, you will want to bring together factors like the average length of your sales cycle, the performance of your salespeople, historical forecasting, and more.
The success of this method hinges upon two key factors within your business:
- the accuracy of your salespeople and their reporting
- the quality of the forecasting tools that you use.
Both of these factors must be in place to make sure this forecasting method has the best chance of success.
Multivariable forecasting is most appropriate for larger and well-organized businesses, as it uses the data and tools necessary to blend various forecasting methods into one. This could be it if you need the most accurate forecast method possible.
Intuitive Forecasting
Your salespeople are on the front; their experience is very valuable. They often have a good idea of how likely they are to close a particular deal and can use educated guesses to assess the situation.
Experienced salespeople can take emotion out of the equation and rely on their experience and knowledge to make accurate predictions. Some businesses decide to incorporate those gut instincts into the way that they forecast a particular sale.
Some businesses, for instance, will add a score to the conversion probability of their various prospects according to the gut feeling of their salespeople.
This intuitive forecasting method is particularly useful for businesses that lack historical data. Without the quantifiable data to provide the basis for your sales forecasting, you might have to turn to more qualitative assessments from your salespeople.
The downside of this sales forecasting method is clear, though. These assessments are highly subjective, and you might find that your salespeople are often more optimistic in their projections. This means those projections should be taken with a pinch of salt, but they are better than nothing.
Sales Forecast Examples
We know the theory, but how about the practice? In these awesome examples, let’s take a closer look at what those sales forecast methods look like.
Standard Business Plan Financials
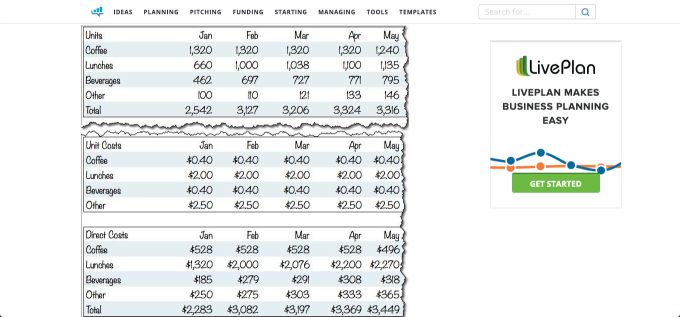
This example from Tim Berry (chairman and founder of Palo Alto Software) looks at what a startup sales forecast might look like .
Tim sets the scene and describes Magda’s situation – she wants to open a small café in an office park.
He goes on to show how Magda would establish a base case, estimate her monthly capacity, and what type of sales she could expect. To wrap up, she goes through her month-by-month estimates for her first year and estimates her direct cost.
This is a great exercise and unmissable reading for new entrepreneurs dreaming up a new venture.
Sales Forecast Guide by Toptal Research
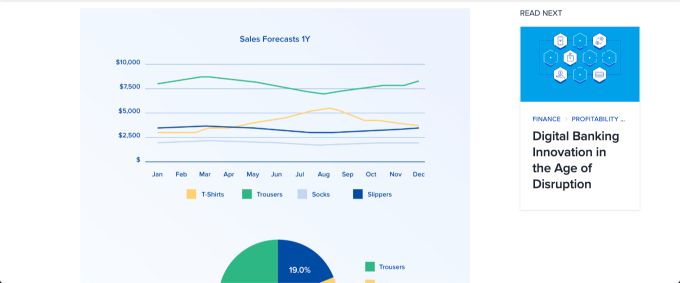
This simple sales forecasting guide from Toptal Research also includes a simple example that forms the basis of the guide. These simple visuals and data will give you a good idea of how you can put your sales forecasting efforts together and what it will look like.
This example also shows that you can attractively forecast sales and inform the sales teams. Sales forecasting doesn’t have to be boring columns of data, but you can bring your sales forecast to life with colorful visuals.
Detailed Sales Forecast by Microsoft
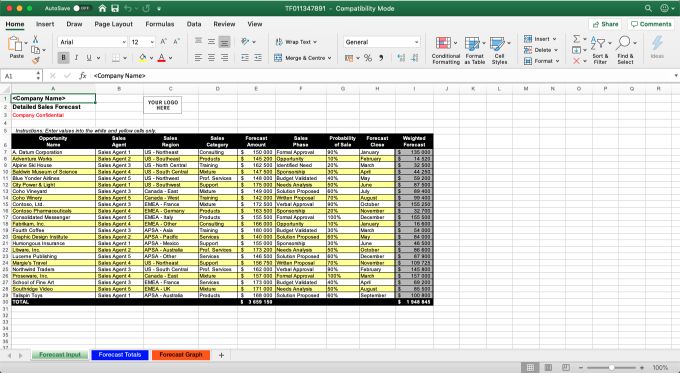
This detailed sales forecast template from Microsoft makes it simple for you to estimate your monthly sales projections.
The formula comes with pre-built formulas and worksheet features that result in an attractive and clear template. The template also relies on a weighted sales forecasting method based on the probability of closing each opportunity.
Even if you do not use this exact template, it’s a great file to use. It can give you a great idea of the information you need to include and how it might come together in a spreadsheet format.
Sales Forecast Templates
Looking for your own sales forecast templates to get a running start? Here’s a look at some of the most practical and useful templates.
Sales Forecast Template for Excel by Vertex42
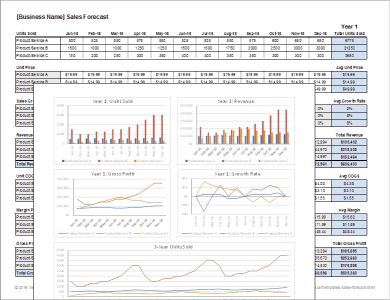
This free sales forecast template helps you keep a handle on key information like unit sales, growth rate, profit margins, and gross profit.
The template is already set up to help you compare and analyze a range of products and services on a monthly basis. The chart also includes a range of sample charts that can be used to effectively and accurately communicate the contents of your sales forecast.
The same worksheet can be used to create monthly and yearly forecasts. You can play with the template to find your desired view and information.
Sales Forecast Template by Freshworks
This simple forecasting template helps you to put together an effective sales forecast. This finished product can then be used to grow your revenues and hit your quotas.
This template is particularly effective for small businesses and startups that need to project sales and prioritize deals at the early stages of their business. Freshworks also explains that the template can help businesses achieve a higher rate of on-time delivery and accurate hiring projections.
The free sales forecast template is very intuitive to use. Again, it’s great to flick through the spreadsheet to understand what you need in a sales forecast and how it can be put together.
Free Sales Forecast Template by Fit Small Business
This sales forecast template is perfect if your CRM doesn’t currently offer built-in sales forecasting. This template can help you create a forecast from scratch that is adjusted to your own particular needs much quicker.
The template is available in various formats, including PDF, Excel, and Google Sheets. This is great news if you create your small business on your own terms and have limited software access .
Again, this template is clear and simple to use. All of the fields are explained within the spreadsheet – you don’t have to worry about going elsewhere to find definitions.
Sales Forecasting Tools
Looking for sales forecasting tools to take your activities to the next level? Here’s a look at some of the standout options.
Pipedrive is a sales CRM that is designed for salespeople by salespeople. It is a robust CRM that includes all of the features a sales team needs to achieve sales success and grow their business.
The tool also includes a forecasting tool. This tool acts as a personal sales manager that helps salespeople to choose the right deals and activities at the right time. This helps salespeople to become better closers.
By all accounts, this function is very useful for salespeople and managers alike. The forecasting tool can also be customized to match the specific needs of salespeople.
Smart Demand Planner
Smart Demand Planner is a consensus demand planning and statistical forecasting solution that understands how accurate critical forecasts are to a business.
The tool was built on the premise that forecasts are often inaccurate and can cause various issues. Moreover, the traditional sales forecast often resides within a complex spreadsheet that is difficult to use, share, and scale.
The tool aims to fix those issues by aligning strategic business forecasting at all levels of your hierarchy. Smart Demand Planner offers a statistically sound objective foundation for your sales activities.
amoCRM is an easy and smart sales solution that focuses on the world of messenger-based sales. The platform understands the popularity and potential of messenger apps, so it offers a whole new way of using the channel to create valuable relationships.
The tool also includes visual, real-time reports that give salespeople and managers powerful insights. These analytics can be used to set targets and also forecast future sales. What’s more, they can measure performance and identify target areas.
The visual look and feel of the platform make this a very intuitive option. It can drive value through accurate forecasting in businesses where messenger-based selling is critical.
As we have seen, forecasts are critical to the success of your business. They can be cost-effective for a new business, keep sales teams and reps informed, and more. However, every business also needs the leads to make those forecasts a reality. Learn more about UpLead today and how our platform can help you to find, connect, and engage with qualified prospects.

Snov.io vs. Hunter.io: Which Tool is Best For Your Business?

Hunter.io vs RocketReach: Which is the Better Email Finder?

Cognism vs. Lead411: Features, Pricing and Data
see uplead in action
Start your free trial today!
Try UpLead free for 7 days.

- Platform Overview
- Buyer Intent
- Knowledge Base
- Search By Industry
- Code Red Safety
- Staffing Future
- Complete Merchant Solutions
- TBM Consulting Group
- Request a Demo
Copyright © 2024 UpLead | All Rights Reserved
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
How to Create a Sales Forecast

11 min. read
Updated October 27, 2023

Business owners are often afraid to forecast sales. But, you shouldn’t be. Because you can successfully forecast your own business’s sales.
You don’t have to be an MBA or CPA. It’s not about some magic right answer that you don’t know. It’s not about training you don’t have. It doesn’t take spreadsheet modeling (much less econometric modeling) to estimate units and price per unit for future sales. You just have to know your own business.
Forecasting isn’t about seeing into the future
Sales forecasting is much easier than you think and much more useful than you imagine.
I was a vice president of a market research firm for several years, doing expensive forecasts, and I saw many times that there’s nothing better than the educated guess of somebody who knows the business well. All those sophisticated techniques depend on data from the past — and the past, by itself, isn’t the best predictor of the future. You are.
It’s not about guessing the future correctly. We’re human; we don’t do that well. Instead, it’s about setting down assumptions, expectations, drivers, tracking, and management. It’s about doing your job, not having precognitive powers.
- Successful forecasting is driven by regular reviews
What really matters is that you review and revise your forecast regularly. Spending should be tied to sales, so the forecast helps you budget and manage. You measure the value of a sales forecast like you do anything in business, by its measurable business results.
That also means you should not back off from forecasting because you have a new product, or new business, without past data. Lay out the sales drivers and interdependencies, to connect the dots, so that as you review plan-versus-actual results every month, you can easily make course corrections.
If you think sales forecasting is hard, try running a business without a forecast. That’s much harder.
Your sales forecast is also the backbone of your business plan . People measure a business and its growth by sales, and your sales forecast sets the standard for expenses , profits, and growth. The sales forecast is almost always going to be the first set of numbers you’ll track for plan versus actual use, even if you do no other numbers.
If nothing else, just forecast your sales, track plan-versus-actual results, and make corrections — that process alone, just the sales forecast and tracking is in itself already business planning. To get started on building your forecast follow these steps.
And if you run a subscription-based business, we have a guide dedicated to building a sales forecast for that business model.
- Step 1: Set up your lines of sales
Most forecasts show several distinct lines of sales. Ideally, your sales lines match your accounting, but not necessarily in the same level of detail.
For example, a restaurant ought not to forecast sales for each item on the menu. Instead, it forecasts breakfasts, lunches, dinners, and drinks, summarized. And a bookstore ought not to forecast sales by book, and not even by topic or author, but rather by lines of sales such as hardcover, softcover, magazines, and maybe categories (such as fiction, non-fiction, travel, etc.) if that works.
Always try to set your streams to match your accounting, so you can look at the difference between the forecast and actual sales later. This is excellent for real business planning. It makes the heart of the process, the regular review, and revision, much easier. The point is better management.
For instance, in a bicycle retail store business plan, the owner works with five lines of sales, as shown in the illustration here.

In this sample case, the revenue includes new bikes, repair, clothing, accessories, and a service contract. The bookkeeping for this retail store tracks sales in those same five categories.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- Step 2: Forecast line by line
There are many ways to forecast a line of sales.
The method for each row depends on the business model
Among the main methods are:.
- Unit sales : My personal favorite. Sales = units times price. You set an average price and forecast the units. And of course, you can change projected pricing over time. This is my favorite for most businesses because it gives you two factors to act on with course corrections: unit sales, or price.
- Service units : Even though services don’t sell physical units, most sell billable units, such as billable hours for lawyers and accountants, or trips for transportations services, engagements for consultants, and so forth.
- Recurring charges : Subscriptions. For each month or year, it has to forecast new signups, existing monthly charges, and cancellations. Estimates depend on both new signups and cancellations, which is often called “churn.”
- Revenue only : For those who prefer to forecast revenue by the stream as just the money, without the extra information of breaking it into units and prices.
Most sales forecast rows are simple math
For a business plan, I recommend you make your sales forecast a detailed look at the next 12 months and then broadly cover two years after that. Here’s how to approach each method of line-by-line forecasting.
Start with units if you can
For unit sales, start by forecasting units month by month, as shown here below for the new bike’s line of sales in the bicycle shop plan:

I recommend looking at the visual as you forecast the units because most of us can see trends easier when we look at the line, as shown in the illustration, rather than just the numbers. You can also see the numbers in the forecast near the bottom. The first year, fiscal 2021 in this forecast, is the sum of those months.
Estimate price assumptions
With a simple revenue-only assumption, you do one row of units as shown in the above illustration, and you are done. The units are dollars, or whatever other currency you are using in your forecast. In this example, the new bicycle product will be sold for an average of $550.00.
That’s a simplifying assumption, taking the average price, not the detailed price for each brand or line. Garrett, the shop owner, uses his past results to determine his actual average price for the most recent year. Then he rounds that estimate and adds his own judgment and educated guess on how that will change.

Multiply price times units
Multiplying units times the revenue per unit generates the sales forecast for this row. So for example the $18,150 shown for October of 2020 is the product of 33 units times $550 each. And the $21,450 shown for the next month is the product of 39 units times $550 each.
Subscription models are more complicated
Lately, a lot of businesses offer their buyers subscriptions, such as monthly packages, traditional or online newspapers, software, and even streaming services. All of these give a business recurring revenues, which is a big advantage.
For subscriptions, you normally estimate new subscriptions per month and canceled subscriptions per month, and leave a calculation for the actual subscriptions charged. That’s a more complicated method, which demands more details.
For that, you can refer to detailed discussions on subscription forecasting in How to Forecast Sales for a Subscription Business .
- But how do you know what numbers to put into your sales forecast?
The math may be simple, yes, but this is predicting the future, and humans don’t do that well. So, don’t try to guess the future accurately for months in advance.
Instead, aim for making clear assumptions and understanding what drives your sales, such as web traffic and conversions, in one example, or the direct sales pipeline and leads, in another. Review results every month, and revise your forecast. Your educated guesses become more accurate over time.
Experience in the field is a huge advantage
In a normal ongoing business, the business owner has ample experience with past sales. They may not know accounting or technical forecasting, but they know their business. They are aware of changes in the market, their own business’s promotions, and other factors that business owners should know. They are comfortable making educated guesses.
If you don’t personally have the experience, try to find information and make guesses based on the experience of an employee, your mentor , or others you’ve spoken within your field.
Use past results as a guide
Use results from the recent past if your business has them. Start a forecast by putting last year’s numbers into next year’s forecast, and then focus on what might be different this year from next.
Do you have new opportunities that will make sales grow? New marketing activities, promotions? Then increase the forecast. New competition, and new problems? Nobody wants to forecast decreasing sales, but if that’s likely, you need to deal with it by cutting costs or changing your focus.
Look for drivers
To forecast sales for a new restaurant, first, draw a map of tables and chairs and then estimate how many meals per mealtime at capacity, and in the beginning. It’s not a random number; it’s a matter of how many people come in.
To forecast sales for a new mobile app, you might get data from the Apple and Android mobile app stores about average downloads for different apps. A good web search might also reveal some anecdotal evidence, blog posts, and news stories, about the ramp-up of existing apps that were successful.
Get those numbers and think about how your case might be different. Maybe you drive downloads with a website, so you can predict traffic from past experience and then assume a percentage of web visitors who will download the app.
- Estimate direct costs
Direct costs are also called the cost of goods sold (COGS) and per-unit costs. Direct costs are important because they help calculate gross margin, which is used as a basis for comparison in financial benchmarks, and are an instant measure (sales less direct costs) of your underlying profitability.
For example, I know from benchmarks that an average sporting goods store makes a 34 percent gross margin. That means that they spend $66 on average to buy the goods they sell for $100.
Not all businesses have direct costs. Service businesses supposedly don’t have direct costs, so they have a gross margin of 100 percent. That may be true for some professionals like accountants and lawyers, but a lot of services do have direct costs. For example, taxis have gasoline and maintenance. So do airlines.
A normal sales forecast includes units, price per unit, sales, direct cost per unit, and direct costs. The math is simple, with the direct costs per unit related to total direct costs the same way price per unit relates to total sales.
Multiply the units projected for any time period by the unit direct costs, and that gives you total direct costs. And here too, assume this view is just a cut-out, it flows to the right. In this example, Garrett the shop owner projected the direct costs of new bikes based on the assumption of 49 percent of sales.

Given the unit forecast estimate, the calculation of units times direct costs produces the forecast shown in the illustration below for direct costs for that product. So therefore the projected direct costs for new bikes in October is $8,894, which is 49% of the projected sales for that month, $18,150.

- Never forecast in a vacuum
Never think of your sales forecast in a vacuum. It flows from the strategic action plans with their assumptions, milestones , and metrics. Your marketing milestones affect your sales. Your business offering milestones affect your sales.
When you change milestones—and you will, because all business plans change—you should change your sales forecast to match.
- Timing matters
Your sales are supposed to refer to when the ownership changes hands (for products) or when the service is performed (for services). It isn’t a sale when it’s ordered, or promised, or even when it’s contracted.
With proper accrual accounting , it is a sale even if it hasn’t been paid for. With so-called cash-based accounting, by the way, it isn’t a sale until it’s paid for. Accrual is better because it gives you a more accurate picture, unless you’re very small and do all your business, both buying and selling, with cash only.
I know that seems simple, but it’s surprising how many people decide to do something different. The penalty for doing things differently is that then you don’t match the standard, and the bankers, analysts, and investors can’t tell what you meant.
This goes for direct costs, too. The direct costs in your monthly profit and loss statement are supposed to be just the costs associated with that month’s sales. Please notice how, in the examples above, the direct costs for the sample bicycle store are linked to the actual unit sales.
- Live with your assumptions
Sales forecasting is not about accurately guessing the future. It’s about laying out your assumptions so you can manage changes effectively as sales and direct costs come out different from what you expected. Use this to adjust your sales forecast and improve your business by making course corrections to deal with what is working and what isn’t.
I believe that even if you do nothing else, by the time you use a sales forecast and review plan versus actual results every month, you are already managing with a business plan . You can’t review actual results without looking at what happened, why, and what to do next.
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- Forecasting isn’t about seeing into the future
Related Articles

3 Min. Read
What Is a Break-Even Analysis?

8 Min. Read
How to Plan Your Exit Strategy

4 Min. Read
How to Create an Expense Budget

5 Min. Read
How to Highlight Risks in Your Business Plan
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
22 Sales Projection Templates for 2021 Forecasts

Casey O'Connor
What Is Sales Forecasting?
Types of sales forecast templates, forecasting templates for startups, forecasting templates for businesses with multiple products, forecasting templates for b2b companies.
Sales projection templates can help you quickly and easily create an accurate, data-driven sales forecast for your team.
Sales forecasting is an important exercise for any sales team that wants to see significant year-over-year growth and the ability to fine-tune their sales process in specific, targeted ways.
In this article, we’ll go over the basics of sales forecasting, as well as provide various forecast templates to help you streamline the process.
Here’s what we’ll cover:
- Top Forecasting Templates for Startups
A sales forecast is a data-driven prediction of the financial outcomes a business will most likely see at the end of a given time period. A sales forecast can provide insight into the performance of individual sales reps, full sales teams, or even entire organizations.
For overworked salespeople, making financial projections about future sales that may or may not come to fruition can seem like an exercise in futility. But a thorough, carefully considered sales forecast can be a huge asset to your business .
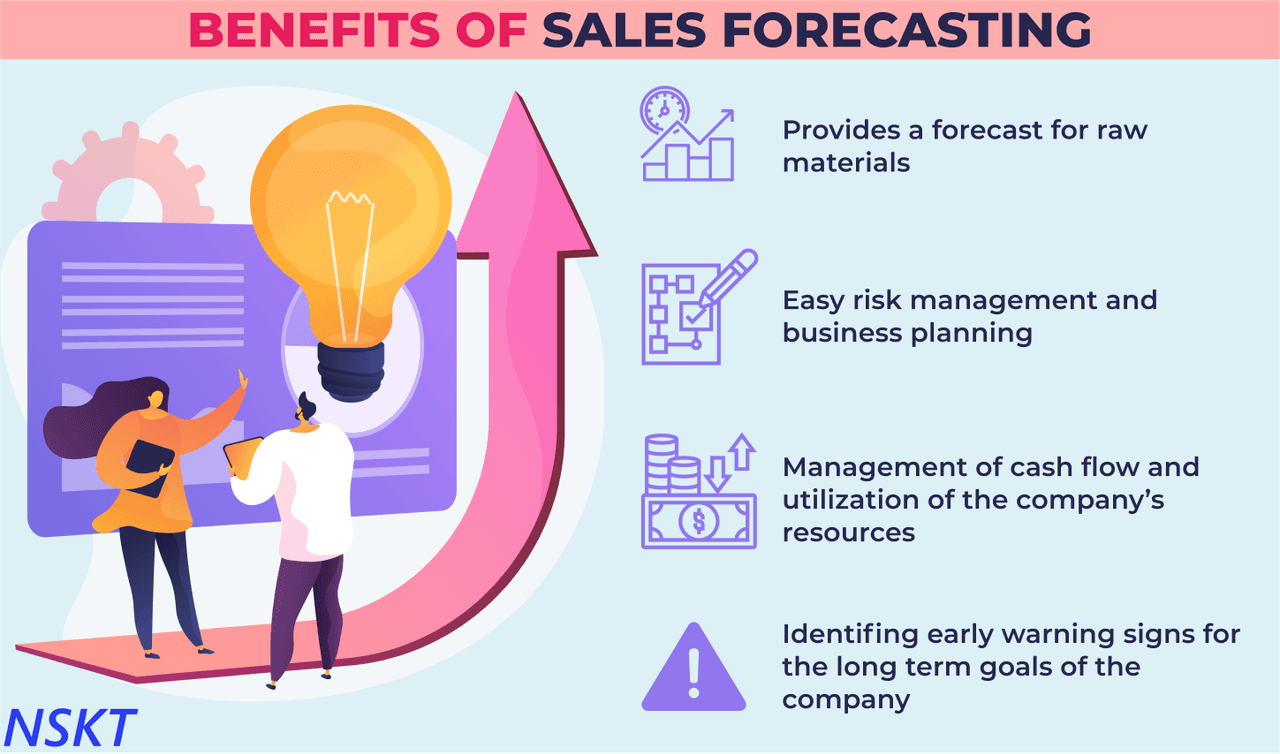
In order to create an accurate sales forecast, consider how the following factors currently impact your bottom line:
Your business goals are a very important benchmark for your sales team to keep in mind as you create your sales forecast. While your goals may not directly factor into the actual template, they will help steer your decision-making processes. Both short-term and long-term SMART goals will help give structure to your forecast.
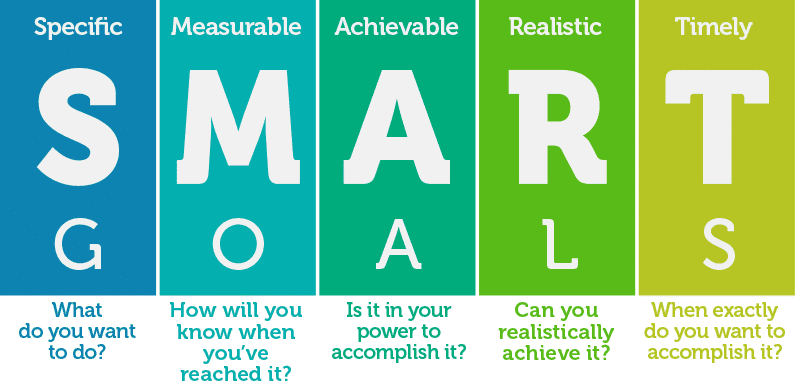
Sales Process
Your sales process map will be another helpful tool in creating your sales forecast (if you don’t have one yet, check out our tips on creating one here ). Use your sales process map to pull data points and determine areas of strength and growth.
Company Standards
Chances are that your sales team is made up of salespeople from all different backgrounds and experiences — what one sales rep considers a “qualified lead” may be entirely different from the next. The same goes for things like follow-up communication — how much is too much? Should the follow-up process start on LinkedIn , or via email?
While it may feel laborious, it’s worth your time to standardize and define these kinds of terms with your team. Use your sales process map to guide this exercise. Having consistency in your metrics will go a long way in pinpointing your sales projections.
In business, every penny counts (this is particularly true for small businesses and start-ups). If you’re not tracking every single penny that goes into and out of your business ( many businesses aren’t ), you need to start ASAP. Your sales projections will only be as accurate as your accounting, and the devil here is in the details.
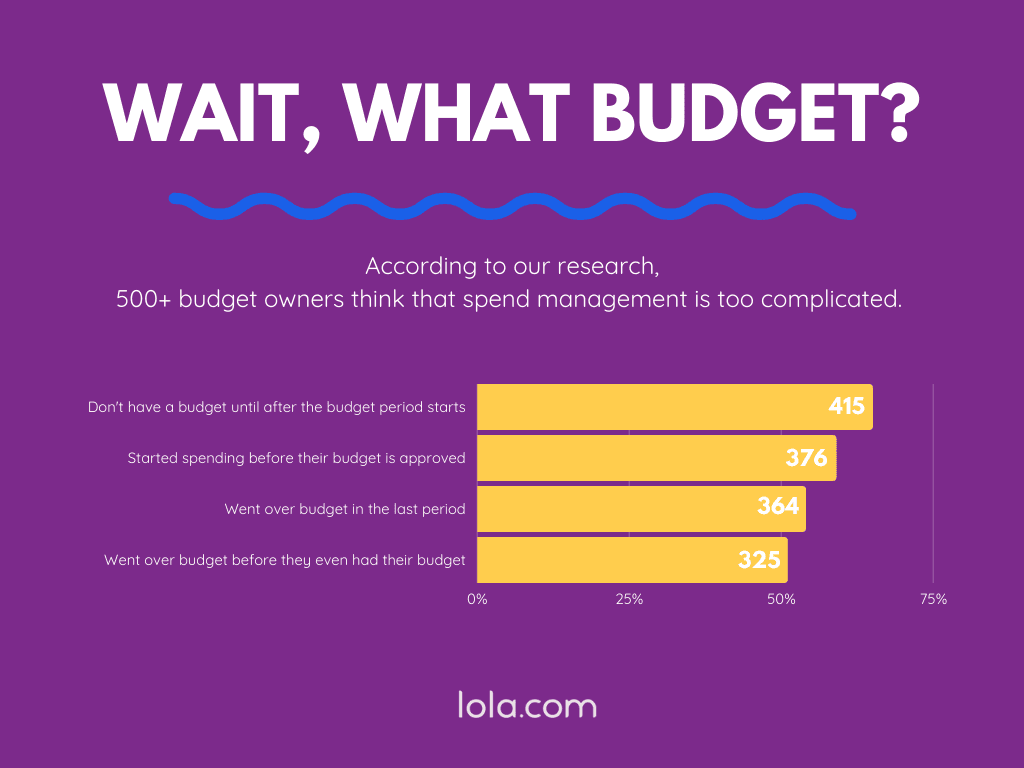
Don’t worry — you don’t need to go and cut funds from every department. Sometimes knowing the numbers is just as powerful as trimming them. But you’ll only reap the benefits of sales forecasting if you take a good hard look at the dollars you’re currently spending — all of them.
Befriend Your CRM
If your company utilizes any CRM software, now’s the time to start maximizing it. Your CRM can be a great way to track the many moving pieces that make up a sales forecast. Make sure you understand its full functionality , as many companies tend to only stick to the surface-level features.
When executed correctly, sales forecasts can give you very valuable insight into various aspects of your sales performance over a period of time. It also gives investors a really compelling reason to inject money into your business — if your forecasted sales are promising, they’ll be much more likely to invest.
Different businesses have different needs for sales forecasting templates. These templates may include things like multiple products, multiple time frames, seasonality considerations, and other variables. It’s important to make sure the template you choose captures the full financial picture without overcomplicating it.
In general, there are seven main types of forecast templates. Some of these standardized templates may work for your business, but you should also feel free to use these as a starting point, and customize as needed
(Don’t be intimidated by this process — you can do most of this with Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets!)
1. Lead Driven Forecasting
With this lead-driven forecasting template , you’ll be relying on extensive knowledge of your leads. Each lead source gets a value assigned, and projections are calculated accordingly.
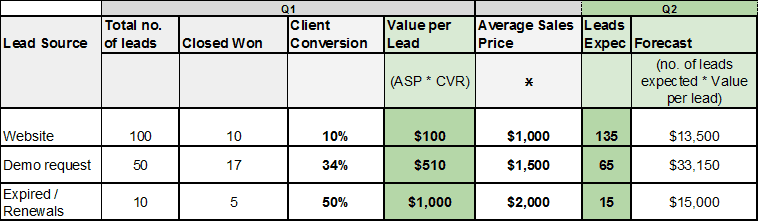
Because this template requires a lot of data about leads and their behaviors, it may not work well for businesses that are just starting out and still researching their customer base.
2. Length of Sales Cycle Forecasting
Length of sales cycle forecasting predicts the probability of a deal closing based on where they are in your sales cycle. It then assigns each deal a value based on how far along they are in the process.
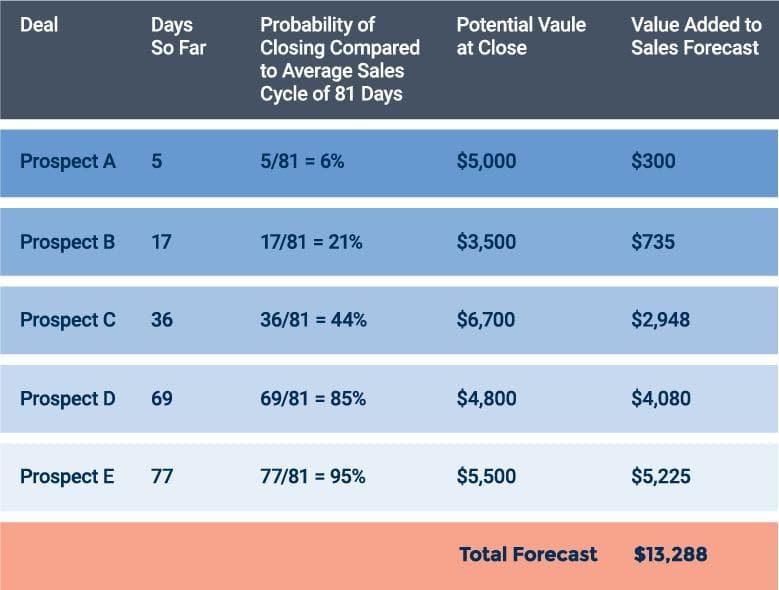
This template works well for companies who have robust CRM or other automation tools.
3. Opportunity Stage Forecasting
Opportunity stage forecasting is similar to the previous two templates, though it doesn’t account for source of leads or exact length of sales cycle. Instead, it assigns a probability to each prospect based on what stage of the sales process they’re in.
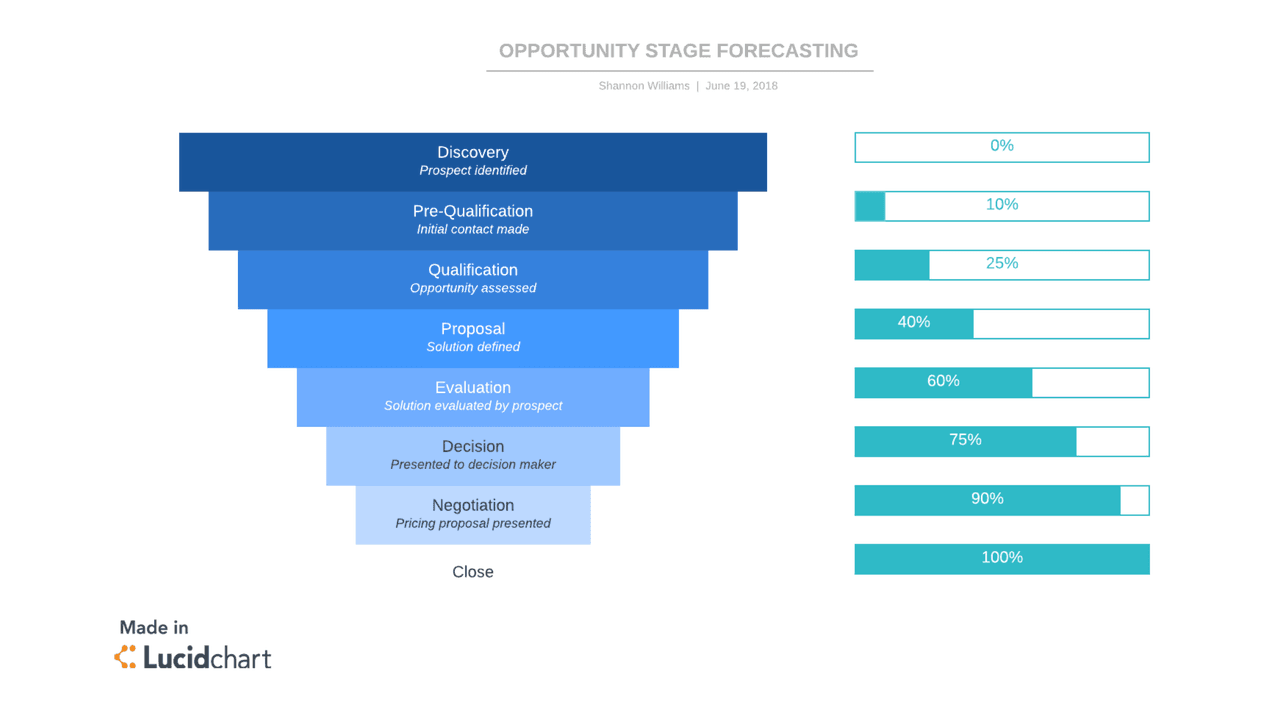
This template will take these probabilities, assign them a value, and add those values into your sales projection as your leads move through the sales process.
4. Intuitive Forecasting
Intuitive forecasting is pretty self-explanatory, and the least objective approach to sales forecasting . It relies on a sales rep’s experience to make judgments about how much value each deal will bring to the company.
Sales reps might consider any of the following as they make their forecast:
This method is difficult to scale, but it also doesn’t require a ton of historical sales data — it’s a good fit for many startups as they gather sales data.
5. Test-Market Analysis Forecasting
Test-market analysis forecast templates are used when launching new products. This method requires that you perform and collect data on a small test launch, and apply those results to your overall forecast.

6. Historical Forecasting
This is a very data-driven approach — it uses your historical sales data to predict future growth. It’s relatively quick and easy, but it has its downfalls.
Historical forecasting does not take any external factors into account, like market conditions or sales team changes. It simply looks at your history of sales. It also assumes year-over-year growth, which isn’t always the case. For most companies, historical sales data is a hugely beneficial piece of the sales forecast, but not the entire basis.
7. Multivariable Analysis
This multivariable analysis example spits out forecasts for gross profit and growth rate, but you could also formulate to predict things like profit margin or total revenue.
Without long-term historical sales data, it can be hard for many startups to create detailed projected sales reports. This is also true for older businesses who are launching a new product. In cases like these, it’s best to start with a simple projections template.
Here are some of the most basic, easiest-to-use templates we found for businesses that are just starting out. Click on the template’s header to download each one.
8. One-year Sales Forecast
One-year Sales Forecast (Google Sheets):
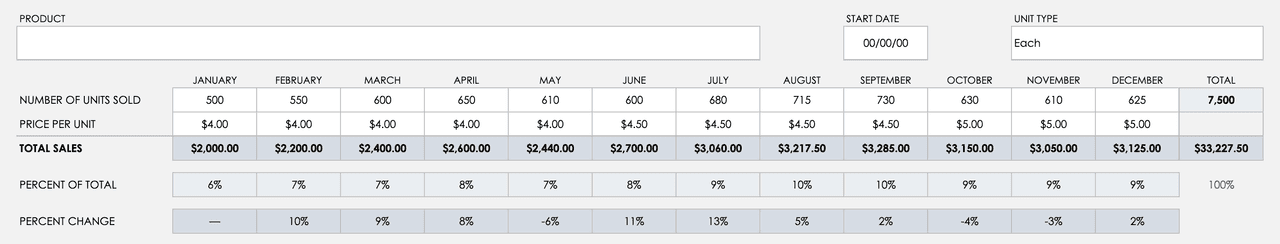
This template has very few inputs for historical sales data. All you need to include are the year, product, unit type, and the number of units sold. The spreadsheet has built-in formulas that will calculate the remaining rows automatically.
9. Best & Worst Case Scenario
Best & Worst Case Scenario (Excel):
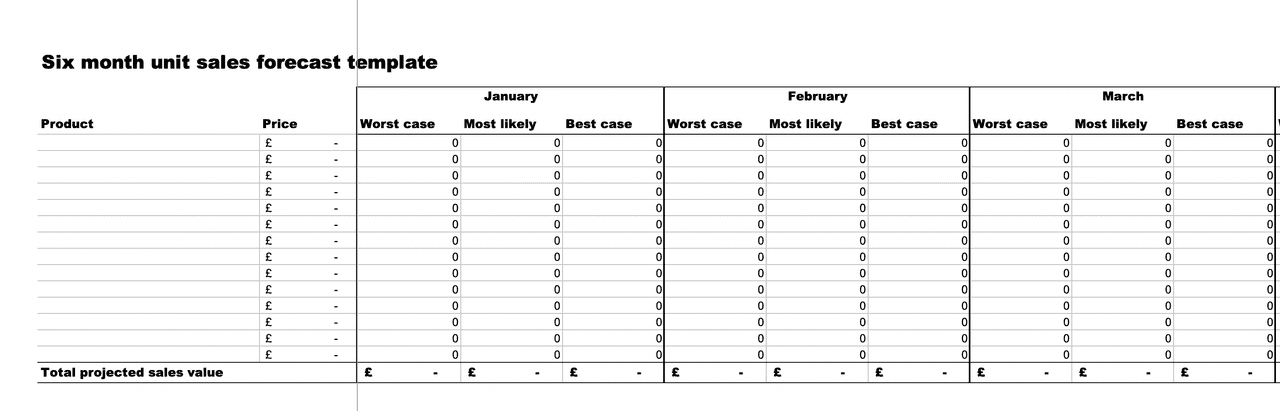
This template works well for companies who have only minimal data, and can give new businesses a target forecast range rather than precise numbers. For startups, this can allow for flexibility while still pursuing aggressive growth.
10. Expense-Focused
Expense-Focused (Excel):
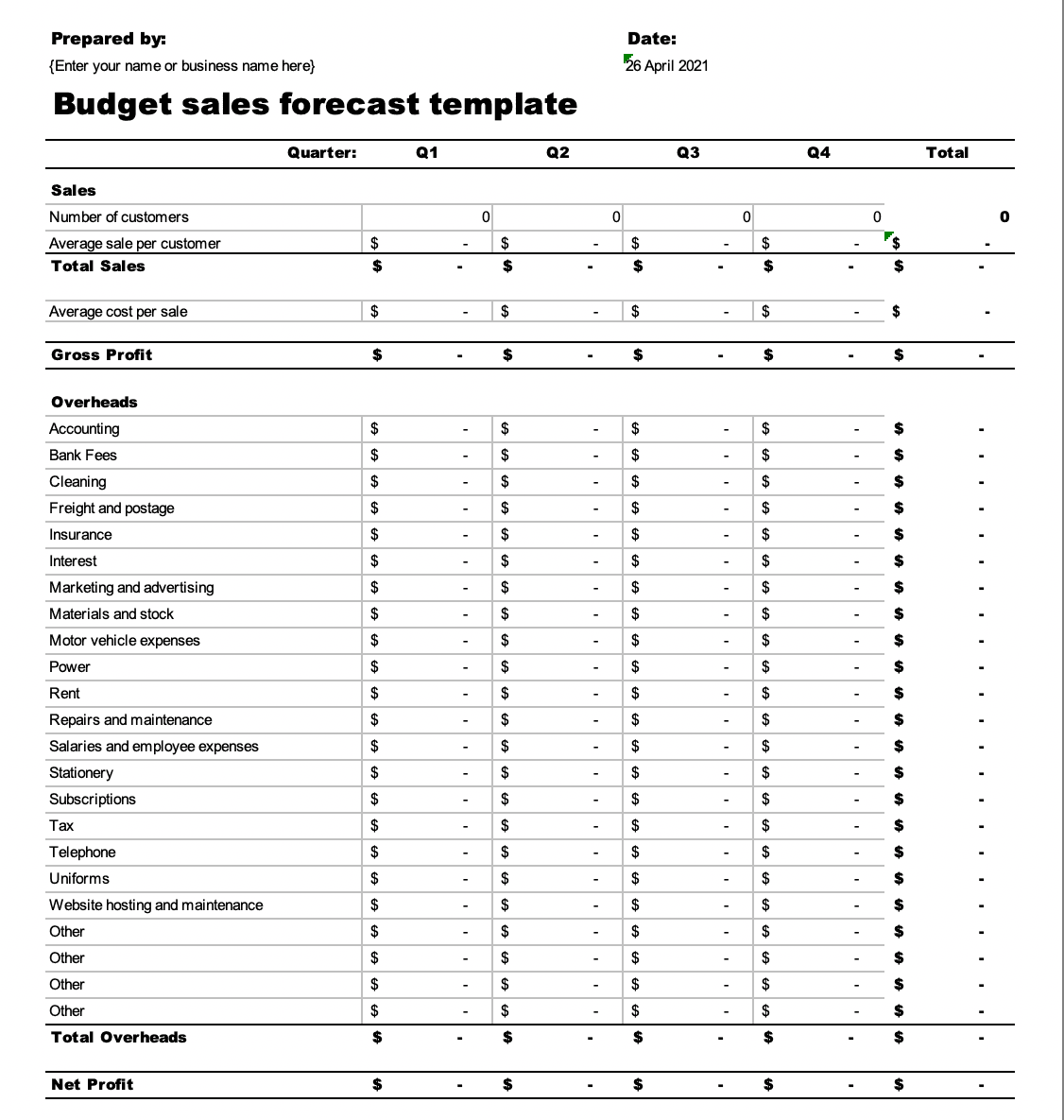
This template does a really nice job of breaking down all the various expenses that go into running a business. It could work really well for startups who are still learning how their cash flows in and out.
11. Monthly Sales
Monthly Sales (Microsoft):
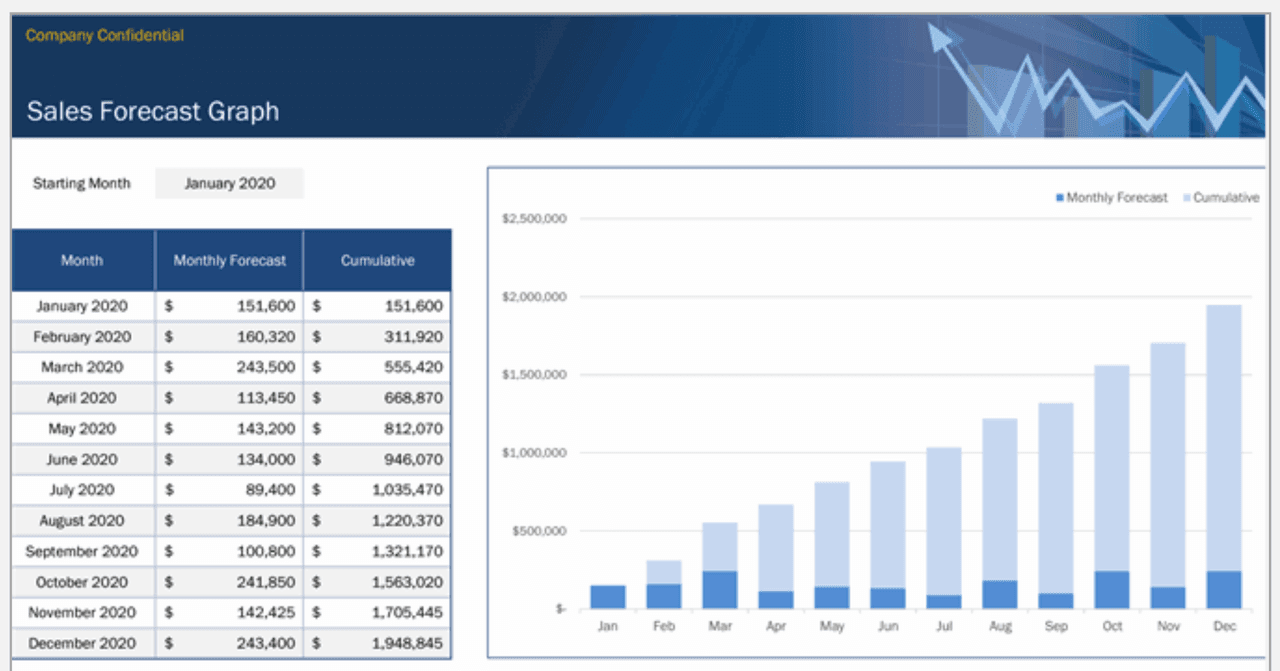
This template is great for startups that want to cut out the extra noise and simply determine whether their efforts are paying off month-to-month while they’re starting out.
12. Simple Monthly Reporting
Simple Monthly Reporting (PDF):

Businesses with multiple products (many e-commerce businesses fit this description, for example) sometimes struggle to create a sales forecasting template that’s fluid enough to capture the performance of many different profit streams.
Take a look at some of the best templates we found that are flexible enough to meet those needs.
13. 12-Month Forecast for Multiple Products
12-Month Forecast for Multiple Products (Excel):
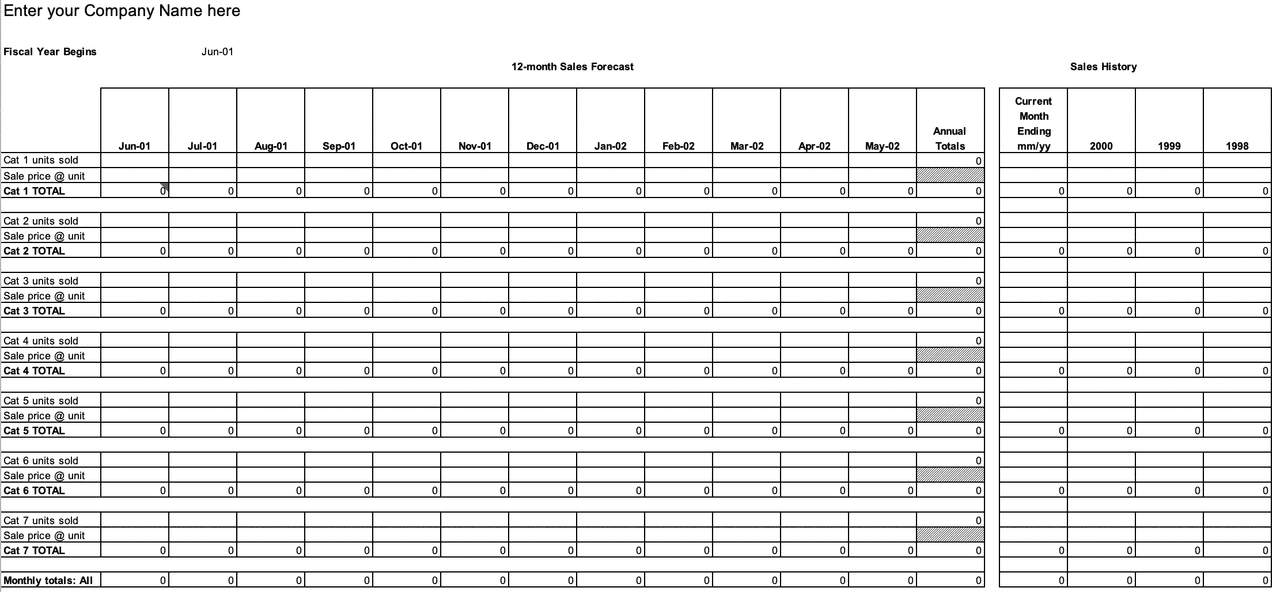
This template is detailed enough to see how each product fits into the bigger picture, but also simple and intuitive enough that a fledgling business could use it effectively.
14. Color-Coded Outputs
Color-Coded Outputs (Excel):
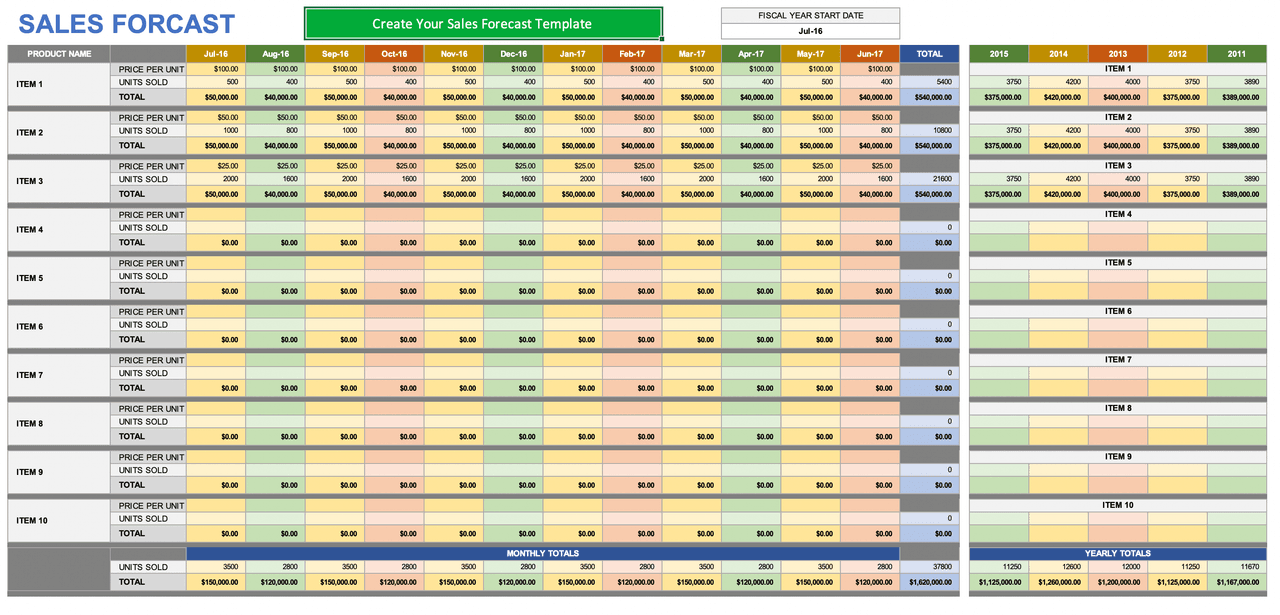
This template does a really nice job of streamlining the data from multiple product sales and arranging them in an aesthetically pleasing and easy-to-read manner.
15. Opportunity-Based
Opportunity-Based :
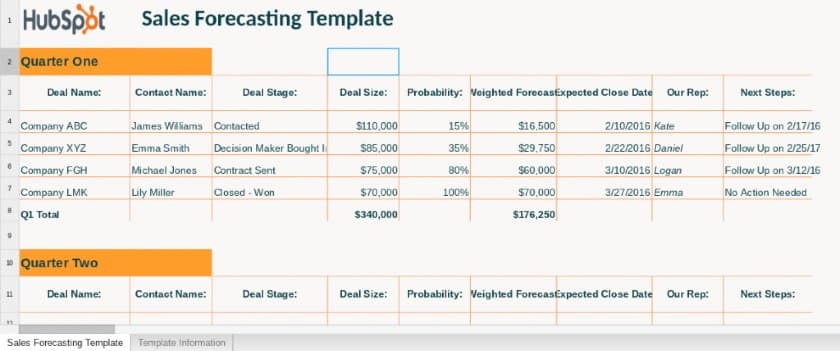
This template allows you to input sales based on deal stage, size, and probability. It’s best suited for companies who have a more developed understanding of their leads and sales process.
16. New Product Launch
New Product Launch (Excel):
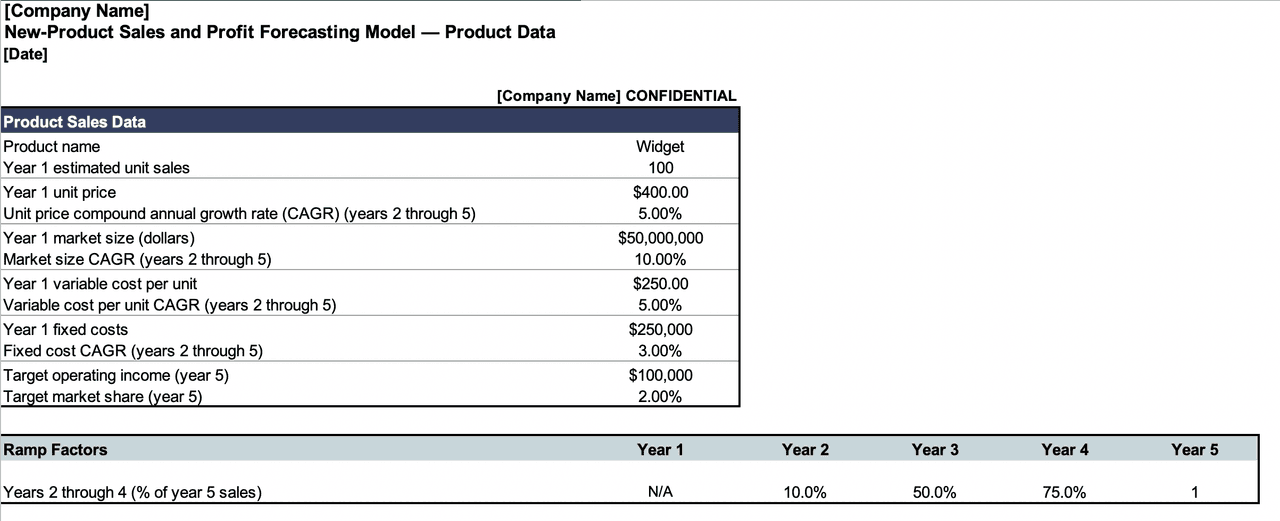
This template is great for companies who are launching a new product and want to look at projections for that product in isolation. Because new products sometimes take longer to get off the ground and aren’t necessarily representative of sales projections as a whole, it can be good to look at their performance removed from the bigger picture — at least in the beginning.
17. Individual Growth Rates by Product
Individual Growth Rates by Product (Excel):
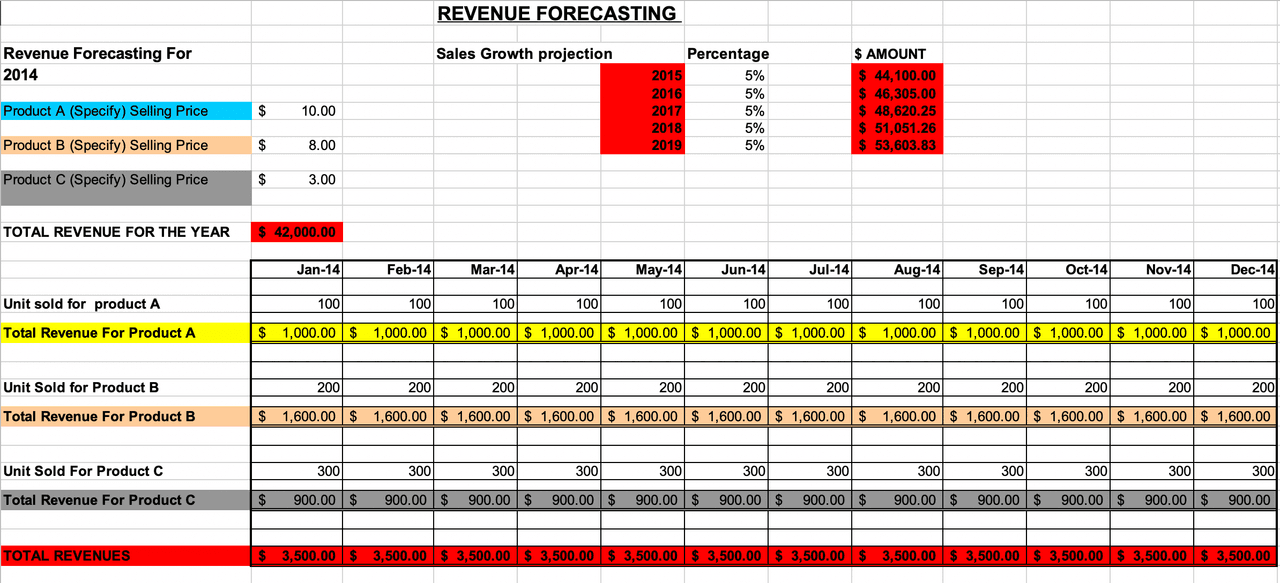
This template does the dirty work for you by breaking down growth rates by individual products, so you can pinpoint the ones that are making the biggest impact.
Here are a few examples of sales forecasting templates for B2B companies.
18. Lead-Driven B2B
Lead-Driven B2B (Excel):
This template allows salespeople to enter data following a lead-driven approach. It assigns a projected value based on what stage the lead is in.
19. Projected Volume
Projected Volume (Excel):
20. Site Traffic Projections
Site Traffic Projections (Google Sheets):
This template download has wonderful step-by-step instructions for inputting your data and analyzing the results. The template uses site traffic as one of its metrics, so it would work best for e-commerce or other heavily web-based businesses.
21. Multivariable Analysis
Multivariable Analysis (Google Sheets):
This template allows for projections based on a number of different variables, including seasonality. The template is great for businesses that have many external variables to consider.
22. Historical Growth Rate
Historical Growth Rate (Excel):
This template uses your historical sales data to predict future growth. Because the only inputs are past sales, it’s important to make sure that this data is very robust — we recommend at least two years of historical sales figures for this template.
Hopefully, one of many of these templates will be a good fit for your sales forecasts. They can be used as a guide to creating your own custom template in Excel or Google Sheets. Make sure to include the constants — things like unit sold and cost of goods sold — but tweaking the templates can go a long way in making them a more powerful tool for your business.
Get sales tips and strategies delivered straight to your inbox.
Yesware will help you generate more sales right from your inbox. Try our Outlook add-on or Gmail Chrome extension for free, forever!
Hit your number every month
Works on Outlook or Gmail (+ many more integrations)
Related Articles
![sales projection in business plan example 10 Best Persuasive Techniques for Sales and Marketing [2022]](https://www.yesware.com/blog/_next/image/?url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.yesware.com%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2021%2F07%2Fyesware-persuasive-techniques.jpg&w=1280&q=75)
10 Best Persuasive Techniques for Sales and Marketing [2022]
Melissa Williams

SPIN Selling: All-In-One Guide for 2022

High-Ticket Sales: How to Sell High-Ticket Products and Services
Sales, deal management, and communication tips for your inbox
We're on a mission to help you build lasting business relationships.
75 Kneeland Street, Floor 15 Boston, MA 02111
FREE Webinar:
New Feature - Industry Data & Insights Register Now

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
How to Do a Sales Forecast for Your Business the Right Way
Posted june 8, 2021 by noah parsons.

New entrepreneurs frequently ask me for advice about forecasting their sales . These entrepreneurs are always optimistic about the future of their new company. However, when it comes to the details, most aren’t sure how to predict future sales and how much money they’re going to make.
It’s an intimidating task, looking into the future. The good thing is, none of us are fortune tellers and none of us know any more about your new business than you do. (If you do happen to be able to see into the future, please just skip the whole startup thing and go play the stock market. It’ll be much easier and make you richer!)
So, my advice is always to just take a deep breath and relax. You’re as well equipped as everyone else to put together a credible, reasonably accurate forecast. Let’s dive right in and figure it out.
What is sales forecasting?
Sales forecasting is the process of estimating future sales with the goal of better informing your decisions. A sales forecast is typically based on any combination of past sales data, industry benchmarks, or economic trends. It’s a method designed to help you better manage your workforce, ash flow, and any other resources that may affect revenue and sales
It’s typically easier for established businesses to create more accurate sales forecasts based on previous sales data. Newer businesses, on the other hand, will have to rely on market research, competitive benchmarks, and other forms of interest to establish a baseline for sales numbers.
Check out our detailed guide on creating a full financial forecast without historical data for more.
Why is sales forecasting important?
Your sales forecast is the foundation of the financial story that you are creating for your business. Once you have your sales forecast complete, you’ll be able to easily create your profit and loss statement , cash flow statement , and balance sheet.
Sales forecasts help you set goals
But beyond just setting the stage for a complete financial forecast, your sales forecast is really all about setting goals for your company . You’re looking to answer questions like:
- What do you hope to achieve in the next month? Year? 5-years?
- How many customers do you hope to have next month and next year?
- How much will each customer hopefully spend with your company?
Your sales forecast will help you answer all of these questions and potentially any others that involve the future of your business.

Sales forecasts inform investors
Having a solid sales forecast also provides a picture of your performance and performance milestones for potential investors. Like you, they want to be sure you have established goals and a firm trajectory for your business laid out. The more detailed, organized, and up-to-date your forecast is, the better you explain the position of your business to third parties and even employees.
How to use your sales forecast for budgeting
Your sales forecast is also your guide to how much you should be spending. Assuming you want to run a profitable business, you’ll use your sales forecast to guide what you should be spending on marketing to acquire new customers and how much you should be spending on operations and administration.
Now, you don’t always need to be profitable, especially if you are trying to expand aggressively. But, you’ll eventually need your expenses to be less than your sales in order to turn a profit.
How detailed should your forecast be?
When you’re forecasting your sales , the first thing you should do is figure out what you should create a forecast for. You don’t want want to be too generic and just forecast sales for your entire company. On the other hand, you don’t want to create a forecast for every individual product or service that you sell.
For example, if you’re starting a restaurant, you don’t want to create forecasts for each item on the menu. Instead, you should focus on broader categories like lunch, dinner, and drinks. If you’re starting a clothing shop, forecast the key categories of clothing that you sell, like outerwear, casual wear, and so on.
You’ll probably want between three to ten categories covering the types of sales that you do. More than ten is going to be a lot of work to forecast and fewer than three probably means that you haven’t divided things up quite enough.
You really can’t get this wrong. After all, it’s just forecasting and you can always come back and adjust your categories later. Just pick a few to get started and move on.
Which forecasting model is best? Top-down or bottom-up?
Before they have much historical sales data, lots of startups make this mistake—and it’s a big one. They forecast “from the top down.” What that means is that they figure out the total size of the market (TAM, or total addressable market) and then decide that they will capture a small percentage of that total market.
For example, in 2015, more than 1.4 billion smartphones were sold worldwide. It’s pretty tempting for a startup to say that they’re going to get 1 percent of that total market. After all, 1 percent is such a tiny little number, it’s got to be believable, right?
The problem is that this kind of guessing is not based on any kind of reality. Sure, it looks like it might be credible on the surface, but you have to dig deeper. What’s driving those sales? How are people finding out about this new smartphone company? Of the people that find out about the new company, how many are going to buy?
So, instead of forecasting “from the top-down,” do a “bottom-up” forecast. Just like the name suggests, bottom-up forecasting is more of an educated guess, starting at the bottom and working up to a forecast.
Start by thinking about how many potential customers you might be able to make contact with; this could be through advertising, sales calls, or other marketing methods. This is your SOM (your “share of the market”), the subset of your 1 percent of the market that you will realistically reach—particularly in the first few years of your business. This is your target market .
Of the people you can reach, how many do you think you’ll be able to bring in the door or get onto your website? And finally, of the people that come in the door, get on the phone, or visit your site, how many will buy?
Here’s an example:
- 10,000 people see my company’s ad online
- 1,000 people click from the ad to my website
- 100 people end up making a purchase
Obviously, these are all nice round numbers, but it should give you an idea of how bottom-up forecasting works.
The last step of the bottom-up forecasting method is to think about the average amount that each of those 100 people in our example ends up spending. On average, do they spend $20? $100? It’s O.K. to guess here, and the best way to refine your guess is to go out and talk to your potential customers and interview them. You’ll be surprised how accurate a number you can get with a few simple interviews.
How to create a sales forecast
Keep in mind that your sales forecast is an estimate of the number of goods and services you believe you can sell over a period of time. This will also include the cost to produce and sell those goods and services, as well as the estimated profit you’ll come away with.
We’ll dive into specific methods, assumptions, and questions you’ll need to ask in order to build a viable sales forecast. But to start, here are the general steps you’ll need to take to create a sales forecast:
- List out the goods and services you sell
- Estimate how much of each you expect to sell
- Define the unit price or dollar value of each good or service sold
- Multiply the number sold by the price
- Determine how much it will cost to produce and sell each good or service
- Multiply this cost by the estimated sales volume
- Subtract the total cost from the total sales
This is a super basic rundown of what is included in your sales forecast to give you an idea of what to expect. For example, you may find the need to aggregate similar items into unified categories, if you sell a large variety of items. And if at all possible, try to keep your forecasted items grouped similarly to how they appear on your accounting statements to make updates easier.
Check out this video for a quick overview of how to forecast sales:
Now let’s dive into some specific elements of your forecast you’ll need to define ahead of time.
Should you forecast in units or dollars?
Let’s start by talking about “unit” sales.
A “unit” is simply a stand-in for whatever it is that you are selling. A single lunch at a restaurant would be a unit. An hour of consulting work is also a unit. The word “unit” is just a generic way to talk about whatever it is that you are selling.
Now that’s out of the way, let’s talk about why you should forecast by units.
Units help you think about the number of products, hours, meals, and so on, that you are selling. It’s easier to think about sales this way rather than to think just in dollars (or yen, or pounds, or rand, etc.).
With a dollar-based forecast, you are only thinking about the total amount of money that you’ll make in a given month, rather than the details of the number of units that you are selling and the average price you are selling each unit for.
To forecast by units, you predict how many units you’re going to sell each month—using the bottom-up method of course. Then, you figure out what the average price is going to be for each unit. Multiply those two numbers together and you have the total sales you plan on making each month.
For example, if you plan on selling 1,000 units at $20 each, you’ll make $20,000.

When you forecast by units, you have a couple of different variables to play with: What if I’m able to sell more units? What if I raise or lower my prices?
Also, there’s another benefit: At the end of a month of sales, I can look back at my forecast and see how I did compared to the forecast in greater detail. Did I meet my goals because I sold more units? Or did I sell for a higher price than I thought I would? This level of detail helps you guide your business and grow it moving forward.
Sales forecast assumptions
One thing to remember is that your sales forecast is built on assumptions. You’re not predicting the future, but aggregating information to help define your future outlook. These assumptions are always changing, meaning that you’ll need to have a pulse on the following:
Market conditions
Having a general understanding of the macro effects on your business can help you better predict overall growth. A growing or shrinking market can either provide a low or high ceiling for potential sales increases. So, you need to understand how your business can react to any changes.
What does the broader market look like? Is the economy slowing or growing? Is the industry you operate in seeing an influx of competition? Maybe there’s a labor or material shortage? Are there new customers you now have access to?
Products and services
You may find yourself making regular changes to your products and services. This can be sales factors that impact the customer, or production factors that impact the overall cost.
Are you making any changes or updates to current offerings? Are you launching a new product or service that compliments or disrupts your existing sales? Are you adjusting prices or sales channels? Are you able to decrease the cost of production? Or are expenses rising due to material, labor, or other production costs?
Seasonality
Depending on what you’re selling, you may find dips or increases in sales at specific times during the year. This seasonality may have to do with the weather, holidays, product/feature releases, or a number of other predictable factors.
If you have been operating for a while, you can likely look at your accounting data to identify any trends. If you’re a new business look to your competitors to see how they act during specific times of the year to help you identify these trends earlier on.
Marketing efforts
How much you spend on marketing, and even your messaging may have an impact on your overall sales. Make sure that you connect any performance changes to marketing efforts that may affect your performance.
Are you launching a new marketing campaign? Are you spending more or less on advertising? Are you adjusting your targeting for digital ads? Are you branching out or removing specific marketing channels from your overall strategy?
Regulatory changes
You may find that specific laws or regulations directly impact your industry. It’s difficult to anticipate what legislation will provide a negative or positive impact, and just how often this type of regulatory change may occur. The best thing you can do is keep your ear to the ground, and be ready to adjust expenses or sales when any changes appear to make traction.
How far forward should you forecast?
I recommend that you forecast monthly for 12 months into the future and then just develop an annual sales forecast for another three to five years.
The further your forecast into the future, the less you’re going to know and the less benefit it’s going to have for you. After all, the world is going to change, your business is going to change, and you’ll be updating your forecast to reflect those changes.
12 months from now is far enough into the future to guess. You’ll have to update your forecasts regularly with actual performance to help keep them accurate.
And don’t forget, all forecasts are wrong—and that’s O.K. Your forecast is just your best guess at what’s going to happen. As you learn more about your business and your customers, you can change and adjust your forecast. It’s not set in stone.
Why using visuals will make forecasting easier
My final word of advice is to make sure that you graph your monthly sales with a chart.

A chart will make it easy to see how your sales might dip during a slow period of the year and then grow again during your peak season. A chart will also highlight potentially unreasonable guesses at your sales growth. If for example, you show a big jump in sales from one month to the next, you should be able to back this up with a strategy that’s going to deliver those sales.
Adjust your forecasts based on actual results
Your sales forecast isn’t done when you start sharing it with lenders and investors. Instead, smart businesses use their sales forecast to measure their progress and ensure that they’re on the right track. Their sales forecast becomes a live forecast . An up-to-date management tool that helps them run their business better.
The easiest way to convert your sales forecast into a management tool is to have a monthly financial review meeting where you look at your business’s finances. You shouldn’t just look at your accounting system, though. You should compare the numbers from your accounting software to your forecast and see if you’re on track.
Are you exceeding your goals? Or maybe you’re falling a little bit short. Either way, knowing if you’re meeting your goals or not will help you determine if you need to make some shifts in strategy. This way, your business numbers drive your strategy.
Forecasting is easier with LivePlan
Sales forecasting tools like LivePlan can help with this. LivePlan uses a smart dashboard to automatically compare your forecast to your numbers from your accounting system—no cutting and pasting or complicated spreadsheets required. And with LivePlan’s LiveForecast feature , you can update the forecasts within your Profit and Loss Statement, with the push of a button.
This allows you to spend less time updating and more time analyzing performance to make better decisions. In fact, the LiveForecast feature allows you to expand the details of your performance and identify the variance in performance within your statements. You’ll know your current cash position and the impact on projected year-end totals at a glance. It provides you with enough information to then explore the dashboard with questions and potential steps in mind.
Sales forecasting isn’t as difficult as you think
Just remember that sales forecasting doesn’t have to be hard. Anyone can do it and you, as an entrepreneur, are the most qualified to do it for your business. You know your customers, and you know your market, so you can forecast your sales.
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Noah Parsons
Posted in financials, join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

9 Free Sales Forecast Templates to Super-Charge Sales Growth in 2024

Sales forecasting templates might not sound all that exciting. Fair enough. After all, who wants to create more reports—on top of all your other responsibilities?
If you're feeling a little skeptical, take a walk with me and imagine this scenario involving two different sales managers :
Which of these sales managers is more likely to get the budget they want?
No brainer. It's Sales Manager 2 every day of the week.
What's the difference between their pitches? A solid sales forecast to back up the substantial investment they're asking the VP to make.
Sales forecasts can be exciting—they give you the superpower to see what's coming down the pipeline. More importantly, they're easy to create using the right sales forecasting templates.
In this guide, we'll give you a step-by-step method to create a sales forecast and access to several free sales forecast templates (in both Microsoft Excel & Google Sheets format).
But first, let’s quickly touch on why sales forecasts are key to growing your sales team—and your business.
Why are Sales Forecasts Crucial for Sales Teams?
Sales forecasting provides a window into your business's future. Depending on the template, it can help you:
- Predict sales figures for the next quarter: Much like projecting total contract value growth, sales forecasting provides a roadmap for anticipated revenue, enabling you to plan and allocate resources accordingly.
- Make more accurate cash flow projections
- Predict expenses
- See where to invest marketing dollars
- Better allocate hiring budgets
- Spot emerging trends early on
- Diagnosis of potential issues in your sales flow early
Lastly, it is a powerful motivation tool for your sales team—especially if you have a longer sales cycle. It allows you to paint a clear picture showing how the work your team is doing today will pay off.
9 Best Sales Forecast Templates (Free Google Sheets + Excel Templates)
Not every sales team needs a super complex sales forecasting model. For instance, small businesses only want (and need) to track a few important metrics. On the other hand, eCommerce companies must track multiple products, which is challenging without a template.
So, we've sorted through all the free sales forecast templates we could find (in Excel + Google Sheets format) and even created one of our own. Choose the best template for your company, sales team, and industry.
1. Best General Forecast Template (without a CRM)
This sales forecasting template from Close provides a simple way to track and forecast two years of sales. The first tab allows for adjusting funnel metrics depending on your sales cycle, average deal size, lead growth, and number of leads.
The second tab forecasts sales by month based on meetings booked, new opportunities created, and leads closed/won. A chart at the bottom displays expected growth.
The only thing better than this is having sales forecasting built right into your CRM ( like with Close ), which enables you to have powerful integrations that enrich your forecasting accuracy and pipeline health over time.
GET THE FREE TEMPLATE HERE
2. Best Forecast Template for a Lead-Driven Sales Process
This template is ideal for companies that track their lead generation efforts and monitor their monthly sales forecast. You’ll see it breaks the year into quarters and tracks leads in all stages of the sales funnel .
The best part? This is a Google Sheets template (which can be accessed via Google apps and can also be downloaded for use in Microsoft Excel).
This template tracks the deal value and uses a weighted forecast model. It can also predict the probability of closing, which is a helpful metric for B2B companies. You can download it right here .
3. Best Free Forecasting Template for Multiple Product Businesses
Does your company sell multiple products or services? This sales projection template could be a great choice for a business with more complex offerings. It tracks the number of units sold for each product line over 12 months on a single spreadsheet to streamline your forecasting accuracy.
It also carries over sales history from three previous years, making it easy to compare sales by unit, month, or year. You can download it right here in Google Sheets or Microsoft Excel format. Just make a copy and start editing the sheet.
4. Best Forecasting Template for Retail Businesses
This template is ideal for retail stores that want to forecast sales, track gross sales, and mark up percentage and profit margin for each item to generate more new business. The yellow cells allow you to input your own data, and the spreadsheet uses smart Excel automation formulas to calculate forecasts.
While it doesn't display the previous year's data in this view, you could easily create a pivot table in Excel or Google Sheets to pull data from several years. That way, you can compare average sales, total sales, and other sales KPIs that matter to your leadership. You can pick this one up right here .
5. Best for Long-Term Future Sales Analysis (36 Months of Historical Data)
This is one of the most colorful templates on the list, but that's not why we included it. This template is ideal for companies that want to monitor long-term data closely.
In addition to 12 months of full historical sales data, you'll also see detailed insights and data for the past five years, including overall revenue for each type of item. This is a good option if you want to focus your sales analysis on the long and short term. You can grab this one right here .
6. Best Sales Forecasting Model for Scenario Planning (New Product Launches)
Forecasting sales for a new product launch can be a challenge—which is why many companies do a soft launch without high expectations.
After a soft launch, use this forecasting template to track initial sales data and project your next five years of sales. Head over here to download this one .
7. Best Free Template for Multiple Products at Different Growth Rates
Looking to track product sales that grow at different rates? This spreadsheet tracks growth and forecasts revenue for 12 months—even if the products or services grow at different rates. This is a great fit for businesses with legacy products that regularly launch new products.
This forecasting chart also includes five years of historical data so you can see overall sales growth at a glance. Pick this template up right here .
8. Best for Short-Term Forecasts
Want to plan your inventory or marketing campaigns for just the next few weeks? This 3-month forecast template can help.
Customize the start date, then enter your number of units and price per unit to get projections. It’s simple and effective. Download this template right here .
9. Best for Daily Forecasts
Now, let’s shorten the projections even more—to a daily window. This one is primarily useful for businesses in the retail, restaurant, and hospitality industries.
With this template, predict your sales on a daily or weekly time frame. This granular vision can help you optimize day-to-day sales. Plus, you can rely on historical sales data and add weekly notes.
Grab this forecast template here .
How to Choose the Right Sales Forecast Template (& Forecasting Methods for Your Business)
The right forecasting template provides access to the sales KPIs that matter most to your sales team. But not all businesses are the same.
Retail businesses may need to track hundreds of products and dozens of different suppliers, while a SaaS company might only offer three pricing plans—but have a really long sales cycle.
You need to find the right template for your business needs. Otherwise, you'll be left floundering in a sea of useless data.
Here's how to select the right sales forecast template for your organization.
Get Clear on Your Sales Goals & Set Realistic Sales Revenue Targets
Different sales goals and revenue targets rely on different data. For example, if you want to predict sales over the next two years, you'll want a forecast template that covers a longer time period.
Goals can also impact which template will work best for your team.
For example, suppose an eCommerce company wants to increase monthly sales by 10 percent and boost customer lifetime value . In this case, they'll need a different template than a small business looking to increase sales from a specific customer segment.
Next, set realistic revenue targets using overall market growth as a benchmark. If your industry expands by 25 percent, a 10 percent growth rate might be too low, while 50 percent is likely too high.
Look for a template that fits your business goals and revenue targets.
Consider Your Business Type & Plan Ahead for Sales Fluctuations
Your business type is one of the most important factors to consider when selecting a template. The size, industry, age, and growth rate can all impact which template will work for you.
Also, consider how often your sales fluctuate. For example, an eCommerce store may have 10 to 15 fluctuations a year, so they need a template that can handle their data. On the other hand, a small fly fishing business may have just two fluctuations—on and off-season.
Look for a template that suits your business model and accommodates your sales fluctuations.
Decide Which Method of Sales Forecasting to Use for Your Sales Team
When it comes to sales forecasting methods, there is no one-size-fits-all solution.
You'll need to adjust your forecasting based on your historical data, the metrics you need to track, and your confidence in the data. Your goals and KPIs also impact the forecasting methods you use.
Here are seven sales forecasting methods, including who should use them:
- Lead-driven forecasting : Looks at previous lead conversion rates and projects future sales based on current lead volume. Best for organizations with clear historical data and a steady stream of inbound leads, such as SaaS or technology companies.
- Length of sales cycle forecasting : Tracks how long a typical lead takes to close based on lead type. Best for organizations with insights into the entire sales pipeline and well-aligned sales and marketing teams, especially B2B.
- Opportunity stage forecasting: Calculates how likely a lead is to close based on specific actions and lead type. Ideal for businesses with good historical data on closing rates.
- Test-market analysis forecasting: Leverages data from a soft release to get a sense of projected revenue. Best for startups or businesses launching a new product line or service.
- Historical forecasting : Forecasting data based on historical data and market trends. Works well for any business with at least a year of historical data.
- Multivariable analysis: A complex analysis that considers multiple factors and closing ratios. Best for companies with varying deal sizes and close rates or selling multiple products or services.
Make sure whatever template you choose fits your analysis method.
Look at Historical Data & Past Sales Metrics
We've already discussed how historical data can impact your sales forecasting, but it's also an important factor in choosing the right template.
Before choosing a template, look at your past metrics and historical data. How much data do you have? Consider a template with a longer forecasting model if you have several years' worth of data.
What data do you want to include based on your business type and forecasting methods? Make sure the template you choose includes the fields important to your business.
Research External Market Conditions to Create an Accurate Sales Forecast
Finally, spend a few hours researching current market conditions and consider how they may impact your sales forecast. For example, if your industry is growing fast, you might select a forecasting template that updates in near real-time.
On the other hand, if a large competitor is acquiring another company, growth might be more challenging, and you might need to lower your growth expectations.
Look for a template that works well with current market conditions.
How Do You Calculate Sales Forecasts Quickly?
Here’s a simple formula that SaaS businesses can use for a specific forecast period:
Number of expected new customers x Average deal size
The accuracy of such a forecast depends on various factors, including your churn rate, upsells, changes to your existing subscriptions, market conditions, etc. The more informed your assumptions, the better your accuracy.

START YOUR FREE TRIAL→
How to Create a Custom Sales Forecast Template: Five Easy Steps
Sometimes, you need to do it yourself. Sales forecasting can be simple—especially if you create a forecasting template based on your own sales process and KPIs. Assuming you’re already tracking your sales, here are the steps to create your own template.
Step 1: Choose Sales Performance Metrics
What do you want to track? Whether it’s the sales quotas of individual sales reps, your gross profit, or simply one-year sales projections, choose KPIs based on your goals.
You can check out this exhaustive list of KPIs , but most SaaS businesses can start by calculating their run rates. Keep in mind that it requires a few months of revenue data to project your annualized revenue.
Here's the sales run rate formula :
Projected sales = Run rate (Current sales/number of sales periods elapsed) X the remaining number of sales periods
This is one of the easiest ways to predict future growth, and it’s a great starting point. We’ll refine it in the fourth step, but now, let’s start creating a template.
Step 2: Create a Layout for Your Template and Add Formulas
Now, add relevant formulas for your chosen metrics so that your sheet can make automatic forecasts based on your data input.
The specific columns you include in your layout depend on the KPIs you want to track and the information you want to include.
If we were calculating the annual run rate, you could use one column for the month, another for the sales in that month, and another for calculating the total sales up to the current month.
Next, you want to create formulas for the average monthly rate and the annual run rate formula (ARR), which will be your average monthly sales X 12. These two can be additional columns.
Step 3: Calculate Your Sales Forecast
Now, it’s time to test your template. Input data and let the spreadsheet automatically calculate your sales forecast. In our example, after inputting data for January through March, here’s what the forecasted annual run rate looked like:
Step 4: Adjust for External Factors and Strategic Business Plans
Our simple run rate formula doesn't consider seasonality, competition, market changes, or business growth.
If seasonality or trends impact your sales, calculate the percent change from your average month during periods of spike or dip. For example, if your sales typically spike by 30 percent in November, you can adjust your sales run rate to account for these trends.
Internal changes can also impact sales forecasting. Are you launching new products ? How have product launches performed in the past? Are you marketing to new customer segments? How many new customers do you expect these new markets to add to your customer file?
Refining your formula will improve your forecast's accuracy, leading to informed sales plans and decisions.
If you want to create a comprehensive SaaS revenue forecast model from scratch in Excel, check out this tutorial .
Step 5: Integrate the Template Into Your Process (& Keep Improving It)
Most sales reps spend only one-third of their day selling to prospects. So, you want to integrate the sales forecasting template into your workflow naturally so it doesn’t diminish productivity. Work to blend it with your team's existing spreadsheets or software.
Set up a regular cadence for importing data into the template—either manually or automatically from another software. Then, generate forecasts based on inputted data.
To keep your forecasts relevant, regularly review the accuracy of the results. Adjust your template as needed, and remember that a change in business strategy or market conditions should also invite revisions.
Want to sophisticate your forecasts and consider advanced trends? Then, you must use evolved sales forecasting methods. Get more detailed insights into sales forecasting here .
Using Forecasting Templates to Predict + Optimize Future Revenue
When it comes to sales forecasting, the right template can make all the difference. If you're still doing the process manually, you might miss out on actionable insights that could help your team meet and exceed your sales goals. Plus, manual forecasting takes a lot of valuable time—and is prone to error.
So, choose one of the above templates to create a standardized forecasting approach for your company, but don’t be afraid to make it your own. Add columns, include metrics that matter, and even plug in your brand color and name.
Or, you can just design a template from scratch.
Remember that your template isn’t static. Keep refining your forecast assumptions, and iterate to improve accuracy. Over time, you'll end up with a custom sales forecasting spreadsheet that makes you look like a superstar—and boosts your revenue potential.
Want even more actionable insights? See how Close gives you access to the reporting metrics that matter .
But even if you’re working without a CRM or using another product to manage your sales process, grab our free sales forecast template to achieve your goals that much faster.

More articles from The Close Blog

Discover our latest free sales tools powered by AI
Learn from the sales pros with our free sales guides.
Forecast any use case, any revenue model. Only in BoostUp

- Call the right number early in the quarter.
- Find growth opportunities quickly.
- Increase revenue per rep.
- Integrations
- Product Tour
- Thought leadership, best practices, and deep insights from the RevOps experts
- Elevating the RevOps community by exchanging ideas and experience
- Shining a light on leaders like you who are disrupting the old game
- Cutting edge data and guides to help you level up your work
Topics covered in this article
The Revenue Blog / How to Calculate Sales Projections - Examples & Tools
How to Calculate Sales Projections - Examples & Tools

March 6, 2024
To run a business, you need not only transparency about the current sales deals and the likelihood of their closure but also a strong vision of the future pipeline.
This is where sales projection comes in, which is used to estimate the future performance of the company based on past indicators. In this article, we explore how to make sales projections, what the key tools are in the process, and how your business can benefit from understanding this future sales potential.
What are Sales Projections?
A sales projection is a forward-looking estimate that anticipates the sales revenue of a business over a specific timeframe. This forecast is crafted through a detailed analysis of past sales data, identifying trends and patterns to envisage future revenue outcomes.
In constructing a sales projection, several critical factors are taken into account, including the broader economic environment, the company's current market positioning, and the allocated budget for acquiring new customers.
Additionally, when launching new products or features, sales teams often prepare for multiple outcomes by creating best-case, worst-case, and most likely-case scenarios to capture a comprehensive range of future possibilities.
The role of sales projections extends beyond mere forecasting; they are integral to strategic business planning. By setting realistic sales targets, companies can monitor progress, adjust strategies timely, and make informed decisions on resource distribution.
These projections are also vital for accounting departments to set budgets, assess financial prospects, manage risks, and undertake holistic business planning. Without accurate sales projections, companies can fluctuate unpredictably between under- and over-achievement, creating a climate of uncertainty and making it difficult to achieve set targets effectively.
How to Do Sales Projections?
Calculating an accurate sales forecast is a multi-layered process that involves understanding your market, analyzing historical sales data, taking external factors into account, and applying certain calculation methods. Here you can find out how to approach the individual aspects:
Understanding Your Market and Customer Base
- Quantify market share potential: Estimate the percentage of the market you can capture based on your understanding of customer preferences and competitor analysis. For example, if market research indicates a growing trend in your sector and you have a strong competitive advantage, you might project an increase in market share, which should be reflected in your sales forecasts.
- Adapt forecasts to customer behavior: Use purchasing behavior data to forecast sales for different industries and customer segments. If the analysis shows that a particular industry or segment is growing, you should adjust your sales forecasts upwards for products that are popular with this group.
Historical Sales Data Analysis
Analyzing past sales data is the basis for predicting future sales. This involves identifying patterns, trends, and seasonal fluctuations in your sales history. By examining how your sales have changed over time, you can make reliable predictions for future sales. This analysis should take into account product life cycles, customer loyalty, and the influence of marketing measures on past sales.
Considering Market Trends and Economic Factors
External factors such as market trends, economic conditions, regulatory changes, and technological advances can have a significant impact on your sales projections. Keeping up to date with these factors and assessing their potential impact on your market and customer base will help you create more accurate forecasts. Both the macroeconomic environment and industry-specific trends need to be taken into account.
How to Calculate Sales Projections Using Formulas
There are various methods for calculating future sales trends. Sales projection formulas range from simple linear models based on historical growth rates to more complex models that take several variables into account. Here's a breakdown of the most utilized formulas:
- Growth rate-based forecast: This approach extrapolates future sales based on past growth rates, making it an easy choice for companies with a constant growth record. For example, a company specializing in cloud storage solutions reported revenue of $8 million in 2023, compared to $6.4 million in 2022. This implies a growth rate of 25% (($8 million - $6.4 million) / $6.4 million × 100). Assuming the growth rate remains constant, the projected revenue in 2024 would be $10 million ($8 million × 1.25), which is in line with their upward trend in the fast-growing cloud services market.
- Acquisition-based forecasts: In this method, future revenues are calculated by analyzing the costs and results of sales-generating activities, such as marketing and sales efforts. Consider a company that offers subscription-based software for project management. It generates $2 million per month from existing clients (organic growth) and plans a $800,000 monthly spend on digital marketing campaigns, assuming an average subscription value of $4,000 at a cost per acquisition (CPA) of $200. The forecasted monthly revenue incorporating these figures would be $14 million: $2 million from organic growth + ($800,000 / $200) × $4,000. With this formula, the company can estimate the return on investment for its marketing spend, which is crucial for budget planning and growth strategy.
- Simple annual sales forecast: This formula is ideal for businesses with stable sales and uses average monthly sales to predict annual sales. For example, a company that provides cybersecurity solutions to other companies generated $24 million in revenue in the first six months. With an average monthly sales figure of $4 million, and six months remaining in the fiscal year, the total projected revenue would be $48 million: $24 million for the first six months + ($4 million × 6 months). This method works well for the cybersecurity company, as the demand for its services is constant at a time when digital threats are omnipresent.
Choosing the right method depends on the availability and quality of your data, the complexity of your market, and your specific business requirements. When you combine these approaches with a clear understanding of your market, a thorough analysis of historical sales data, and consideration of external factors, you can create accurate and reliable sales projections.
Navigating Through Sales Projection Tools
Navigating through the myriad of tools available for sales projections can seem daunting, but if you know the general categories of these tools, you can make the process much easier. These tools range from sophisticated platforms that are deeply integrated with your sales data to simpler, more intuitive applications that allow you to quickly get started with forecasting.
CRM and Sales Analytics Platforms
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and sales analytics platforms are essential for tracking and analyzing sales activity. Instead of the old sales projections templates, these platforms provide a central repository for all sales-related data, including customer interactions, sales transactions, and lead history. By leveraging the data stored in these systems, companies can gain insights into sales trends, customer behavior, and pipeline health to make informed projections about future sales performance.
Financial Modeling Software
Financial modeling software offers a more numbers-driven approach to sales projections, allowing companies to create detailed financial models and scenarios. These tools allow users to input various financial and operational data to simulate different future states based on assumptions about growth rates, market conditions, and business strategies. This approach is particularly useful for companies that want to align their sales projections with overall financial planning and analysis.
AI and Machine Learning Tools
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning tools represent the cutting edge in sales projection technology. These tools analyze large amounts of data to identify patterns and predict future results with high sales forecasting accuracy . By incorporating factors such as market trends, competitor activity, and even social media sentiment, AI-powered tools can create dynamic and highly nuanced sales forecasts. This category of tools is particularly valuable for companies operating in fast-changing markets where traditional forecasting methods struggle to keep pace. BoostUp combines sales analytics with AI capabilities, offering your business a never-before-seen depth into past, present, and future sales performance. Interested in learning more? See BoostUp in action now!
FAQ - Sales Forecasting
Sales projections are forward-looking estimates that predict the sales revenue of a business over a specific timeframe. They are based on past sales data, current market conditions, and other factors such as economic trends and customer behavior.
How to Calculate Sales Projections?
Calculating sales projections starts by collecting and analyzing historical sales data. Segment the data by product, region, or sales channel and consider external factors such as regulatory changes, technological advances, and economic conditions to understand market trends. Depending on your business needs and the available data, you can use different forecasting methods like growth rate-based forecasts, acquisition-based forecasts, or simple annual sales forecasts for calculating sales projections.
Why are Sales Projections Important?
Sales projections have an important role in strategic business planning. They help companies set realistic sales targets, monitor progress, adjust strategies, allocate resources efficiently, and make informed financial decisions.
What is the Difference Between Sales Forecast vs. Projection?
The terms "sales projection" and "sales forecast" are used interchangeably. Both aim to predict future sales based on past data, market conditions, and other influencing factors.
What Kind of Sales Projection Tools are Available?
Sales projection tools include CRM and sales analytics platforms, financial modeling software, and AI/machine learning tools. Each tool type offers unique capabilities to help businesses create accurate sales forecasts based on their specific needs.
BoostUp’s Revenue Command Center offers integrated forecasting, deal inspection and rep coaching with advanced AI capabilities, providing your business with unparalleled insight into historical, current & future sales performance.
How Do CRM and Sales Analytics Platforms Aid in Sales Projection?
CRM and sales analytics platforms centralize sales-related data, enabling businesses to track and analyze sales activities, customer interactions, and sales trends. This data-driven approach provides insights necessary for accurate sales projections and strategic planning.
How Can AI and Machine Learning Enhance Sales Projections?
AI and machine learning tools analyze large datasets to identify patterns and predict future results for creating a highly accurate sales projection. These tools incorporate various factors like market trends, social media metrics, and competitor activity, making them especially valuable for dynamic and fast-changing markets.
What are the Key Benefits of Accurate Sales Projections?
Accurate sales projections help businesses set realistic targets, allocate resources efficiently, monitor progress, and make informed decisions. They are essential for strategic planning, budgeting, and risk management.
About the Author
Batu Apaydin is the Director of Marketing at BoostUp and leads all product and content marketing efforts.
Get a product tour
See how BoostUp delivers.
Join +10,000 subscribers and get our weekly Revenue newsletter
Other posts you might be interested in
How fast-growing startups overcome forecasting challenges..
Stepping into a Series B or C round we see companies start to hit a stride to go down the path of rapid growth which really comes from a couple of things— you’ve found a way to predictable revenue, and you have a fantastic sales leader in order to project and present the profile of […]

Sharad Verma
January 15, 2020
What is Predictive Sales Forecasting and How to Do It?
Explore how predictive sales forecasting with AI can transform your business, enhancing sales strategies with data-driven insights and market trends analysis.

Batu Apaydin
December 11, 2023
The Hockey Stick Sales Forecast Problem.
Accurately project when deals will close by leveraging engagement and risk scoring.
July 24, 2019
Filter by Keywords
10 Free Sales Forecast Templates in Excel and ClickUp
Praburam Srinivasan
Growth Marketing Manager
February 15, 2024
Start using ClickUp today
- Manage all your work in one place
- Collaborate with your team
- Use ClickUp for FREE—forever
An effective sales forecast ensures the organization (or the sales team) hits the targets by setting realistic goals. A sales forecast template makes it easy for a busy manager to forecast sales and revenue.
Let’s take two scenarios:
Sales Manager A asks the VP of Sales to hire more people to crush their 2025 goals. The manager has a rough idea of how many sales reps they need.
On the other hand, Sales Manager B has a solid plan of how many reps they need and what the sales projections and future revenue look like based on market trends, customer data, and the revised headcount.
If you were the VP of Sales, whose sales forecasting would you opt for?
Manager B, naturally. Why? Because Manager B provides a solid sales forecast to back what they’re asking for.
This article covers the sales forecast templates in Excel and ClickUp to improve your business forecasting accuracy and decision-making.
What is a Sales Forecast Template?
What makes a good sales forecast template, 1. clickup sales forecast template, 2. clickup sales report template, 3. clickup sales crm template, 4. clickup sales page template, 5. clickup sales pipeline template, 6. clickup sales kpi template, 7. excel sales forecast template by salesflare , 8. excel sales forecast template by excel skills, 9. sheets retail businesses forecasting template by close, 10. excel sales forecast template by gong.
A sales forecast template is a customizable form that gives you expected sales and revenue over a specific period.
Your sales forecast template can predict the increase in the average order value for an existing product or the number of units sold, the growth rate for a specific time (weekly/monthly/quarterly), and the number of new customers you’re likely to add.
Sale forecast templates are helpful during the planning stage as they help businesses allocate resources, estimate costs, and assess if the business actions align with the short and long-term organizational goals.
Business owners rely on the sales forecasting template to develop budgets for hiring and plan the production cycles. Sales teams use them for territory and quota planning and to drive their sales strategy with channel and partner sales.
For the sales project template to be functional, it should be:
- Clear and simple: The template should be easy to use along with essential sections such as financial projections, revenue targets, and sales quotas
- Customizable: A good sales projection template is customizable to fit your organization’s decision-making process and adapt to your sales cycle
- Collaborative: The free sales forecasting template should allow input from stakeholders, the sales team , and leadership to promote cross-departmental collaboration
- Visually engaging: You should be able to add charts, tables, whiteboards, and diagrams to understand future sales revenue targets at a glance
- Workflow automation: For an accurate sales forecast, you need automation to convert raw numbers into insights and assign follow-up tasks rather than doing it manually
- Integrations: Choose a sales forecast template that integrates with Google Sheets, strategic planning templates , customer relationship management (CRM) software, and tools your sales team uses
- Artificial intelligence: Does the sales forecasting template have built-in AI tools to complete the template or speed up the process?
10 Sales Forecast Templates to Use in 2024

ClickUp’s Sales Forecast Template helps you visualize the pipeline and current sales process, set future goals, and collaborate with your team in one place.
Here’s how to use this template effectively:
- Gather historical data of order volumes, revenue by accounts, profit margin, or deal value. Create a spreadsheet of your company data and add relevant data using Table View in ClickUp to project growth
- Analyze the data and look for trends and patterns. There are 17 custom attributes such as product name, month, shipping cost for average sale, lead conversion rates for multiple products, and forecast amount to help you visualize the trends easily
- Set realistic goals for sales growth considering consumer feedback, historical sales data, and upcoming market opportunities. Create tasks to track your progress toward the goals
- Project future revenue based on the goals you’ve set. Assess different scenarios, such as high-growth and low-growth situations, and use Gantt charts in Clickup to visualize your projections
- Monitor and course-correct the forecasts as you progress toward your goals
One of the most widely used free sales forecasting templates, it ensures you include all viable deals when making future growth projections.
Even seasonal businesses use this template as their go-to tool to make accurate sales forecasts.

Presenting an efficient sales report helps you stay organized and builds trust with the leadership team. Whatever sales forecasting methods you use, this sales report template gives you an overview of your sales efforts by breaking down your annual, quarterly, and monthly sales.
Compare historical performance for multiple years by exporting data from sales plan templates .
Clickup Sales Report Template is your go-to guide to stay organized and monitor sales performance. Understand what has worked in the past and gain insights into how you’re doing and where you’re headed.
Slice and dice the information using key data points such as geography, key account managers, sales achievements, and sales goals. Set up custom views to generate monthly, quarterly, and annual growth rates and have this information at your fingertips.
Use this template to highlight dependency warnings, track capabilities, and improve sales performance tracking.
ClickUp’s beginner-friendly forecast template lets you track your actual sales against projections and break them up by service type or how many units are sold if you have multiple products. Track the impact of seasonality in retail stores or compare how different regions are performing against each other and export other relevant information from your sales report template .
Use this data in your after-action report data templates to evaluate the performance in tangible terms, such as technical correction or lessons learned.

Managing and tracking leads is exhausting, and sales reps detest it. Any sales rep would rather spend time building relationships and closing deals than making manual entries.
ClickUp’s Sales CRM Template serves as a backbone to your team. Whether you are a small business or a large enterprise, having a robust CRM is essential to stay ahead of the competition and focus on the factors that matter most.
With a robust no-code database and real-time analytics, you can trust ClickUp’s Sales CRM Template to:
- Help your sales team stay organized
- Gain visibility into customer interactions and buying cycles
- Identify prospects, customers, in-active users, and uncover insights about closed deals
- Gain clarity into customer communications
- Store and access customer data from a central location
- Increase productivity by eliminating manual tasks and automating processes
Use toggles and dropdowns to move lead status such as Onboarding, Active, and Payment Pending to monitor the progress on every sale. Set key customer demographics and interests to personalize your campaigns and automate follow-up emails.
Build a transparent sales forecasting process wherein everyone can see the shared sales data, forecast revenue, and other critical data points.
Use quarterly business review (QBR) templates to align organizational goals, hold everyone accountable, and drive continuous improvement.

ClickUp’s Sales Page Template lets you create engaging and visually appealing sales pages to take your product to more customers.
This template gives you a starting point to create the best possible page with capabilities such as:
- Generate more leads and improve conversions
- Communicate product offerings with customers
- Organize and track sales key performance indicators (KPIs) such as forecasted sales easily
- Encourage website visitors to take the next action (sign-ups or become paying customers)
- Highlight your product features and benefits with multiple media formats such as text, images, or videos
Although not a forecast template per se, the Sales Page Template lets you create sales pages without dependency on your tech teams.
Tips to best use this template:
- Define your target audience and understand who you’re trying to reach to create a page that directly speaks to their needs. Use ClickUp Docs to note all the characteristics of your potential customers and your sales goals
- Use tasks to list the key features and benefits of your product or multiple products and make this the basis of your sales page
- Write a compelling copy for your sales page while focusing on the benefits and addressing your target audience’s pain points in Docs
- Design an engaging sales page that keeps your visitors engaged using ClickUp Whiteboard
- Once the page is live, A/B test different versions of the page to see the best-performing version and optimize it further. The Board view lets you track sales page versions and their performance
- Lastly, collect user feedback to improve the landing page and your product. The key to achieving projected revenue is keeping an open mind and the ability to make changes based on user input

As a sales leader, the last thing you want to do is follow up with your team members to know the total sales vs. the sales projections vs. sales goals and the growth rate. You should have all these details with you 24/7.
A structured and efficient sales pipeline management process takes you from stressful month-end to more focused and strategy-driven conversations with your sales team.
Unless you have a structured sales pipeline, the leaders have limited visibility on how close or far the sales reps are in meeting their quotas.
Clickup’s Sales Pipeline Template gives you an ultimate toolkit to monitor and optimize every stage of your sales process. Use this forecast template to get a bird’s eye view of the pipeline and sort your actions based on urgency, value, and potential.
Consider adding the daily sales forecast and monthly sales projection template to your workflow to visualize the entire sales funnel in a single view.

KPIs track critical sales metrics to improve sales performance, identify opportunities and prospects, and increase revenue generation. While they’re an excellent resource to measure the success of your sales strategy, with so many metrics, deciding which ones to track becomes overwhelming.
ClickUp Sales KPI Template helps you set measurable goals and track them across the sales funnel. The free sales forecasting template offers visibility into a team’s efforts and assesses if they maximize organizational goals.
This template provides an easy solution for sales leaders and their teams to understand the metrics they drive, provide clarity and transparency on performance, and take corrective actions.
Visualize relevant KPIs using custom fields such as Upsell Attempts, Value of Quotes, and Repeat Sales Revenue and send regular reports to your C-suite.

If a small business owner needs a template for forecasting sales or keeping track of expected revenue, Salesflare’s Excel Sales Forecast Template is a good starting point.
Or, if you’re facing scalability challenges using an Excel sheet as your budget forecast template, use this template to forecast your revenue, track historical sales data, and improve your sales process.
Create your sales funnel, record the probability of closing deals, set targets for your team, and assign them tasks. Use pre-built charts to fine-tune your forecast for quarterly, annually, or for any specific time.
Set sales OKRs for your team, closure probabilities, and a custom # of days after which you would like to follow up. This tells you how your sales reps are doing and how their conversions look and equips you to take relevant action.
Salesflare lets you import your Excel and Google Sheets templates into its CRM, making extra space for you to focus on building relationships.

Excel Skills Sales Forecast Template is effective when you have shorter sales cycles and don’t need pipeline-level lead tracking. This template compiles monthly sales forecasts for three years.
Compared to other sales forecast templates by ClickUp, the caveat is you must manually enter data such as monthly sales volumes, selling prices, and gross profit percentages for each product category. All the other calculations are automatically updated.
This sales projections template has pre-built functions showing you total sales, cost of sales, and monthly gross profit. The template includes five product categories, but you can add additional categories by simply inserting the appropriate number of rows in each sales forecast section.
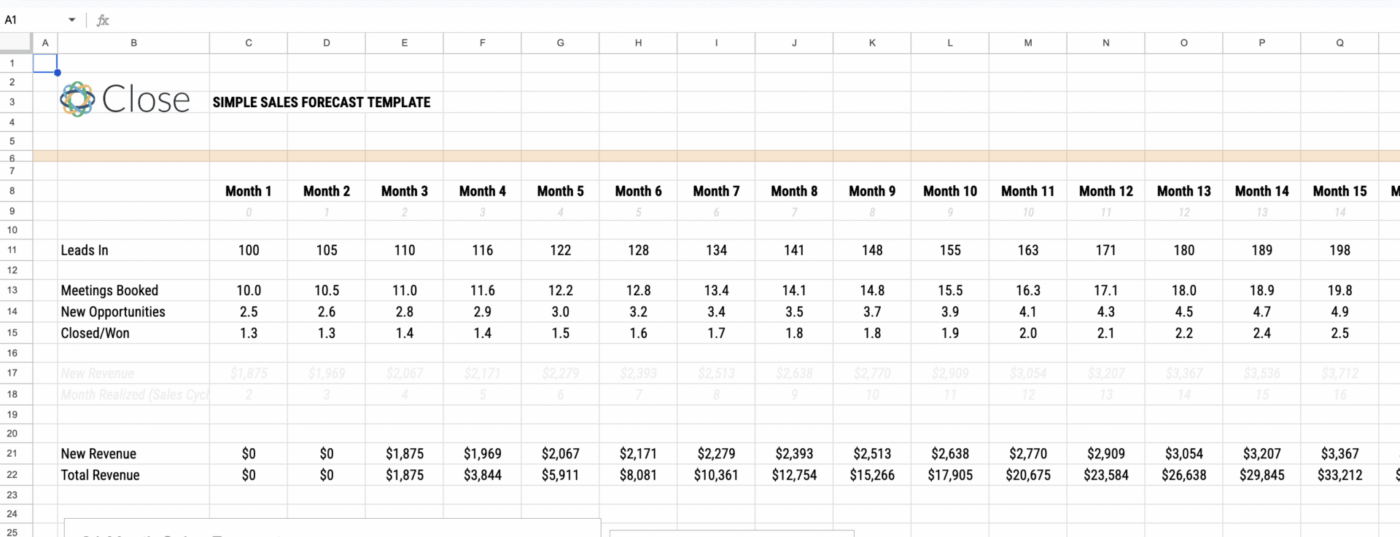
While the other sales forecast templates in this list are industry-agonistic, the Retail Business Forecasting Template by Close is for retail businesses.
Traditionally, retail sales forecasts happen over spreadsheets. This beginner-friendly retail sales forecast template allows retail shops to compile monthly sales forecasts, allocate budgets, spot trends, and catch potential pitfalls early.
The different ways to use this Excel-native template are:
- Track your leads and meetings and get a complete view of your sales pipeline
- Perform monthly and yearly forecasting to plan your sales projections
- Customize the free sales forecasting template with adjustable funnel metrics
- Interpret data using visual graphs

Do you forecast in the dark? Are your committed deals backing out? Need help with low quota issues?
If you answer yes to any or all of these issues, Gong’s Excel Sales Forecast Template is for you. Designed in Excel, this simple and free sales forecast template identifies gaps in your pipeline and ensures your team hits its targets.
Within the pre-built template, you must enter your team-specific numbers, and the premade formulas make your forecasts in minutes.
This sales forecasting template covers you from weekly sales forecast, pipeline coverage, or total pipeline coverage.
Predict and Optimize Your Future Revenue with the Right Sales Forecasting Template
Manual forecasting is time-consuming and erroneous. You’re missing out on all the actionable insights that could help your sales managers meet and exceed their sales goals.
A suitable sales forecast template will make all the difference—you don’t have to create forecasting frameworks from scratch every time.
Modern sales teams and business owners love ClickUp’s forecast templates as they’re customizable, integrate with third-party tools, and combine project management with forecasting.
Sign up on ClickUp to get started for free.
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months
How to write a sales forecast for a business plan
Table of Contents
What is a sales forecast?
Why do you need a sales forecast, how do you write a sales forecast, top-down or bottom-up, writing your sales forecast, calculating a sales forecast, how can countingup help manage your forecasting.
Sales forecasts are an important part of your business plan . If done correctly, they can give accurate projections of your business’ cash flow, and let you better prepare for the year ahead. They can also make it easier to find the right investors . While it’s easier for existing businesses with plenty of data, you can still calculate a sales forecast for a new business .
In this guide, we’ll explore:
- How can you manage your forecasting?
A sales forecast is a prediction of your business’ future revenue. In order to be an accurate prediction, the forecast is based on previous sales, current economic trends, and industry performance. Having a sales forecast is a useful tool, because it gives you a better idea of how to manage your business.
Having a sales forecast is like using the past to have a peek into the future of your company. It might not be 100% accurate, but it can help you plan any future spending, or prevent any cash flow issues from occurring.
You can also use your sales forecast to monitor your business’ progress. For instance, if your business regularly performs better than your forecast, it could be a sign that your business is continuing to grow. On the other hand, if your actual sales are frequently less than expected, this could be a sign that your business is struggling and needs adjustment.
It’s important to remember that any projections you make aren’t guaranteed, there can be advantages and disadvantages of financial forecasting .
Now we’ve run through why having a sales forecast can help you run your business, let’s look at how to write one.
While there are two types of sales forecasting (top-down and bottom-up), one is a lot more accurate for small businesses than the other. A top-down forecast looks at the market as a whole and attributes a portion of the market to your business.
A top-down approach may work for large businesses that already own a significant chunk of the market. When forecasting for a small business, it’s easy to overestimate your market share. For example, a 1% market share may not seem like a lot, but a small restaurant owning 1% of the £89.5 billion UK market is extremely unrealistic.
The alternative to top-down is bottom-up. A bottom-up sales forecast starts with existing company data (like customer or product information) and works up to revenue. Since this starts with the company, it’s easier to
Your sales forecast is ultimately a prediction of your revenue over a set period. It considers the amount you think you’ll sell, and the cost of those sales. We’ve included how to calculate a sales forecast below.
A sales forecast consists of three separate values: revenue, cost of goods sold, and gross profit. For estimating values in the calculations below, it’s best to use any existing business data to be as accurate as possible.
To calculate your predicted revenue:
- Make a list of your available goods and services
- Note the price of each of your goods and services
- Estimate the expected sales of each good or service
- Multiply the price by the estimated sales to get your estimated revenue
- Add them all together to get your total revenue
For example, if your food truck business sold pizzas at £10 and burgers at £5, you would multiply these values by how much you expected to sell. For calculating a weekly sales forecast, you might estimate selling 60 pizzas and 80 burgers. Your predicted revenue for that week would be £600 for pizzas and £400 for burgers — giving £1,000 total.
In order to figure out how much profit you’ll make, you also need to calculate your costs for those predicted sales. To calculate your predicted costs:
- Figure out how much each good or service will cost per unit
- Multiply each cost by the projected sales
Using the same example as above, assume a single pizza cost £3.50 to make and a burger cost £2. Using the estimated sales, the total cost for your pizzas (3.5 x 60) would be £210, and £160 for your burgers (2 x 80). Combining these two figures gives you a total cost of £370.
The last step is to work out your gross profit , and it’s a relatively simple calculation.
- Subtract the total predicted cost from your total predicted revenue
Continuing with the example above, your revenue (£1,000) minus your costs (£370), leaves you with a projected gross profit of £630 for the week. Using this estimate, you can then plan how much working capital your business should have access to. It’s important to remember that these are only estimates, and your actual values can be higher or lower than your forecast.
If you want your forecasts to be as accurate as possible, you need to refer to all of your business’ financial data. Since collecting and collating this data can be challenging, you may want to use financial management software like the Countingup app.
When trying to calculate your sales forecasts, having an up-to-date log of your current sales can be hugely beneficial. By combining a business current account with accounting software, Countingup is the only software that provides real-time cash flow tracking.
The Countingup app also provides business owners with access to automatically generated profit and loss statements. These can prove invaluable when trying to stay aware of all your business’ costs.
Start your three-month free trial today. Find out more here .

- Counting Up on Facebook
- Counting Up on Twitter
- Counting Up on LinkedIn
Related Resources
Personal finance vs business finance: how to keep your accounts separate.
The main difference between a personal account and a business account is that
Business insurance from Superscript
We’re partnered with insurance experts, Superscript to provide you with small business insurance.
How to register a company in the UK
There are over five million companies registered in the UK and 500,000 new
How to set up a TikTok shop (2024)
TikTok can be an excellent platform for growing a business, big or small.
Best Side Hustle Ideas To Make Extra Money In 2024 (UK Edition)
Looking to start a new career? Or maybe you’re looking to embrace your
How to throw a launch party for a new business
So your business is all set up, what next? A launch party can
How to set sales goals
Want to make manageable and achievable sales goals for your business? Find out
10 key tips to starting a business in the UK
10 things you need to know before starting a business in the UK
How to set up your business: Sole trader or limited company
If you’ve just started a business, you’ll likely be faced with the early
How to register as a sole trader
Running a small business and considering whether to register as a sole trader?
How to open a Barclays business account
When starting a new business, one of the first things you need to
6 examples of objectives for a small business plan
Your new company’s business plan is a crucial part of your success, as
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

How To Create Financial Projections for Your Business Plan
Building a financial projection as you write out your business plan can help you forecast how much money your business will bring in.

Planning for the future, whether it’s with growth in mind or just staying the course, is central to being a business owner. Part of this planning effort is making financial projections of sales, expenses, and—if all goes well—profits.
Even if your business is a startup that has yet to open its doors, you can still make projections. Here’s how to prepare your business plan financial projections, so your company will thrive.
What are business plan financial projections?
Business plan financial projections are a company’s estimates, or forecasts, of its financial performance at some point in the future. For existing businesses, draw on historical data to detail how your company expects metrics like revenue, expenses, profit, and cash flow to change over time.
Companies can create financial projections for any span of time, but typically they’re for between one and five years. Many companies revisit and amend these projections at least annually.
Creating financial projections is an important part of building a business plan . That’s because realistic estimates help company leaders set business goals, execute financial decisions, manage cash flow , identify areas for operational improvement, seek funding from investors, and more.
What are financial projections used for?
Financial forecasting serves as a useful tool for key stakeholders, both within and outside of the business. They often are used for:
Business planning
Accurate financial projections can help a company establish growth targets and other goals . They’re also used to determine whether ideas like a new product line are financially feasible. Future financial estimates are helpful tools for business contingency planning, which involves considering the monetary impact of adverse events and worst-case scenarios. They also provide a benchmark: If revenue is falling short of projections, for example, the company may need changes to keep business operations on track.
Projections may reveal potential problems—say, unexpected operating expenses that exceed cash inflows. A negative cash flow projection may suggest the business needs to secure funding through outside investments or bank loans, increase sales, improve margins, or cut costs.
When potential investors consider putting their money into a venture, they want a return on that investment. Business projections are a key tool they will use to make that decision. The projections can figure in establishing the valuation of your business, equity stakes, plans for an exit, and more. Investors may also use your projections to ensure that the business is meeting goals and benchmarks.
Loans or lines of credit
Lenders rely on financial projections to determine whether to extend a business loan to your company. They’ll want to see historical financial data like cash flow statements, your balance sheet , and other financial statements—but they’ll also look very closely at your multi-year financial projections. Good candidates can receive higher loan amounts with lower interest rates or more flexible payment plans.
Lenders may also use the estimated value of company assets to determine the collateral to secure the loan. Like investors, lenders typically refer to your projections over time to monitor progress and financial health.
What information is included in financial projections for a business?
Before sitting down to create projections, you’ll need to collect some data. Owners of an existing business can leverage three financial statements they likely already have: a balance sheet, an annual income statement , and a cash flow statement .
A new business, however, won’t have this historical data. So market research is crucial: Review competitors’ pricing strategies, scour research reports and market analysis , and scrutinize any other publicly available data that can help inform your projections. Beginning with conservative estimates and simple calculations can help you get started, and you can always add to the projections over time.
One business’s financial projections may be more detailed than another’s, but the forecasts typically rely on and include the following:
True to its name, a cash flow statement shows the money coming into and going out of the business over time: cash outflows and inflows. Cash flows fall into three main categories:

Income statement
Projected income statements, also known as projected profit and loss statements (P&Ls), forecast the company’s revenue and expenses for a given period.
Generally, this is a table with several line items for each category. Sales projections can include the sales forecast for each individual product or service (many companies break this down by month). Expenses are a similar setup: List your expected costs by category, including recurring expenses such as salaries and rent, as well as variable expenses for raw materials and transportation.
This exercise will also provide you with a net income projection, which is the difference between your revenue and expenses, including any taxes or interest payments. That number is a forecast of your profit or loss, hence why this document is often called a P&L.
Balance sheet
A balance sheet shows a snapshot of your company’s financial position at a specific point in time. Three important elements are included as balance sheet items:
- Assets. Assets are any tangible item of value that the company currently has on hand or will in the future, like cash, inventory, equipment, and accounts receivable. Intangible assets include copyrights, trademarks, patents and other intellectual property .
- Liabilities. Liabilities are anything that the company owes, including taxes, wages, accounts payable, dividends, and unearned revenue, such as customer payments for goods you haven’t yet delivered.
- Shareholder equity. The shareholder equity figure is derived by subtracting total liabilities from total assets. It reflects how much money, or capital, the company would have left over if the business paid all its liabilities at once or liquidated (this figure can be a negative number if liabilities exceed assets). Equity in business is the amount of capital that the owners and any other shareholders have tied up in the company.
They’re called balance sheets because assets always equal liabilities plus shareholder equity.
5 steps for creating financial projections for your business
- Identify the purpose and timeframe for your projections
- Collect relevant historical financial data and market analysis
- Forecast expenses
- Forecast sales
- Build financial projections
The following five steps can help you break down the process of developing financial projections for your company:
1. Identify the purpose and timeframe for your projections
The details of your projections may vary depending on their purpose. Are they for internal planning, pitching investors, or monitoring performance over time? Setting the time frame—monthly, quarterly, annually, or multi-year—will also inform the rest of the steps.
2. Collect relevant historical financial data and market analysis
If available, gather historical financial statements, including balance sheets, cash flow statements, and annual income statements. New companies without this historical data may have to rely on market research, analyst reports, and industry benchmarks—all things that established companies also should use to support their assumptions.
3. Forecast expenses
Identify future spending based on direct costs of producing your goods and services ( cost of goods sold, or COGS) as well as operating expenses, including any recurring and one-time costs. Factor in expected changes in expenses, because this can evolve based on business growth, time in the market, and the launch of new products.
4. Forecast sales
Project sales for each revenue stream, broken down by month. These projections may be based on historical data or market research, and they should account for anticipated or likely changes in market demand and pricing.
5. Build financial projections
Now that you have projected expenses and revenue, you can plug that information into Shopify’s cash flow calculator and cash flow statement template . This information can also be used to forecast your income statement. In turn, these steps inform your calculations on the balance sheet, on which you’ll also account for any assets and liabilities .
Business plan financial projections FAQ
What are the main components of a financial projection in a business plan.
Generally speaking, most financial forecasts include projections for income, balance sheet, and cash flow.
What’s the difference between financial projection and financial forecast?
These two terms are often used interchangeably. Depending on the context, a financial forecast may refer to a more formal and detailed document—one that might include analysis and context for several financial metrics in a more complex financial model.
Do I need accounting or planning software for financial projections?
Not necessarily. Depending on factors like the age and size of your business, you may be able to prepare financial projections using a simple spreadsheet program. Large complicated businesses, however, usually use accounting software and other types of advanced data-management systems.
What are some limitations of financial projections?
Projections are by nature based on human assumptions and, of course, humans can’t truly predict the future—even with the aid of computers and software programs. Financial projections are, at best, estimates based on the information available at the time—not ironclad guarantees of future performance.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.
The Guide to Sales Projection in 2024
Benjamin Franklin once said, “If you fail to plan, you plan to fail.” 200+ years later, it still rings equally true when trying to grow your business.
You have something to reference when you have a plan. You can see if you’re headed in the right direction and at the right speed.
But vague plans alone won’t help you estimate your growth rate. That’s what makes sales projections so important. They can help you set clear sales goals, explore different potentialities, and grow your customer base consistently.
Below, we’ll define a sales projection and why you need one. Then, we’ll show you a few different ways to make sales projections and cover some of the challenges you may run into.
What is a sales projection?
A sales projection is a document in which you estimate future sales figures over a specific period. You can create them for various theoretical scenarios to better plan your actions.

For example, you could predict that you will sell 1,000 packages in 2022, compared to the 800 from last year, since you’ve hired an additional sales team.
Sales projection vs. sales forecast: What’s the difference?
The terms sales projection and sales forecast are often used interchangeably. They aren’t too different, but they have varying levels of “optimism” and realism.
An accurate sales forecast estimates your likely sales figures based on historical data within your business and the current sales trend. It’s the more realistic of the two. Because of this, forecasts tend to have shorter timeframes.
On the other hand, a sales projection is slightly more theoretical and “what-if.” It looks at your desired sales numbers based on different potential scenarios, making them useful for decision-making.
For example, you might make a sales projection if you’re considering targeting a new type of customer. You’d want to estimate how that could impact sales figures before you invest in targeting this new market.
Show how your product CRUSHES the competition. Get case study request templates, collection form templates, and case study questions FREE here!
Eight reasons to make sales projections
Sales projections can be great tools for making decisions about future actions in your business. Here are some reasons to start making them:
1. Estimate demand and inventory needed
Accurately estimating demand is necessary to purchase the right amount of inventory.
Too little inventory, and you can’t meet that demand. You run out and end up with unhappy customers. The last thing you want is to lose out on a big sales opportunity because you don’t have the product.
But buy too much inventory, and you tie up tons of money in stock that doesn’t sell fast enough. That leaves you less cash to invest in other things. Or worse — you have to dispose of that unsold inventory and take a loss.

This is where sales projections help most. Getting some ideas of your sales figures in the future shows you how much inventory you should buy — usually, projections skew slightly on the side of “too much” so you don’t run out. This is especially true if you sell consumer products, as you should always maintain a sizable stock surplus.
2. Make funding your business easier
Business lenders risk not getting their money back by lending to a business that eventually defaults on its debt or goes under. This is different than working with a debt factoring provider . Amplifying this strategic approach further, the utilization of a business loan calculator solidifies your preparedness. By providing a detailed sales projection and a calculated loan payback scheme, you effectively reiterate to potential lenders that thoughtful planning has ensured the firm’s growth and capacity to successfully manage financial obligations.
Investors also want to make sure they earn a return on their investment — making accurate sales projections even more critical.
The more evidence you have of strong potential business growth , the more investors you could persuade—every potential sale matters.
3. Plan out marketing and sales efforts
Projecting your sales revenue numbers helps you plan your sales and marketing goals and campaigns.
This is especially true for businesses with predictable sales fluctuations throughout the year. You can note times where sales might be weak and offer limited-time discounts or invest more in your marketing.
On the other hand, you can potentially raise your prices during times of stronger sales, take your foot off the marketing and sales gas pedal, and reinvest that surplus into other areas. If your sales are lagging in a quarter, try to educate your team on effective sales skills to close more deals.
4. Make smart decisions about product development
Sales projections are great tools for making decisions about your products and services. Imagine that you’re considering a new product or service line. Projecting its sales revenues gives you a more concrete picture of whether the new offer will help you grow.
On the other side of the coin, projections can help you look at your worst-performing offers and see if you’re better off ending them.
Put these together, and you could cut out the offers that don’t sell and reinvest the resources you free up into the offers that do sell.
5. Improve budgeting accuracy
Each product you make costs something. Usually, the cost-per-unit is fairly predictable — at least, for expenses associated with your product. So by projecting your sales, you can increase your budgeting accuracy when it comes to these costs.
6. Improve financial planning
Once you project your sales, you can estimate your revenue by multiplying your sales figures by your price per product.
Then, calculate your total cost of goods sold — the cost of producing those goods.
Subtract the cost of goods sold and other expenses from your revenues to get a rough profit projection. With this info, you can plan out potential business investments and your personal finances. You can even estimate your taxes.
7. Make hiring decisions
Sales are a key indicator of growth potential. With fast growth often comes the need to hire people — such as a sales team to keep up with those growing sales.

By projecting your sales and estimating your total revenue, you can begin planning to recruit team members ahead of time. This gives you more space to define what types of roles you need to hire for and what you’re looking for in candidates.
8. Benchmark and assess sales performance
Projections serve as a measuring tool for your sales performance, especially if you make pessimistic, realistic, and optimistic projections.
Each one serves as a different benchmark. Your pessimistic projection is your worst-case scenario, your realistic projection is what you expect to achieve, and your optimistic projection is your “stretch” goal. You can measure performance against each one and reevaluate your goals during and at the end of each projection period.
Assumptions that can impact sales projections
Sales projections estimate future revenues, so there’s plenty of uncertainty. Several variables can impact what kind of sales performance you project, including the following:
Your products or services
Launching new products and services and changing or removing existing offers will affect your total sales. Your new products or improvements could bring in more customers, whereas cutting out product lines could decrease sales.
Production costs are another part of your products and services. Increasing production costs means you may have to raise prices or cut necessary costs elsewhere, ultimately reducing your potential sales.
Your marketing
Marketing plays a direct role in your sales. This includes how effective your marketing efforts are and how much you invest in them.
For example, if you’re scaling up a wildly successful marketing campaign or retargeting ads to a market that fits better, you could project much higher sales figures.
Time of year/seasonality
Various factors dealing with the seasons and time of year can impact your sales projections. It could be because of weather, holidays, or other reasons.

Take an electronics retailer, for example. They’ll project far more sales during the fall and winter. Customers are out doing their holiday shopping, and many video games release during the holiday season.
They might then project fewer sales in the early months of the following year as the holiday season ends.
Economic conditions
The economy at large is an important factor to consider when creating accurate sales projections.
For instance, you may have to raise your prices in times of higher inflation. This could decrease your project sales figures as fewer customers are willing or able to pay those higher prices.
On the other hand, in a booming economy, your projections might increase.
Legal or regulatory changes
Changes in laws and industry regulations could impact your projections, especially if they’re targeted toward your industry.
Of course, it’s hard to predict when new regulations will come and how exactly they’ll impact your operation. This is why it’s essential to monitor for these changes regularly.
How to create a sales projection: Top-down vs. bottom-up
Broadly speaking, creating a sales projection involves a few steps:
- Reviewing and analyzing past sales and financial data
- Assessing market trends, price changes, and other assumptions
- Using this information to estimate total sales revenue
Once you’ve done that, you can go a step further by subtracting overall projected expenses to estimate your gross profit margin.
That said, there are two ways to make projections, top-down and bottom-up. Below, we’ll briefly explain each one, then discuss which type you should use.
Top-down projection
A top-down projection looks at the total size of the market you’re in. This is called the Total Addressable Market, or TAM. The projection then predicts how much market share a sales organization could capture.
For example, a market might be $100 million. A small business estimates it could get about 5% of that, so it would project a total of $5 million in revenue per year.
This projection is relatively simple, but it’s much more theoretical. You’re working with a few big, abstract numbers without drilling down into what’s behind your sales.
Bottom-up projection
A bottom-up projection starts with the number of units you expect to sell. It then multiplies that by your price per unit to get your total projection.
These projections can factor in many other details, such as the number of sales reps or locations. As a result, bottom-up numbers tend to be more grounded and better suited for established businesses with existing products and customers.
Which one should you use?
As you can see, the bottom-up projection is usually more accurate, but it relies on having real data, like the number of stores, sales reps, and historical data to go on. So if you’re starting a business or launching a new product, you might want to use a top-down projection.
Otherwise, the bottom-up projection is the way to go — except it can be a lot of work.
The shortcut to an accurate bottom-up projection — use a CRM report
If you’re currently using a customer relationship management platform to manage your sales pipeline , it probably offers some sort of report or dashboard you can use to project sales.
For example, in the ActiveCampaign CRM , you have the Deal Forecast report that forecasts the number of deals and the likely revenue that they’ll generate based on historical data.

Beyond the dashboard, it also offers state-of-the-art sales automation features to help drive more sales and keep your customers happy.
Common challenges with making accurate sales projections
Sales projections aren’t perfect — 100% accurate forecasts are impossible to make. Keeping the following limitations in mind will temper your expectations — preventing you from becoming disappointed and disillusioned if your business performance strays far from your expectations.
Subjectivity
You’ll always deal with human subjectivity when attempting to predict the future, even if you have historical data to work with.
That said, predictive analytics tools can go a long way in cutting out human bias from the equation. They can analyze data and scenarios without subjectivity getting in the way.
For example, if you sell B2B products or services , you probably have a long sales process with a large number of leads in the pipeline. A different business model with lower-cost items, like B2C, may have much shorter sales cycles.
Unreliability of past data
Projections do use past data to help estimate future revenues, but that data may not always be reliable — especially if you’re a new business.
At that point, you don’t have much data to work off of at all. It’s hard to picture various theoretical future scenarios when you barely know what an average year looks like.
Similarly, your business might be crawling at a snail’s pace for its early existence, causing you to make relatively unimpressive projections — even if you predict your business to grow.
However, you might strike gold one year and hit massive business growth, rendering even your optimistic projection unhelpful.
Time investment
The most tangible drawback to making sales projections is that they simply take resources away from the activities that move the needle — like actual lead nurturing and selling. Small businesses and solopreneurs will feel this pain the most since they may not have experts on hand to crank out accurate sales projections.

You don’t want to take away valuable time from a key sales rep or sales manager — or worse, crunch the numbers yourself. Instead, invest in software that helps you make these projections automatically based on data.
Plan the future of your business with sales projections
Business success doesn’t happen by accident. You have to plan, set goals, and measure your progress to know if you’re getting anywhere.
That’s what makes sales projections so helpful. Your projections will rarely be right on the money, but they provide you direction, give you realistic numbers to strive for, and help you make decisions in all areas of your business. If you don’t want to create projections from scratch, that’s something ActiveCampaign’s Deals CRM can help you with. You can quickly generate custom projections based on historical data.
Click here to try it free for 14 days.
No credit card required. Instant set-up.
Please enter a valid email address to continue.
Related Posts

Whether you just created a website on WordPress or have had one for years, one of the most important parts...

The power of personalization in email marketing has become more than just a buzzword; it’s a pivotal strategy for engaging...

Do you have any of these business goals? You need to reach these goals in a sustainable way. A big...
Try it now, for free
Call Us (877) 968-7147 Login
Most popular blog categories
- Payroll Tips
- Accounting Tips
- Accountant Professional Tips

Sales Projections for Small Business Owners
As a small business owner, you know it’s rare for things to go according to plan. But, without a sense of direction, you’re steering your business blindly into the future. You need to know where you’re headed in order to make smart decisions. To get an outlook on your business, you can learn how to make sales projections.
Knowing how to calculate sales projections isn’t about being able to predict revenue flawlessly. The goal is to make connections between sales and expenses. Look at past patterns and your current conditions to make reasonable forecasts. The patterns help you understand the cause and effect of choices you make.
How to create a sales forecast
Projecting sales might seem difficult. But if your accounting books are organized, you can use simple methods to make forecasts .
Parts of a sales forecast
There are several factors to consider when learning how to estimate sales projections. But first, let’s go over what a basic forecast looks like.
Sales projections are made up of rows and columns, much like a chart of accounts .
Your forecast should have manageable units that offer key insight into your business. To decide which units to measure, split your sales items into categories. The categories depend on the kind of business you run.
Let’s say you own a restaurant. Chances are, you sell a lot of different items. You wouldn’t want to project each plate and beverage you sell. Instead, divide the items into categories, such as lunches, dinners, and drinks. These categories are your units.
Every business’s units are different. Focus on the information that is the most useful and relevant to your company.
Creating a sales projection
Once you choose categories, project how many units you will sell. To forecast sales, multiply the number of units by the price you sell them for. Create projections for each month.
For example, you own a car wash. In April, you project you will wash 800 cars. A car wash is $15.800 cars X $15 per car wash = $12,000 sales projection
800 cars X $15 per car wash = $12,000 sales projection
Your sales forecast will show a projection of $12,000 in car wash sales for April.
As the projected month passes, look at the difference between expected outcomes and actual results. To make comparing easier, organize the forecasts similar to how you set up your accounting books for small business .
How to create a sales forecast example:
| Units | Jan. | Feb. | March |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lunches | $720 | $820 | $900 |
| Lunch Beverages | $400 | $400 | $500 |
| Dinners | $1,080 | $1,080 | $1,200 |
| Dinner Beverages | $600 | $700 | $650 |
| Other | $200 | $200 | $250 |
| Total | $3,000 | $3,200 | $3,500 |
Things that affect your sales projections
You now know to make projections in units each month. But there’s still the question: How do I know which numbers to forecast?
Obviously, you can’t pull out a crystal ball and see what the future holds. However, there are clues around you that point to where your business is headed. Consider the following factors when creating a sales forecast.
Past financial results
The first place to start when projecting sales is, ironically, the past. Review your financial statements to determine forecasts. Look at your records over time for patterns. Ask questions like:
- How much did you make last month?
- How much did you make during this time last year compared to now?
You’re not a financial expert, but you know your business. By looking at patterns, you can make reliable assumptions about sales. If you know how fast your company has grown, you have a good idea of how fast it will gain momentum.
Sales drivers
Right now, your sales might be climbing at a steady rate. But, you know that could change in an instant. There is an unlimited number of factors that can affect your business.
When creating a sales forecast, consider things that can shift the patterns in your books. Some influencers are out of your control, like changes in the market and business seasonality. Other aspects are results of the decisions you make, such as holding a promotional sale or adding new products and services.
Other businesses
Financial information from similar companies can be helpful for sales projections. You can see if you are above or below industry averages, and make changes based on your findings.
Looking at other businesses is especially helpful if you are a new business owner. You do not have past financial records to base your projections off of. When reviewing other companies, keep in mind details like the location, size, items offered, and age of the business.
Don’t be afraid to ask for advice. Your peers and mentors can offer perspectives on what to expect during upcoming months and years.
Direct expenses
As sales increase, so do the direct expenses that go into your products and services. The more you sell, the more you need to spend to keep up with operations. Direct expenses, also called the cost of goods sold (COGS), affect sales projections. Projected sales and direct expenses help you determine profitability.
Projecting the costs of goods sold is similar to projecting sales. Forecast the number of units you will sell. Then, multiply the number of units by the direct expenses it takes to produce them. For example, you expect to sell 100 units. It costs you $5 to make each unit. You can project to spend $500 in direct expenses.
Review and revise
When it comes to creating a sales forecast, expect to make a lot of revisions. Projections need to be adaptable. Start predicting your sales early so you have time to make changes as interruptions occur.
As Tim Berry, Founder & Chairman of Palo Alto Software and BPlans.com, says:
Projections in business plans should be an exercise in identifying the drivers and triggers that make the business work.”
Keep in mind that your sales forecast is a guide to where your business is headed. But, it is not 100% reliable. Be prepared for the unexpected.
Don’t make projections and then leave them to sit and collect dust. Use forecasting as a helpful tool for making business decisions. Schedule a regular time to review and revise your sales projections each month.
Need a simple way to track your income and expenses? Patriot’s online accounting software is easy-to-use and made for the small business owner. We offer free, U.S.-based support. Try it for free today.
This article is updated from its original publication date of March 23, 2017.
Stay up to date on the latest accounting tips and training
You may also be interested in:
Need help with accounting? Easy peasy.
Business owners love Patriot’s accounting software.
But don’t just take our word…

Explore the Demo! Start My Free Trial
Relax—run payroll in just 3 easy steps!
Get up and running with free payroll setup, and enjoy free expert support. Try our payroll software in a free, no-obligation 30-day trial.

Relax—pay employees in just 3 steps with Patriot Payroll!
Business owners love Patriot’s award-winning payroll software.

Watch Video Demo!
Watch Video Demo
Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies
AI PPT Maker
Powerpoint Templates
PPT Bundles
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 7 Sales Projection Templates with Examples and Samples

Siranjeev Santhanam
For every business, gaining foresight into the future is invaluable. Knowing the projected sales volume, timing, locations, and long-term outcomes holds tremendous benefits for your growth and success.
You don’t need a crystal ball for this. You need sales projection.
Sales projection is a powerful asset for businesses of all sizes, giving them the tools to navigate the changing market and plan for the long term. This exercise uses data-driven models to estimate the expected sales of a product or service over a given period of time, taking into account a range of factors such as market trends, past growth, etc. This information is used by businesses to make critical decisions about marketing, pricing, and staffing. When done right, sales projection can help businesses create accurate and realistic forecasts that elevate their operational productivity and move on the right path.
Building accurate projections is easier said than done, and leading businesses would have to analyze the data, apply the right projection techniques and interpret the information correctly. It can be tricky, and pre-designed templates can help you take some of the load off your back.
We’ve got more on this subject if you’re interested! Click here to read our other blog on the top 5 Cash Flow Projection Templates right away.
This blog will discuss seven sales projection templates you can download and apply to gain expertise in this area. These templates are rich with content and have a simple, easy-to-use technical side, helping users save time and effort.
Let’s begin.
Template 1: Sale Projection Powerpoint Bundles
Expand your company’s sales architecture and enhance your commercial standing, all with the help of this comprehensive twenty-five slides PowerPoint deck. It contains a great wellspring of data that can assist you in reinventing your sales projection methods. Some highlights of this compilation include a team sales projection and deal conversion report, a yearly sales comparison and projections for the IT store, a three-year sales quantity projections report, and much more. Download this PPT template and build a stronger sales toolkit that allows for sustainable, long-term performance.

Download now
Template 2: Pharmaceutical Sales Project Quarterly Performance Dashboard
This slide features a map, a table, and a chart that organizes the data in a stunning and informative way. This slide can map vital details and outline sales growth rates by area, condition, and channel. Incorporate some essential details such as prescribed drugs performance, quarterly sales, non-prescribed drug sales, quarterly sales by condition, and more. Craft a stronger public image and spur your employees into action by deploying this creatively made slide.
Template 3: Sales Projections PPT Slide
Gain mastery of the sales domain by implementing a methodical, focused, and meticulous working mechanism, and use this PPT theme as a roadmap on your journey there. The slide helps you to make curated projections across the short-term, mid-term, and long-term views. Break down your sales projections and revenue forecasts and apply them within appropriate contexts to strengthen your broader sales strategy. Get this slide now.

Template 4: Weekly Sales Projections Table
Enhance your internal sales mechanisms by adding structure to the overall process, all with the aid of this PPT slide. It can help you present your sales projections in a weekly view, with five columns representing the days of the week. You can use this slide to portray sales performance with a host of customizable variables. Review your sales performance and underline drawbacks, analyze your sales performance and identify patterns, and boost overall performance by incorporating this PPT into your methodology.
Template 5: Sales Projections Monthly Goal Template
Use this dashboard to craft a professional, engaging presentation that underscores your sales expertise. This slide features a table with columns for monthly goal, actual, and variance and a chart that visualizes the data. You can use this slide to exhibit how your sales performance compares to your sales goals and isolate gaps in the broader vision.
Template 6: Sales Projections PPT Template
Get this vibrantly rendered PPT theme to help you structure your sales projections in a clear and effective manner. You can employ this slide to streamline the flow of information around your sales performance and revenue forecasts. It features a six-stage process diagram with icons and text placeholders that you can customize according to your needs, with highlights such as comparing with actuals, managing sales opportunities, and sales reviews. Demonstrate your confidence and gain credibility in your area of work using this resource.
Template 7: One Pager Sales Projection Sheet Infographic
Seeking to exhibit your sales performance and revenue growth in an appealing and easy-to-understand format? Check out this PPT layout, a simple and effective way to project competence to your stakeholders. The template lets you display your future sales estimates and past sales results in a cohesive and customizable manner. It features a professional layout with a table, bar charts, and icons that help to underscore the key information and data. Get this PPT now and impress your audience with a visually stunning and informative presentation.
Accurate Sales Projection Mastery
The sales projection is crucial for any business that seeks to plan for the future and optimize performance. It can help firms in knowing potential challenges beforehand and allocate resources accordingly. Sales projection, however, brings uncertainties and inaccuracies, and it is crucial to use reliable data sources, appropriate methodologies, and the right tools for making projections. Download our pre-designed, ready-to-use sales projection templates and gain the upper hand in this area, achieving your goals in an ever-changing, competitive environment.
- If you are looking for Sales Action Plan templates, here’s a handy guide with the most popular samples and examples.
FAQs on Sales Projection
How do you calculate sales projection.
Below are some leading methods for generating sales projections:
Top-down approach
This method adopts the business's overarching goals and then separates them into smaller, more manageable units based on regions, products, or channels. The sales forecast is then made for each specific unit, and the total sales forecast is made by adding the individual forecasts.
Bottom-up approach
This method takes the individual units of the business and then aggregates them to arrive at a total, concrete forecast. The forecast for each unit is made by approximating the number of units to be sold and multiplying them by the price charged for each unit.
Mixed approach
This method presents a fusion of both the top-down and bottom-up approaches. The sales forecast is generated for each unit by untiring the bottom-up approach, and the individual unit forecasts are then consolidated using the top-down approach.
How important is sales projection?
The sales projection is a vital part of the business exercise and is crucial for businesses seeking to compete in a changing and evolving market. It can help businesses plan their production, marketing, and distribution, assess their sales performance and strategies and regulate risk for the long term. By having sales projections, a business can make informed decisions based on a clear and actionable vision of its future sales potential. Sales projections help businesses plan, execute, survey, and improve their sales activities and outcomes.
What is a 5-year sales projection?
A 5-year sales projection is a data-driven estimation of the revenue a business is set to accrue in the next five years. It is based on a host of factors, including market trends, historical data, competition, product development, and more. Such a projection can aid a business in managing its production and distribution strategies while managing cash flow.
Related posts:
- Top 10 Sales Business Plan Templates with Examples and Samples
- Must-Have Financial Projections Templates with Samples and Examples
- Top 30 Sales Pitch Deck PowerPoint Templates To Win Over Clients
- Top 20 Performance Review Templates For a Perfect Performance Evaluation
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Agile Process Templates with Samples and Examples

Must-Have Vehicle Bill of Sale Templates with Examples and Samples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Plan Projections
ideas to numbers .. simple financial projections
Home > Financial Projections > Sales Projection

Sales Projection
A sales projection for your business plan.
A sales projection of your product or service is the starting point and the key to preparing financial projections, so it is important to use a realistic estimate.
Most businesses have different types of sales e.g. product lines, departments, customer groups etc. so you’ll eventually need an estimate for each main type for your sales projection. We would suggest no more than seven types and perhaps a final one for sundry sales. If you can’t breakdown into types at this stage of your sales projection then work with the total sales figure.
How do you get the Estimate for the Sales projection?
- If you have historical annual sales information for your business use that as your starting point. If you have a number of years then average them, but try and take into account unusual fluctuations e.g. particularly bad weather, economic climate, new products coming on line etc.
- Use information from companies in the same or similar type of business, trade associations, company accounts of similar businesses to give you an idea of the level of sales for your industry and location.
- Use market data and statistics, if you’re in retailing for example its usually possible to get an idea of the typical sales volume per square foot of space for shops in similar locations and sizes. This sales volume multiplied by your average price should give you an estimate of sales.
- Use national government demographic data and average spend data to estimate the total market for the product in your area and then calculate your market share by dividing this estimate by the number of competitors plus one in your area. You’ll need to use your own judgment and adjust this figure (probably downwards, for the first year)
- If you are in a business with a fixed capacity use a bottom up method by calculating your available capacity (e.g. in a restaurant use the available seating and multiply this by the average meal price), and then estimate a likely usage, say 50% to give a sales estimate for the year.
The important thing is to get a best estimate and start the sales projection; it can always be adjusted later as the plan takes shape.
Finally a few words of warning, avoid wishful thinking, (take 20-30% off the figure you first thought of), avoid too much detail in analysing the types of sale you have, and make sure the sales are within your businesses capacity, for example if you are manufacturing widgets with a given capacity, there’s no point in a sales projection well above this unless you have plans to expand.
Our free revenue projection template can be used to help estimate sales for up to 5 years.
About the Author
Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Plan Projections. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries. He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own. He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University.
You May Also Like
- Business Planning
Business Plan Financial Projections
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Financial projections are forecasted analyses of your business’ future that include income statements, balance sheets and cash flow statements. We have found them to be an crucial part of your business plan for the following reasons:
- They can help prove or disprove the viability of your business idea. For example, if your initial projections show your company will never make a sizable profit, your venture might not be feasible. Or, in such a case, you might figure out ways to raise prices, enter new markets, or streamline operations to make it profitable.
- Financial projections give investors and lenders an idea of how well your business is likely to do in the future. They can give lenders the confidence that you’ll be able to comfortably repay their loan with interest. And for equity investors, your projections can give them faith that you’ll earn them a solid return on investment. In both cases, your projections can help you secure the funding you need to launch or grow your business.
- Financial projections help you track your progress over time and ensure your business is on track to meet its goals. For example, if your financial projections show you should generate $500,000 in sales during the year, but you are not on track to accomplish that, you’ll know you need to take corrective action to achieve your goal.
Below you’ll learn more about the key components of financial projections and how to complete and include them in your business plan.
What Are Business Plan Financial Projections?
Financial projections are an estimate of your company’s future financial performance through financial forecasting. They are typically used by businesses to secure funding, but can also be useful for internal decision-making and planning purposes. There are three main financial statements that you will need to include in your business plan financial projections:
1. Income Statement Projection
The income statement projection is a forecast of your company’s future revenues and expenses. It should include line items for each type of income and expense, as well as a total at the end.
There are a few key items you will need to include in your projection:
- Revenue: Your revenue projection should break down your expected sales by product or service, as well as by month. It is important to be realistic in your projections, so make sure to account for any seasonal variations in your business.
- Expenses: Your expense projection should include a breakdown of your expected costs by category, such as marketing, salaries, and rent. Again, it is important to be realistic in your estimates.
- Net Income: The net income projection is the difference between your revenue and expenses. This number tells you how much profit your company is expected to make.
Sample Income Statement
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenues | ||||||
| Total Revenues | $360,000 | $793,728 | $875,006 | $964,606 | $1,063,382 | |
| Expenses & Costs | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | $64,800 | $142,871 | $157,501 | $173,629 | $191,409 | |
| Lease | $50,000 | $51,250 | $52,531 | $53,845 | $55,191 | |
| Marketing | $10,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | |
| Salaries | $157,015 | $214,030 | $235,968 | $247,766 | $260,155 | |
| Initial expenditure | $10,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Expenses & Costs | $291,815 | $416,151 | $454,000 | $483,240 | $514,754 | |
| EBITDA | $68,185 | $377,577 | $421,005 | $481,366 | $548,628 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| EBIT | $41,025 | $350,417 | $393,845 | $454,206 | $521,468 | |
| Interest | $23,462 | $20,529 | $17,596 | $14,664 | $11,731 | |
| PRETAX INCOME | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Use of Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Taxable Income | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Income Tax Expense | $6,147 | $115,461 | $131,687 | $153,840 | $178,408 | |
| NET INCOME | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 |
2. Cash Flow Statement & Projection
The cash flow statement and projection are a forecast of your company’s future cash inflows and outflows. It is important to include a cash flow projection in your business plan, as it will give investors and lenders an idea of your company’s ability to generate cash.
There are a few key items you will need to include in your cash flow projection:
- The cash flow statement shows a breakdown of your expected cash inflows and outflows by month. It is important to be realistic in your projections, so make sure to account for any seasonal variations in your business.
- Cash inflows should include items such as sales revenue, interest income, and capital gains. Cash outflows should include items such as salaries, rent, and marketing expenses.
- It is important to track your company’s cash flow over time to ensure that it is healthy. A healthy cash flow is necessary for a successful business.
Sample Cash Flow Statements
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASH FLOW FROM OPERATIONS | ||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 | |
| Change in working capital | ($19,200) | ($1,966) | ($2,167) | ($2,389) | ($2,634) | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Operations | $19,376 | $239,621 | $269,554 | $310,473 | $355,855 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM INVESTMENTS | ||||||
| Investment | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Investments | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM FINANCING | ||||||
| Cash from equity | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Cash from debt | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow | $154,257 | $194,502 | $224,436 | $265,355 | $310,736 | |
| Cash at Beginning of Period | $0 | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | |
| Cash at End of Period | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 |
3. Balance Sheet Projection
The balance sheet projection is a forecast of your company’s future financial position. It should include line items for each type of asset and liability, as well as a total at the end.
A projection should include a breakdown of your company’s assets and liabilities by category. It is important to be realistic in your projections, so make sure to account for any seasonal variations in your business.
It is important to track your company’s financial position over time to ensure that it is healthy. A healthy balance is necessary for a successful business.
Sample Balance Sheet
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASSETS | ||||||
| Cash | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 | |
| Accounts receivable | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Inventory | $30,000 | $33,072 | $36,459 | $40,192 | $44,308 | |
| Total Current Assets | $184,257 | $381,832 | $609,654 | $878,742 | $1,193,594 | |
| Fixed assets | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $54,320 | $81,480 | $108,640 | $135,800 | |
| Net fixed assets | $153,790 | $126,630 | $99,470 | $72,310 | $45,150 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 | |
| LIABILITIES & EQUITY | ||||||
| Debt | $315,831 | $270,713 | $225,594 | $180,475 | $135,356 | |
| Accounts payable | $10,800 | $11,906 | $13,125 | $14,469 | $15,951 | |
| Total Liability | $326,631 | $282,618 | $238,719 | $194,944 | $151,307 | |
| Share Capital | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Retained earnings | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| Total Equity | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES & EQUITY | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 |
How to Create Financial Projections
Creating financial projections for your business plan can be a daunting task, but it’s important to put together accurate and realistic financial projections in order to give your business the best chance for success.
Cost Assumptions
When you create financial projections, it is important to be realistic about the costs your business will incur, using historical financial data can help with this. You will need to make assumptions about the cost of goods sold, operational costs, and capital expenditures.
It is important to track your company’s expenses over time to ensure that it is staying within its budget. A healthy bottom line is necessary for a successful business.
Capital Expenditures, Funding, Tax, and Balance Sheet Items
You will also need to make assumptions about capital expenditures, funding, tax, and balance sheet items. These assumptions will help you to create a realistic financial picture of your business.
Capital Expenditures
When projecting your company’s capital expenditures, you will need to make a number of assumptions about the type of equipment or property your business will purchase. You will also need to estimate the cost of the purchase.
When projecting your company’s funding needs, you will need to make a number of assumptions about where the money will come from. This might include assumptions about bank loans, venture capital, or angel investors.
When projecting your company’s tax liability, you will need to make a number of assumptions about the tax rates that will apply to your business. You will also need to estimate the amount of taxes your company will owe.
Balance Sheet Items
When projecting your company’s balance, you will need to make a number of assumptions about the type and amount of debt your business will have. You will also need to estimate the value of your company’s assets and liabilities.
Financial Projection Scenarios
Write two financial scenarios when creating your financial projections, a best-case scenario, and a worst-case scenario. Use your list of assumptions to come up with realistic numbers for each scenario.
Presuming that you have already generated a list of assumptions, the creation of best and worst-case scenarios should be relatively simple. For each assumption, generate a high and low estimate. For example, if you are assuming that your company will have $100,000 in revenue, your high estimate might be $120,000 and your low estimate might be $80,000.
Once you have generated high and low estimates for all of your assumptions, you can create two scenarios: a best case scenario and a worst-case scenario. Simply plug the high estimates into your financial projections for the best-case scenario and the low estimates into your financial projections for the worst-case scenario.
Conduct a Ratio Analysis
A ratio analysis is a useful tool that can be used to evaluate a company’s financial health. Ratios can be used to compare a company’s performance to its industry average or to its own historical performance.
There are a number of different ratios that can be used in ratio analysis. Some of the more popular ones include the following:
- Gross margin ratio
- Operating margin ratio
- Return on assets (ROA)
- Return on equity (ROE)
To conduct a ratio analysis, you will need financial statements for your company and for its competitors. You will also need industry average ratios. These can be found in industry reports or on financial websites.
Once you have the necessary information, you can calculate the ratios for your company and compare them to the industry averages or to your own historical performance. If your company’s ratios are significantly different from the industry averages, it might be indicative of a problem.
Be Realistic
When creating your financial projections, it is important to be realistic. Your projections should be based on your list of assumptions and should reflect your best estimate of what your company’s future financial performance will be. This includes projected operating income, a projected income statement, and a profit and loss statement.
Your goal should be to create a realistic set of financial projections that can be used to guide your company’s future decision-making.
Sales Forecast
One of the most important aspects of your financial projections is your sales forecast. Your sales forecast should be based on your list of assumptions and should reflect your best estimate of what your company’s future sales will be.
Your sales forecast should be realistic and achievable. Do not try to “game” the system by creating an overly optimistic or pessimistic forecast. Your goal should be to create a realistic sales forecast that can be used to guide your company’s future decision-making.
Creating a sales forecast is not an exact science, but there are a number of methods that can be used to generate realistic estimates. Some common methods include market analysis, competitor analysis, and customer surveys.
Create Multi-Year Financial Projections
When creating financial projections, it is important to generate projections for multiple years. This will give you a better sense of how your company’s financial performance is likely to change over time.
It is also important to remember that your financial projections are just that: projections. They are based on a number of assumptions and are not guaranteed to be accurate. As such, you should review and update your projections on a regular basis to ensure that they remain relevant.
Creating financial projections is an important part of any business plan. However, it’s important to remember that these projections are just estimates. They are not guarantees of future success.
Business Plan Financial Projections FAQs
What is a business plan financial projection.
A business plan financial projection is a forecast of your company's future financial performance. It should include line items for each type of asset and liability, as well as a total at the end.
What are annual income statements?
The Annual income statement is a financial document and a financial model that summarize a company's revenues and expenses over the course of a fiscal year. They provide a snapshot of a company's financial health and performance and can be used to track trends and make comparisons with other businesses.
What are the necessary financial statements?
The necessary financial statements for a business plan are an income statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet.
How do I create financial projections?
You can create financial projections by making a list of assumptions, creating two scenarios (best case and worst case), conducting a ratio analysis, and being realistic.
Free Financial Projection and Forecasting Templates
By Andy Marker | January 3, 2024
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
We’ve collected the top free financial projection and forecasting templates. These templates enable business owners, CFOs, accountants, and financial analysts to plan future growth, manage cash flow, attract investors, and make informed decisions. On this page, you'll find many helpful, free, customizable financial projection and forecasting templates, including a 1 2-month financial projection template , a startup financial projection template , a 3-year financial projection template , and a small business financial forecast template , among others. You’ll also find details on the elements in a financial projection template , types of financial projection and forecasting templates , and related financial templates .
Simple Financial Projection Template

Download a Sample Simple Financial Projection Template for
Excel | Google Sheets
Download a Blank Simple Financial Projection Template for
Excel | Google Sheets
Small business owners and new entrepreneurs are the ideal users for this simple financial projection template. Just input your expected revenues and expenses. This template stands out due to its ease of use and focus on basic, straightforward financial planning, making it perfect for small-scale or early-stage businesses. Available with or without sample text, this tool offers clear financial oversight, better budget management, and informed decision-making regarding future business growth.
Looking for help with your business plan? Check out these free financial templates for a business plan to streamline the process of organizing your business's financial information and presenting it effectively to stakeholders.
Financial Forecast Template
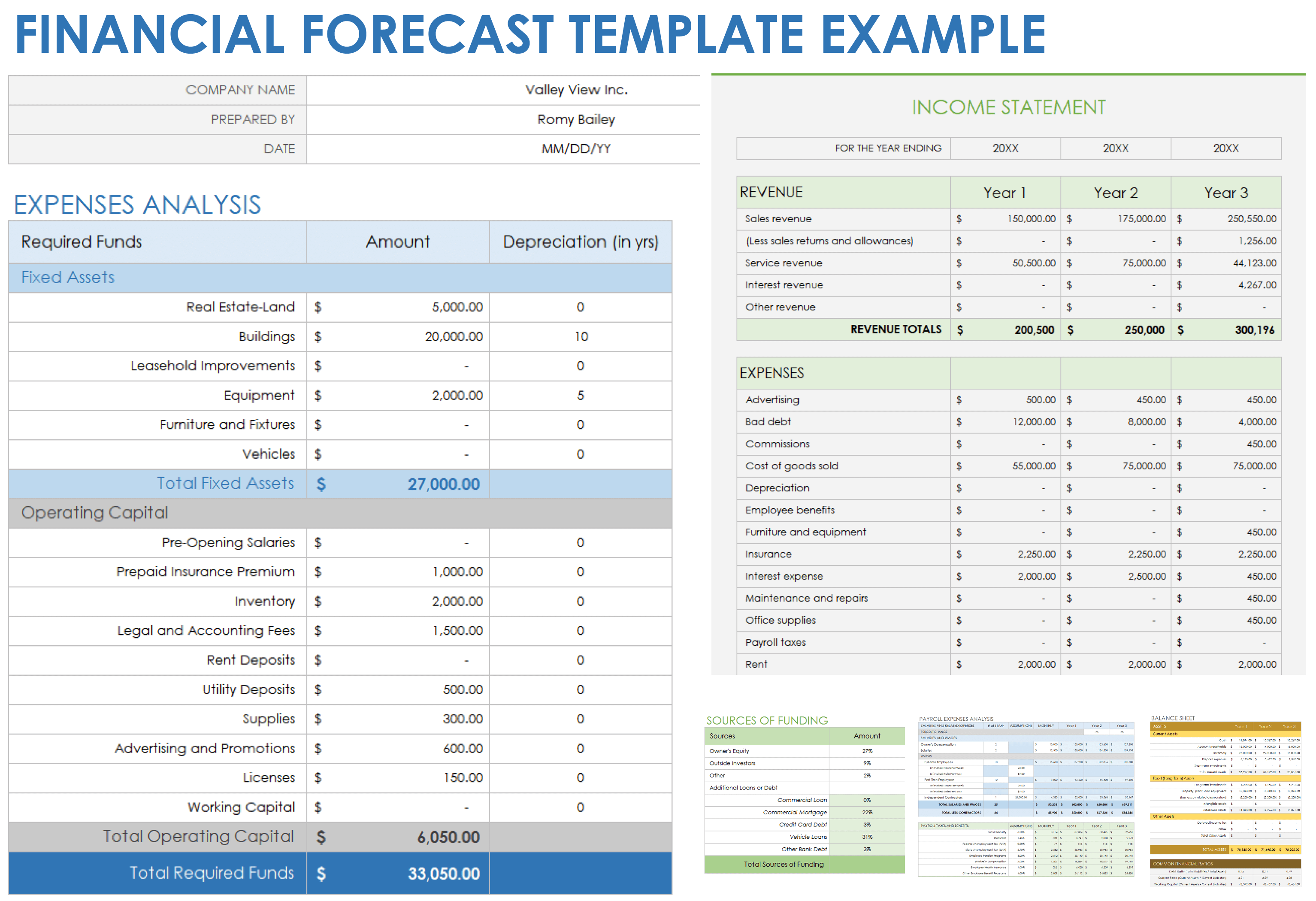
Download a Sample Financial Forecast Template for
Download a Blank Financial Forecast Template for
This template is perfect for businesses that require a detailed and all-encompassing forecast. Users can input various financial data, such as projected revenues, costs, and market trends, to generate a complete financial outlook. Available with or without example text, this template gives you a deeper understanding of your business's financial trajectory, aiding in strategic decision-making and long-term financial stability.
These free cash-flow forecast templates help you predict your business’s future cash inflows and outflows, allowing you to manage liquidity and optimize financial planning.
12-Month Financial Projection Template
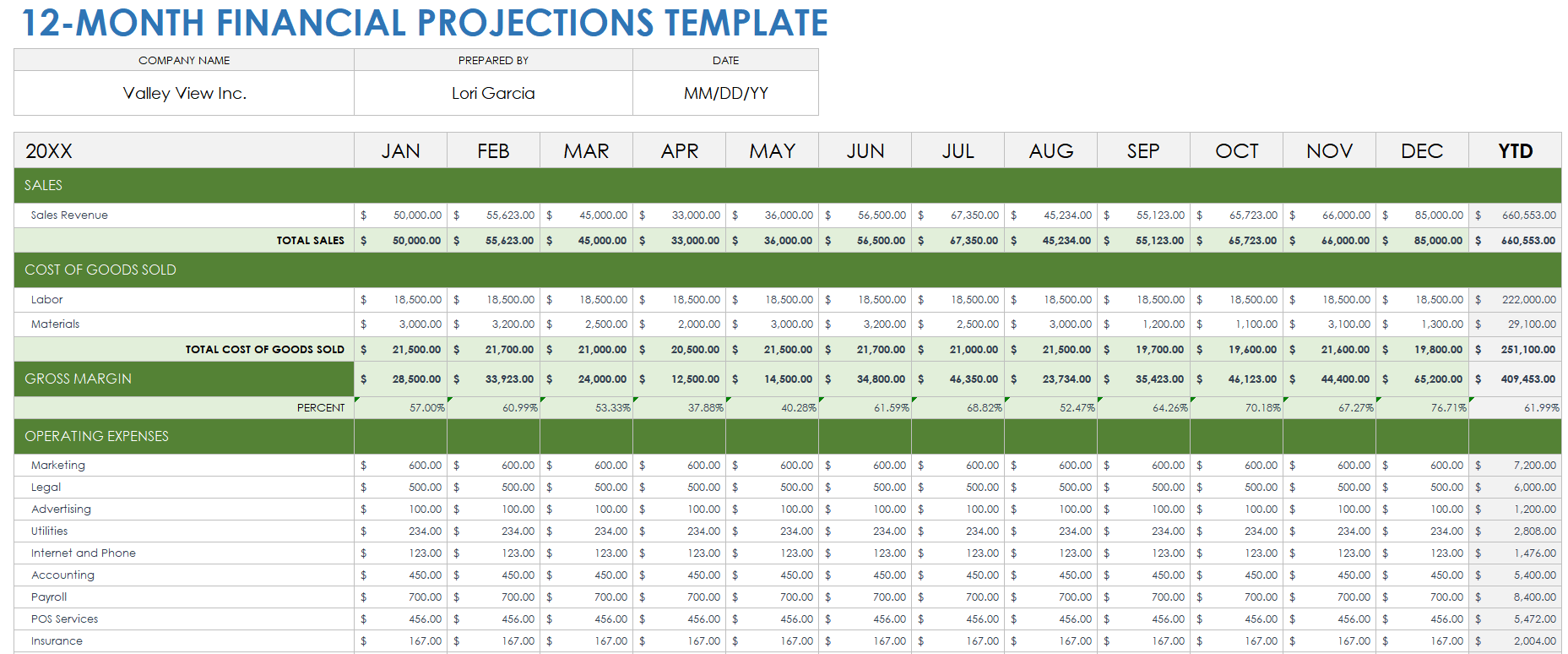
Download a Sample 12-Month Financial Projection Template for
Download a Blank 12-Month Financial Projection Template for
Use this 12-month financial projection template for better cash-flow management, more accurate budgeting, and enhanced readiness for short-term financial challenges and opportunities. Input estimated monthly revenues and expenses, tracking financial performance over the course of a year. Available with or without sample text, this template is ideal for business owners who need to focus on short-term financial planning. This tool allows you to respond quickly to market shifts and plan effectively for the business's crucial first year.
Download free sales forecasting templates to help your business predict future sales, enabling better inventory management, resource planning, and decision-making.
Startup Financial Projection Template
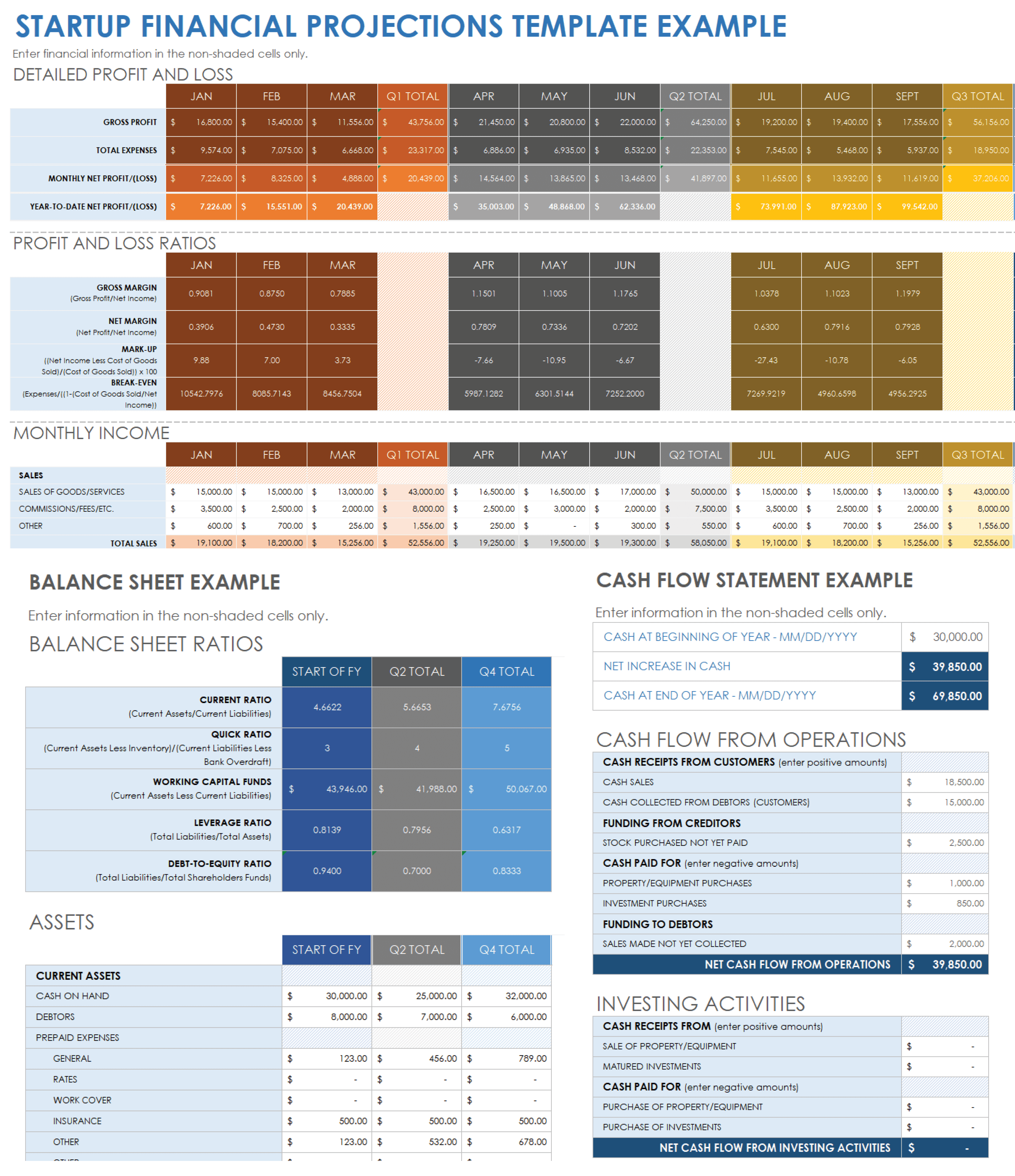
Download a Sample Startup Financial Projection Template for
Download a Blank Startup Financial Projection Template for
This dynamic startup financial projection template is ideal for startup founders and entrepreneurs, as it's designed specifically for the unique needs of startups. Available with or without example text, this template focuses on clearly outlining a startup's initial financial trajectory, an essential component for attracting investors. Users can input projected revenues, startup costs, and funding sources to create a comprehensive financial forecast.
3-Year Financial Projection Template
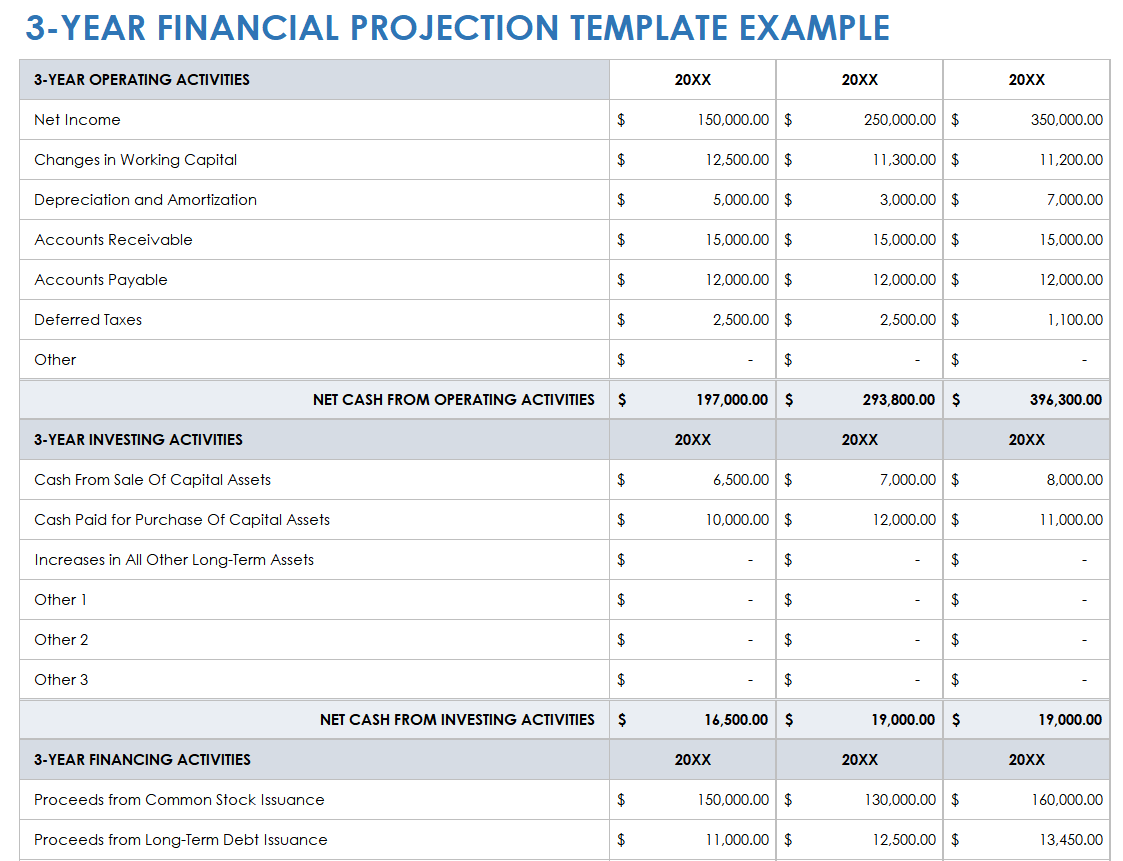
Download a Sample 3-Year Financial Projection Template for
Download a Blank 3-Year Financial Projection Template for
This three-year financial projection template is particularly useful for business strategists and financial planners who are looking for a medium-term financial planning tool. Input data such as projected revenues, expenses, and growth rates for the next three years. Available with or without sample text, this template lets you anticipate financial challenges and opportunities in the medium term, aiding in strategic decision-making and ensuring sustained business growth.
5-Year Financial Forecasting Template
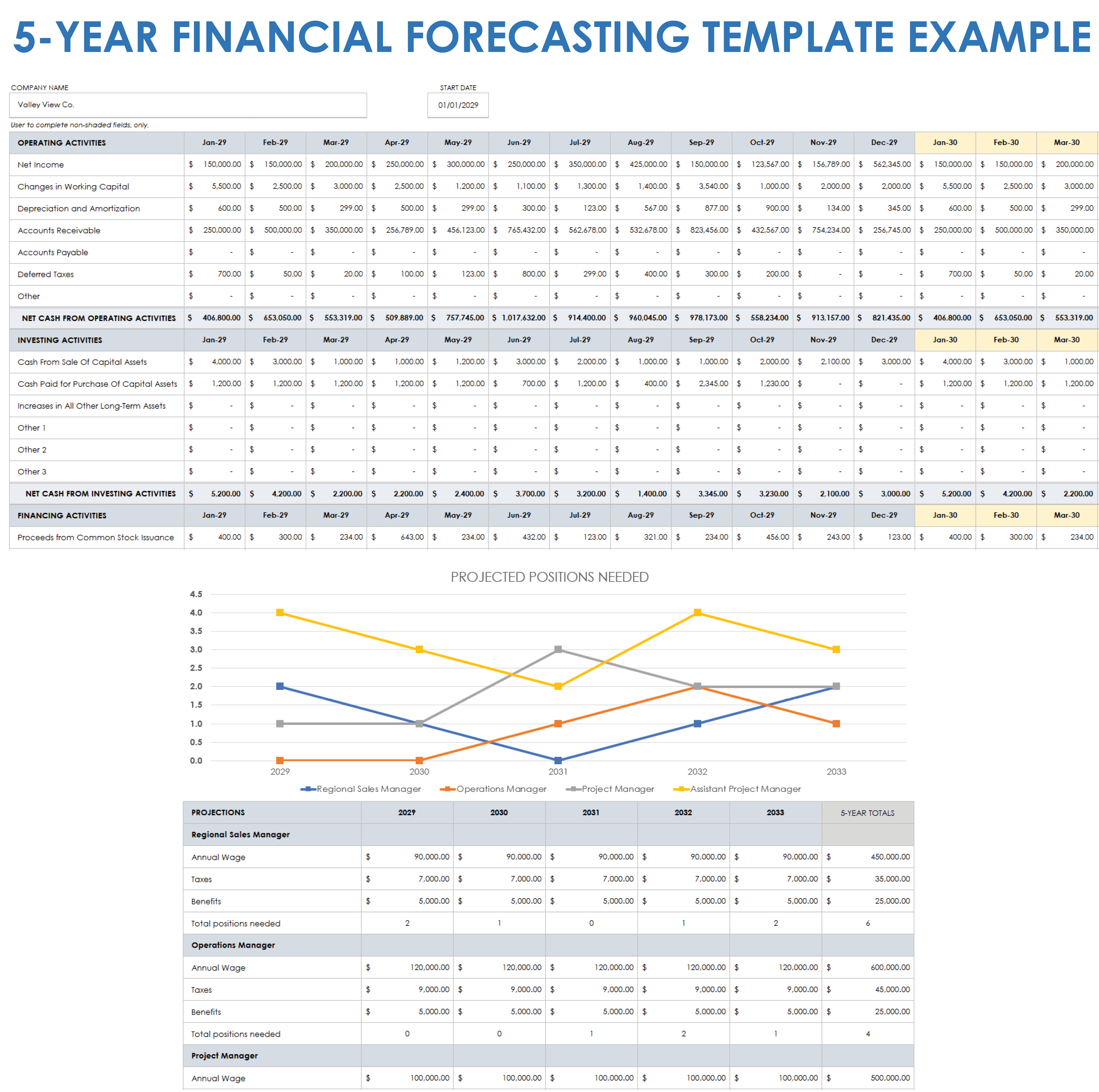
Download a Sample 5-Year Financial Forecasting Template for
Download a Blank 5-Year Financial Forecasting Template for
CFOs and long-term business planners can use this five-year financial forecasting template to get a clear, long-range financial vision. Available with or without example text, this template allows you to plan strategically and invest wisely, preparing your business for future market developments and opportunities. This unique tool offers an extensive outlook for your business’s financial strategy. Simply input detailed financial data spanning five years, including revenue projections, investment plans, and expected market growth. Visually engaging bar charts of key metrics help turn data into engaging narratives.
Small Business Financial Forecast Template
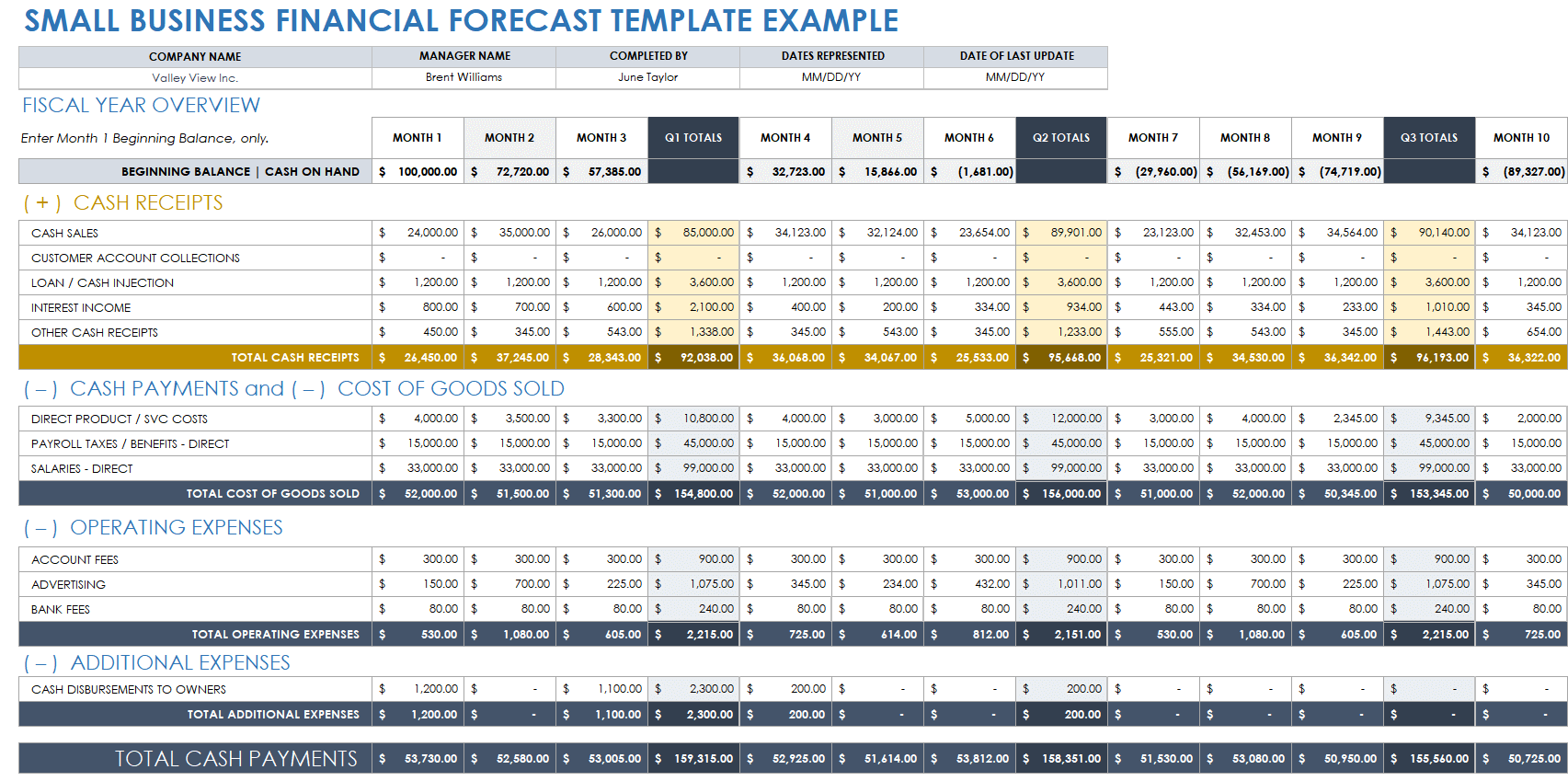
Download a Sample Small Business Financial Forecast Template for
Download a Blank Small Business Financial Forecast Template for
Excel | Google Sheets
The small business financial forecast template is tailored specifically for the scale and specific requirements of small enterprises. Business owners and financial managers can simply input data such as projected sales or expenses. Available with or without sample text, this tool offers the ability to do the following: envision straightforward financial planning; anticipate future financial needs and challenges; make informed decisions; and steer the business toward steady growth.
Elements in a Financial Projection Template
The elements in a financial projection template include future sales, costs, profits, and cash flow. This template illustrates expected receivables, payables, and break-even dates. This tool helps you plan for your business's financial future and growth.
Here are the standard elements in a financial projection template:
- Revenue Projection: This estimates future income from various sources over a specific period.
- Expense Forecast: This predicts future costs, including both fixed and variable expenses.
- Profit and Loss Forecast: This projects the profit or loss by subtracting projected expenses from projected revenues.
- Cash-Flow Projection: This assesses the inflows and outflows of cash, indicating liquidity over time.
- Balance Sheet Projection: This predicts the future financial position, showing assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Break-Even Analysis: This calculates the point at which total revenues equal total costs.
- Capital Expenditure Forecast: This estimates future spending on fixed assets such as equipment or property.
- Debt Repayment Plan: This outlines the schedule for paying back any borrowed funds.
- Sales Forecast: This predicts future sales volume, often broken down by product or service.
- Gross Margin Analysis: This looks at the difference between revenue and cost of goods sold.
Types of Financial Projection and Forecasting Templates
There are many types of financial projection and forecasting templates: basic templates for small businesses; detailed ones for big companies; special ones for startup businesses; and others. There are also sales forecasts, cash-flow estimates, and profit and loss projections.
In addition, financial projection and forecasting templates include long-term planning templates, break-even analyses, budget forecasts, and templates made for specific industries such as retail or manufacturing.
Each template serves different financial planning needs. Determine which one best suits your requirements based on the scale of your business, the complexity of its financial structure, and the specific department that you want to analyze.
Here's a list of the top types of financial projection and forecasting templates:
- Basic Financial Projection Template: Ideal for small businesses or startups, this template provides a straightforward approach to forecasting revenue, expenses, and cash flow.
- Detailed Financial Projection Template: Best for larger businesses or those with complex financial structures, this template offers in-depth projections, including balance sheets, income statements, and cash-flow statements.
- Startup Financial Projection Template: Tailored for startups, this template focuses on funding requirements and early-stage revenue forecasts, both crucial for attracting investors and planning initial operations.
- Sales Forecasting Template: Used by sales and marketing teams to predict future sales, this template helps you set targets and plan marketing strategies.
- Cash-Flow Forecast Template: Essential for financial managers who need to monitor the liquidity of the business, this template projects cash inflows and outflows over a period.
- Profit and Loss Forecast Template (P&L): Useful for business owners and financial officers who need to anticipate profit margins, this template enables you to forecast revenues and expenses.
- Three-Year / Five-Year Financial Projection Template: Suitable for long-term business planning, these templates provide a broader view of your company’s financial future, improving your development strategy and investor presentations.
- Break-Even Analysis Template: Used by business strategists and financial analysts, this template helps you determine when your business will become profitable.
- Budget Forecasting Template: Designed for budget managers, this template uses historical financial data to help you plan your future spending.
- Sector-Specific Financial Projection Template: Designed for specific industries (such as retail or manufacturing), these templates take into account industry-specific factors and benchmarks.
Related Financial Templates
Check out this list of free financial templates related to financial projections and forecasting. You'll find templates for budgeting, tracking profits and losses, planning your finances, and more. These tools help keep your company’s money matters organized and clear.
Free Project Budget Templates
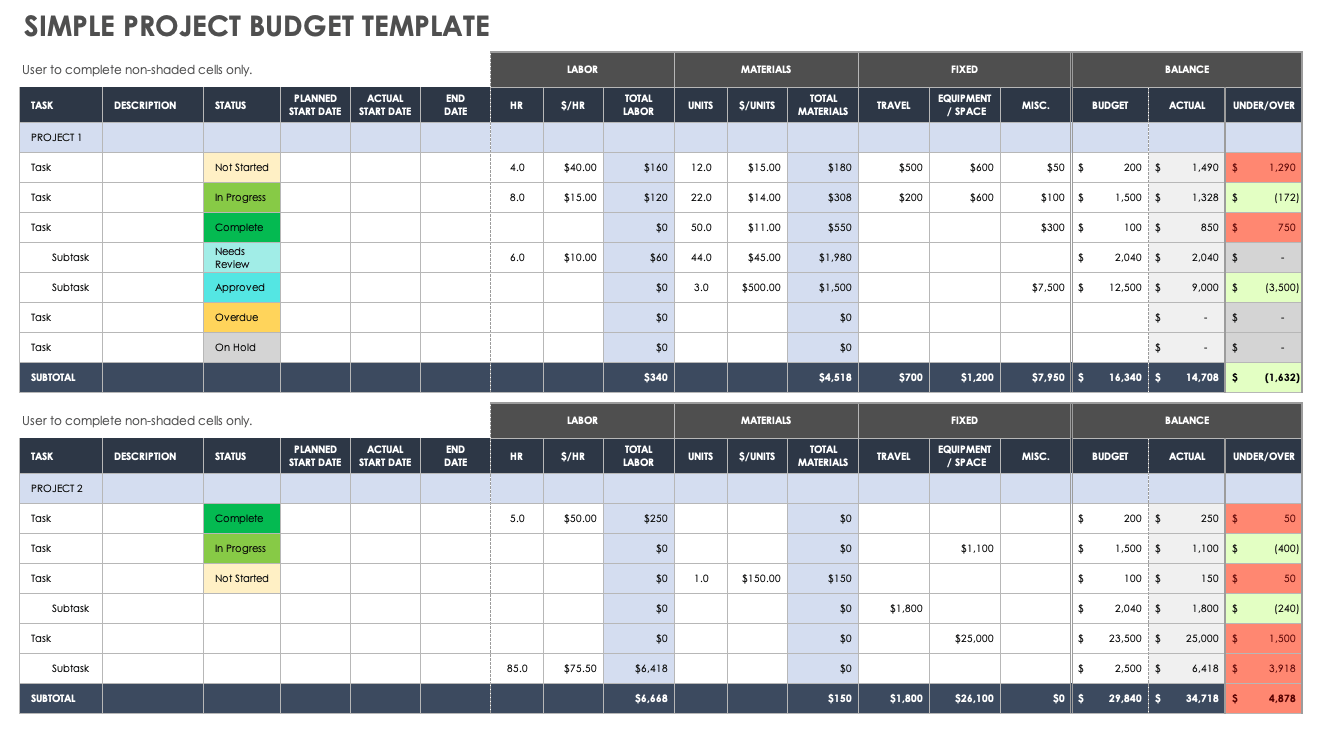
Use one of these project budget templates to maintain control over project finances, ensuring costs stay aligned with the allocated budget and improving overall financial management.
Free Monthly Budget Templates
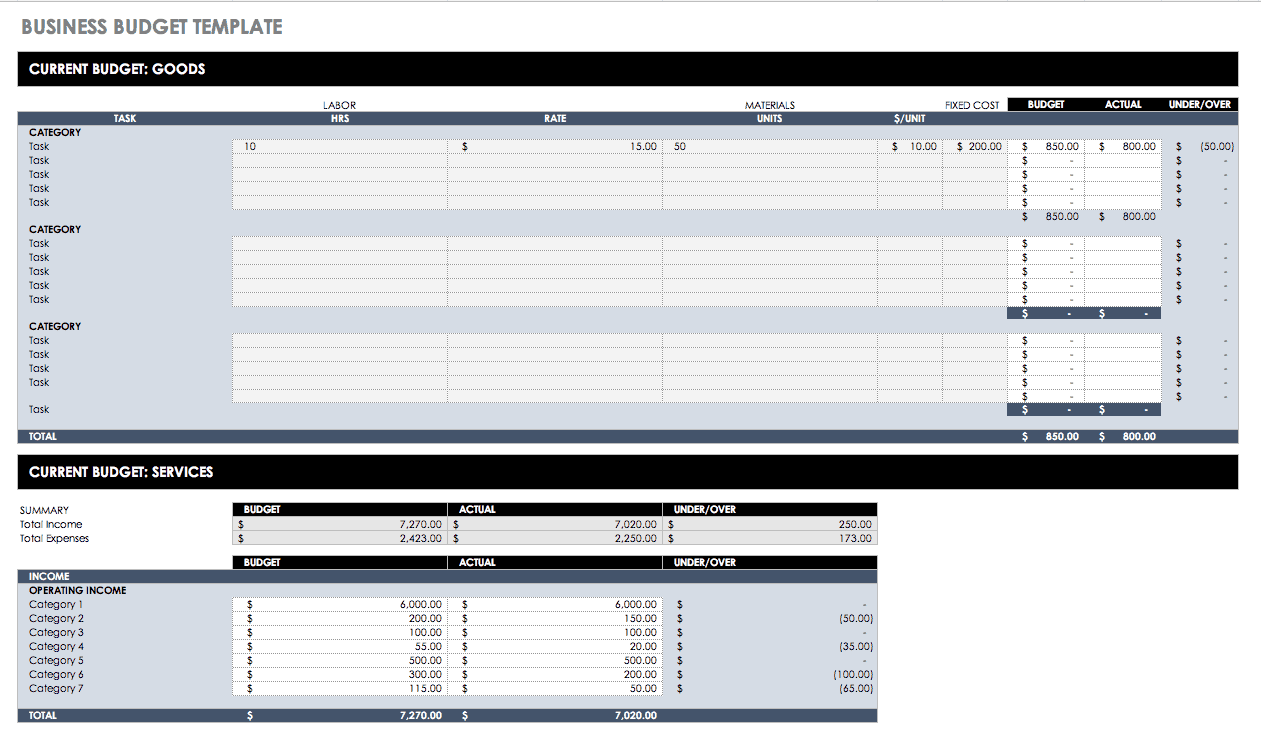
Use one of these monthly budget templates to effectively track and manage your business’s income and expenses, helping you plan financially and save money.
Free Expense Report Templates
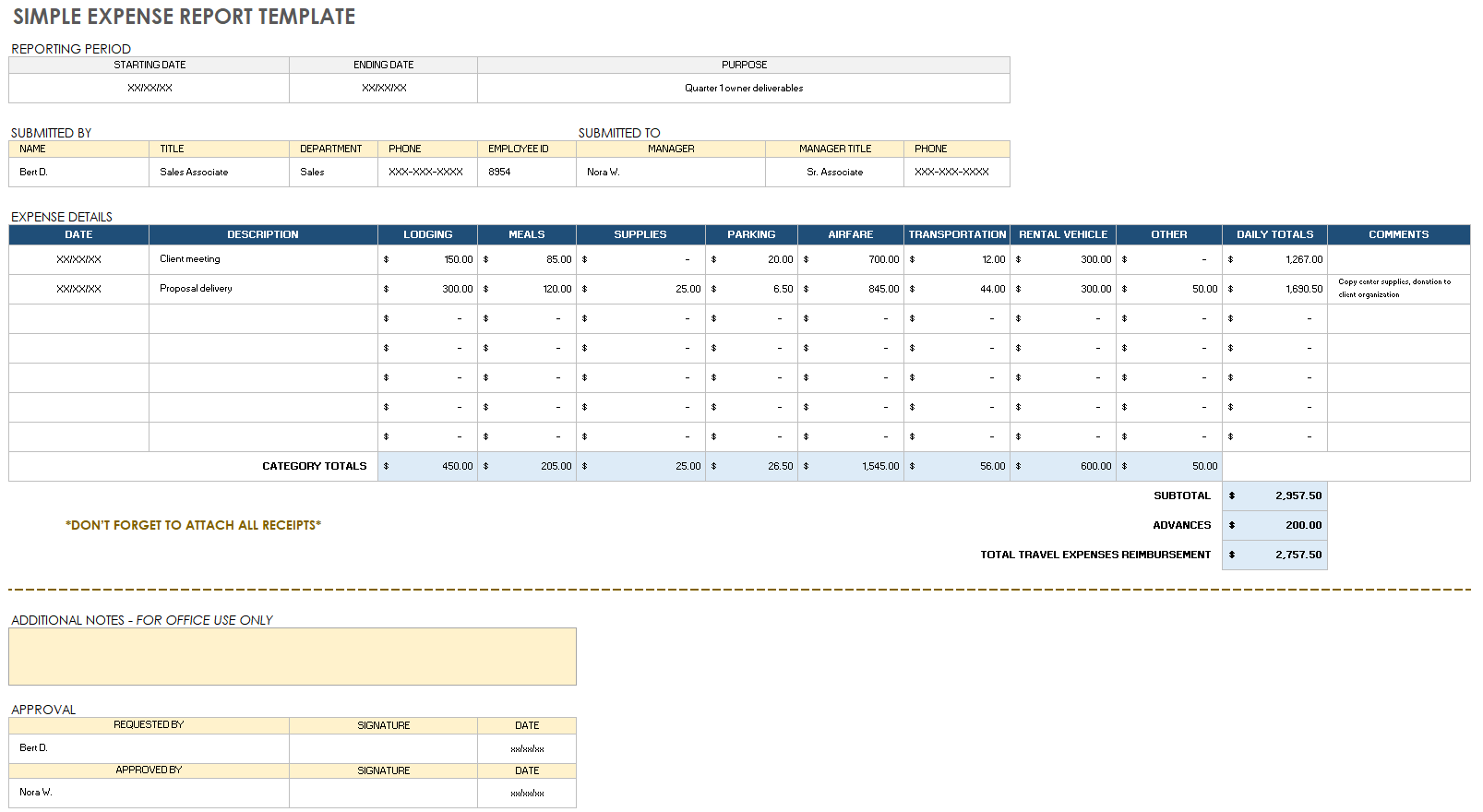
Use one of these expense report templates to systematically track and document all business-related expenditures, ensuring accurate reimbursement and efficient financial record-keeping.
Free Balance Sheet Templates
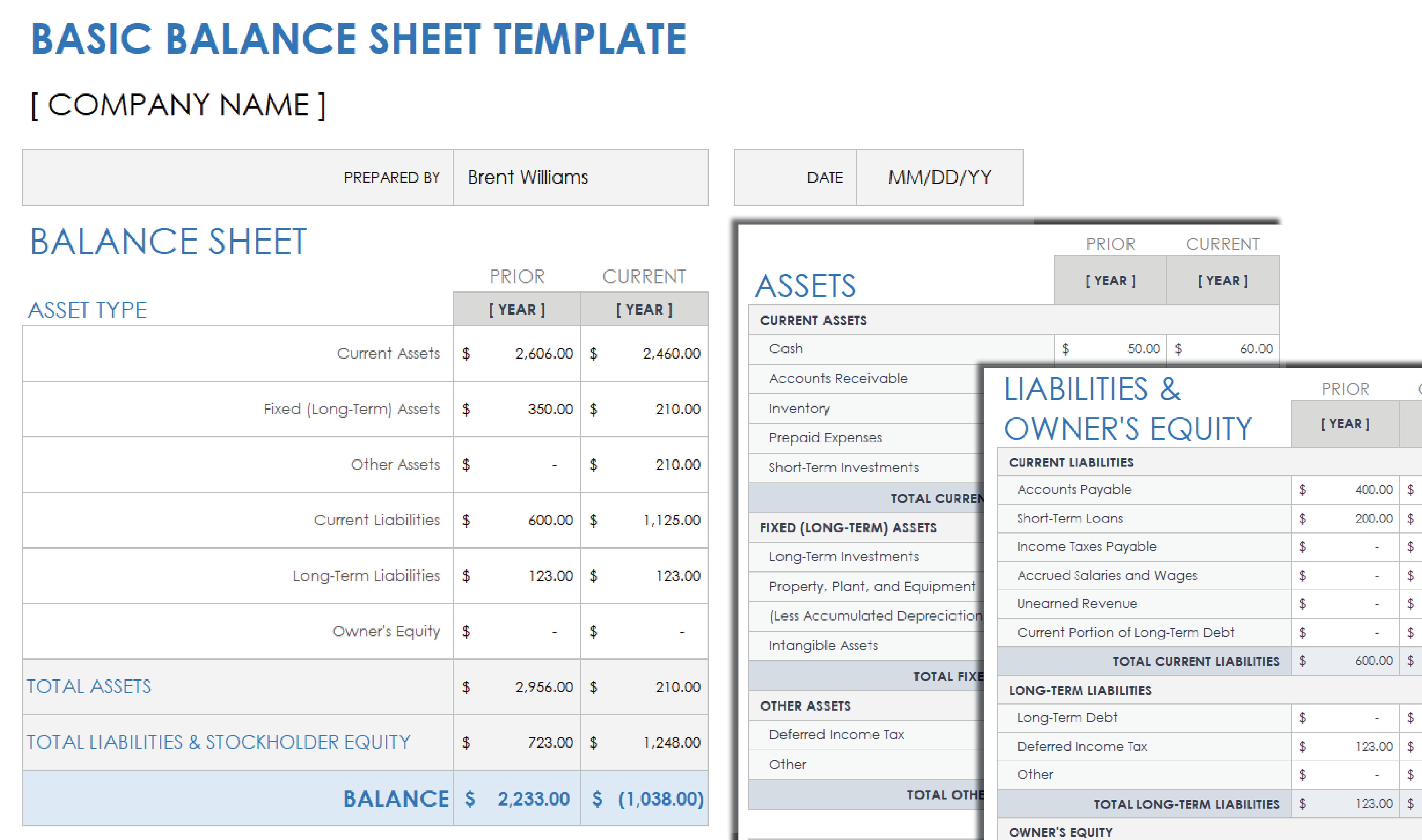
Use one of these balance sheet templates to summarize your company's financial position at a given time.
Free Cash-Flow Forecast Templates
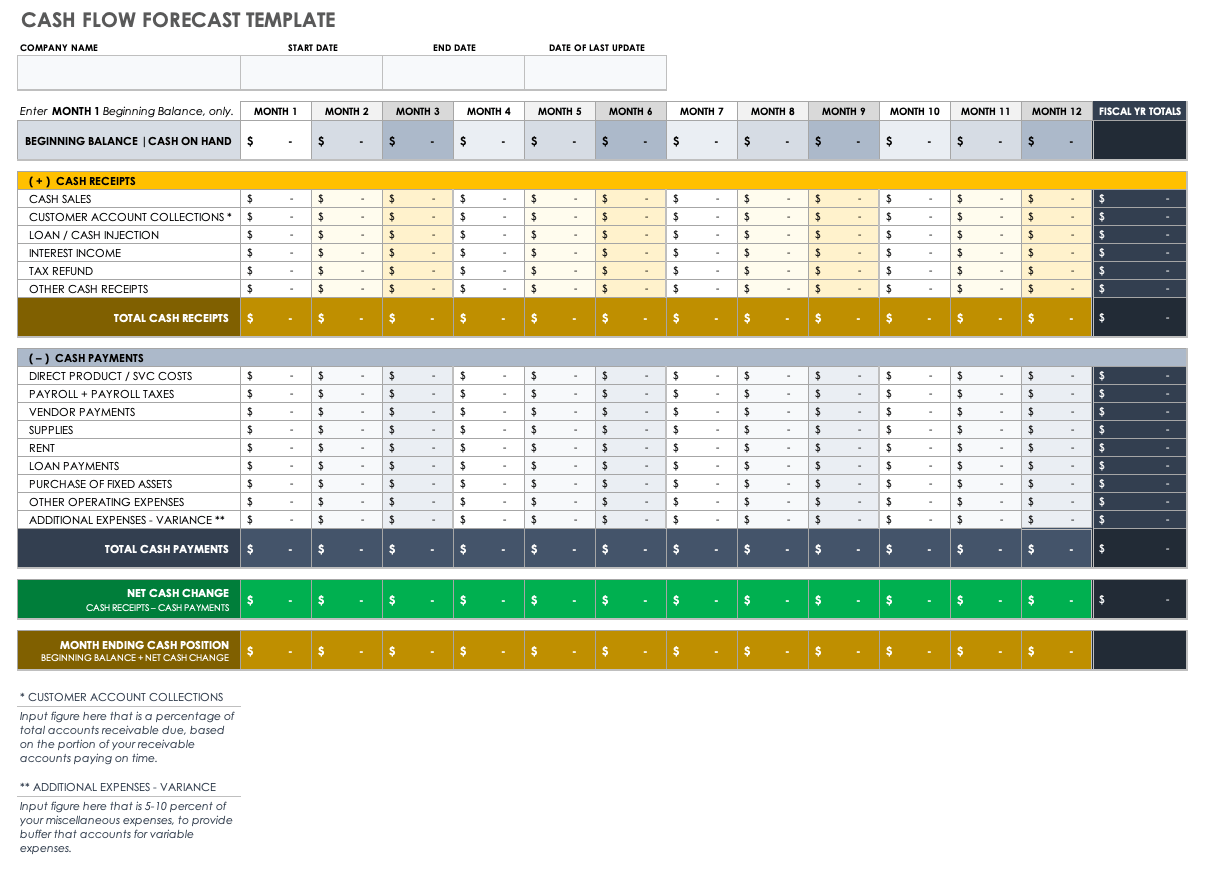
Use one of these cash-flow forecast templates to predict future cash inflows and outflows, helping you manage liquidity and make informed financial decisions.
Free Cash-Flow Statement Templates
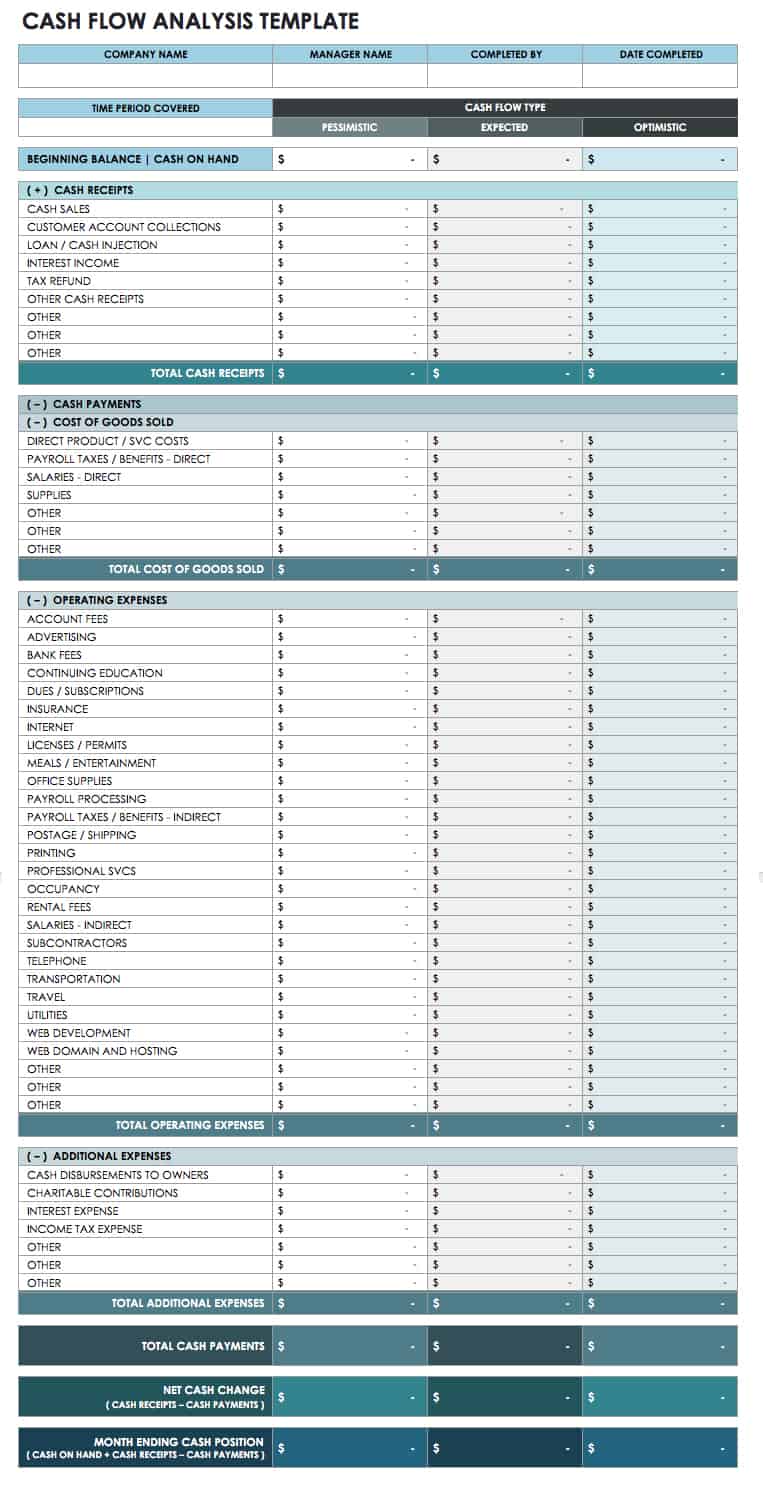
Use one of these cash-flow statement templates to track the movement of cash in and out of your business, so you can assess your company’s level of liquidity and financial stability.
Free Discounted Cash-Flow (DCF) Templates
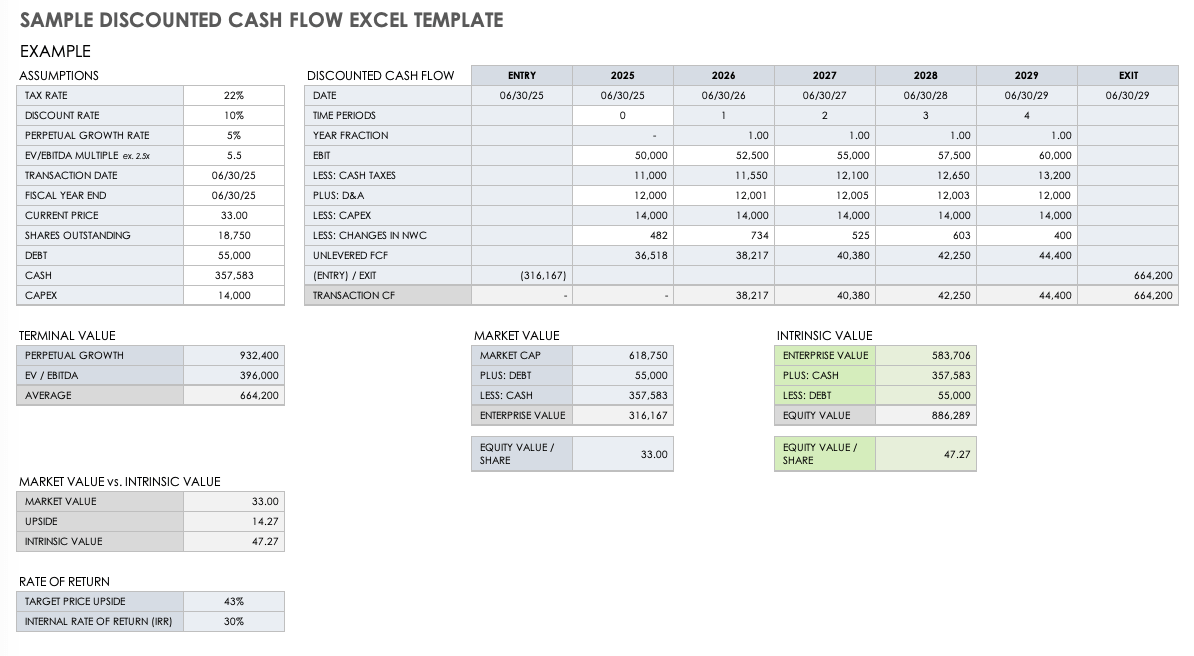
Use one of these discounted cash-flow (DCF) templates to evaluate the profitability of investments or projects by calculating their present value based on future cash flows.
Free Financial Dashboard Templates
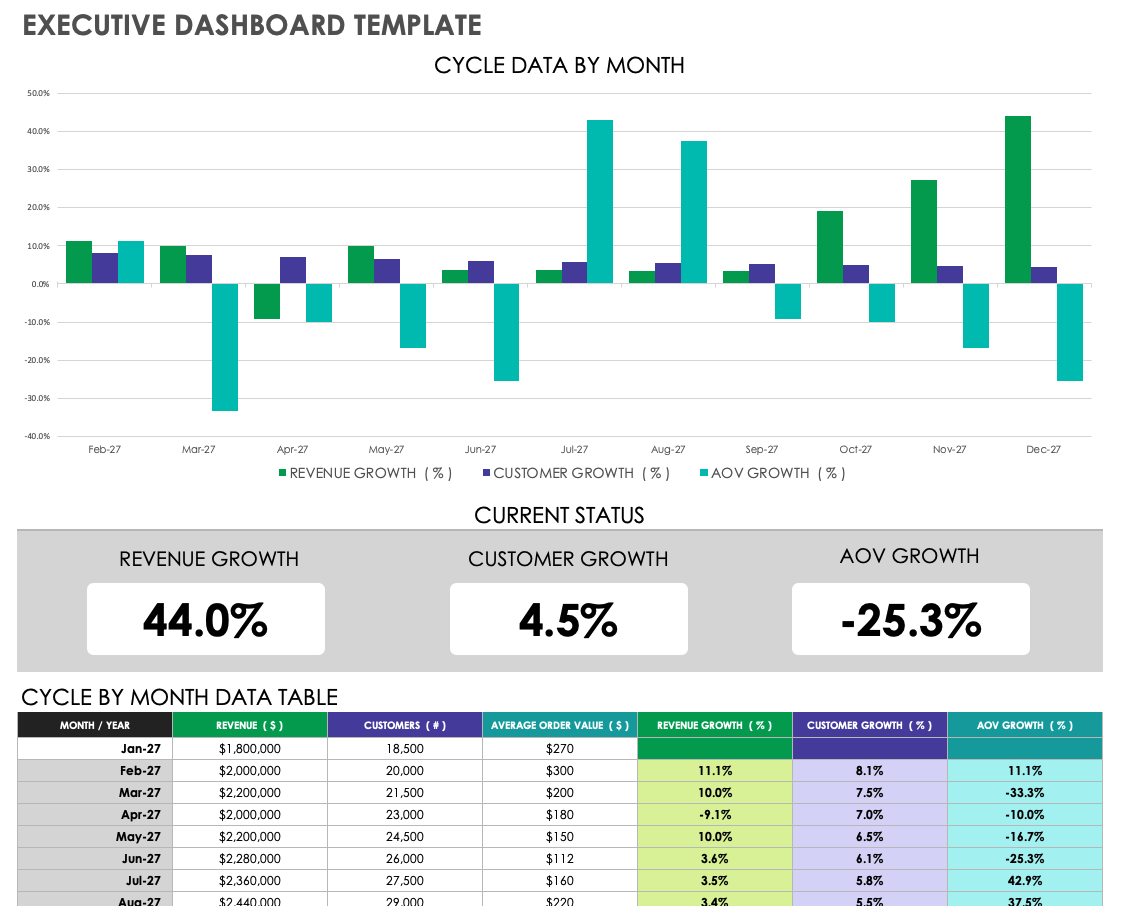
Use one of these financial dashboard templates to get an at-a-glance view of key financial metrics, so you can make decisions quickly and manage finances effectively.
Related Customer Stories
Free financial planning templates.
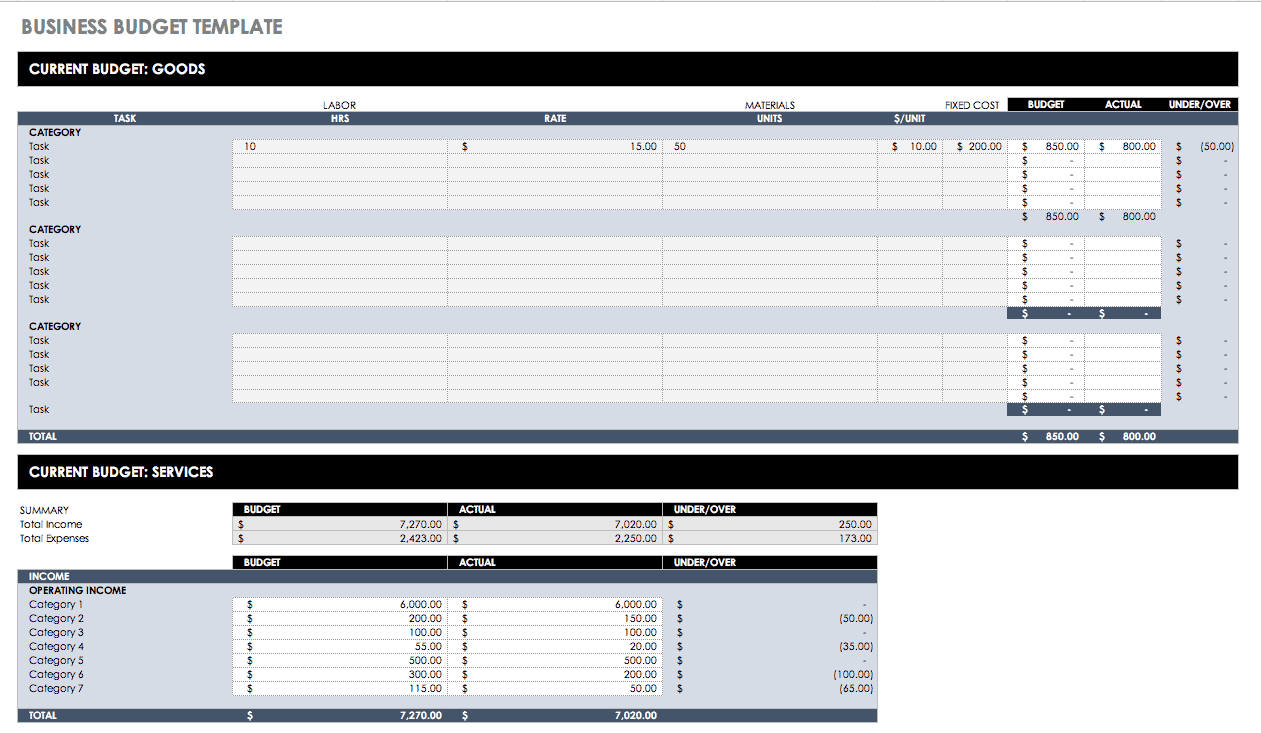
Use one of these financial planning templates to strategically organize and forecast future finances, helping you set realistic financial goals and ensure long-term business growth.
Free Profit and Loss (P&L) Templates
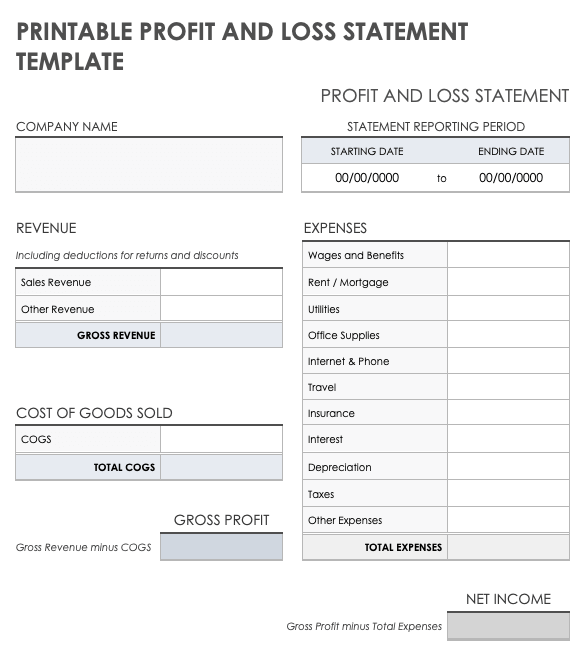
Use one of these profit and loss (P&L) templates to systematically track income and expenses, giving you a clear picture of your company's profitability over a specific period.
Free Billing and Invoice Templates
Use one of these billing and invoice templates to streamline the invoicing process and ensure that you bill clients accurately and professionally for services or products.
Plan and Manage Your Company’s Financial Future with Financial Projection and Forecasting Templates from Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
Financial modeling spreadsheets and templates in Excel & Google Sheets
- Your cart is empty.

Retail Business Plan Examples That Inspire Success

Creating a successful retail business requires careful planning and sharp insights, and one of the most vital tools for achieving this is a comprehensive retail business plan. Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting your journey, having a well-structured business plan can significantly increase your chances of success. It not only helps in outlining your goals and strategies but also serves as a vital communication tool for potential investors and stakeholders. By including specific retail business plan examples, you can better showcase your vision and operational strategies, thereby enhancing the credibility of your overall plan. A solid plan not only identifies the direction of your retail venture but also anticipates the challenges you may face along the way.
As you embark on the journey of creating your retail business plan, understanding key components will be essential. This article aims to shed light on the fundamental elements that contribute to effective retail business plan examples. From the executive summary to market analysis, each section plays an important role in setting a strong foundation for your business. By examining these components in detail, you can cultivate a deeper understanding of what makes a retail business plan not only informative but also actionable. In essence, this guide will provide you with practical insights to craft a robust plan that aligns with your business objectives and market demands.
Key Elements of Effective Retail Business Plan Examples
Creating an effective retail business plan is essential for anyone looking to start or grow a retail business. It sets the foundation for your venture and provides a roadmap for financial success. Here are some key elements that should be included in your retail business plan examples to ensure it is both informative and insightful.
Executive Summary
Your retail business plan should begin with an executive summary. This section provides a snapshot of your business idea, including the mission statement and the vision for your retail operation. Make sure to highlight the unique selling proposition (USP) that distinguishes your business from competitors. A well-crafted executive summary grabs attention and encourages potential investors or partners to read on.
Market Analysis
Understanding the market you’re entering is crucial. Conduct thorough market research to identify your target audience, their shopping behaviors, and preferences. Your market analysis should include:
- Industry Overview: Discuss the current trends and dynamics affecting the retail industry.
- Target Audience: Define who your customers are. Are they families, young professionals, or retirees?
- Competitive Analysis: Identify your key competitors and explain how you plan to differentiate your offerings.
Sales and Marketing Strategy
Your sales and marketing strategy outlines how you will attract and retain customers. Be as specific as possible. Here are some elements to include:
- Promotion: What marketing channels will you use? This could range from social media to local newspapers.
- Pricing Strategy: How will you price your products or services? Consider going through cost-plus or competitive pricing models.
- Sales Process: Describe your approach to sales, including any training for staff and customer service initiatives.
Operational Plan
This section explains how your retail business will function daily. You’ll want to offer clear details on several key aspects:
- Location: Describe the business location and why it’s suitable for your target market.
- Inventory Management: Outline how you plan to manage your inventory, including ordering and stocking.
- Technology: Discuss any software or systems you will use for sales, inventory, and customer relationship management .
Financial Projections
One of the most critical parts of your retail business plan is the financial projections section. Clearly outline your expected revenue, profit margins, and expenses. Essential components of this section include:
- Sales Forecast: Predict your sales for the next 1-3 years based on market research.
- Break-even Analysis: Identify how long it will take to cover your initial investment.
- Funding Requirements: If you’re seeking investment, specify how much you need and how you plan to use the funds.
Management Team
Your management team plays a vital role in your retail business’s success. Include bios of key team members, outlining their experience and skills. Don’t forget to highlight what each member brings to the table, as this will instill confidence in investors or partners.
Include an appendix if you have additional information relevant to your business plan that can’t be included in the main sections. This could contain charts, graphs, or important legal documents.
Crafting a well-rounded retail business plan is a critical step toward achieving your entrepreneurial goals. Make sure you cover all these elements in your examples to attract investors and guide your operations effectively. Whether you’re opening a small boutique or a large department store, a solid business plan will lay the foundation for sustained success in the retail industry.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Retail Business Plans
Creating a retail business plan is an essential step for anyone looking to start or grow a retail business. This plan serves as a roadmap that outlines your strategy, objectives, and the steps needed to reach your goals. However, many entrepreneurs make common mistakes that can lead to setbacks or even failure. By understanding these pitfalls, you can ensure that your retail business plan is effective and sets you up for success.
Neglecting Market Research
One of the primary mistakes people make is skipping thorough market research. Knowing your target audience and understanding the competition is vital. It’s not enough to assume that your product will sell. You must gather data on customer preferences, pricing strategies, and market trends. This insight will help you tailor your offerings and marketing efforts effectively.
Setting Unrealistic Financial Projections
Financial projections are a crucial component of your business plan, but many entrepreneurs set overly optimistic sales targets. While it’s great to be ambitious, unrealistic projections can mislead investors and set you up for disappointment. Instead, base your predictions on solid data and historical trends. Consider creating several scenarios—best-case, worst-case, and realistic expectations—to prepare for different outcomes.
Ignoring Inventory Management Strategies
Inventory management plays a significant role in the success of your retail business. A common mistake is not detailing how you will manage stock levels. Consider the following strategies:
- Just-In-Time (JIT): Reduce storage costs by receiving goods only as needed.
- ABC Analysis: Prioritize your inventory based on sales volume and profitability.
- Safety Stock: Maintain an additional stock to prevent stockouts.
Including a clear inventory management strategy in your business plan can help you avoid cash flow issues and ensure customer satisfaction.
Overlooking the Importance of Marketing
Effective marketing strategies are fundamental to getting your brand recognized and driving sales. A common mistake is failing to outline a comprehensive marketing plan in your business document. Your marketing strategy should detail how you will reach potential customers, including:
- Online and offline advertising
- Social media strategies
- Promotional events and discounts
- Email marketing campaigns
Your business plan should clearly state how you plan to communicate your value proposition and convert leads into customers.
Being Vague about Business Operations
Another frequent oversight in retail business plans is a lack of details regarding operational processes. You need to outline how everyday activities will be conducted. Specifics about staffing, supply chain logistics, and day-to-day management contribute to a well-rounded business plan. Make sure to address:
- Staffing needs and roles
- Supplier relations and contracts
- Store layout and customer experience strategies
Failing to Establish Clear Objectives
Your retail business plan should clearly define what success looks like. Many entrepreneurs mention broad goals without measurable objectives. Instead of saying, “I want to increase sales,” consider stating, “I aim to boost sales by 20% within the first year by launching a loyalty program and expanding our product range.” Clear, measurable objectives help track progress and adjust strategies as needed.
Neglecting to Prepare for Challenges
Every business faces challenges, but many retail entrepreneurs do not include contingency plans in their business documents. Address potential risks, such as economic downturns, changed consumer behavior, or supply chain disruptions. By outlining how you will handle challenges, it shows investors that you are prepared and resilient.
Not Reviewing and Revising the Plan Regularly
A common misconception is that a business plan is a one-time document. In reality, it should be a living document that is reviewed and revised regularly. As your business grows and the market evolves, you should adapt your goals and strategies accordingly. Schedule regular reviews to assess performance against objectives and revise your business plan as necessary.
A well-crafted retail business plan is vital for success. By avoiding these common mistakes, you can develop a clearer, more effective strategy that increases your chances of thriving in the competitive retail landscape. Your future customers, investors, and employees will appreciate the thoughtfulness of a comprehensive document that thoroughly outlines your vision and operational goals.
How to Tailor Retail Business Plans for Various Markets
Creating a retail business plan involves careful consideration of the market you aim to serve. Each market has its unique characteristics, challenges, and opportunities, which means you need to tailor your business plan accordingly. Adapting your strategy can define your success and engagement with potential customers. Below are important strategies for customizing your retail business plan for various markets.
Understand Market Research
Before crafting your plan, invest time in market research. Look at demographic trends, consumer behavior, and local economics. Knowledge of your target audience will shape your strategies effectively. Here are key aspects to focus on:
- Demographics: Age, gender, income level, and education.
- Trends: What’s popular in the market currently?
- Competitor Analysis: Who are your competitors? What strategies are they using?
- Customer Preferences: What do potential customers in this market value most?
Define Your Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
Your Unique Selling Proposition sets you apart from competitors. It answers why customers should choose your retail business over others. Tailoring your USP to resonate with the specific market’s needs helps in building brand loyalty. Elements to consider while defining your USP include:
- Local Sourcing: If your market values local products, emphasize this aspect.
- Quality over Quantity: Highlight quality if your target market leans toward premium options.
- Convenience: For busy consumers, emphasize fast shipping or easy returns.
Develop a Marketing Strategy
Effective marketing is key to reaching your audience. The channels you choose should reflect their preferences. Whether it’s social media, traditional advertising, or influencer partnerships, a targeted marketing strategy can elevate your visibility. Consider the following:
- Social Media Platforms: Use the platforms where your target demographic spends their time.
- Content Marketing: Create blog posts or articles that directly address your market’s interests.
- Local Advertising: Flyers or promotions in community centers can yield local engagement.
Align Your Product Offering
Your product range must align with the specific market demands. Tailoring your inventory can significantly improve your sales. Take into account:
- Seasonal Demands: Adjust your stock based on seasonality specific to the market.
- Product Variations: Consider different sizes, colors, or styles that may appeal to the local audience.
- Price Sensitivity: Understand the average spending power and adjust your product price points.
Focus on Customer Service
Outstanding customer service can differentiate your retail business significantly. Developing a customer-service strategy tailored to your market’s expectations is paramount. Strategies include:
- Personalization: Provide tailored recommendations based on customer preferences.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Implement easy ways for customers to give feedback, such as surveys or suggestion boxes.
- Training Staff: Ensure that your team is knowledgeable about the local culture and can interact positively with customers.
Adapt Your Financial Projections
Your financial plan should reflect the realities of your chosen market. Ensure your projections are realistic based on thorough research. Key components include:
- Startup Costs: Estimate reliable costs based on local suppliers and rent.
- Profit Margins: Tailor projections on margins based on market price sensitivities.
- Sales Forecasts: Use historical data relevant to similar businesses for a realistic outlook.
When tailoring your retail business plan for various markets, the focus should be on conducting thorough research, developing a suitable marketing strategy, aligning product offerings, focusing on customer service, and adapting financial projections. Each of these elements plays a critical role in creating a successful retail venture that speaks directly to your target audience.
The Role of Market Research in Crafting a Retail Business Plan
Understanding the market is crucial when you are crafting a retail business plan. Market research provides valuable insights that can shape your strategy, align your offerings with customer needs, and keep you ahead of competitors. Here’s how you can leverage market research effectively.
Identifying Target Customers
The first step in market research is identifying your target customers. You need to know who you are selling to, which helps in tailoring your offerings. Consider these factors:
- Demographics: Age, gender, income level, and education are key factors that define your target market.
- Psychographics: Look into customer interests, lifestyles, and values to understand their purchasing behavior.
- Geographics: Understanding where your customers live, work, and play can help you choose the right location for your retail outlet.
Analyzing Competitors
Market research helps you analyze your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses. By studying their business models, marketing strategies, and customer feedback, you can find opportunities for differentiation. Here’s how to go about it:
- Competitive Analysis: Identify your main competitors and assess their market position.
- SWOT Analysis: Understand the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of your competitors. This can help you spot gaps in the market.
- Market Trends: Stay updated on the latest trends in retail. What are the customers responding to? What innovations are competitors implementing?
Consumer Buying Behavior
Knowing how consumers make purchasing decisions is vital. Market research allows you to study various aspects, including:
- Factors Influencing Purchases: Understand if customers prioritize price, quality, branding, or customer service when buying.
- Shopping Preferences: Know whether customers prefer shopping online, in-store, or through mobile devices.
- Seasonal Trends: Identifying peak shopping seasons can help you plan inventory and marketing strategies effectively.
Testing Your Ideas
Before launching your retail business, you can use market research to test your ideas. This is how:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Conduct surveys to gather opinions about your products and services. This helps you validate concepts before investing heavily.
- Focus Groups: Organize focus groups to gain deeper insights into customer perceptions and preferences.
- Prototype Testing: If applicable, create a prototype of your product and get feedback to refine it.
Financial Forecasting
Accurate financial forecasts are essential for any retail business plan. Market research can help you make informed projections. Consider these elements:
- Sales Projections: Use data on market size and consumer behavior to estimate your potential sales volume.
- Pricing Strategy: Market research will help you determine how to price your products competitively while maintaining profit margins.
- Market Growth: Understand the overall growth prospects of your sector to anticipate opportunities and challenges.
Regulatory and Compliance Factors
In retail, being aware of regulations and industry standards is important. Market research can reveal:
- Licenses and Permits: Identify necessary permits you need to operate legally in your location.
- Industry Standards: Ensure your retail offerings meet the relevant health, safety, and quality standards.
- Environmental Regulations: Consider sustainability practices that might be important to your customers.
Comprehensive market research is not just a formality; it’s the foundation of a successful retail business plan. By understanding your customers, analyzing competition, testing ideas, and forecasting finances, you position your business for success. Engage in ongoing research, and adapt your plan as market dynamics shift. This proactive approach will keep you competitive and increase the likelihood of long-term sustainability in the retail market.
Financial Projections and Budgeting in Retail Business Plans
When creating a retail business plan, financial projections and budgeting are essential elements that can make or break your venture. These components will not only help you estimate your expenses and revenues but also provide clarity to potential investors and lenders about your growth potential. By addressing these areas thoroughly, you can set realistic goals and build a robust roadmap for your business.
Understanding Financial Projections
Financial projections serve as your business’s financial forecast for the next three to five years. They predict how much money your retail business will make, spend, and keep. To make informed projections, consider the following key components:
- Sales Forecast: Estimate your monthly sales based on market research and analysis of competitors. Consider seasonal trends, customer demand, and pricing strategies.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Calculate the direct costs linked to producing your goods. This includes material costs, labor, and any other expenses directly tied to creating your products.
- Operating Expenses: Include all the necessary ongoing costs to run your business, such as rent, utilities, salaries, marketing, and insurance.
Your financial projections should provide a well-rounded picture of your retail business’s potential. Use realistic assumptions based on data rather than guesswork, as this will instill confidence in your business plan.
Budgeting Basics for Retail
Budgeting is the process of creating a plan to spend your money wisely. With a sound budget, you can manage your resources effectively while keeping your financial goals in sight. Here are key steps to create a productive budget:
- List Income Sources: Identify all potential revenue streams for your retail business. This can include sales from different product lines, services, and online sales.
- Estimate Fixed Costs: Fixed costs don’t change with sales volume. This includes rent and salaries. Knowing these costs helps you determine the minimum sales you need to break even.
- Variable Costs: These costs fluctuate with your production or sales volume. They include COGS, utility expenses, and marketing costs. Assess how these costs will change with different sales levels.
- Set Up a Cash Flow Statement: This statement helps you track the flow of cash in and out of your retail business. Understanding your cash flow will enable you to predict potential shortfalls.
Keeping an ongoing budget will allow you to spot discrepancies early, making adjustments easier. Regularly review your budget against actual performance to better understand your financial dynamics.
Importance of Break-Even Analysis
A break-even analysis reveals the point at which your retail business covers all expenses and begins to make a profit. This is a crucial metric as it helps in setting realistic sales targets. To calculate the break-even point, you need to determine your fixed and variable costs:
Break-even Point Formula = Fixed Costs / (Selling Price per Unit – Variable Cost per Unit)
Knowing your break-even point lets you establish sales goals and provides critical insights into your pricing strategy. If your break-even point is too high, it may be necessary to reevaluate your costs or adjust your pricing.
Utilizing Financial Statements
Creating financial statements helps in providing a comprehensive overview of your business’s financial health. Key statements to consider include:
- Income Statement: Reflects your revenues and expenses over a specific period, which helps to evaluate profitability.
- Balance Sheet: Offers a snapshot of your assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific time.
- Cash Flow Statement: Provides insights into cash inflows and outflows, crucial for maintaining liquidity.
By regularly updating these financial statements, you can monitor your financial health, make informed decisions, and adjust your strategies accordingly.
Preparing for Investor Engagement
If you’re seeking investment for your retail business, strong financial projections and a solid budget are vital. Investors want to see realistic figures that demonstrate growth potential and the ability to manage cash flow effectively. Present your projections clearly, and be prepared to explain how you arrived at your estimates.
Investors often appreciate transparency. Do not shy away from discussing risks or uncertainties in your projections. Showcasing how you plan to mitigate these risks can build trust and confidence among potential investors.
Having strong financial projections and a well-thought-out budget is crucial for the success of your retail business. These components provide clarity, facilitate informed decision-making, and help you attract investments. As you develop your retail business plan, prioritize these areas to build a sustainable and profitable retail venture.
Real-World Case Studies: Successful Retail Business Plans
When diving into the world of retail, a solid business plan can be your roadmap to success. Real-world case studies of successful retail business plans showcase diverse strategies and approaches that different brands have used to reach their goals. By examining these examples, you can glean valuable insights that can guide your own retail venture.
First, let’s look at **Target**. Initially a discount store, Target shifted its brand identity to compete with upscale retailers. Their business plan emphasized enhancing the customer experience, focusing on product quality, and effective marketing strategies. By defining a clear target demographic and integrating stylish, low-cost products, they successfully attracted a broader audience. This shift not only boosted sales but also solidified Target’s position in the retail sector.
Another inspiring example is **Zara**, part of the Inditex group. Zara’s retail business plan is built on a rapid production model and trend responsiveness. Unlike traditional retailers that forecast fashion trends months in advance, Zara produces small quantities of a design and gauging customer interest before mass production. This ability to adapt quickly has allowed Zara to stay in tune with customer desires while minimizing inventory costs. Their approach showcases the importance of flexibility in a retail plan.
Next, consider **Warby Parker**. They revolutionized the eyewear industry through a disruptive retail business plan. Instead of relying solely on physical retail spaces, Warby Parker launched an online platform allowing customers to try glasses at home before making a purchase. This direct-to-consumer model reduced overhead costs and provided a unique shopping experience that customers loved. Their plan also included a social mission—donating a pair of glasses for every pair sold—making it a brand that resonates emotionally with consumers.
One more example is **Costco**, which operates on a membership warehouse model. Their retail business plan focuses on offering quality goods at lower prices, capitalizing on bulk buying and low overhead costs. Costco utilizes a no-frills shopping experience that emphasizes value over luxury. They keep their business model simple, offering a limited selection of high-quality items, and relying heavily on member loyalty to generate consistent revenue. This approach allows them to compete against larger general retailers effectively.
To further illustrate successful retail business plans, let’s look at some key elements that these brands implemented:
- Target Market Understanding: Each of these retailers knew their customer base well and tailored their offerings accordingly.
- Value Proposition: Whether through quality, affordability, or a unique shopping experience, each brand provided clear value to consumers.
- Operational Efficiency: Efficient production and operational models helped these retailers reduce costs and improve profit margins.
- Brand Loyalty: Creating an emotional connection through social responsibility or distinctive shopping experiences helped foster loyalty among their customers.
- Flexibility and Adaptation: Rapidly adjusting to market trends or customer feedback played a critical role in many of these case studies.
Learning from these examples can be particularly beneficial for aspiring retail entrepreneurs. As you develop your retail business plan, think about how you can infuse similar strategies into your approach. Ask yourself some questions based on these case studies:
- What is your unique value proposition? How can you stand out in a crowded marketplace?
- How well do you understand your target audience, and how can you tailor your offerings to meet their needs?
- What type of operational efficiencies can you implement to keep costs low while maintaining quality?
- How can you build brand loyalty and create emotional connections with your customers?
- Are you prepared to adapt your business model based on market trends and customer feedback?
Your retail business plan doesn’t have to reinvent the wheel. By studying successful examples like Target, Zara, Warby Parker, and Costco, you can find inspiration to shape your strategy. Remember, a strong business plan is not just about financial forecasts; it’s about a comprehensive approach to addressing customer needs, market dynamics, and your unique place in the retail landscape.
Using real-world case studies of successful retail business plans provides practical insights that can help you avoid common pitfalls and enhance your chances of success. The journey of launching a retail business can be challenging, but with lessons learned from those who came before you, you’re better equipped to navigate the complexities of the market with confidence.
Tips for Presenting Your Retail Business Plan to Investors
When it’s time to showcase your retail business plan to potential investors, you want to make a lasting impression. A well-prepared presentation can make all the difference when securing funding. Here are some essential tips to help you present your retail business plan effectively and confidently.
Understand Your Audience
Before creating your presentation, take time to understand who your investors are. Ask yourself:
- What do they value most? Is it profitability, growth potential, or something else?
- What industries do they typically invest in? Are they familiar with retail?
- Have they supported similar ventures? This can provide insight into what they expect from your plan.
This knowledge will allow you to tailor your presentation to meet their expectations and resonate with their interests.
Be Clear and Concise
Investors appreciate clarity. Your retail business plan should be straightforward and to the point. Aim to cover critical areas such as:
- Your business concept and unique selling proposition (USP)
- Target market and customer demographic
- Market analysis and competition
- Financial projections and funding requirements
Use bullet points, charts, and visuals to present this information. Visual aids can enhance understanding and retention, allowing investors to grasp complex concepts quickly.
Tell Your Story
A compelling narrative can capture the attention of investors. Share your journey—what inspired you to start this retail venture? Discuss the challenges you’ve faced and how you’ve overcome them. Make your story relatable, and let your passion shine through.
This personal touch helps build an emotional connection, demonstrating your commitment and dedication to the business. It’s not just about the numbers; it’s about the people behind them.
Highlight Market Potential
Buddying up your business plan with industry statistics can significantly strengthen your case. Investors want to see that there’s a demand for your offerings. Provide data on market size, growth trends, and consumer behavior. This will give your plan credibility and paint a picture of lucrative opportunities.
Consider discussing:
- Emerging trends in retail that align with your business
- Demographics of your target audience and their buying behaviors
- Forecasted growth in your market niche
Present Strong Financial Projections
Financials are a key focus area for any investor. They want to know how their investment will benefit them. Be prepared to present:
- Revenue forecasts for at least the next three years
- Estimated costs, including startup costs and operational expenses
- Break-even analysis and expected profit margins
- Potential return on investment (ROI)
Ensure your figures are realistic and backed by research. Overly optimistic projections can raise red flags.
Prepare for Questions
Anticipate the questions investors may ask and prepare thorough responses. Common queries include:
- What are your biggest risks, and how will you mitigate them?
- Who are your competitors, and how do you plan to stand out?
- What is your marketing strategy to attract customers?
Being prepared for these questions shows that you have a comprehensive understanding of your business and the market, which builds investor confidence.
Practice Your Delivery
Your presentation skills can greatly influence the outcome of your pitch. Practice your delivery multiple times to ensure fluency and confidence. Consider the following:
- Rehearse with friends or mentors and ask for feedback.
- Time yourself to maintain an appropriate length.
- Use storytelling techniques to keep the presentation engaging.
After your presentation, don’t forget to follow up with investors. A thank-you email expressing your gratitude for their time can go a long way. Include a summary of key points discussed and a reiteration of your excitement about the opportunity to work together.
Presenting your retail business plan to investors is an opportunity to showcase your hard work and vision. By understanding your audience, being clear and concise, sharing your story, and preparing for questions, you can create a compelling pitch that engages and interests them.
With these strategies, you’re more likely to leave a positive and lasting impression, increasing your chances of securing the funding you need to bring your retail vision to life.
Crafting a successful retail business plan involves several crucial elements that can set you on a path to success. By focusing on the key components, such as clear goals, detailed market analysis, and realistic financial projections, you can create a roadmap tailored to your vision. Avoiding common pitfalls, like overly optimistic assumptions or failing to address your target audience, enhances your plan’s effectiveness and credibility.
Knowing how to tailor your business plan for various markets is vital . Each market has its unique characteristics, and a customized approach can significantly improve your chances of impressing potential investors. Market research plays a central role in this process, allowing you to understand consumer behavior, competition, and trends that affect your niche.
Financial projections are not just numbers; they tell a story about your business’s viability. Proper budgeting reflects your understanding of cash flow, expenses, and potential profits, making your plan much more compelling. Real-world case studies of successful retail businesses serve as powerful examples. They not only inspire but also provide practical insights into what works, offering strategies that can be replicated in your venture.
Presenting your retail business plan effectively is just as important as creating it. Engaging storytelling that highlights your passion and clarity can capture the interest of investors and stakeholders. By combining thorough preparation with a strategic presentation, you increase your chances of garnering the support you need for your retail venture. Embrace these strategies to build a robust retail business plan that sets you apart from the competition.

Trading Multiples / Comparables Template
A Trading Multiples/Comparables excel file with detailed company and industry margin analysis, growth analysis, and valuations analysis.
- Excel Template – $0.00 Version 1

Preferred Equity Fund Excel Model
This model was designed for use by a sponsor looking to raise a vehicle to programmatically invest in preferred equity transactions. The model can also be used for various debt instruments (senior, junior, mezzanine, etc.) as the deal level character... read more
- Full Excel Model – $174.99 Version 1
- PDF Preview w/ Condensed Rows – $0.00 Version 1
- PDF Preview w/ Expanded Rows – $0.00 Version 1

Personal Finance- University Starter Budgeting Tool
This University Starters Budgeting tool helps students manage income, expenses, and savings. It provides an easy-to-use interface for tracking monthly finances, visualizing spending categories, and setting financial goals, promoting informed decision... read more
- Excel Template – $8.88 Version 1
- PDF Preview – $0.00 Version 1

YouTube Channel Financial Model (10 Year Financial Forecast)
This YouTube Channel Financial Model Template has been built for use by any YouTube Channel entrepreneur looking for a simple to use 3 way financial model (Income Statement, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow). This model also incorporates a company valuati... read more
- Excel Model Template – $49.99 Version 2

EdTech Financial Model
This EdTech Financial Model Template has been built for use by any company founder or executive in the EdTech space, Investors or Analysts looking at researching EdTech businesses, or Students looking to study how an EdTech Business operates and the ... read more
- Excel Model Template – $49.99 Version 1

Massage Salon Financial Model
This Massage Salon Financial Model Template has been built for use by any Founder or Executive in the Massage Salon space looking for a simple to use 3 way financial model (Income Statement, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow). This model also incorporates ... read more

Mining Bundle Financial Models
This Mining Bundle includes a Gold Mining Financial Model, Copper Mining Financial Model and Lithium Mining Financial Model. These templates have all been built for use by any company founder or executive in the Mining space, Investors or Analysts lo... read more
- Template Bundle – $99.99 Version 1

Student Special Bundle: 7 Financial Model Templates
This Student Bundle includes financial model templates from various industries that Students may be interested in learning about and seeing how each Business Model operates. Each of these has unique Business Models, Company Revenue Drivers, Operating... read more
- Template Bundle – $150.00 Version 1

Pet Hotel 5-Year Financial & DCF Model
The Pet Hotel DCF Model (5 Years) provides a detailed financial analysis of a pet boarding business, projecting revenue, costs, and profitability over a five-year period. It includes key components such as customer growth, operating costs, and room o... read more
- Free PDF – $0.00 Version 1
- Paid Excel Model – $119.00 Version 1

Dropshipping Financial Model (10 Year Financial Forecast)
This Dropshipping Financial Model Template has been built for use by any Dropshipping entrepreneur looking for a simple to use 3 way financial model (Income Statement, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow). This model also incorporates a company valuation ass... read more

9 Box Grid Excel Model
Our 9-box grid assessment template offers a comprehensive approach to evaluating employee performance and potential.
- Excel Template – $29.00 Version 1
Semiconductor Chip Manufacturing – 10 Year Financial Model
Financial Model providing a dynamic up to 10-year financial forecast for a startup Semiconductor Chips Manufacturing Factory.
- Excel Financial Model – $139.00 Version 1
- PDF Free Demo – $0.00 Version 1
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
B2B Sales Enablement: 4 Steps to Implement a Strategy and Why You Should
Published: September 17, 2024
My sales career has largely centered around helping SaaS organizations navigate the sometimes rocky transition from founder-led sales to a more structured and scalable approach. Because so many inbound leads in the former circumstance have pre-existing relationships with the company founder(s), it’s common to see those relationships doing most of the heavy lifting when it comes to moving the prospect through the sales funnel.

My first order of business in these situations isn’t to sell. Instead, the immediate goal is to establish a robust sales enablement process that will eliminate the gap — or chasm, really — between initial touch points and closed deals and ultimately set the stage for sales success.

Table of Contents
What Is B2B Sales Enablement?
The benefits of b2b sales enablement, how to develop a b2b sales enablement strategy, tips for b2b sales enablement.
B2B sales enablement is the process of supporting a sales team and helping them close more deals — whether that involves equipping them with the right tech stack, providing training resources for internal and external tools, creating a library of content that helps deals progress, or ideally, all these and more.
Think of a football team now that fall is upon us. The players might be the ones in the trenches, but they’re supported day in and day out by coaching staff with playbooks and advice, physicians who mitigate the risk of injury and help get injured players back on the field, nutritionists who help the team perform at its physical peak, and more.
I don’t have much advice to share about a championship diet and exercise regimen, but I can certainly chime in on the transformational benefits of a solid B2B sales enablement strategy .
This one may come as a shock, but sales enablement content can actually help you… sell more.
In addition to my own anecdotal experience, HubSpot’s 2024 Sales Trends Report found that sales pros who use sales enablement content in their role are 58% more likely to be performing over goal this year than those who don’t use it. Perhaps even more telling is that most salespeople acknowledge the causation, with 79% reporting that enablement content was important in making a sale.
Increase Efficiency
Sales enablement strategies often include a lead qualification system, ensuring that sales reps are investing valuable time in the leads that fit your company the best. For example, HubSpot’s Sale Hub includes a predictive lead scoring feature powered by machine learning that allows reps to automatically prioritize leads based on thousands of data points.
Even if you’re on a shoestring budget, you can start with a much less sophisticated implementation. Simply identify some key properties (company size, site visits, social media engagement, etc.) that have historically been a good indicator of a prospect’s potential value. Assign positive scores for promising qualifications while penalizing qualities that point to a prospect likely being a poor fit, and you’re off to the races with a basic scoring system that you can expand and iterate on over time.
Improve the Customer Experience
Sales enablement isn’t just about making more sales, faster. When salespeople are better equipped to do their jobs, customers benefit as well. G2 provides a key insight here, finding that sales enablement can cut onboarding times by 40-50% . That accelerated timeline means your customers are getting a faster return on their investment, improving their experience and making them more likely to stick with your solution for the long run.
There are even more benefits to be had, but hopefully, I’ve convinced you. While enablement initiatives will vary in scope depending on your organization’s size, budget, and appetite, I’ve got four actionable steps that will help you put together a clear B2B sales enablement strategy and help your sales team win more — however you define those wins.

Free Sales Plan Template
Outline your company's sales strategy in one simple, coherent sales plan.
- Target Market
- Prospecting Strategy
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
1. Identify (and Agree On) Clear Goals
Create SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound) goals that your sales enablement strategy will work toward. You might want to shorten your sales cycle, increase your win rates, or bolster the size of your average deal, for example. Of course, you inevitably want to do all three, but I’d recommend keeping your scope narrow and focusing on a single goal a time.
It’s also important to align departments around the enablement goals. If your sales team is trying to win more deals but the marketing team is attempting to increase the typical deal size, you’re unlikely to make significant progress in either endeavor — and in some cases you might find different goals are actually at odds.
2. Map the Ideal Customer Journey
How do customers currently move through the buying process ? How did they get from the initial interaction all the way to a closed deal? Which pain points were the most pressing for them, and what objections did the sales team need to overcome to progress through each stage?

How to Build A Sales Enablement Framework

7 Sales Playbooks to Help You Score in the Final Quarter

A Business Playbook Can Help You Scale Your Business Faster and Smarter. Here’s How.
![sales projection in business plan example How to Use Battle Cards in Your Sales Process [Templates]](https://knowledge.hubspot.com/hubfs/competitiveintelligencebattlecards.webp)
How to Use Battle Cards in Your Sales Process [Templates]

The Sales Playbook That Increased the Lessonly SDR Team's ARR by 63% in 4 Months
Outline your company's sales strategy in one simple, coherent plan.
Powerful and easy-to-use sales software that drives productivity, enables customer connection, and supports growing sales orgs

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Make better decisions. Sales projections provide important data that helps business leaders make informed decisions about product pricing, finances, staffing needs, marketing strategy, and sales processes. Business teams usually have more confidence in these decisions because they're not made on a whim. 2.
2% conversion rate. $50 average purchase price. This is how could look like a simplified sales forecast example for an online business: 3. Lead-acquisition businesses. Forecasting sales for a lead-acquisition business. Lead-acquisition businesses are companies that make sales through their sales teams efforts.
A sales forecast predicts future sales revenue using past business data. You can use sales forecasting to assess your financial projections and change your business plan if necessary. Learn how a sales forecast template can help you set goals, budget, and refine your sales cycle.
Download Monthly Sales Projection Template. Excel | Google Sheets. This monthly sales projection template is customizable and shows forecasts in a monthly and yearly view. Enter the year forecasted at the top, add total projected sales goals for new business and reorders for each month, and then add actual sales for comparison.
2. Long-term Sales Projection Forecast. Part of creating a sales plan is forecasting long-term revenue goals and sales projections, then laying out the strategies and tactics you'll use to hit your performance goals. Long-term sales projection templates usually provide three- to five-year projections. These templates are accessible in both Excel and Google Sheets.
Proposal sent: 40% probability of closing. Negotiating: 60% probability of closing. Contract sent: 90% probability of closing. Using these probabilities, you can extrapolate an opportunity stage sales forecast. You'll want to take the deal's potential value and multiply that by the win likelihood.
Your sales forecast obviously gives you an idea of how much you will sell in the future, but sales forecasting has other important use cases. Here are five ways you can apply your forecast to business questions: Sales Planning: As noted earlier, your sales plan encompasses your goals, tactics, and processes for achieving your sales forecast. As ...
Step 1: Set up your lines of sales. Most forecasts show several distinct lines of sales. Ideally, your sales lines match your accounting, but not necessarily in the same level of detail. For example, a restaurant ought not to forecast sales for each item on the menu.
This template allows for projections based on a number of different variables, including seasonality. The template is great for businesses that have many external variables to consider. 22. Historical Growth Rate. Historical Growth Rate (Excel): This template uses your historical sales data to predict future growth. Because the only inputs are ...
But to start, here are the general steps you'll need to take to create a sales forecast: List out the goods and services you sell. Estimate how much of each you expect to sell. Define the unit price or dollar value of each good or service sold. Multiply the number sold by the price.
1. Best General Forecast Template (without a CRM) This sales forecasting template from Close provides a simple way to track and forecast two years of sales. The first tab allows for adjusting funnel metrics depending on your sales cycle, average deal size, lead growth, and number of leads.
This implies a growth rate of 25% ( ($8 million - $6.4 million) / $6.4 million × 100). Assuming the growth rate remains constant, the projected revenue in 2024 would be $10 million ($8 million × 1.25), which is in line with their upward trend in the fast-growing cloud services market.
Use this forecast template to get a bird's eye view of the pipeline and sort your actions based on urgency, value, and potential. Consider adding the daily sales forecast and monthly sales projection template to your workflow to visualize the entire sales funnel in a single view. 6. ClickUp Sales KPI Template.
Estimate the expected sales of each good or service. Multiply the price by the estimated sales to get your estimated revenue. Add them all together to get your total revenue. For example, if your food truck business sold pizzas at £10 and burgers at £5, you would multiply these values by how much you expected to sell.
Collect relevant historical financial data and market analysis. Forecast expenses. Forecast sales. Build financial projections. The following five steps can help you break down the process of developing financial projections for your company: 1. Identify the purpose and timeframe for your projections.
Sales projections. For example, you could predict that you will sell 1,000 packages in 2022, compared to the 800 from last year, since you've hired an additional sales team. ... Plan the future of your business with sales projections. Business success doesn't happen by accident. You have to plan, set goals, and measure your progress to ...
Image source. This three-year sales forecast template by Vertex42 is great for projecting long term sales figures. It's a useful option for local businesses or startups seeking financial support as banks and investors want to know about your sales plan that will help your business generate revenue in the long term. You can easily plug in your sales-related information.
To forecast sales, multiply the number of units by the price you sell them for. Create projections for each month. For example, you own a car wash. In April, you project you will wash 800 cars. A car wash is $15.800 cars X $15 per car wash = $12,000 sales projection. 800 cars X $15 per car wash = $12,000 sales projection.
Template 1: Sale Projection Powerpoint Bundles. Expand your company's sales architecture and enhance your commercial standing, all with the help of this comprehensive twenty-five slides PowerPoint deck. It contains a great wellspring of data that can assist you in reinventing your sales projection methods.
A Sales Projection for your Business Plan. ... Our free revenue projection template can be used to help estimate sales for up to 5 years. Last modified August 6th, 2020 by Michael Brown. About the Author. Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Plan Projections. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 ...
7 steps for writing a sales projection. Here are seven steps to follow when developing a sales projection at work: 1. Identify potential sales opportunities. The first step in the preparation of a sales projection is to clearly identify potential sales opportunities.
Financial projections are forecasted analyses of your business' future that include income statements, balance sheets and cash flow statements. We have found them to be an crucial part of your business plan for the following reasons: They can help prove or disprove the viability of your business idea. For example, if your initial projections ...
Sales Forecasting Template: Used by sales and marketing teams to predict future sales, this template helps you set targets and plan marketing strategies. Cash-Flow Forecast Template: Essential for financial managers who need to monitor the liquidity of the business, this template projects cash inflows and outflows over a period.
Explore inspiring retail business plan examples to fuel your entrepreneurial journey and drive success in your retail venture. Get inspired today! ... Market research can help you make informed projections. Consider these elements: Sales Projections: Use data on market size and consumer behavior to estimate your potential sales volume.
How to Develop a B2B Sales Enablement Strategy 1. Identify (and Agree On) Clear Goals. Create SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound) goals that your sales enablement strategy will work toward. You might want to shorten your sales cycle, increase your win rates, or bolster the size of your average deal, for example.