Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 31 August 2024

Knowledge mapping and evolution of research on older adults’ technology acceptance: a bibliometric study from 2013 to 2023
- Xianru Shang ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0000-8906-3216 1 ,
- Zijian Liu 1 ,
- Chen Gong 1 ,
- Zhigang Hu 1 ,
- Yuexuan Wu 1 &
- Chengliang Wang ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2208-3508 2
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 11 , Article number: 1115 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
- Science, technology and society
The rapid expansion of information technology and the intensification of population aging are two prominent features of contemporary societal development. Investigating older adults’ acceptance and use of technology is key to facilitating their integration into an information-driven society. Given this context, the technology acceptance of older adults has emerged as a prioritized research topic, attracting widespread attention in the academic community. However, existing research remains fragmented and lacks a systematic framework. To address this gap, we employed bibliometric methods, utilizing the Web of Science Core Collection to conduct a comprehensive review of literature on older adults’ technology acceptance from 2013 to 2023. Utilizing VOSviewer and CiteSpace for data assessment and visualization, we created knowledge mappings of research on older adults’ technology acceptance. Our study employed multidimensional methods such as co-occurrence analysis, clustering, and burst analysis to: (1) reveal research dynamics, key journals, and domains in this field; (2) identify leading countries, their collaborative networks, and core research institutions and authors; (3) recognize the foundational knowledge system centered on theoretical model deepening, emerging technology applications, and research methods and evaluation, uncovering seminal literature and observing a shift from early theoretical and influential factor analyses to empirical studies focusing on individual factors and emerging technologies; (4) moreover, current research hotspots are primarily in the areas of factors influencing technology adoption, human-robot interaction experiences, mobile health management, and aging-in-place technology, highlighting the evolutionary context and quality distribution of research themes. Finally, we recommend that future research should deeply explore improvements in theoretical models, long-term usage, and user experience evaluation. Overall, this study presents a clear framework of existing research in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance, providing an important reference for future theoretical exploration and innovative applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Research progress and intellectual structure of design for digital equity (DDE): A bibliometric analysis based on citespace
Exploring the role of interaction in older-adult service innovation: insights from the testing stage

Smart device interest, perceived usefulness, and preferences in rural Alabama seniors
Introduction.
In contemporary society, the rapid development of information technology has been intricately intertwined with the intensifying trend of population aging. According to the latest United Nations forecast, by 2050, the global population aged 65 and above is expected to reach 1.6 billion, representing about 16% of the total global population (UN 2023 ). Given the significant challenges of global aging, there is increasing evidence that emerging technologies have significant potential to maintain health and independence for older adults in their home and healthcare environments (Barnard et al. 2013 ; Soar 2010 ; Vancea and Solé-Casals 2016 ). This includes, but is not limited to, enhancing residential safety with smart home technologies (Touqeer et al. 2021 ; Wang et al. 2022 ), improving living independence through wearable technologies (Perez et al. 2023 ), and increasing medical accessibility via telehealth services (Kruse et al. 2020 ). Technological innovations are redefining the lifestyles of older adults, encouraging a shift from passive to active participation (González et al. 2012 ; Mostaghel 2016 ). Nevertheless, the effective application and dissemination of technology still depends on user acceptance and usage intentions (Naseri et al. 2023 ; Wang et al. 2023a ; Xia et al. 2024 ; Yu et al. 2023 ). Particularly, older adults face numerous challenges in accepting and using new technologies. These challenges include not only physical and cognitive limitations but also a lack of technological experience, along with the influences of social and economic factors (Valk et al. 2018 ; Wilson et al. 2021 ).
User acceptance of technology is a significant focus within information systems (IS) research (Dai et al. 2024 ), with several models developed to explain and predict user behavior towards technology usage, including the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) (Davis 1989 ), TAM2, TAM3, and the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) (Venkatesh et al. 2003 ). Older adults, as a group with unique needs, exhibit different behavioral patterns during technology acceptance than other user groups, and these uniquenesses include changes in cognitive abilities, as well as motivations, attitudes, and perceptions of the use of new technologies (Chen and Chan 2011 ). The continual expansion of technology introduces considerable challenges for older adults, rendering the understanding of their technology acceptance a research priority. Thus, conducting in-depth research into older adults’ acceptance of technology is critically important for enhancing their integration into the information society and improving their quality of life through technological advancements.
Reviewing relevant literature to identify research gaps helps further solidify the theoretical foundation of the research topic. However, many existing literature reviews primarily focus on the factors influencing older adults’ acceptance or intentions to use technology. For instance, Ma et al. ( 2021 ) conducted a comprehensive analysis of the determinants of older adults’ behavioral intentions to use technology; Liu et al. ( 2022 ) categorized key variables in studies of older adults’ technology acceptance, noting a shift in focus towards social and emotional factors; Yap et al. ( 2022 ) identified seven categories of antecedents affecting older adults’ use of technology from an analysis of 26 articles, including technological, psychological, social, personal, cost, behavioral, and environmental factors; Schroeder et al. ( 2023 ) extracted 119 influencing factors from 59 articles and further categorized these into six themes covering demographics, health status, and emotional awareness. Additionally, some studies focus on the application of specific technologies, such as Ferguson et al. ( 2021 ), who explored barriers and facilitators to older adults using wearable devices for heart monitoring, and He et al. ( 2022 ) and Baer et al. ( 2022 ), who each conducted in-depth investigations into the acceptance of social assistive robots and mobile nutrition and fitness apps, respectively. In summary, current literature reviews on older adults’ technology acceptance exhibit certain limitations. Due to the interdisciplinary nature and complex knowledge structure of this field, traditional literature reviews often rely on qualitative analysis, based on literature analysis and periodic summaries, which lack sufficient objectivity and comprehensiveness. Additionally, systematic research is relatively limited, lacking a macroscopic description of the research trajectory from a holistic perspective. Over the past decade, research on older adults’ technology acceptance has experienced rapid growth, with a significant increase in literature, necessitating the adoption of new methods to review and examine the developmental trends in this field (Chen 2006 ; Van Eck and Waltman 2010 ). Bibliometric analysis, as an effective quantitative research method, analyzes published literature through visualization, offering a viable approach to extracting patterns and insights from a large volume of papers, and has been widely applied in numerous scientific research fields (Achuthan et al. 2023 ; Liu and Duffy 2023 ). Therefore, this study will employ bibliometric methods to systematically analyze research articles related to older adults’ technology acceptance published in the Web of Science Core Collection from 2013 to 2023, aiming to understand the core issues and evolutionary trends in the field, and to provide valuable references for future related research. Specifically, this study aims to explore and answer the following questions:
RQ1: What are the research dynamics in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance over the past decade? What are the main academic journals and fields that publish studies related to older adults’ technology acceptance?
RQ2: How is the productivity in older adults’ technology acceptance research distributed among countries, institutions, and authors?
RQ3: What are the knowledge base and seminal literature in older adults’ technology acceptance research? How has the research theme progressed?
RQ4: What are the current hot topics and their evolutionary trajectories in older adults’ technology acceptance research? How is the quality of research distributed?
Methodology and materials
Research method.
In recent years, bibliometrics has become one of the crucial methods for analyzing literature reviews and is widely used in disciplinary and industrial intelligence analysis (Jing et al. 2023 ; Lin and Yu 2024a ; Wang et al. 2024a ; Xu et al. 2021 ). Bibliometric software facilitates the visualization analysis of extensive literature data, intuitively displaying the network relationships and evolutionary processes between knowledge units, and revealing the underlying knowledge structure and potential information (Chen et al. 2024 ; López-Robles et al. 2018 ; Wang et al. 2024c ). This method provides new insights into the current status and trends of specific research areas, along with quantitative evidence, thereby enhancing the objectivity and scientific validity of the research conclusions (Chen et al. 2023 ; Geng et al. 2024 ). VOSviewer and CiteSpace are two widely used bibliometric software tools in academia (Pan et al. 2018 ), recognized for their robust functionalities based on the JAVA platform. Although each has its unique features, combining these two software tools effectively constructs mapping relationships between literature knowledge units and clearly displays the macrostructure of the knowledge domains. Particularly, VOSviewer, with its excellent graphical representation capabilities, serves as an ideal tool for handling large datasets and precisely identifying the focal points and hotspots of research topics. Therefore, this study utilizes VOSviewer (version 1.6.19) and CiteSpace (version 6.1.R6), combined with in-depth literature analysis, to comprehensively examine and interpret the research theme of older adults’ technology acceptance through an integrated application of quantitative and qualitative methods.
Data source
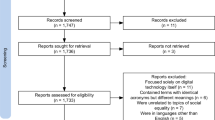
Web of Science is a comprehensively recognized database in academia, featuring literature that has undergone rigorous peer review and editorial scrutiny (Lin and Yu 2024b ; Mongeon and Paul-Hus 2016 ; Pranckutė 2021 ). This study utilizes the Web of Science Core Collection as its data source, specifically including three major citation indices: Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE), Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI), and Arts & Humanities Citation Index (A&HCI). These indices encompass high-quality research literature in the fields of science, social sciences, and arts and humanities, ensuring the comprehensiveness and reliability of the data. We combined “older adults” with “technology acceptance” through thematic search, with the specific search strategy being: TS = (elder OR elderly OR aging OR ageing OR senile OR senior OR old people OR “older adult*”) AND TS = (“technology acceptance” OR “user acceptance” OR “consumer acceptance”). The time span of literature search is from 2013 to 2023, with the types limited to “Article” and “Review” and the language to “English”. Additionally, the search was completed by October 27, 2023, to avoid data discrepancies caused by database updates. The initial search yielded 764 journal articles. Given that searches often retrieve articles that are superficially relevant but actually non-compliant, manual screening post-search was essential to ensure the relevance of the literature (Chen et al. 2024 ). Through manual screening, articles significantly deviating from the research theme were eliminated and rigorously reviewed. Ultimately, this study obtained 500 valid sample articles from the Web of Science Core Collection. The complete PRISMA screening process is illustrated in Fig. 1 .
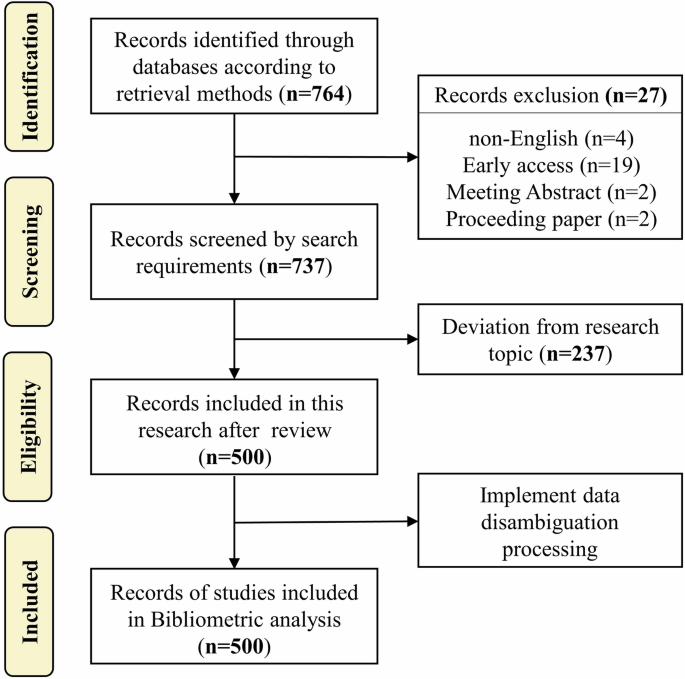
Presentation of the data culling process in detail.
Data standardization
Raw data exported from databases often contain multiple expressions of the same terminology (Nguyen and Hallinger 2020 ). To ensure the accuracy and consistency of data, it is necessary to standardize the raw data (Strotmann and Zhao 2012 ). This study follows the data standardization process proposed by Taskin and Al ( 2019 ), mainly executing the following operations:
(1) Standardization of author and institution names is conducted to address different name expressions for the same author. For instance, “Chan, Alan Hoi Shou” and “Chan, Alan H. S.” are considered the same author, and distinct authors with the same name are differentiated by adding identifiers. Diverse forms of institutional names are unified to address variations caused by name changes or abbreviations, such as standardizing “FRANKFURT UNIV APPL SCI” and “Frankfurt University of Applied Sciences,” as well as “Chinese University of Hong Kong” and “University of Hong Kong” to consistent names.
(2) Different expressions of journal names are unified. For example, “International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction” and “Int J Hum Comput Interact” are standardized to a single name. This ensures consistency in journal names and prevents misclassification of literature due to differing journal names. Additionally, it involves checking if the journals have undergone name changes in the past decade to prevent any impact on the analysis due to such changes.
(3) Keywords data are cleansed by removing words that do not directly pertain to specific research content (e.g., people, review), merging synonyms (e.g., “UX” and “User Experience,” “aging-in-place” and “aging in place”), and standardizing plural forms of keywords (e.g., “assistive technologies” and “assistive technology,” “social robots” and “social robot”). This reduces redundant information in knowledge mapping.
Bibliometric results and analysis
Distribution power (rq1), literature descriptive statistical analysis.
Table 1 presents a detailed descriptive statistical overview of the literature in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance. After deduplication using the CiteSpace software, this study confirmed a valid sample size of 500 articles. Authored by 1839 researchers, the documents encompass 792 research institutions across 54 countries and are published in 217 different academic journals. As of the search cutoff date, these articles have accumulated 13,829 citations, with an annual average of 1156 citations, and an average of 27.66 citations per article. The h-index, a composite metric of quantity and quality of scientific output (Kamrani et al. 2021 ), reached 60 in this study.
Trends in publications and disciplinary distribution
The number of publications and citations are significant indicators of the research field’s development, reflecting its continuity, attention, and impact (Ale Ebrahim et al. 2014 ). The ranking of annual publications and citations in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance studies is presented chronologically in Fig. 2A . The figure shows a clear upward trend in the amount of literature in this field. Between 2013 and 2017, the number of publications increased slowly and decreased in 2018. However, in 2019, the number of publications increased rapidly to 52 and reached a peak of 108 in 2022, which is 6.75 times higher than in 2013. In 2022, the frequency of document citations reached its highest point with 3466 citations, reflecting the widespread recognition and citation of research in this field. Moreover, the curve of the annual number of publications fits a quadratic function, with a goodness-of-fit R 2 of 0.9661, indicating that the number of future publications is expected to increase even more rapidly.
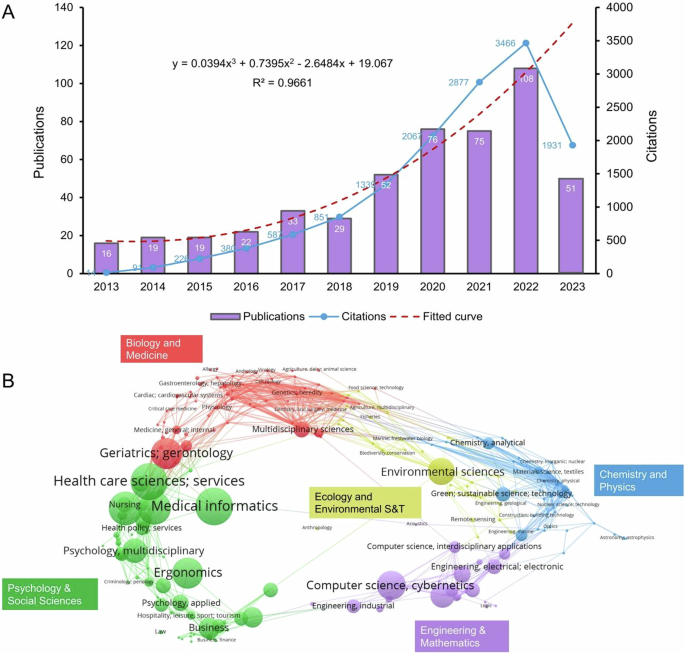
A Trends in trends in annual publications and citations (2013–2023). B Overlay analysis of the distribution of discipline fields.
Figure 2B shows that research on older adults’ technology acceptance involves the integration of multidisciplinary knowledge. According to Web of Science Categories, these 500 articles are distributed across 85 different disciplines. We have tabulated the top ten disciplines by publication volume (Table 2 ), which include Medical Informatics (75 articles, 15.00%), Health Care Sciences & Services (71 articles, 14.20%), Gerontology (61 articles, 12.20%), Public Environmental & Occupational Health (57 articles, 11.40%), and Geriatrics & Gerontology (52 articles, 10.40%), among others. The high output in these disciplines reflects the concentrated global academic interest in this comprehensive research topic. Additionally, interdisciplinary research approaches provide diverse perspectives and a solid theoretical foundation for studies on older adults’ technology acceptance, also paving the way for new research directions.
Knowledge flow analysis
A dual-map overlay is a CiteSpace map superimposed on top of a base map, which shows the interrelationships between journals in different domains, representing the publication and citation activities in each domain (Chen and Leydesdorff 2014 ). The overlay map reveals the link between the citing domain (on the left side) and the cited domain (on the right side), reflecting the knowledge flow of the discipline at the journal level (Leydesdorff and Rafols 2012 ). We utilize the in-built Z-score algorithm of the software to cluster the graph, as shown in Fig. 3 .
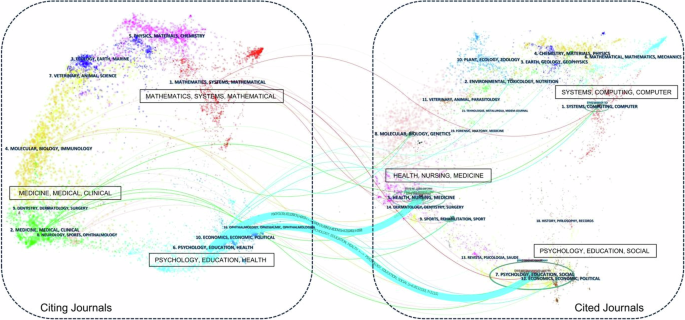
The left side shows the citing journal, and the right side shows the cited journal.
Figure 3 shows the distribution of citing journals clusters for older adults’ technology acceptance on the left side, while the right side refers to the main cited journals clusters. Two knowledge flow citation trajectories were obtained; they are presented by the color of the cited regions, and the thickness of these trajectories is proportional to the Z-score scaled frequency of citations (Chen et al. 2014 ). Within the cited regions, the most popular fields with the most records covered are “HEALTH, NURSING, MEDICINE” and “PSYCHOLOGY, EDUCATION, SOCIAL”, and the elliptical aspect ratio of these two fields stands out. Fields have prominent elliptical aspect ratios, highlighting their significant influence on older adults’ technology acceptance research. Additionally, the major citation trajectories originate in these two areas and progress to the frontier research area of “PSYCHOLOGY, EDUCATION, HEALTH”. It is worth noting that the citation trajectory from “PSYCHOLOGY, EDUCATION, SOCIAL” has a significant Z-value (z = 6.81), emphasizing the significance and impact of this development path. In the future, “MATHEMATICS, SYSTEMS, MATHEMATICAL”, “MOLECULAR, BIOLOGY, IMMUNOLOGY”, and “NEUROLOGY, SPORTS, OPHTHALMOLOGY” may become emerging fields. The fields of “MEDICINE, MEDICAL, CLINICAL” may be emerging areas of cutting-edge research.
Main research journals analysis
Table 3 provides statistics for the top ten journals by publication volume in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance. Together, these journals have published 137 articles, accounting for 27.40% of the total publications, indicating that there is no highly concentrated core group of journals in this field, with publications being relatively dispersed. Notably, Computers in Human Behavior , Journal of Medical Internet Research , and International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction each lead with 15 publications. In terms of citation metrics, International Journal of Medical Informatics and Computers in Human Behavior stand out significantly, with the former accumulating a total of 1,904 citations, averaging 211.56 citations per article, and the latter totaling 1,449 citations, with an average of 96.60 citations per article. These figures emphasize the academic authority and widespread impact of these journals within the research field.
Research power (RQ2)
Countries and collaborations analysis.
The analysis revealed the global research pattern for country distribution and collaboration (Chen et al. 2019 ). Figure 4A shows the network of national collaborations on older adults’ technology acceptance research. The size of the bubbles represents the amount of publications in each country, while the thickness of the connecting lines expresses the closeness of the collaboration among countries. Generally, this research subject has received extensive international attention, with China and the USA publishing far more than any other countries. China has established notable research collaborations with the USA, UK and Malaysia in this field, while other countries have collaborations, but the closeness is relatively low and scattered. Figure 4B shows the annual publication volume dynamics of the top ten countries in terms of total publications. Since 2017, China has consistently increased its annual publications, while the USA has remained relatively stable. In 2019, the volume of publications in each country increased significantly, this was largely due to the global outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has led to increased reliance on information technology among the elderly for medical consultations, online socialization, and health management (Sinha et al. 2021 ). This phenomenon has led to research advances in technology acceptance among older adults in various countries. Table 4 shows that the top ten countries account for 93.20% of the total cumulative number of publications, with each country having published more than 20 papers. Among these ten countries, all of them except China are developed countries, indicating that the research field of older adults’ technology acceptance has received general attention from developed countries. Currently, China and the USA were the leading countries in terms of publications with 111 and 104 respectively, accounting for 22.20% and 20.80%. The UK, Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands also made significant contributions. The USA and China ranked first and second in terms of the number of citations, while the Netherlands had the highest average citations, indicating the high impact and quality of its research. The UK has shown outstanding performance in international cooperation, while the USA highlights its significant academic influence in this field with the highest h-index value.
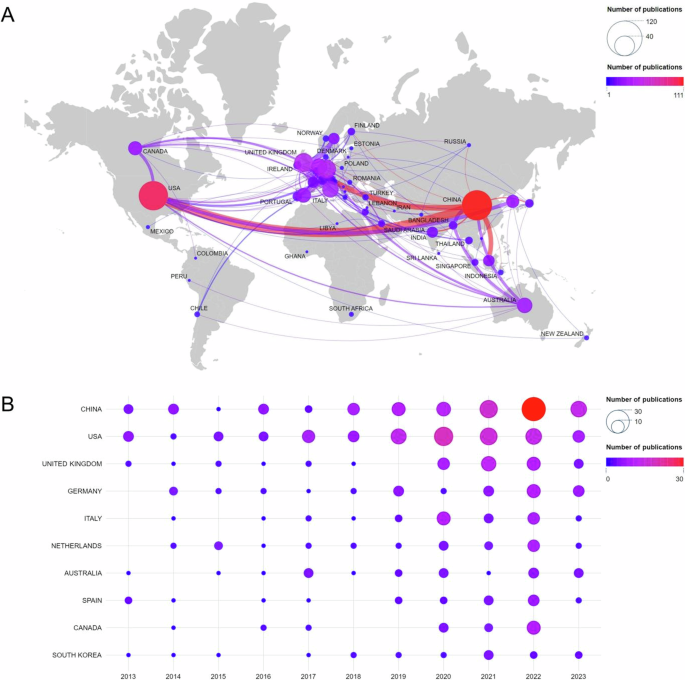
A National collaboration network. B Annual volume of publications in the top 10 countries.
Institutions and authors analysis
Analyzing the number of publications and citations can reveal an institution’s or author’s research strength and influence in a particular research area (Kwiek 2021 ). Tables 5 and 6 show the statistics of the institutions and authors whose publication counts are in the top ten, respectively. As shown in Table 5 , higher education institutions hold the main position in this research field. Among the top ten institutions, City University of Hong Kong and The University of Hong Kong from China lead with 14 and 9 publications, respectively. City University of Hong Kong has the highest h-index, highlighting its significant influence in the field. It is worth noting that Tilburg University in the Netherlands is not among the top five in terms of publications, but the high average citation count (130.14) of its literature demonstrates the high quality of its research.
After analyzing the authors’ output using Price’s Law (Redner 1998 ), the highest number of publications among the authors counted ( n = 10) defines a publication threshold of 3 for core authors in this research area. As a result of quantitative screening, a total of 63 core authors were identified. Table 6 shows that Chen from Zhejiang University, China, Ziefle from RWTH Aachen University, Germany, and Rogers from Macquarie University, Australia, were the top three authors in terms of the number of publications, with 10, 9, and 8 articles, respectively. In terms of average citation rate, Peek and Wouters, both scholars from the Netherlands, have significantly higher rates than other scholars, with 183.2 and 152.67 respectively. This suggests that their research is of high quality and widely recognized. Additionally, Chen and Rogers have high h-indices in this field.
Knowledge base and theme progress (RQ3)
Research knowledge base.
Co-citation relationships occur when two documents are cited together (Zhang and Zhu 2022 ). Co-citation mapping uses references as nodes to represent the knowledge base of a subject area (Min et al. 2021). Figure 5A illustrates co-occurrence mapping in older adults’ technology acceptance research, where larger nodes signify higher co-citation frequencies. Co-citation cluster analysis can be used to explore knowledge structure and research boundaries (Hota et al. 2020 ; Shiau et al. 2023 ). The co-citation clustering mapping of older adults’ technology acceptance research literature (Fig. 5B ) shows that the Q value of the clustering result is 0.8129 (>0.3), and the average value of the weight S is 0.9391 (>0.7), indicating that the clusters are uniformly distributed with a significant and credible structure. This further proves that the boundaries of the research field are clear and there is significant differentiation in the field. The figure features 18 cluster labels, each associated with thematic color blocks corresponding to different time slices. Highlighted emerging research themes include #2 Smart Home Technology, #7 Social Live, and #10 Customer Service. Furthermore, the clustering labels extracted are primarily classified into three categories: theoretical model deepening, emerging technology applications, research methods and evaluation, as detailed in Table 7 .
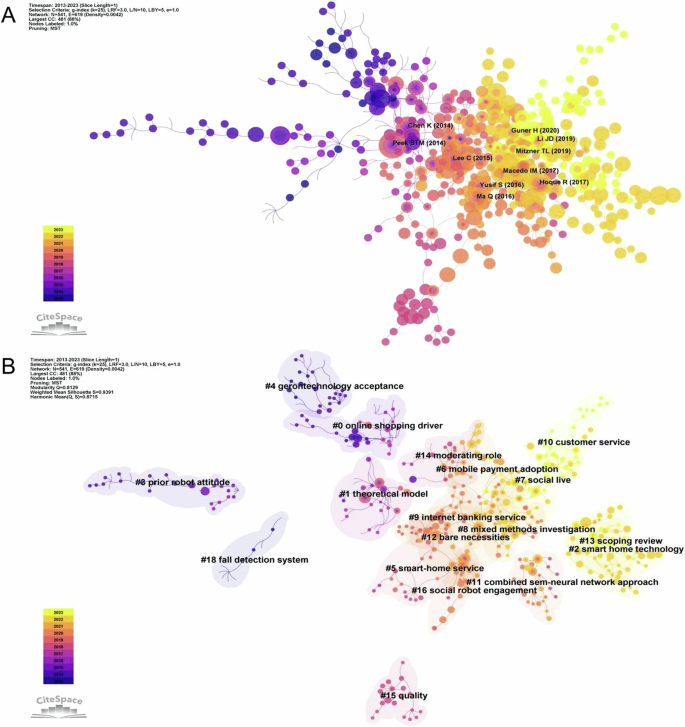
A Co-citation analysis of references. B Clustering network analysis of references.
Seminal literature analysis
The top ten nodes in terms of co-citation frequency were selected for further analysis. Table 8 displays the corresponding node information. Studies were categorized into four main groups based on content analysis. (1) Research focusing on specific technology usage by older adults includes studies by Peek et al. ( 2014 ), Ma et al. ( 2016 ), Hoque and Sorwar ( 2017 ), and Li et al. ( 2019 ), who investigated the factors influencing the use of e-technology, smartphones, mHealth, and smart wearables, respectively. (2) Concerning the development of theoretical models of technology acceptance, Chen and Chan ( 2014 ) introduced the Senior Technology Acceptance Model (STAM), and Macedo ( 2017 ) analyzed the predictive power of UTAUT2 in explaining older adults’ intentional behaviors and information technology usage. (3) In exploring older adults’ information technology adoption and behavior, Lee and Coughlin ( 2015 ) emphasized that the adoption of technology by older adults is a multifactorial process that includes performance, price, value, usability, affordability, accessibility, technical support, social support, emotion, independence, experience, and confidence. Yusif et al. ( 2016 ) conducted a literature review examining the key barriers affecting older adults’ adoption of assistive technology, including factors such as privacy, trust, functionality/added value, cost, and stigma. (4) From the perspective of research into older adults’ technology acceptance, Mitzner et al. ( 2019 ) assessed the long-term usage of computer systems designed for the elderly, whereas Guner and Acarturk ( 2020 ) compared information technology usage and acceptance between older and younger adults. The breadth and prevalence of this literature make it a vital reference for researchers in the field, also providing new perspectives and inspiration for future research directions.
Research thematic progress
Burst citation is a node of literature that guides the sudden change in dosage, which usually represents a prominent development or major change in a particular field, with innovative and forward-looking qualities. By analyzing the emergent literature, it is often easy to understand the dynamics of the subject area, mapping the emerging thematic change (Chen et al. 2022 ). Figure 6 shows the burst citation mapping in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance research, with burst citations represented by red nodes (Fig. 6A ). For the ten papers with the highest burst intensity (Fig. 6B ), this study will conduct further analysis in conjunction with literature review.
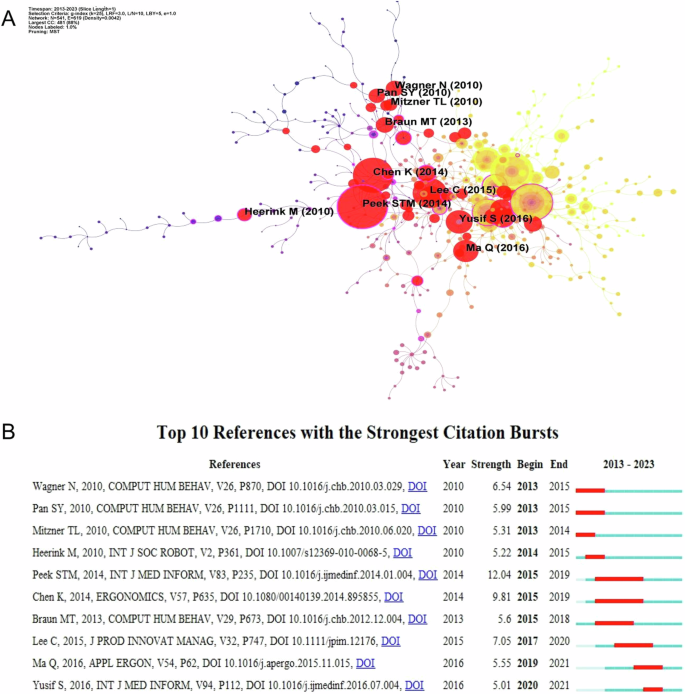
A Burst detection of co-citation. B The top 10 references with the strongest citation bursts.
As shown in Fig. 6 , Mitzner et al. ( 2010 ) broke the stereotype that older adults are fearful of technology, found that they actually have positive attitudes toward technology, and emphasized the centrality of ease of use and usefulness in the process of technology acceptance. This finding provides an important foundation for subsequent research. During the same period, Wagner et al. ( 2010 ) conducted theory-deepening and applied research on technology acceptance among older adults. The research focused on older adults’ interactions with computers from the perspective of Social Cognitive Theory (SCT). This expanded the understanding of technology acceptance, particularly regarding the relationship between behavior, environment, and other SCT elements. In addition, Pan and Jordan-Marsh ( 2010 ) extended the TAM to examine the interactions among predictors of perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, subjective norm, and convenience conditions when older adults use the Internet, taking into account the moderating roles of gender and age. Heerink et al. ( 2010 ) adapted and extended the UTAUT, constructed a technology acceptance model specifically designed for older users’ acceptance of assistive social agents, and validated it using controlled experiments and longitudinal data, explaining intention to use by combining functional assessment and social interaction variables.
Then the research theme shifted to an in-depth analysis of the factors influencing technology acceptance among older adults. Two papers with high burst strengths emerged during this period: Peek et al. ( 2014 ) (Strength = 12.04), Chen and Chan ( 2014 ) (Strength = 9.81). Through a systematic literature review and empirical study, Peek STM and Chen K, among others, identified multidimensional factors that influence older adults’ technology acceptance. Peek et al. ( 2014 ) analyzed literature on the acceptance of in-home care technology among older adults and identified six factors that influence their acceptance: concerns about technology, expected benefits, technology needs, technology alternatives, social influences, and older adult characteristics, with a focus on differences between pre- and post-implementation factors. Chen and Chan ( 2014 ) constructed the STAM by administering a questionnaire to 1012 older adults and adding eight important factors, including technology anxiety, self-efficacy, cognitive ability, and physical function, based on the TAM. This enriches the theoretical foundation of the field. In addition, Braun ( 2013 ) highlighted the role of perceived usefulness, trust in social networks, and frequency of Internet use in older adults’ use of social networks, while ease of use and social pressure were not significant influences. These findings contribute to the study of older adults’ technology acceptance within specific technology application domains.
Recent research has focused on empirical studies of personal factors and emerging technologies. Ma et al. ( 2016 ) identified key personal factors affecting smartphone acceptance among older adults through structured questionnaires and face-to-face interviews with 120 participants. The study found that cost, self-satisfaction, and convenience were important factors influencing perceived usefulness and ease of use. This study offers empirical evidence to comprehend the main factors that drive smartphone acceptance among Chinese older adults. Additionally, Yusif et al. ( 2016 ) presented an overview of the obstacles that hinder older adults’ acceptance of assistive technologies, focusing on privacy, trust, and functionality.
In summary, research on older adults’ technology acceptance has shifted from early theoretical deepening and analysis of influencing factors to empirical studies in the areas of personal factors and emerging technologies, which have greatly enriched the theoretical basis of older adults’ technology acceptance and provided practical guidance for the design of emerging technology products.
Research hotspots, evolutionary trends, and quality distribution (RQ4)
Core keywords analysis.
Keywords concise the main idea and core of the literature, and are a refined summary of the research content (Huang et al. 2021 ). In CiteSpace, nodes with a centrality value greater than 0.1 are considered to be critical nodes. Analyzing keywords with high frequency and centrality helps to visualize the hot topics in the research field (Park et al. 2018 ). The merged keywords were imported into CiteSpace, and the top 10 keywords were counted and sorted by frequency and centrality respectively, as shown in Table 9 . The results show that the keyword “TAM” has the highest frequency (92), followed by “UTAUT” (24), which reflects that the in-depth study of the existing technology acceptance model and its theoretical expansion occupy a central position in research related to older adults’ technology acceptance. Furthermore, the terms ‘assistive technology’ and ‘virtual reality’ are both high-frequency and high-centrality terms (frequency = 17, centrality = 0.10), indicating that the research on assistive technology and virtual reality for older adults is the focus of current academic attention.
Research hotspots analysis
Using VOSviewer for keyword co-occurrence analysis organizes keywords into groups or clusters based on their intrinsic connections and frequencies, clearly highlighting the research field’s hot topics. The connectivity among keywords reveals correlations between different topics. To ensure accuracy, the analysis only considered the authors’ keywords. Subsequently, the keywords were filtered by setting the keyword frequency to 5 to obtain the keyword clustering map of the research on older adults’ technology acceptance research keyword clustering mapping (Fig. 7 ), combined with the keyword co-occurrence clustering network (Fig. 7A ) and the corresponding density situation (Fig. 7B ) to make a detailed analysis of the following four groups of clustered themes.
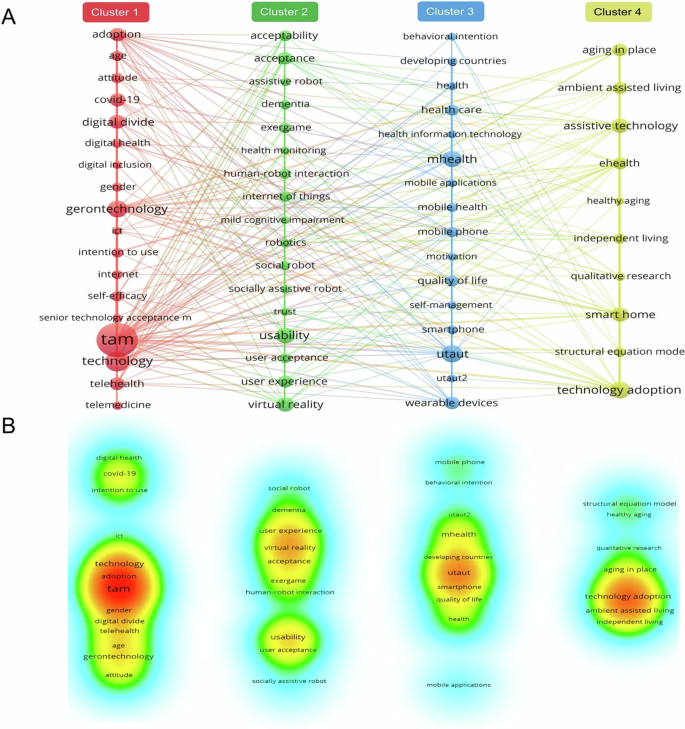
A Co-occurrence clustering network. B Keyword density.
Cluster #1—Research on the factors influencing technology adoption among older adults is a prominent topic, covering age, gender, self-efficacy, attitude, and and intention to use (Berkowsky et al. 2017 ; Wang et al. 2017 ). It also examined older adults’ attitudes towards and acceptance of digital health technologies (Ahmad and Mozelius, 2022 ). Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic, significantly impacting older adults’ technology attitudes and usage, has underscored the study’s importance and urgency. Therefore, it is crucial to conduct in-depth studies on how older adults accept, adopt, and effectively use new technologies, to address their needs and help them overcome the digital divide within digital inclusion. This will improve their quality of life and healthcare experiences.
Cluster #2—Research focuses on how older adults interact with assistive technologies, especially assistive robots and health monitoring devices, emphasizing trust, usability, and user experience as crucial factors (Halim et al. 2022 ). Moreover, health monitoring technologies effectively track and manage health issues common in older adults, like dementia and mild cognitive impairment (Lussier et al. 2018 ; Piau et al. 2019 ). Interactive exercise games and virtual reality have been deployed to encourage more physical and cognitive engagement among older adults (Campo-Prieto et al. 2021 ). Personalized and innovative technology significantly enhances older adults’ participation, improving their health and well-being.
Cluster #3—Optimizing health management for older adults using mobile technology. With the development of mobile health (mHealth) and health information technology, mobile applications, smartphones, and smart wearable devices have become effective tools to help older users better manage chronic conditions, conduct real-time health monitoring, and even receive telehealth services (Dupuis and Tsotsos 2018 ; Olmedo-Aguirre et al. 2022 ; Kim et al. 2014 ). Additionally, these technologies can mitigate the problem of healthcare resource inequality, especially in developing countries. Older adults’ acceptance and use of these technologies are significantly influenced by their behavioral intentions, motivational factors, and self-management skills. These internal motivational factors, along with external factors, jointly affect older adults’ performance in health management and quality of life.
Cluster #4—Research on technology-assisted home care for older adults is gaining popularity. Environmentally assisted living enhances older adults’ independence and comfort at home, offering essential support and security. This has a crucial impact on promoting healthy aging (Friesen et al. 2016 ; Wahlroos et al. 2023 ). The smart home is a core application in this field, providing a range of solutions that facilitate independent living for the elderly in a highly integrated and user-friendly manner. This fulfills different dimensions of living and health needs (Majumder et al. 2017 ). Moreover, eHealth offers accurate and personalized health management and healthcare services for older adults (Delmastro et al. 2018 ), ensuring their needs are met at home. Research in this field often employs qualitative methods and structural equation modeling to fully understand older adults’ needs and experiences at home and analyze factors influencing technology adoption.
Evolutionary trends analysis
To gain a deeper understanding of the evolutionary trends in research hotspots within the field of older adults’ technology acceptance, we conducted a statistical analysis of the average appearance times of keywords, using CiteSpace to generate the time-zone evolution mapping (Fig. 8 ) and burst keywords. The time-zone mapping visually displays the evolution of keywords over time, intuitively reflecting the frequency and initial appearance of keywords in research, commonly used to identify trends in research topics (Jing et al. 2024a ; Kumar et al. 2021 ). Table 10 lists the top 15 keywords by burst strength, with the red sections indicating high-frequency citations and their burst strength in specific years. These burst keywords reveal the focus and trends of research themes over different periods (Kleinberg 2002 ). Combining insights from the time-zone mapping and burst keywords provides more objective and accurate research insights (Wang et al. 2023b ).
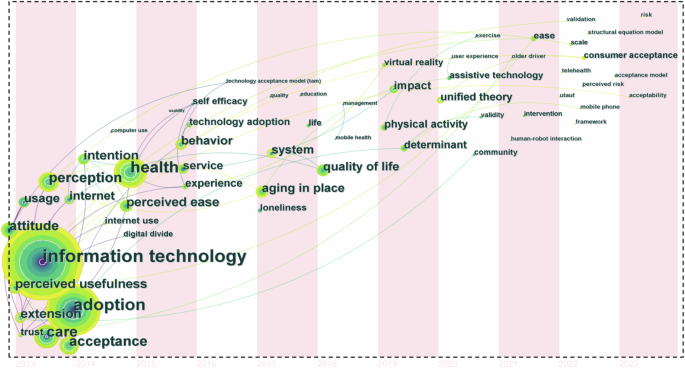
Reflecting the frequency and time of first appearance of keywords in the study.
An integrated analysis of Fig. 8 and Table 10 shows that early research on older adults’ technology acceptance primarily focused on factors such as perceived usefulness, ease of use, and attitudes towards information technology, including their use of computers and the internet (Pan and Jordan-Marsh 2010 ), as well as differences in technology use between older adults and other age groups (Guner and Acarturk 2020 ). Subsequently, the research focus expanded to improving the quality of life for older adults, exploring how technology can optimize health management and enhance the possibility of independent living, emphasizing the significant role of technology in improving the quality of life for the elderly. With ongoing technological advancements, recent research has shifted towards areas such as “virtual reality,” “telehealth,” and “human-robot interaction,” with a focus on the user experience of older adults (Halim et al. 2022 ). The appearance of keywords such as “physical activity” and “exercise” highlights the value of technology in promoting physical activity and health among older adults. This phase of research tends to make cutting-edge technology genuinely serve the practical needs of older adults, achieving its widespread application in daily life. Additionally, research has focused on expanding and quantifying theoretical models of older adults’ technology acceptance, involving keywords such as “perceived risk”, “validation” and “UTAUT”.
In summary, from 2013 to 2023, the field of older adults’ technology acceptance has evolved from initial explorations of influencing factors, to comprehensive enhancements in quality of life and health management, and further to the application and deepening of theoretical models and cutting-edge technologies. This research not only reflects the diversity and complexity of the field but also demonstrates a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of older adults’ interactions with technology across various life scenarios and needs.
Research quality distribution
To reveal the distribution of research quality in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance, a strategic diagram analysis is employed to calculate and illustrate the internal development and interrelationships among various research themes (Xie et al. 2020 ). The strategic diagram uses Centrality as the X-axis and Density as the Y-axis to divide into four quadrants, where the X-axis represents the strength of the connection between thematic clusters and other themes, with higher values indicating a central position in the research field; the Y-axis indicates the level of development within the thematic clusters, with higher values denoting a more mature and widely recognized field (Li and Zhou 2020 ).
Through cluster analysis and manual verification, this study categorized 61 core keywords (Frequency ≥5) into 11 thematic clusters. Subsequently, based on the keywords covered by each thematic cluster, the research themes and their directions for each cluster were summarized (Table 11 ), and the centrality and density coordinates for each cluster were precisely calculated (Table 12 ). Finally, a strategic diagram of the older adults’ technology acceptance research field was constructed (Fig. 9 ). Based on the distribution of thematic clusters across the quadrants in the strategic diagram, the structure and developmental trends of the field were interpreted.
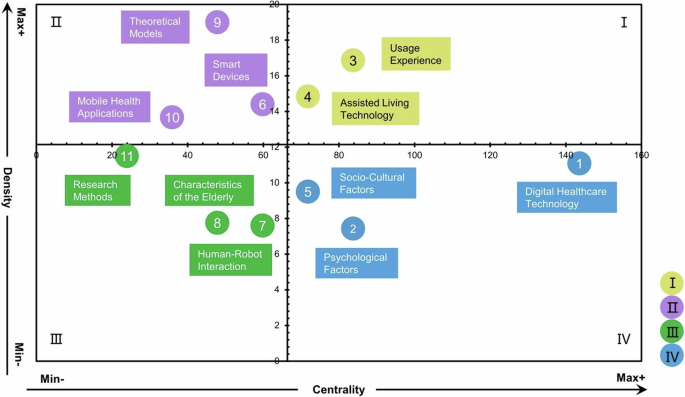
Classification and visualization of theme clusters based on density and centrality.
As illustrated in Fig. 9 , (1) the theme clusters of #3 Usage Experience and #4 Assisted Living Technology are in the first quadrant, characterized by high centrality and density. Their internal cohesion and close links with other themes indicate their mature development, systematic research content or directions have been formed, and they have a significant influence on other themes. These themes play a central role in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance and have promising prospects. (2) The theme clusters of #6 Smart Devices, #9 Theoretical Models, and #10 Mobile Health Applications are in the second quadrant, with higher density but lower centrality. These themes have strong internal connections but weaker external links, indicating that these three themes have received widespread attention from researchers and have been the subject of related research, but more as self-contained systems and exhibit independence. Therefore, future research should further explore in-depth cooperation and cross-application with other themes. (3) The theme clusters of #7 Human-Robot Interaction, #8 Characteristics of the Elderly, and #11 Research Methods are in the third quadrant, with lower centrality and density. These themes are loosely connected internally and have weak links with others, indicating their developmental immaturity. Compared to other topics, they belong to the lower attention edge and niche themes, and there is a need for further investigation. (4) The theme clusters of #1 Digital Healthcare Technology, #2 Psychological Factors, and #5 Socio-Cultural Factors are located in the fourth quadrant, with high centrality but low density. Although closely associated with other research themes, the internal cohesion within these clusters is relatively weak. This suggests that while these themes are closely linked to other research areas, their own development remains underdeveloped, indicating a core immaturity. Nevertheless, these themes are crucial within the research domain of elderly technology acceptance and possess significant potential for future exploration.
Discussion on distribution power (RQ1)
Over the past decade, academic interest and influence in the area of older adults’ technology acceptance have significantly increased. This trend is evidenced by a quantitative analysis of publication and citation volumes, particularly noticeable in 2019 and 2022, where there was a substantial rise in both metrics. The rise is closely linked to the widespread adoption of emerging technologies such as smart homes, wearable devices, and telemedicine among older adults. While these technologies have enhanced their quality of life, they also pose numerous challenges, sparking extensive research into their acceptance, usage behaviors, and influencing factors among the older adults (Pirzada et al. 2022 ; Garcia Reyes et al. 2023 ). Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic led to a surge in technology demand among older adults, especially in areas like medical consultation, online socialization, and health management, further highlighting the importance and challenges of technology. Health risks and social isolation have compelled older adults to rely on technology for daily activities, accelerating its adoption and application within this demographic. This phenomenon has made technology acceptance a critical issue, driving societal and academic focus on the study of technology acceptance among older adults.
The flow of knowledge at the level of high-output disciplines and journals, along with the primary publishing outlets, indicates the highly interdisciplinary nature of research into older adults’ technology acceptance. This reflects the complexity and breadth of issues related to older adults’ technology acceptance, necessitating the integration of multidisciplinary knowledge and approaches. Currently, research is primarily focused on medical health and human-computer interaction, demonstrating academic interest in improving health and quality of life for older adults and addressing the urgent needs related to their interactions with technology. In the field of medical health, research aims to provide advanced and innovative healthcare technologies and services to meet the challenges of an aging population while improving the quality of life for older adults (Abdi et al. 2020 ; Wilson et al. 2021 ). In the field of human-computer interaction, research is focused on developing smarter and more user-friendly interaction models to meet the needs of older adults in the digital age, enabling them to actively participate in social activities and enjoy a higher quality of life (Sayago, 2019 ). These studies are crucial for addressing the challenges faced by aging societies, providing increased support and opportunities for the health, welfare, and social participation of older adults.
Discussion on research power (RQ2)
This study analyzes leading countries and collaboration networks, core institutions and authors, revealing the global research landscape and distribution of research strength in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance, and presents quantitative data on global research trends. From the analysis of country distribution and collaborations, China and the USA hold dominant positions in this field, with developed countries like the UK, Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands also excelling in international cooperation and research influence. The significant investment in technological research and the focus on the technological needs of older adults by many developed countries reflect their rapidly aging societies, policy support, and resource allocation.
China is the only developing country that has become a major contributor in this field, indicating its growing research capabilities and high priority given to aging societies and technological innovation. Additionally, China has close collaborations with countries such as USA, the UK, and Malaysia, driven not only by technological research needs but also by shared challenges and complementarities in aging issues among these nations. For instance, the UK has extensive experience in social welfare and aging research, providing valuable theoretical guidance and practical experience. International collaborations, aimed at addressing the challenges of aging, integrate the strengths of various countries, advancing in-depth and widespread development in the research of technology acceptance among older adults.
At the institutional and author level, City University of Hong Kong leads in publication volume, with research teams led by Chan and Chen demonstrating significant academic activity and contributions. Their research primarily focuses on older adults’ acceptance and usage behaviors of various technologies, including smartphones, smart wearables, and social robots (Chen et al. 2015 ; Li et al. 2019 ; Ma et al. 2016 ). These studies, targeting specific needs and product characteristics of older adults, have developed new models of technology acceptance based on existing frameworks, enhancing the integration of these technologies into their daily lives and laying a foundation for further advancements in the field. Although Tilburg University has a smaller publication output, it holds significant influence in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance. Particularly, the high citation rate of Peek’s studies highlights their excellence in research. Peek extensively explored older adults’ acceptance and usage of home care technologies, revealing the complexity and dynamics of their technology use behaviors. His research spans from identifying systemic influencing factors (Peek et al. 2014 ; Peek et al. 2016 ), emphasizing familial impacts (Luijkx et al. 2015 ), to constructing comprehensive models (Peek et al. 2017 ), and examining the dynamics of long-term usage (Peek et al. 2019 ), fully reflecting the evolving technology landscape and the changing needs of older adults. Additionally, the ongoing contributions of researchers like Ziefle, Rogers, and Wouters in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance demonstrate their research influence and leadership. These researchers have significantly enriched the knowledge base in this area with their diverse perspectives. For instance, Ziefle has uncovered the complex attitudes of older adults towards technology usage, especially the trade-offs between privacy and security, and how different types of activities affect their privacy needs (Maidhof et al. 2023 ; Mujirishvili et al. 2023 ; Schomakers and Ziefle 2023 ; Wilkowska et al. 2022 ), reflecting a deep exploration and ongoing innovation in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance.
Discussion on knowledge base and thematic progress (RQ3)
Through co-citation analysis and systematic review of seminal literature, this study reveals the knowledge foundation and thematic progress in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance. Co-citation networks and cluster analyses illustrate the structural themes of the research, delineating the differentiation and boundaries within this field. Additionally, burst detection analysis offers a valuable perspective for understanding the thematic evolution in the field of technology acceptance among older adults. The development and innovation of theoretical models are foundational to this research. Researchers enhance the explanatory power of constructed models by deepening and expanding existing technology acceptance theories to address theoretical limitations. For instance, Heerink et al. ( 2010 ) modified and expanded the UTAUT model by integrating functional assessment and social interaction variables to create the almere model. This model significantly enhances the ability to explain the intentions of older users in utilizing assistive social agents and improves the explanation of actual usage behaviors. Additionally, Chen and Chan ( 2014 ) extended the TAM to include age-related health and capability features of older adults, creating the STAM, which substantially improves predictions of older adults’ technology usage behaviors. Personal attributes, health and capability features, and facilitating conditions have a direct impact on technology acceptance. These factors more effectively predict older adults’ technology usage behaviors than traditional attitudinal factors.
With the advancement of technology and the application of emerging technologies, new research topics have emerged, increasingly focusing on older adults’ acceptance and use of these technologies. Prior to this, the study by Mitzner et al. ( 2010 ) challenged the stereotype of older adults’ conservative attitudes towards technology, highlighting the central roles of usability and usefulness in the technology acceptance process. This discovery laid an important foundation for subsequent research. Research fields such as “smart home technology,” “social life,” and “customer service” are emerging, indicating a shift in focus towards the practical and social applications of technology in older adults’ lives. Research not only focuses on the technology itself but also on how these technologies integrate into older adults’ daily lives and how they can improve the quality of life through technology. For instance, studies such as those by Ma et al. ( 2016 ), Hoque and Sorwar ( 2017 ), and Li et al. ( 2019 ) have explored factors influencing older adults’ use of smartphones, mHealth, and smart wearable devices.
Furthermore, the diversification of research methodologies and innovation in evaluation techniques, such as the use of mixed methods, structural equation modeling (SEM), and neural network (NN) approaches, have enhanced the rigor and reliability of the findings, enabling more precise identification of the factors and mechanisms influencing technology acceptance. Talukder et al. ( 2020 ) employed an effective multimethodological strategy by integrating SEM and NN to leverage the complementary strengths of both approaches, thus overcoming their individual limitations and more accurately analyzing and predicting older adults’ acceptance of wearable health technologies (WHT). SEM is utilized to assess the determinants’ impact on the adoption of WHT, while neural network models validate SEM outcomes and predict the significance of key determinants. This combined approach not only boosts the models’ reliability and explanatory power but also provides a nuanced understanding of the motivations and barriers behind older adults’ acceptance of WHT, offering deep research insights.
Overall, co-citation analysis of the literature in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance has uncovered deeper theoretical modeling and empirical studies on emerging technologies, while emphasizing the importance of research methodological and evaluation innovations in understanding complex social science issues. These findings are crucial for guiding the design and marketing strategies of future technology products, especially in the rapidly growing market of older adults.
Discussion on research hotspots and evolutionary trends (RQ4)
By analyzing core keywords, we can gain deep insights into the hot topics, evolutionary trends, and quality distribution of research in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance. The frequent occurrence of the keywords “TAM” and “UTAUT” indicates that the applicability and theoretical extension of existing technology acceptance models among older adults remain a focal point in academia. This phenomenon underscores the enduring influence of the studies by Davis ( 1989 ) and Venkatesh et al. ( 2003 ), whose models provide a robust theoretical framework for explaining and predicting older adults’ acceptance and usage of emerging technologies. With the widespread application of artificial intelligence (AI) and big data technologies, these theoretical models have incorporated new variables such as perceived risk, trust, and privacy issues (Amin et al. 2024 ; Chen et al. 2024 ; Jing et al. 2024b ; Seibert et al. 2021 ; Wang et al. 2024b ), advancing the theoretical depth and empirical research in this field.
Keyword co-occurrence cluster analysis has revealed multiple research hotspots in the field, including factors influencing technology adoption, interactive experiences between older adults and assistive technologies, the application of mobile health technology in health management, and technology-assisted home care. These studies primarily focus on enhancing the quality of life and health management of older adults through emerging technologies, particularly in the areas of ambient assisted living, smart health monitoring, and intelligent medical care. In these domains, the role of AI technology is increasingly significant (Qian et al. 2021 ; Ho 2020 ). With the evolution of next-generation information technologies, AI is increasingly integrated into elder care systems, offering intelligent, efficient, and personalized service solutions by analyzing the lifestyles and health conditions of older adults. This integration aims to enhance older adults’ quality of life in aspects such as health monitoring and alerts, rehabilitation assistance, daily health management, and emotional support (Lee et al. 2023 ). A survey indicates that 83% of older adults prefer AI-driven solutions when selecting smart products, demonstrating the increasing acceptance of AI in elder care (Zhao and Li 2024 ). Integrating AI into elder care presents both opportunities and challenges, particularly in terms of user acceptance, trust, and long-term usage effects, which warrant further exploration (Mhlanga 2023 ). These studies will help better understand the profound impact of AI technology on the lifestyles of older adults and provide critical references for optimizing AI-driven elder care services.
The Time-zone evolution mapping and burst keyword analysis further reveal the evolutionary trends of research hotspots. Early studies focused on basic technology acceptance models and user perceptions, later expanding to include quality of life and health management. In recent years, research has increasingly focused on cutting-edge technologies such as virtual reality, telehealth, and human-robot interaction, with a concurrent emphasis on the user experience of older adults. This evolutionary process demonstrates a deepening shift from theoretical models to practical applications, underscoring the significant role of technology in enhancing the quality of life for older adults. Furthermore, the strategic coordinate mapping analysis clearly demonstrates the development and mutual influence of different research themes. High centrality and density in the themes of Usage Experience and Assisted Living Technology indicate their mature research status and significant impact on other themes. The themes of Smart Devices, Theoretical Models, and Mobile Health Applications demonstrate self-contained research trends. The themes of Human-Robot Interaction, Characteristics of the Elderly, and Research Methods are not yet mature, but they hold potential for development. Themes of Digital Healthcare Technology, Psychological Factors, and Socio-Cultural Factors are closely related to other themes, displaying core immaturity but significant potential.
In summary, the research hotspots in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance are diverse and dynamic, demonstrating the academic community’s profound understanding of how older adults interact with technology across various life contexts and needs. Under the influence of AI and big data, research should continue to focus on the application of emerging technologies among older adults, exploring in depth how they adapt to and effectively use these technologies. This not only enhances the quality of life and healthcare experiences for older adults but also drives ongoing innovation and development in this field.
Research agenda
Based on the above research findings, to further understand and promote technology acceptance and usage among older adults, we recommend future studies focus on refining theoretical models, exploring long-term usage, and assessing user experience in the following detailed aspects:
Refinement and validation of specific technology acceptance models for older adults: Future research should focus on developing and validating technology acceptance models based on individual characteristics, particularly considering variations in technology acceptance among older adults across different educational levels and cultural backgrounds. This includes factors such as age, gender, educational background, and cultural differences. Additionally, research should examine how well specific technologies, such as wearable devices and mobile health applications, meet the needs of older adults. Building on existing theoretical models, this research should integrate insights from multiple disciplines such as psychology, sociology, design, and engineering through interdisciplinary collaboration to create more accurate and comprehensive models, which should then be validated in relevant contexts.
Deepening the exploration of the relationship between long-term technology use and quality of life among older adults: The acceptance and use of technology by users is a complex and dynamic process (Seuwou et al. 2016 ). Existing research predominantly focuses on older adults’ initial acceptance or short-term use of new technologies; however, the impact of long-term use on their quality of life and health is more significant. Future research should focus on the evolution of older adults’ experiences and needs during long-term technology usage, and the enduring effects of technology on their social interactions, mental health, and life satisfaction. Through longitudinal studies and qualitative analysis, this research reveals the specific needs and challenges of older adults in long-term technology use, providing a basis for developing technologies and strategies that better meet their requirements. This understanding aids in comprehensively assessing the impact of technology on older adults’ quality of life and guiding the optimization and improvement of technological products.
Evaluating the Importance of User Experience in Research on Older Adults’ Technology Acceptance: Understanding the mechanisms of information technology acceptance and use is central to human-computer interaction research. Although technology acceptance models and user experience models differ in objectives, they share many potential intersections. Technology acceptance research focuses on structured prediction and assessment, while user experience research concentrates on interpreting design impacts and new frameworks. Integrating user experience to assess older adults’ acceptance of technology products and systems is crucial (Codfrey et al. 2022 ; Wang et al. 2019 ), particularly for older users, where specific product designs should emphasize practicality and usability (Fisk et al. 2020 ). Researchers need to explore innovative age-appropriate design methods to enhance older adults’ usage experience. This includes studying older users’ actual usage preferences and behaviors, optimizing user interfaces, and interaction designs. Integrating feedback from older adults to tailor products to their needs can further promote their acceptance and continued use of technology products.
Conclusions
This study conducted a systematic review of the literature on older adults’ technology acceptance over the past decade through bibliometric analysis, focusing on the distribution power, research power, knowledge base and theme progress, research hotspots, evolutionary trends, and quality distribution. Using a combination of quantitative and qualitative methods, this study has reached the following conclusions:
Technology acceptance among older adults has become a hot topic in the international academic community, involving the integration of knowledge across multiple disciplines, including Medical Informatics, Health Care Sciences Services, and Ergonomics. In terms of journals, “PSYCHOLOGY, EDUCATION, HEALTH” represents a leading field, with key publications including Computers in Human Behavior , Journal of Medical Internet Research , and International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction . These journals possess significant academic authority and extensive influence in the field.
Research on technology acceptance among older adults is particularly active in developed countries, with China and USA publishing significantly more than other nations. The Netherlands leads in high average citation rates, indicating the depth and impact of its research. Meanwhile, the UK stands out in terms of international collaboration. At the institutional level, City University of Hong Kong and The University of Hong Kong in China are in leading positions. Tilburg University in the Netherlands demonstrates exceptional research quality through its high average citation count. At the author level, Chen from China has the highest number of publications, while Peek from the Netherlands has the highest average citation count.
Co-citation analysis of references indicates that the knowledge base in this field is divided into three main categories: theoretical model deepening, emerging technology applications, and research methods and evaluation. Seminal literature focuses on four areas: specific technology use by older adults, expansion of theoretical models of technology acceptance, information technology adoption behavior, and research perspectives. Research themes have evolved from initial theoretical deepening and analysis of influencing factors to empirical studies on individual factors and emerging technologies.
Keyword analysis indicates that TAM and UTAUT are the most frequently occurring terms, while “assistive technology” and “virtual reality” are focal points with high frequency and centrality. Keyword clustering analysis reveals that research hotspots are concentrated on the influencing factors of technology adoption, human-robot interaction experiences, mobile health management, and technology for aging in place. Time-zone evolution mapping and burst keyword analysis have revealed the research evolution from preliminary exploration of influencing factors, to enhancements in quality of life and health management, and onto advanced technology applications and deepening of theoretical models. Furthermore, analysis of research quality distribution indicates that Usage Experience and Assisted Living Technology have become core topics, while Smart Devices, Theoretical Models, and Mobile Health Applications point towards future research directions.
Through this study, we have systematically reviewed the dynamics, core issues, and evolutionary trends in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance, constructing a comprehensive Knowledge Mapping of the domain and presenting a clear framework of existing research. This not only lays the foundation for subsequent theoretical discussions and innovative applications in the field but also provides an important reference for relevant scholars.
Limitations
To our knowledge, this is the first bibliometric analysis concerning technology acceptance among older adults, and we adhered strictly to bibliometric standards throughout our research. However, this study relies on the Web of Science Core Collection, and while its authority and breadth are widely recognized, this choice may have missed relevant literature published in other significant databases such as PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar, potentially overlooking some critical academic contributions. Moreover, given that our analysis was confined to literature in English, it may not reflect studies published in other languages, somewhat limiting the global representativeness of our data sample.
It is noteworthy that with the rapid development of AI technology, its increasingly widespread application in elderly care services is significantly transforming traditional care models. AI is profoundly altering the lifestyles of the elderly, from health monitoring and smart diagnostics to intelligent home systems and personalized care, significantly enhancing their quality of life and health care standards. The potential for AI technology within the elderly population is immense, and research in this area is rapidly expanding. However, due to the restrictive nature of the search terms used in this study, it did not fully cover research in this critical area, particularly in addressing key issues such as trust, privacy, and ethics.
Consequently, future research should not only expand data sources, incorporating multilingual and multidatabase literature, but also particularly focus on exploring older adults’ acceptance of AI technology and its applications, in order to construct a more comprehensive academic landscape of older adults’ technology acceptance, thereby enriching and extending the knowledge system and academic trends in this field.
Data availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available in the Dataverse repository: https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/6K0GJH .
Abdi S, de Witte L, Hawley M (2020) Emerging technologies with potential care and support applications for older people: review of gray literature. JMIR Aging 3(2):e17286. https://doi.org/10.2196/17286
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Achuthan K, Nair VK, Kowalski R, Ramanathan S, Raman R (2023) Cyberbullying research—Alignment to sustainable development and impact of COVID-19: Bibliometrics and science mapping analysis. Comput Human Behav 140:107566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2022.107566
Article Google Scholar
Ahmad A, Mozelius P (2022) Human-Computer Interaction for Older Adults: a Literature Review on Technology Acceptance of eHealth Systems. J Eng Res Sci 1(4):119–126. https://doi.org/10.55708/js0104014
Ale Ebrahim N, Salehi H, Embi MA, Habibi F, Gholizadeh H, Motahar SM (2014) Visibility and citation impact. Int Educ Stud 7(4):120–125. https://doi.org/10.5539/ies.v7n4p120
Amin MS, Johnson VL, Prybutok V, Koh CE (2024) An investigation into factors affecting the willingness to disclose personal health information when using AI-enabled caregiver robots. Ind Manag Data Syst 124(4):1677–1699. https://doi.org/10.1108/IMDS-09-2023-0608
Baer NR, Vietzke J, Schenk L (2022) Middle-aged and older adults’ acceptance of mobile nutrition and fitness apps: a systematic mixed studies review. PLoS One 17(12):e0278879. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0278879
Barnard Y, Bradley MD, Hodgson F, Lloyd AD (2013) Learning to use new technologies by older adults: Perceived difficulties, experimentation behaviour and usability. Comput Human Behav 29(4):1715–1724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2013.02.006
Berkowsky RW, Sharit J, Czaja SJ (2017) Factors predicting decisions about technology adoption among older adults. Innov Aging 3(1):igy002. https://doi.org/10.1093/geroni/igy002
Braun MT (2013) Obstacles to social networking website use among older adults. Comput Human Behav 29(3):673–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2012.12.004
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Campo-Prieto P, Rodríguez-Fuentes G, Cancela-Carral JM (2021) Immersive virtual reality exergame promotes the practice of physical activity in older people: An opportunity during COVID-19. Multimodal Technol Interact 5(9):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti5090052
Chen C (2006) CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol 57(3):359–377. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.20317
Chen C, Dubin R, Kim MC (2014) Emerging trends and new developments in regenerative medicine: a scientometric update (2000–2014). Expert Opin Biol Ther 14(9):1295–1317. https://doi.org/10.1517/14712598.2014.920813
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Chen C, Leydesdorff L (2014) Patterns of connections and movements in dual‐map overlays: A new method of publication portfolio analysis. J Assoc Inf Sci Technol 65(2):334–351. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.22968
Chen J, Wang C, Tang Y (2022) Knowledge mapping of volunteer motivation: A bibliometric analysis and cross-cultural comparative study. Front Psychol 13:883150. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.883150
Chen JY, Liu YD, Dai J, Wang CL (2023) Development and status of moral education research: Visual analysis based on knowledge graph. Front Psychol 13:1079955. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1079955
Chen K, Chan AH (2011) A review of technology acceptance by older adults. Gerontechnology 10(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.4017/gt.2011.10.01.006.00
Chen K, Chan AH (2014) Gerontechnology acceptance by elderly Hong Kong Chinese: a senior technology acceptance model (STAM). Ergonomics 57(5):635–652. https://doi.org/10.1080/00140139.2014.895855
Chen K, Zhang Y, Fu X (2019) International research collaboration: An emerging domain of innovation studies? Res Policy 48(1):149–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2018.08.005
Chen X, Hu Z, Wang C (2024) Empowering education development through AIGC: A systematic literature review. Educ Inf Technol 1–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-024-12549-7
Chen Y, Chen CM, Liu ZY, Hu ZG, Wang XW (2015) The methodology function of CiteSpace mapping knowledge domains. Stud Sci Sci 33(2):242–253. https://doi.org/10.16192/j.cnki.1003-2053.2015.02.009
Codfrey GS, Baharum A, Zain NHM, Omar M, Deris FD (2022) User Experience in Product Design and Development: Perspectives and Strategies. Math Stat Eng Appl 71(2):257–262. https://doi.org/10.17762/msea.v71i2.83
Dai J, Zhang X, Wang CL (2024) A meta-analysis of learners’ continuance intention toward online education platforms. Educ Inf Technol 1–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-024-12654-7
Davis FD (1989) Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Q 13(3):319–340. https://doi.org/10.2307/249008
Delmastro F, Dolciotti C, Palumbo F, Magrini M, Di Martino F, La Rosa D, Barcaro U (2018) Long-term care: how to improve the quality of life with mobile and e-health services. In 2018 14th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications (WiMob), pp. 12–19. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/WiMOB.2018.8589157
Dupuis K, Tsotsos LE (2018) Technology for remote health monitoring in an older population: a role for mobile devices. Multimodal Technol Interact 2(3):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti2030043
Ferguson C, Hickman LD, Turkmani S, Breen P, Gargiulo G, Inglis SC (2021) Wearables only work on patients that wear them”: Barriers and facilitators to the adoption of wearable cardiac monitoring technologies. Cardiovasc Digit Health J 2(2):137–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cvdhj.2021.02.001
Fisk AD, Czaja SJ, Rogers WA, Charness N, Sharit J (2020) Designing for older adults: Principles and creative human factors approaches. CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420080681
Friesen S, Brémault-Phillips S, Rudrum L, Rogers LG (2016) Environmental design that supports healthy aging: Evaluating a new supportive living facility. J Hous Elderly 30(1):18–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/02763893.2015.1129380
Garcia Reyes EP, Kelly R, Buchanan G, Waycott J (2023) Understanding Older Adults’ Experiences With Technologies for Health Self-management: Interview Study. JMIR Aging 6:e43197. https://doi.org/10.2196/43197
Geng Z, Wang J, Liu J, Miao J (2024) Bibliometric analysis of the development, current status, and trends in adult degenerative scoliosis research: A systematic review from 1998 to 2023. J Pain Res 17:153–169. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S437575
González A, Ramírez MP, Viadel V (2012) Attitudes of the elderly toward information and communications technologies. Educ Gerontol 38(9):585–594. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601277.2011.595314
Guner H, Acarturk C (2020) The use and acceptance of ICT by senior citizens: a comparison of technology acceptance model (TAM) for elderly and young adults. Univ Access Inf Soc 19(2):311–330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10209-018-0642-4
Halim I, Saptari A, Perumal PA, Abdullah Z, Abdullah S, Muhammad MN (2022) A Review on Usability and User Experience of Assistive Social Robots for Older Persons. Int J Integr Eng 14(6):102–124. https://penerbit.uthm.edu.my/ojs/index.php/ijie/article/view/8566
He Y, He Q, Liu Q (2022) Technology acceptance in socially assistive robots: Scoping review of models, measurement, and influencing factors. J Healthc Eng 2022(1):6334732. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/6334732
Heerink M, Kröse B, Evers V, Wielinga B (2010) Assessing acceptance of assistive social agent technology by older adults: the almere model. Int J Soc Robot 2:361–375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12369-010-0068-5
Ho A (2020) Are we ready for artificial intelligence health monitoring in elder care? BMC Geriatr 20(1):358. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-020-01764-9
Hoque R, Sorwar G (2017) Understanding factors influencing the adoption of mHealth by the elderly: An extension of the UTAUT model. Int J Med Inform 101:75–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2017.02.002
Hota PK, Subramanian B, Narayanamurthy G (2020) Mapping the intellectual structure of social entrepreneurship research: A citation/co-citation analysis. J Bus Ethics 166(1):89–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-019-04129-4
Huang R, Yan P, Yang X (2021) Knowledge map visualization of technology hotspots and development trends in China’s textile manufacturing industry. IET Collab Intell Manuf 3(3):243–251. https://doi.org/10.1049/cim2.12024
Article ADS Google Scholar
Jing Y, Wang C, Chen Y, Wang H, Yu T, Shadiev R (2023) Bibliometric mapping techniques in educational technology research: A systematic literature review. Educ Inf Technol 1–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-12178-6
Jing YH, Wang CL, Chen ZY, Shen SS, Shadiev R (2024a) A Bibliometric Analysis of Studies on Technology-Supported Learning Environments: Hotopics and Frontier Evolution. J Comput Assist Learn 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12934
Jing YH, Wang HM, Chen XJ, Wang CL (2024b) What factors will affect the effectiveness of using ChatGPT to solve programming problems? A quasi-experimental study. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11:319. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-02751-w
Kamrani P, Dorsch I, Stock WG (2021) Do researchers know what the h-index is? And how do they estimate its importance? Scientometrics 126(7):5489–5508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-021-03968-1
Kim HS, Lee KH, Kim H, Kim JH (2014) Using mobile phones in healthcare management for the elderly. Maturitas 79(4):381–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2014.08.013
Article MathSciNet PubMed Google Scholar
Kleinberg J (2002) Bursty and hierarchical structure in streams. In Proceedings of the eighth ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, pp. 91–101. https://doi.org/10.1145/775047.775061
Kruse C, Fohn J, Wilson N, Patlan EN, Zipp S, Mileski M (2020) Utilization barriers and medical outcomes commensurate with the use of telehealth among older adults: systematic review. JMIR Med Inform 8(8):e20359. https://doi.org/10.2196/20359
Kumar S, Lim WM, Pandey N, Christopher Westland J (2021) 20 years of electronic commerce research. Electron Commer Res 21:1–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10660-021-09464-1
Kwiek M (2021) What large-scale publication and citation data tell us about international research collaboration in Europe: Changing national patterns in global contexts. Stud High Educ 46(12):2629–2649. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2020.1749254
Lee C, Coughlin JF (2015) PERSPECTIVE: Older adults’ adoption of technology: an integrated approach to identifying determinants and barriers. J Prod Innov Manag 32(5):747–759. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpim.12176
Lee CH, Wang C, Fan X, Li F, Chen CH (2023) Artificial intelligence-enabled digital transformation in elderly healthcare field: scoping review. Adv Eng Inform 55:101874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aei.2023.101874
Leydesdorff L, Rafols I (2012) Interactive overlays: A new method for generating global journal maps from Web-of-Science data. J Informetr 6(2):318–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2011.11.003
Li J, Ma Q, Chan AH, Man S (2019) Health monitoring through wearable technologies for older adults: Smart wearables acceptance model. Appl Ergon 75:162–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apergo.2018.10.006
Article ADS PubMed Google Scholar
Li X, Zhou D (2020) Product design requirement information visualization approach for intelligent manufacturing services. China Mech Eng 31(07):871, http://www.cmemo.org.cn/EN/Y2020/V31/I07/871
Google Scholar
Lin Y, Yu Z (2024a) An integrated bibliometric analysis and systematic review modelling students’ technostress in higher education. Behav Inf Technol 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144929X.2024.2332458
Lin Y, Yu Z (2024b) A bibliometric analysis of artificial intelligence chatbots in educational contexts. Interact Technol Smart Educ 21(2):189–213. https://doi.org/10.1108/ITSE-12-2022-0165
Liu L, Duffy VG (2023) Exploring the future development of Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications in chatbots: a bibliometric analysis. Int J Soc Robot 15(5):703–716. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12369-022-00956-0
Liu R, Li X, Chu J (2022) Evolution of applied variables in the research on technology acceptance of the elderly. In: International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp 500–520. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-05581-23_5
Luijkx K, Peek S, Wouters E (2015) “Grandma, you should do it—It’s cool” Older Adults and the Role of Family Members in Their Acceptance of Technology. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12(12):15470–15485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph121214999
Lussier M, Lavoie M, Giroux S, Consel C, Guay M, Macoir J, Bier N (2018) Early detection of mild cognitive impairment with in-home monitoring sensor technologies using functional measures: a systematic review. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 23(2):838–847. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2018.2834317
López-Robles JR, Otegi-Olaso JR, Porto Gomez I, Gamboa-Rosales NK, Gamboa-Rosales H, Robles-Berumen H (2018) Bibliometric network analysis to identify the intellectual structure and evolution of the big data research field. In: International Conference on Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning, Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp 113–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03496-2_13
Ma Q, Chan AH, Chen K (2016) Personal and other factors affecting acceptance of smartphone technology by older Chinese adults. Appl Ergon 54:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apergo.2015.11.015
Ma Q, Chan AHS, Teh PL (2021) Insights into Older Adults’ Technology Acceptance through Meta-Analysis. Int J Hum-Comput Interact 37(11):1049–1062. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2020.1865005
Macedo IM (2017) Predicting the acceptance and use of information and communication technology by older adults: An empirical examination of the revised UTAUT2. Comput Human Behav 75:935–948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.06.013
Maidhof C, Offermann J, Ziefle M (2023) Eyes on privacy: acceptance of video-based AAL impacted by activities being filmed. Front Public Health 11:1186944. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2023.1186944
Majumder S, Aghayi E, Noferesti M, Memarzadeh-Tehran H, Mondal T, Pang Z, Deen MJ (2017) Smart homes for elderly healthcare—Recent advances and research challenges. Sensors 17(11):2496. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112496
Article ADS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mhlanga D (2023) Artificial Intelligence in elderly care: Navigating ethical and responsible AI adoption for seniors. Available at SSRN 4675564. 4675564 min) Identifying citation patterns of scientific breakthroughs: A perspective of dynamic citation process. Inf Process Manag 58(1):102428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2020.102428
Mitzner TL, Boron JB, Fausset CB, Adams AE, Charness N, Czaja SJ, Sharit J (2010) Older adults talk technology: Technology usage and attitudes. Comput Human Behav 26(6):1710–1721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2010.06.020
Mitzner TL, Savla J, Boot WR, Sharit J, Charness N, Czaja SJ, Rogers WA (2019) Technology adoption by older adults: Findings from the PRISM trial. Gerontologist 59(1):34–44. https://doi.org/10.1093/geront/gny113
Mongeon P, Paul-Hus A (2016) The journal coverage of Web of Science and Scopus: a comparative analysis. Scientometrics 106:213–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-015-1765-5
Mostaghel R (2016) Innovation and technology for the elderly: Systematic literature review. J Bus Res 69(11):4896–4900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.04.049
Mujirishvili T, Maidhof C, Florez-Revuelta F, Ziefle M, Richart-Martinez M, Cabrero-García J (2023) Acceptance and privacy perceptions toward video-based active and assisted living technologies: Scoping review. J Med Internet Res 25:e45297. https://doi.org/10.2196/45297
Naseri RNN, Azis SN, Abas N (2023) A Review of Technology Acceptance and Adoption Models in Consumer Study. FIRM J Manage Stud 8(2):188–199. https://doi.org/10.33021/firm.v8i2.4536
Nguyen UP, Hallinger P (2020) Assessing the distinctive contributions of Simulation & Gaming to the literature, 1970–2019: A bibliometric review. Simul Gaming 51(6):744–769. https://doi.org/10.1177/1046878120941569
Olmedo-Aguirre JO, Reyes-Campos J, Alor-Hernández G, Machorro-Cano I, Rodríguez-Mazahua L, Sánchez-Cervantes JL (2022) Remote healthcare for elderly people using wearables: A review. Biosensors 12(2):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020073
Pan S, Jordan-Marsh M (2010) Internet use intention and adoption among Chinese older adults: From the expanded technology acceptance model perspective. Comput Human Behav 26(5):1111–1119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2010.03.015
Pan X, Yan E, Cui M, Hua W (2018) Examining the usage, citation, and diffusion patterns of bibliometric map software: A comparative study of three tools. J Informetr 12(2):481–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2018.03.005
Park JS, Kim NR, Han EJ (2018) Analysis of trends in science and technology using keyword network analysis. J Korea Ind Inf Syst Res 23(2):63–73. https://doi.org/10.9723/jksiis.2018.23.2.063
Peek ST, Luijkx KG, Rijnaard MD, Nieboer ME, Van Der Voort CS, Aarts S, Wouters EJ (2016) Older adults’ reasons for using technology while aging in place. Gerontology 62(2):226–237. https://doi.org/10.1159/000430949
Peek ST, Luijkx KG, Vrijhoef HJ, Nieboer ME, Aarts S, van der Voort CS, Wouters EJ (2017) Origins and consequences of technology acquirement by independent-living seniors: Towards an integrative model. BMC Geriatr 17:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-017-0582-5
Peek ST, Wouters EJ, Van Hoof J, Luijkx KG, Boeije HR, Vrijhoef HJ (2014) Factors influencing acceptance of technology for aging in place: a systematic review. Int J Med Inform 83(4):235–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2014.01.004
Peek STM, Luijkx KG, Vrijhoef HJM, Nieboer ME, Aarts S, Van Der Voort CS, Wouters EJM (2019) Understanding changes and stability in the long-term use of technologies by seniors who are aging in place: a dynamical framework. BMC Geriatr 19:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-019-1241-9
Perez AJ, Siddiqui F, Zeadally S, Lane D (2023) A review of IoT systems to enable independence for the elderly and disabled individuals. Internet Things 21:100653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iot.2022.100653
Piau A, Wild K, Mattek N, Kaye J (2019) Current state of digital biomarker technologies for real-life, home-based monitoring of cognitive function for mild cognitive impairment to mild Alzheimer disease and implications for clinical care: systematic review. J Med Internet Res 21(8):e12785. https://doi.org/10.2196/12785
Pirzada P, Wilde A, Doherty GH, Harris-Birtill D (2022) Ethics and acceptance of smart homes for older adults. Inform Health Soc Care 47(1):10–37. https://doi.org/10.1080/17538157.2021.1923500
Pranckutė R (2021) Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus: The titans of bibliographic information in today’s academic world. Publications 9(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/publications9010012
Qian K, Zhang Z, Yamamoto Y, Schuller BW (2021) Artificial intelligence internet of things for the elderly: From assisted living to health-care monitoring. IEEE Signal Process Mag 38(4):78–88. https://doi.org/10.1109/MSP.2021.3057298
Redner S (1998) How popular is your paper? An empirical study of the citation distribution. Eur Phys J B-Condens Matter Complex Syst 4(2):131–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100510050359
Sayago S (ed.) (2019) Perspectives on human-computer interaction research with older people. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-06076-3
Schomakers EM, Ziefle M (2023) Privacy vs. security: trade-offs in the acceptance of smart technologies for aging-in-place. Int J Hum Comput Interact 39(5):1043–1058. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2022.2078463
Schroeder T, Dodds L, Georgiou A, Gewald H, Siette J (2023) Older adults and new technology: Mapping review of the factors associated with older adults’ intention to adopt digital technologies. JMIR Aging 6(1):e44564. https://doi.org/10.2196/44564
Seibert K, Domhoff D, Bruch D, Schulte-Althoff M, Fürstenau D, Biessmann F, Wolf-Ostermann K (2021) Application scenarios for artificial intelligence in nursing care: rapid review. J Med Internet Res 23(11):e26522. https://doi.org/10.2196/26522
Seuwou P, Banissi E, Ubakanma G (2016) User acceptance of information technology: A critical review of technology acceptance models and the decision to invest in Information Security. In: Global Security, Safety and Sustainability-The Security Challenges of the Connected World: 11th International Conference, ICGS3 2017, London, UK, January 18-20, 2017, Proceedings 11:230-251. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-51064-4_19
Shiau WL, Wang X, Zheng F (2023) What are the trend and core knowledge of information security? A citation and co-citation analysis. Inf Manag 60(3):103774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2023.103774
Sinha S, Verma A, Tiwari P (2021) Technology: Saving and enriching life during COVID-19. Front Psychol 12:647681. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.647681
Soar J (2010) The potential of information and communication technologies to support ageing and independent living. Ann Telecommun 65:479–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12243-010-0167-1
Strotmann A, Zhao D (2012) Author name disambiguation: What difference does it make in author‐based citation analysis? J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol 63(9):1820–1833. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.22695
Talukder MS, Sorwar G, Bao Y, Ahmed JU, Palash MAS (2020) Predicting antecedents of wearable healthcare technology acceptance by elderly: A combined SEM-Neural Network approach. Technol Forecast Soc Change 150:119793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2019.119793
Taskin Z, Al U (2019) Natural language processing applications in library and information science. Online Inf Rev 43(4):676–690. https://doi.org/10.1108/oir-07-2018-0217
Touqeer H, Zaman S, Amin R, Hussain M, Al-Turjman F, Bilal M (2021) Smart home security: challenges, issues and solutions at different IoT layers. J Supercomput 77(12):14053–14089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-021-03825-1
United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (2023) World population ageing 2023: Highlights. https://www.un.org/zh/193220
Valk CAL, Lu Y, Randriambelonoro M, Jessen J (2018) Designing for technology acceptance of wearable and mobile technologies for senior citizen users. In: 21st DMI: Academic Design Management Conference (ADMC 2018), Design Management Institute, pp 1361–1373. https://www.dmi.org/page/ADMC2018
Van Eck N, Waltman L (2010) Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 84(2):523–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
Vancea M, Solé-Casals J (2016) Population aging in the European Information Societies: towards a comprehensive research agenda in eHealth innovations for elderly. Aging Dis 7(4):526. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2015.1214
Venkatesh V, Morris MG, Davis GB, Davis FD (2003) User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Q 27(3):425–478. https://doi.org/10.2307/30036540
Wagner N, Hassanein K, Head M (2010) Computer use by older adults: A multi-disciplinary review. Comput Human Behav 26(5):870–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2010.03.029
Wahlroos N, Narsakka N, Stolt M, Suhonen R (2023) Physical environment maintaining independence and self-management of older people in long-term care settings—An integrative literature review. J Aging Environ 37(3):295–313. https://doi.org/10.1080/26892618.2022.2092927
Wang CL, Chen XJ, Yu T, Liu YD, Jing YH (2024a) Education reform and change driven by digital technology: a bibliometric study from a global perspective. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-02717-y
Wang CL, Dai J, Zhu KK, Yu T, Gu XQ (2023a) Understanding the Continuance Intention of College Students Toward New E-learning Spaces Based on an Integrated Model of the TAM and TTF. Int J Hum-comput Int 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2023.2291609
Wang CL, Wang HM, Li YY, Dai J, Gu XQ, Yu T (2024b) Factors Influencing University Students’ Behavioral Intention to Use Generative Artificial Intelligence: Integrating the Theory of Planned Behavior and AI Literacy. Int J Hum-comput Int 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2024.2383033
Wang J, Zhao W, Zhang Z, Liu X, Xie T, Wang L, Zhang Y (2024c) A journey of challenges and victories: a bibliometric worldview of nanomedicine since the 21st century. Adv Mater 36(15):2308915. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202308915
Wang J, Chen Y, Huo S, Mai L, Jia F (2023b) Research hotspots and trends of social robot interaction design: A bibliometric analysis. Sensors 23(23):9369. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239369
Wang KH, Chen G, Chen HG (2017) A model of technology adoption by older adults. Soc Behav Personal 45(4):563–572. https://doi.org/10.2224/sbp.5778
Wang S, Bolling K, Mao W, Reichstadt J, Jeste D, Kim HC, Nebeker C (2019) Technology to Support Aging in Place: Older Adults’ Perspectives. Healthcare 7(2):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare7020060
Wang Z, Liu D, Sun Y, Pang X, Sun P, Lin F, Ren K (2022) A survey on IoT-enabled home automation systems: Attacks and defenses. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 24(4):2292–2328. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2022.3201557
Wilkowska W, Offermann J, Spinsante S, Poli A, Ziefle M (2022) Analyzing technology acceptance and perception of privacy in ambient assisted living for using sensor-based technologies. PloS One 17(7):e0269642. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0269642
Wilson J, Heinsch M, Betts D, Booth D, Kay-Lambkin F (2021) Barriers and facilitators to the use of e-health by older adults: a scoping review. BMC Public Health 21:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-11623-w
Xia YQ, Deng YL, Tao XY, Zhang SN, Wang CL (2024) Digital art exhibitions and psychological well-being in Chinese Generation Z: An analysis based on the S-O-R framework. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11:266. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-02718-x
Xie H, Zhang Y, Duan K (2020) Evolutionary overview of urban expansion based on bibliometric analysis in Web of Science from 1990 to 2019. Habitat Int 95:102100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2019.10210
Xu Z, Ge Z, Wang X, Skare M (2021) Bibliometric analysis of technology adoption literature published from 1997 to 2020. Technol Forecast Soc Change 170:120896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120896
Yap YY, Tan SH, Choon SW (2022) Elderly’s intention to use technologies: a systematic literature review. Heliyon 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e08765
Yu T, Dai J, Wang CL (2023) Adoption of blended learning: Chinese university students’ perspectives. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 10:390. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01904-7
Yusif S, Soar J, Hafeez-Baig A (2016) Older people, assistive technologies, and the barriers to adoption: A systematic review. Int J Med Inform 94:112–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2016.07.004
Zhang J, Zhu L (2022) Citation recommendation using semantic representation of cited papers’ relations and content. Expert Syst Appl 187:115826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115826
Zhao Y, Li J (2024) Opportunities and challenges of integrating artificial intelligence in China’s elderly care services. Sci Rep 14(1):9254. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-60067-w
Article ADS MathSciNet PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Social Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province in China (Grant No. 2023J014).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Art and Design, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi’an, China
Xianru Shang, Zijian Liu, Chen Gong, Zhigang Hu & Yuexuan Wu
Department of Education Information Technology, Faculty of Education, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China
Chengliang Wang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization, XS, YW, CW; methodology, XS, ZL, CG, CW; software, XS, CG, YW; writing-original draft preparation, XS, CW; writing-review and editing, XS, CG, ZH, CW; supervision, ZL, ZH, CW; project administration, ZL, ZH, CW; funding acquisition, XS, CG. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have read and approved the re-submission of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Chengliang Wang .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was not required as the study did not involve human participants.
Informed consent
Informed consent was not required as the study did not involve human participants.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Shang, X., Liu, Z., Gong, C. et al. Knowledge mapping and evolution of research on older adults’ technology acceptance: a bibliometric study from 2013 to 2023. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11 , 1115 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03658-2
Download citation
Received : 20 June 2024
Accepted : 21 August 2024
Published : 31 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03658-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
The Critical Blog
The home of critical thinking, observations and reflections on my first year placement.

This essay was written by Adrian Bloxham and was the winning social work entry in this year’s Critical Writing Prize 2019. Adrian is studying for an MA at Anglia Ruskin University and he was nominated by his lecturer Dr Wendy Coxshall.
I am currently on placement in a Supported Housing Hostel for adults in Cambridgeshire. This assignment is based on my work with one particular resident who I will refer to using the pseudonym ‘Alice’. The case study will explore core social work tenets including relevant knowledge and skills, critical reflection, processes of oppression and discrimination, communication and partnership working. I will seek to examine and reflect on my interactions with Alice, primarily by applying a reflective model to a ‘critical incident’. I will also attempt to view Alice’s life, and my professional relationship with her, from a broader social work perspective. My initial observations and impressions of the hostel were largely defined by the levels of socio-economic deprivation that dominate many of the residents’ lives. In virtually all cases the people that live at the project either have an underlying mental health condition or experience drug or alcohol misuse, often there are a combination of these factors. The very nature of this type of accommodation means that the population is transient. This often means that residents have little consistency and no control over who they live with, resulting in an enforced togetherness that can lead to feelings of insecurity, anxiety and fear (Bengtsson-Tops, et al., 2014). I observed during my early conversations with Alice that she often seemed subdued and that her mood fluctuated unpredictably. As the initial phase of my placement progressed I became increasingly aware of Alice’s persistent and chronic low self-esteem and her tendency to depressive episodes. I noted this in my journal and tried to “…think, to be self-aware and to question…” as a first step towards reflecting on practice (Rutter & Brown, 2012, p. 30). My vague sense of unease and concern about Alice and her general well-being crystalized early one morning as I arrived at work to find Alice upset and in tears in the communal lounge. I now recognise the ensuing conversation as a ‘critical incident’ that changed my learning and the way that I thought about the staff and my placement setting. What qualifies as a critical incident is not rigidly defined but the event should be important or significant in some way to the practitioner and should offer the opportunity for professional learning (Fook & Gardner, 2007, p. 77). During the course of this exchange Alice disclosed to me that she felt trapped, bullied by a member of staff and other residents, and that she was feeling utterly powerless with no hope of moving on from the hostel. Alice showed me a scar on her right wrist and stated that she had tried to commit suicide in the past and was now experiencing suicidal ideation once again. This type of situation, with all its complexities and difficulties, is described in the seminal work of Schön (1983) as the ‘swampy lowlands’ of practice (Schon, 1983). In more recent times ‘reflective practice’ has been developed further into a concept of ‘critical reflection’ (Payne, 2014). The application of critical reflection challenges accepted modes of thought, social organisation, dominant discourses and assumptions (Graham, 2017; Savaya & Gardner, 2012; Thompson, 2010). The two-stage reflective model developed by Fook & Gardner (2007) seeks to examine power relations and structures of domination, which in turn intrinsically challenges oppressive and discriminatory thought processes and practice (Graham, 2017, p.49; Fook, 2012, p.47). As will become apparent, forms of oppression and discrimination are a vital aspect of Alice’s narrative, and for this reason I propose to apply Fook & Gardner’s (2007) model to my critical incident and the subject of my case study. Alice’s disclosure was deeply concerning and very challenging for a number of reasons. My inexperience, the fact that Alice has a diagnosis of schizophrenia and the gravity of what she was saying all contributed to a feeling of unease. The first ‘stage’ of the reflective model is designed to question the underlying structural and social assumptions of the practitioner and analyse how and why feelings of discomfort and concern have been generated (Fook & Gardner, 2007, p.92). Adopting this process has helped me to identify possible assumptions that I suspect I may have held. For example, could my knowledge of Alice’s dysfunctional relationships in the past have resulted in me making assumptions about inherent personality ‘traits’? Did I view her mood swings and depression as simply emanating from her diagnosis of schizophrenia? Did my upbringing, that instilled and encouraged a deference to authority and ‘professional’ figures, blunt my critical faculties in relation to the ‘care’ and ‘support’ offered by individual staff members? It would also be remiss to discount the influence of gender and class on the assumptions I may have held. A closer critical analysis of the factors and experiences that have shaped Alice’s life expose the fundamental flaws and prejudices in my misplaced assumptions. As I began to work with Alice it became increasingly clear to me that she had experienced discrimination and oppression throughout her life. I learnt that Alice had endured severe and multiple adverse childhood experiences. Both of her parents committed suicide, she was raped and endured physically abusive relationships with two consecutive partners. This culminated in Alice being admitted to various psychiatric institutions in order to treat her schizophrenia and personality disorder. Eventually Alice became homeless, living on the street and addicted to heroin. The physical scars on Alice’s body as a result of these experiences can be understood from a postmodern perspective as embodied manifestations of power and oppression (Tangenburg & Kemp, 2002). Taking a postmodern perspective that conceptualises the body as the site of power relations (Foucalt, 1977) leads to an understanding that “…the body is fundamentally implicated in mechanisms of domination and control.” (Tangenburg & Kemp, 2002). Postmodernism rejects overarching general theories, instead adopting an approach that acknowledges individual narratives, social context and recognises multiple identities that may intersect (Graham, 2017; Fook, 2012). The intersection of Alice’s gender, her adverse experiences both as a child and as an adult, her diagnosis of schizophrenia and the fact that she has experienced poverty for the entirety of her life has led to oppression and discrimination at multiple levels. A reliance on members of staff who are experienced as oppressive reinforces feelings of hopelessness, stigma, discrimination and disempowerment (Williams, et al., 2015). Alice has been exploited by fellow residents who target her on the days when she receives benefits, this form of oppression takes place at a personal level and is often experienced by adults with serious mental illnesses in the “…forced intimacy of supportive housing.” (Forenza & Bermea, 2017). Oppression and discrimination also takes place at a wider level. People diagnosed with schizophrenia are often stigmatized by a discourse of ‘otherness’ which portrays people with mental health challenges as a ‘problem’ who must be ‘controlled’ by bio-medical, biogenetic models (Beresford & Wilson, 2002). Despite the dogged insistence of the dominant ‘medical model’ discourse, contemporary evidence points to a causal link between social factors and a diagnosis of schizophrenia (Read, 2010). Typical triggers include poverty, adverse childhood experiences, rape and physical or psychological violence (Read, 2010; Burns, et al., 2014). It is essential that social workers acknowledge this increasingly influential discourse which suggests that schizophrenia and other forms of mental illness are bio-psycho-social manifestations of social conditions and health inequalities, not an inherent physiological condition (Bywaters, 2015; Karban, 2017; Friedli, 2009; Marmot, 2010; Read 2010). Revisiting the assumptions that I outlined above has helped me to explore how I experienced the initial incident. Firstly, I now believe that I saw and understood the situation in simplistic, binary terms. Identifying assumptions and binary thinking, regardless of how uncomfortable this may be for the practitioner, is crucial and demonstrates reflexivity (Fook, 2012, p.107). By ‘deconstructing’ and ‘resisting’ this binary thinking the practitioner can then go on to address how change might be achieved and what values and assumptions have been challenged (Fook & Gardner, 2007). Arriving at an understanding of the multiple levels of oppression and discrimination that have shaped and distorted Alice’s life has not only heightened my awareness in this particular case but it has also changed the way I will approach practice situations in the future. The importance of recognising multiple perspectives and social contexts in a non-linear, fluid and multifaceted way leads to more ‘bottom up’ practice that in turn empowers marginalised people by recognising and legitimising their experiences and voice (Fook, 2012; Graham, 2017; Parton & O’Byrne, 2000). Alice’s deteriorating mental health led me to conclude that her social worker needed to be informed of the situation. The worker expressed a great deal of frustration at the lack of inter-agency communication, written or otherwise, and a failure to disclose key pieces of information. This can often be attributed to a defensiveness on the part of housing organisations “…due to fear of damaging reputation…or fear of over-reaction” (Parry, 2013, p.19). As a plethora of Serious Case Reviews illustrate, clarity of inter-professional and interagency communication is vital for safe practice (Moss, 2017; Hall & Slembrouck, 2009; Flynn, 2010). In the case of Alice there are three primary agencies involved. In addition to this, Alice also has contact with a psychiatrist and regular medical reviews with her GP. The number of professions and agencies involved with this single client illustrates the multiple points of contact and potential challenges that operating in this contemporary inter-agency environment presents. Understanding the communication process requires an acknowledgement of the complexity and meaning of language itself. That is to say, ‘communication’ is not neutral and does not necessarily have a universal meaning to each element of the agency or profession (Hall & Slembrouck, 2009). ‘Communication’ can be seen as a process whereby “…information passes from one person to another and is understood by them.” (White & Featherstone, 2005, p. 214). This rather simple statement camouflages the multi-layered nature of the exchange which involves an array of subjective attitudes and feelings which are projected onto the communicated information both from the perspective of ‘sender’ and ‘receiver’ (Sarangi & Slembrouck, 1996). The diversity of roles within Alice’s network highlights the danger that various professions and agencies may assign different levels of priority or even conceptualisations to the arising issues (Hudson, 2015). This means that each communication is potentially ‘categorised’ differently and therefore there is a danger that co-agencies conceive of a given situation in completely different ways (Hall & Slembrouck, 2009). I continued to learn more about Alice’s life over the following weeks. I observed the patience and empathy that Alice’s social worker demonstrated during the interview process. Often Alice would experience what appeared to be moments of psychosis during which she seemed to be transported back in time to a particularly traumatic event which resulted in repetitive phrases and sentences being used to describe what had happened. Although these moments appeared to be traumatic for Alice she said on many occasions that she wanted to speak about her past. I noted the way that Alice’s social worker handled difficult or emotionally salient passages during interviews (Goss, 2011), particularly the use of silence and the importance of being patient rather than asking superfluous questions to fill uncomfortable pauses (Trevithick, 2012). The importance of ‘iatrogenic health’, the process whereby possibilities and opportunities are acknowledged and explored, is part of a constructive narrative approach founded on a postmodern perspective (Parton & O’Byrne, 2000). The whole thrust of the conversations, whilst acknowledging the trauma of the past and the difficulties of the present, were very much focused on the aim of Alice moving-on in both a literal and metaphorical sense. The social worker talked through the steps that needed to be taken by Alice and the support that she would need in order to achieve this goal, a process referred to as the amplification of personal agency (Parton & O’Byrne, 2000, p.60). This relationship-based work (Woodcock Ross, 2011) with Alice highlights the importance of partnership working and emphasises the need to avoid ‘top-down’ structural models (Hudson, 2015, p.102). Whilst the idea of ‘partnership’ suggests equality and collaboration, practitioners should still manage power relations with service users carefully, especially where a lack of confidence inhibits the service user from taking on the responsibility of partnership (Dalrymple & Burke, 2006). This aspect of partnership practice was and is very pertinent in the relationship between Alice and her social worker. The asymmetry between the social worker and service user emphasises the need for the practitioner to be cognizant of the inherent power imbalance in the relationship (Leung, 2011). Even where social work is undertaken with the best of intentions, for example in anti-oppressive practice, there is a danger that the voice and knowledge of the service user is lost by the intervention of the ‘expert’ practitioner (Wilson & Beresford, 2000). The difficulties Alice experienced at the hostel which culminated in such a troubled state of mind calls into question the place of adult safeguarding both within the organisation and in the wider context. The implementation of The Care Act 2014 introduced new responsibilities and statutory duties on local authorities and partner agencies with an emphasis on moving away from process-driven practice (Cass, 2015). The new legislation was adopted into Company policy, statutory guidance makes it clear that there is an onus on employers to ensure that staff working in a housing environment are adequately trained in recognising signs of abuse or neglect, which includes self-neglect under the terms of The Care Act 2014 (Department of Health, 2014). At the time of my critical incident Alice was failing to attend to personal hygiene on a regular basis, frequently appeared to be experiencing low mood and would often break down in tears even when engaging in mundane, everyday conversation. Supported housing is often regarded as a positive environment that promotes recovery-oriented practice (Harvey, et al., 2012), but it can also be experienced as an oppressive and hostile setting where staff are at best indifferent to the needs of service users or can actively act as the oppressor (Bengtsson-Tops, et al., 2014). This is especially concerning when one considers that housing staff may be the only service that residents have contact with (Cass, 2015). Risk assessments are an integral aspect of work with vulnerable people (Parry, 2013). Yet risks remain, in essence, unpredictable phenomena that defy reliably accurate outcomes (Munro & Rumgay, 2000). From a postmodern perspective, practitioners should not seek to totally eliminate risk by a ‘scientized’, calculated approach because this is doomed to failure (Parton, 1998, p. 23). Instead, there should be an acceptance that uncertainty and complexity are inherent in human interaction and therefore consideration should be given not only to ‘negative’ risk but also to the benefits of ‘positive’ risk (Macdonald & Macdonald, 2010). Risk management can be seen as a continuum (Nolan & Quinn, 2012), so whilst service user vulnerabilities must be taken into account when assessing risks there is also a balance to be struck. Planned risk-taking can and should promote a good quality of life, develop new skills and expand life experiences (Barry, 2007). Alice wishes to live independently and this is the preferred option for the social worker. However, a judgment will ultimately need to be made as to whether the rights and needs of a vulnerable service user are best served by advocating for Alice’s wishes or actively encouraging another course of action that is ‘safer’ for Alice (Kemshall, et al., 2013). This case study has demonstrated the complexity and breadth of contemporary social work. Whilst there is not universal agreement (Ixer, 2016), the central importance of critical reflection to the profession of social work is widely accepted (Thompson, 2010, p. 183). The opportunity to work with Alice has provided much to reflect on and learn from. My work with Alice has taught me many things, most notably the impact of personal and structural processes of oppression and discrimination. However, I believe the key lesson that I take from my professional relationship with Alice is to try and show the same level of astonishing resilience and generosity of spirit that Alice has demonstrated throughout her life to the present day. Works Cited Barry, M., 2007. Effective Approaches to Risk Assessment in Social Work: An International Literature Review. [Online] Available at: www.scotland.gov.uk/Resource/doc/194419/0052192.pdf BASW, 2014. The Code of Ethics for Social Work, Birmingham: BASW. Bengtsson-Tops, A., Ericsson, U. & Ehliasson, K., 2014. Living in supportive housing for people with serious mental illness: A paradoxical everyday life. International Journal of Mental Health Nursing, 1(23), pp. 409-418. Beresford, P. & Wilson, A., 2002. Genes Spell Danger: Mental health service users/ survivors, bioethics and control. Disability & Society, 17(5), pp. 541-553 Bywaters, P., 2015. Inequalities in Child Welfare: Towards a New Policy, Research and Action Agenda. British Journal of Social Work, 45(1), pp. 6-23. Cass, E., 2015. The role of housing in adult safeguarding. Housing, Care And Support, 18(2), pp. 51-55. Dalrymple, J. & Burke, B., 2006. Anti-Oppressive Practice Social Care and the Law. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education. Department of Education, 2018. Knowledge and skills for child and family practitioners, London: HMSO. Department of Health, 2014. Care and Support Statutory Guidance. London: HMSO. Department of Health, 2015. Knowledge and Skills Statement for Social Workers in Adult Services. [Online] Available at: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_ data/file/411957/KSS.pdf Fook, J., 2012. Social Work: A Critical Approach to Practice. 1st ed. London: SAGE. Fook, J. & Gardner, F., 2007. Practising Critical Reflection: A Resource Handbook. 1st ed. Maidenhead: Open University Press. Forenza, B. & Bermea, A. M., 2017. An Exploratory Analysis of Unhealthy and Abusive Relationships for Adults with Serious Mental Illnesses Living in Supportive Housing. Community Mental Health , Volume 53, pp. 679-687. Friedli, L., 2009. Mental Health, Resilience and Inequalities, Copenhagen: World Health Organisation. Goss, J., 2011. Poetics in Schizophrenic Language: Speech, Gesture and Biosemiotics. Biosemiotics, 4(3), pp. 291-307. Graham, M. J., 2017. Reflective Thinking in Social Work: Learning from Student Narratives. 1st ed. Abingdon: Routledge. Hall, C. & Slembrouck, S., 2009. Professional Categorization, Risk Management and InterAgency Communication in Public Inquiries into Disastrous Outcomes. British Journal of Social Work, 39(1), pp. 280-298. Harvey, C., Killackey, E., Groves, A. & Herrman, H., 2012. A place to live: Housing needs for people with psychotic disorders identified in the second Australian national survey of psychosis. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 46(9), pp. 840-850. HCPC, 2017. Social workers in England, London: HCPC. Healy, K., 2012. Social Work Methods and Skills: The Essential Foundations of Practice. 1st ed. Basingstoke: Palgrave MacMillan. Hudson, A., 2015. Social Work: a “forgotten” piece of the integration jigsaw?. Journal of Integrated Care, 23(2), pp. 96-103. Ingram, R., 2013. Locating Emotional Intelligence at the Heart of Social Work Practice. British Journal of Social Work, Volume 43, pp. 987-1004. Ixer, G., 2016. The concept of reflection: is it skill based or values?. Social Work Education, 35(7), pp. 809-824. Karban, K., 2017. Developing a Health Inequalities Approach for Mental Health Social Work. British Journal of Social Work, Volume 47, pp. 885-902. Kemshall, H., Wilkinson, B. & Baker, K., 2013. Working with Risk. 1st ed. Cambridge: Polity Press. Laird, S., 2011. Anti-Racist and Anti-Oppressive Practice. 1st ed. Maidenhead: SAGE. Lam, C. M., Wong, H. & Leung, T. T. F., 2007. An Unfinished Reflexive Journey: Social Work Students’ Reflection on their Placement Experiences. British Journal of Social Work, 1(37), pp. 91-105. Leung, T., 2011. Client Participation in Managing Social Work Service-An Unfinished Quest. Social Work, 56(1), pp. 43-52. Lishman, J., 2009. Communication in Social Work. Basingstoke: Palgrave MacMillan. Macdonald, G. & Macdonald, K., 2010. Safeguarding: A Case for Intelligent Risk Management. British Journal of Social Work, 40(1), pp. 1174-1191. Marmot, M., 2010. Fair Society, Healthy Lives: Strategic Review of Health Inequalities in England post 2010. [Online] Available at: www.parliament.uk/documents/fair-society-healthy-lives-full-report Moss, B., 2017. Communication Skills in Health and Social Care. 4th ed. London: SAGE. Munro, E., 2011. The Munro Review of Child Protection, Final Report, A child-centerd system, London: The Stationary Office. Munro, E. & Rumgay, J., 2000. Role of risk assessment in reducing homicides by people with mental illness. British Journal of Psychiatry, 176(2), pp. 116-120. Nerdrum, P., 1997. Maintenance of the Effect of Training in Communication Skills: A Controlled Follow-Up Study of Level of Communicated Empathy. British Journal of Social Work, 27(1), pp. 705-722. Nolan, D. & Quinn, N., 2012. The Context of Risk Management in Mental Health Social Work. Practice: Social Work in Action, 24(3), pp. 175-188. Norrie, C. et al., 2017. The Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Models of Organising Adult Safeguarding. British Journal of Social Work, 47(1), pp. 1205-1223. Parrish, M., 2014. Social Work Perspectives on Human Behaviour. 2nd ed. Maidenhead: Open University Press. Parrish, M., 2014. Social Work Perspectives on Human Behaviour. 1st ed. Maidenhead: Open University Press. Parry, I., 2013. Adult safeguarding and the role of housing. The Journal of Adult Protection, 15(1), pp. 15-25. Parton, N., 1998. Risk, Advanced Liberalism and Child Welfare: The Need to Rediscover Uncertainty and Ambiguity. British Journal of Social Work, 28(1), pp. 5-27. Parton, N. & O’Byrne, P., 2000. Constructive Social Work. 1st ed. Basingstoke: MacMillan Press Ltd. Payne, M., 2014. Modern Social Work Theory. 4th ed. Basingstoke: Palgrave MacMillan. Piat, M., Sabetti, J. & Padgett, D., 2017. Supported housing for adults with psychiatric disabilities: How tenants confront the problem of loneliness. Health Soc Care Community, Volume 26, pp. 191-198. Read, J., 2010. Can Poverty Drive You Mad? ‘Schizophrenia’, Socio-Economic Status and the Case for Primary Prevention. New Zealand Journal of Psychology, 39(2), pp. 7-19. Rutter, L. & Brown, K., 2012. Critical Thinking and Professional Judgment for Social Work. 3rd ed. London: SAGE. Sarangi, S. & Slembrouck, S., 1996. Language, Bureaucracy & Social Control. 1st ed. Harlow: Addison Wesley Longman Limited. Savaya, R. & Gardner, F., 2012. Critical Reflection to Identify Gaps between Espoused Theory and Theory-in-Use. Social Work, 57(2), pp. 145-154. Savaya, R., Gardner, F. & Stange, D., 2011. Stressful Encounters with Social Work Clients: A Descriptive Account Based on Critical Incidents. Social Work: National Association of Social Workers, 56(1), pp. 63-72. Schon, D., 1983. The Reflective Practitioner: How Professionals Think in Action. New York:Basic Books Schön, D., 1987. Educating The Reflective Practitioner. 1st ed. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. Schwartz, S., 1982. Is there a schizophrenic language?. The Behavioural and Brain Sciences, 5(1), pp. 579-626. Skills for Care, 2015. The Social Work ASYE: Guidance for NQSWs completeing the ASYE in adults and child settings. [Online] Available at: www.skillsforcare.org.uk Tangenburg, K. M. & Kemp, S., 2002. Embodied Practice: Claiming the Body’s Experience, Agency, and Knowledge for Social Work. Social Work, 47(1), pp. 9-18. Tannebaum, R. P., Hall, A. H. & Deaton, C. M., 2013. The Development of Reflective Practice in American Education. Ameican Educational History Journal, 40(2), pp. 241-259. Teater, B., 2014. Contemporary Social Work Practice. 1st ed. Maidenhead: Open University Press. Thompson, N., 2010. Theorizing Social Work Practice. 1st ed. Basingstoke: Palgrave MacMillan. Trevithick, P., 2012. Social Work Skills and Knowledge ; A Practice Handbook. 3rd ed. Maidenhead: Open University. White, S. & Featherstone, B., 2005. Communicating misunderstandings: Multi agency work as social practice. Child and Family Social Work, 10(2), pp. 207-216. Williams, C. C., Almeida, M. & Knyahnytska, Y., 2015. Towards a Biopsychosociopolitical Frame for Recovery in the Context of Mental Illness. British Journal of Social Work, 45(1), pp. i9-i26. Wilson, A. & Beresford, P., 2000. ‘Anti-Oppressive Practice”: Emancipation or Appropriation. British Journal of Social Work, 30(1), pp. 553-573. Woodcock Ross, J., 2011. Specialist Communication Skills for Social Workers: Focusing on Service Users’ Needs. 1st ed. Basingstoke: Palgrave MacMillan.
Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Additional menu
Student voices
Get the inside view on student life at York.
- My experience as a Social Work student
19 January 2022 by Charlotte
I have always been the type of person to care about those around me and always wanted a career where I could help people to improve themselves and/or the situation they are in. I felt social work was the perfect career path for me as the whole nature of the job is to support and empower people within society.
What kind of impact do you want to make on people’s lives?
I hope to make a positive, hopefully, life-changing impact on people’s lives. I would like to think that the social worker I become is able to better people’s lives and empower them for the future.
What advice would you give to any A-level or BTEC students about their studies?
When it came to uni, I found it helpful to have an understanding of social work and be able to apply elements of it to my personal life. My advice would be if you can get any work experience or volunteering in then definitely do that – you can reflect on it in your university interviews!
What advice would you give to these students about: a) getting relevant work experience; and b) about developing the right skills and knowledge for social work?
In my opinion, any work experience working with people is beneficial as you come across things that relate to social work every day! But make sure you get work experience in something that interests you. I had mine in a primary school!
Before I started the degree, I did some wider reading and understanding of what social work involves, as well as understanding the Professional Capabilities Framework (PCF) model and other important frameworks. Many unis put reading lists available online for you to find before starting your degree.
What have I enjoyed the most about the course so far?
In my opinion, the people on my course are what I have enjoyed the most, getting to know each other and our personal life experiences. As well as making new friends and getting to know the supervisors and lecturers.
Has anything surprised you?
I found the assignment rather enjoyable, which was a shock to me as I hated writing in A level studies. I liked how you are able to apply your learning actively when writing the assignment. As well as researching your answer and learning new things within them.
Has your understanding of social work changed since you started the course and if so, how?
I would say my understanding of social work has changed since the course has begun. Now, I have a wider understanding of the history of social work and how it has changed over the past century within the UK and will continue to change. I would also say my understanding of how social policy impacts social work has changed – I never realised how much social work is dependent on policies.
Read more student stories about studying Social Work at York

About Charlotte
Hi, I'm Charlotte, a 2nd Year Social Work student here at York.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
About this blog
These blogs represent students’ views and reflections, at the time of publish. For course details and the official information please always refer to the University of York website .
To get in contact with us about anything on this blog you can email us .
- What I wish I knew before starting my placement in the Operating Theatre
- Freshers' Week as a student who doesn't drink
- My guide on what to pack for University
- My placement experience: highlights and reflections

A reflection On My Internship as a Social Worker
Pssst… we can write an original essay just for you.
Any subject. Any type of essay. We’ll even meet a 3-hour deadline.
writers online
How I Demonstrated Leadership as an Intern
Don't use plagiarised sources.Get your custom essay just from $11/page
The Skills to Develop and Improve on in My career
Having known that in social work, great leaders not only a guide but add value to this noble profession by articulating goals. It is crucial to develop and improve some skills to achieve this. The facility I was in was always flooded with clients who needed various services from social work practitioners. Juggling of many clients at ago became very difficult for me to handle; it’s challenging being a new intern. At one point, one of the clients went back unattended due to the time factor. My internship experience exposed how I desperately needed a high level of organization and management skills in keeping up with several client issues. At the same time, the skills deemed essential in organizing paperwork that is a major required during the internship and after e mployment . I am flexible and yearning to improve my organizational skills by either training or looking for more experience in the same area. The field of social work is for critical thinkers which discourage generalization of ideas, how can an individual respond to a spontaneous problem? Just like in the case study I provided before, maybe I would have solved things amicably with my colleagues without offending them. I had in mind that our field is congested with very emotional people. It also dawned on me that a social worker should be an empathetic person. Practicing empathy in a strict person is very difficult. Some clients are rigid and hard to control. I realized it is good for me to improve on my empathetic skills in the future to serve better.
I saw the felt the plight of the aged during my internship program. Most adults were rendered homeless, with no one to take care of them. Have you imagined being left outside an old home gate with no identification? This became my nightmare during my internship. From experience, I realized one policy area that needs reassessment is the increase of funds to the housing policy. One of the intended outcomes of the plan is to bring an end to homelessness by providing dignity to the elderly who should remain in contact with their communities, families, and the nation at large. Baby boomers are at risk!
On the contrary, families of older people might take advantage of them, posing a great stretch on the general economy. I celebrate that, in the future, I will step up on opportunities that will take pride in my career, such as leadership skills. My hope is I become an experience social work leader with excellent skills ready to inspire other aspiring members of the nation by stepping into the fullest of my potential. I realized, social workers are naturally skilled, innovative leaders.
Remember! This is just a sample.
Save time and get your custom paper from our expert writers.
In case you can’t find a sample example, our professional writers are ready to help you with writing your own paper. All you need to do is fill out a short form and submit an order

10 MSW Personal Statement Examples (with Commentary)
Get inspired by some of the best MSW personal statement examples below.
These personal statement examples are inspired by actual essays from students with whom we’ve collaborated, essays that contributed to their successful admissions. For confidentiality, key details have been altered.
If you’re looking for Personal Statement Help, Get Started Here !
Table of Contents
Example 1: NYU MSW Personal Statement Sample
Prompt: ‘why i want to be a social worker’ essay.
At the tender age of five, as my family faced the challenges of immigrating to the United States, I quickly became attuned to the complexities surrounding us. This early brush with adversity sparked my quest for understanding, especially in the realm of adolescent experiences. Growing up in a household where my mother tirelessly cared for us, while my father remained emotionally distant, I learned to seek solace in introspection and daydreaming. These experiences laid the foundation for my deep empathy towards others and a commitment to understanding them beyond surface-level perceptions.
My ability to empathize with others, particularly adolescents, has been a guiding force in my life. Working with XXXX as a counselor, I revisited my own teenage years, recognizing the crucial need for guidance during this transformative phase. This realization has fueled my determination to specialize in counseling and therapy for adolescents, a path I am eager to pursue through NYU’s Master of Social Work program. I am convinced that effective counseling during adolescence is pivotal in shaping capable, responsible adults.
My internship at XXXX Health was a turning point. Observing clinical behavioral health therapists and working alongside a psychiatrist specializing in post-incarceration life, I gained profound insights into the long-lasting impact of disrupted adolescent experiences. Hearing the narratives of former inmates underscored the importance of early intervention in defining one’s identity. This experience intensified my desire to work with young individuals struggling to find their place in the world.
Choosing NYU Silver was a natural decision. The school’s esteemed faculty, particularly Dr. Kirk Jae James, resonates with my journey as an immigrant. Dr. James’ dedication to overcoming his challenging past and disproving stereotypes is not just inspiring; it mirrors the resilience and determination I strive to embody. His work with those affected by mass incarceration aligns closely with my aspiration to be a clinical therapist who can bring change to young lives.
New York City, the vibrant and diverse backdrop of NYU Silver, also greatly appeals to me. The city’s rich history of nurturing notable figures like Andy Warhol, Roy Halston, and Jean Basquiat speaks to its capacity to foster self-discovery and belonging. I am excited to immerse myself in this melting pot of cultures and ideas, which will undoubtedly enrich my learning and practice in clinical therapy.
My personal history, particularly my father’s struggle with his traumatic childhood, has taught me that resilience and determination are key to overcoming adversity. His journey, though fraught with challenges, has instilled in me the belief that embracing the unknown and being steadfast in one’s goals can lead to remarkable achievements. Carrying this lesson with me, I step into NYU Silver poised to embark on a journey towards becoming an influential clinical therapist for adolescents.
My path to NYU Silver is more than an academic pursuit; it is a commitment to my dream of guiding adolescents through their most vulnerable years. By combining my personal experiences with the comprehensive training at NYU Silver, I am ready to make a meaningful impact in the field of clinical therapy, helping young individuals navigate their formative years with understanding and resilience.
Commentary:
- Personal and Cultural Background : Effectively connects early experiences as an immigrant to developing empathy, crucial for social work.
- Professional Aspirations : Clearly links past experiences with seniors and an internship to a focused interest in clinical therapy for adolescents.
- Academic Motivation : Draws a parallel between personal experiences and the inspiration found in NYU Silver’s faculty and New York City’s diversity.
- Resilience and Determination : Reflects on lessons learned from family, particularly the father, instilling a belief in achieving ambitious goals.
- Career Vision : Articulates a strong desire to impact adolescent lives, demonstrating an understanding of the field’s challenges and opportunities.
Verdict: The personal statement is heartfelt and well-structured, showing a clear link between the candidate’s background, their professional drive, and their chosen academic path. The reflection on personal and family resilience adds depth, positioning the candidate as a motivated individual ready to leverage their experiences for meaningful social work.
Example 2: Columbia MSW Personal Statement Sample
- Part 1: Reflecting upon your decision and motivation to pursue the MSW, describe how attending CSSW will enable you to meet your goals as a social worker. What are your immediate and long-term social work goals?
- Part 2: Describe a social problem of significance to you. Please discuss it in regard to societal contributions to the origin of the problem, experiences that have contributed to your identification and understanding of the problem, and possible ways of addressing the problem.
- Part 3: Choose two attributes and provide examples as to how you exemplify these traits. Choose one attribute you would like to improve. How will attending the MSW program at CSSW help you in doing so?
1. Motivation and Goals for Pursuing MSW:
From a young age, I have been acutely aware of the disparities and injustices in my community. Growing up in a low-income neighborhood in Chicago, I witnessed firsthand the detrimental effects of poverty, limited access to quality education, and the cycle of violence. These early observations fueled my passion for social work, specifically my desire to develop community-based programs aimed at youth empowerment and education. My immediate goal is to work in a non-profit organization focused on urban youth development, while my long-term ambition is to establish a foundation dedicated to providing educational resources and mentorship programs for at-risk youth.
Attending the Columbia School of Social Work (CSSW) will provide me with the critical skills, knowledge, and network necessary to achieve these goals. CSSW’s commitment to social justice, its comprehensive curriculum, and the opportunity to learn from esteemed faculty and diverse peers will equip me with a nuanced understanding of social issues and effective intervention strategies.
2. A Significant Social Problem:
The social problem that resonates most with me is the school-to-prison pipeline, an issue rampant in many urban communities, including my own. This problem arises from a combination of societal factors such as underfunded public schools, zero-tolerance policies, and systemic racial discrimination. My understanding of this issue deepened through volunteering at a local youth center, where I encountered numerous teens who had been expelled from school and were at risk of entering the juvenile justice system.
Addressing this problem requires a multi-faceted approach, starting with policy reform to prioritize education and rehabilitation over punishment. Community-based intervention programs focusing on mentorship, counseling, and educational support can play a vital role in diverting at-risk youth from the criminal justice system. At CSSW, I hope to explore these interventions in-depth and develop effective strategies to dismantle the school-to-prison pipeline.
3. Personal Attributes and Areas for Improvement:
Empathy : My empathy has been a guiding force in my social work journey. A poignant example was when I volunteered at a local youth center. There, I met a teenager named Marcus who had been expelled from school. By actively listening and engaging with him, I learned about his challenges at home and his struggles with learning disabilities. Understanding his situation, I worked with the youth center staff to develop a personalized educational plan and connect him with a mentor. This experience deepened my ability to empathize with individuals from diverse backgrounds, recognizing the unique challenges they face.
Resilience : My resilience was particularly tested when I spearheaded a community project to revitalize a rundown public park. The project faced numerous setbacks, including funding shortages and bureaucratic hurdles. Despite these challenges, I mobilized the community, organized fundraising events, and negotiated with local officials. The successful completion of the park not only provided a safe space for children but also reinforced my ability to persist in the face of adversity, a crucial trait for a social worker.
Area for Improvement – Policy Advocacy : My experience in grassroots initiatives has been rewarding, but it also highlighted the limitations of addressing social issues without policy change. For instance, while volunteering at the youth center, I realized that individual interventions, though beneficial, could not alone prevent the systemic issue of school expulsions leading to juvenile detentions. This recognition has fueled my desire to improve my skills in policy advocacy, an area where I see great growth potential. CSSW’s program, with its emphasis on policy practice, will be instrumental in helping me acquire the necessary knowledge and skills to advocate effectively for systemic changes.
Conclusion:
Attending Columbia School of Social Work will be a pivotal step in my journey to becoming an impactful social worker. I am eager to engage with the CSSW community, learn from diverse experiences, and contribute my perspective towards creating meaningful change. I am committed to using the knowledge and skills gained from CSSW to fight for social justice and empower the youth in communities like mine.
- Clarity of Motivation : The essay effectively communicates the candidate’s personal experiences and observations of disparities in their community as key motivators for pursuing social work.
- Goal-Oriented : Clearly outlines immediate and long-term goals, demonstrating a focused vision for a career in social work.
- Understanding of a Social Issue : The candidate’s insight into the school-to-prison pipeline, informed by volunteer experiences, indicates a deep understanding of this complex social problem.
- Attributes and Self-Improvement : Demonstrates empathy and resilience through specific examples. Identifies policy advocacy as an area for improvement and connects this to CSSW’s curriculum.
- Personal and Professional Growth : The candidate’s experiences, challenges faced, and the growth they seek align well with the offerings of the CSSW program.
Verdict: The candidate’s personal statement is compelling and well-crafted. It showcases a strong personal connection to the field, a clear understanding of relevant social issues, and a desire for professional growth that aligns with the CSSW program.
Example 3: UC Berkeley MSW Statement of Purpose Sample
Please address each of the following in your statement:
- Describe your aptitude, motivation and preparation for graduate study in the field of social welfare; your future career goals in the profession of social work; and achievements that demonstrate your professional promise and leadership potential as a social worker.
- Describe your academic and professional areas of interest in social work, including your chosen area(s) of specialization.
- Demonstrate your understanding of contemporary issues and challenges in the professional practice of social work by posing a question or identifying a relevant problem/current issue you would like to explore, and how you might address it from the perspective of a masters’-level social worker.
My journey into the world of social work began with a deeply personal experience – caring for my youngest daughter who faced developmental and language delays. This challenge opened my eyes to the struggles of parents with special needs children and sparked my commitment to helping vulnerable groups. I founded a non-profit organization to support children in rural Russian orphanages, which expanded my drive to assist not only children but also adults suffering from trauma and PTSD. This path has led me to pursue the Master of Social Welfare program at Berkeley, where I aim to deepen my knowledge and skills for effective global impact.
My background is richly diverse. As a mother of four bilingual, multicultural children, I developed a keen interest in early bilingualism. For my thesis at XXXX State Linguistic University, I explored bilingual language development in infants and toddlers, focusing on methods used by parents raising bilingual children. This research, recommended for publication as a guide for multilingual families, heightened my awareness of the challenges immigrant families face globally. It solidified my resolve to find research-based solutions to social issues, a commitment I bring to Berkeley’s rigorous program.
Professionally, I thrived as a XXXX Director for XXXX in Russia, where I honed leadership skills by building a team of passionate educators. A notable achievement was our collaboration with XXXX Department, providing educational programs to young patients. This experience was transformative, broadening my perspective on social change and reinforcing my desire to make a meaningful difference.
As a certified life and leadership coach, I focused on assisting Russian-speaking immigrants and refugee women, many confronting dire challenges like domestic abuse and PTSD. These encounters underscored the need for specialized social welfare skills, steering me towards a Master’s in Social Work. My goal is to become a Licensed Clinical Social Worker, specializing in trauma and PTSD, and to contribute on an international scale, possibly with organizations like Doctors Without Borders.
Recognizing the critical role of language in social work, I have been learning Spanish and French to better connect with diverse patient populations. My linguistic background enhances my ability to engage effectively in multicultural settings. To gain practical experience, I completed a 90-hour training at Crisis Support Services of XXXX and began volunteering on their crisis line. This hands-on involvement, particularly during these challenging times, has further motivated me toward my LCSW goal.
UC Berkeley’s MSW program, known for its diverse student body and commitment to public service, is the ideal environment for me to grow. Surrounded by peers and faculty who share a dedication to social justice, I am eager to expand my understanding and prepare for a career dedicated to improving the lives of vulnerable individuals, families, and communities.
- Personal Experience as Motivation : The statement effectively uses the candidate’s personal experience of caring for a child with developmental delays as a catalyst for their interest in social work.
- Global Perspective : Showcases a strong commitment to international social issues through work with Russian orphanages and immigrant communities.
- Professional Achievements : Highlights relevant professional experiences, including leadership roles and work with vulnerable populations.
- Educational Goals and Alignment : Clearly articulates the desire to specialize in trauma and PTSD, aligning with Berkeley’s MSW program’s strengths.
- Multicultural and Linguistic Skills : Demonstrates an understanding of the importance of cultural competence in social work, supported by multilingual abilities.
Verdict: The candidate presents a compelling mix of personal motivation, professional experience, and academic alignment with the MSW program at UC Berkeley. Their diverse background and specific career goals make them an ideal candidate for the program.
Example 4: Cal State Fullerton MSW Personal Statement Sample
The quality of the writing in the personal statement will be evaluated, as will the applicant’s ability to thoroughly address the questions outlined below:
- Describe how your personal background and life experiences have influenced your decision to pursue a graduate education in social work. Please include any challenges or hardships you may have overcome on your journey.
- What are your expectations of graduate education at Cal State Fullerton in terms of your own development? Indicate any problems or limitations that should be taken into account in planning your graduate program.
- Specify your career objectives as a professional social worker as you now conceive them. Indicate the fields of practice in which you are interested.
- Describe your experiences with diverse populations and groups, and how those experiences have contributed to your interest in social work. Which population (defined by culture, ethnicity, sexual orientation, socio-economic status, psychological and/or physical functioning) would you like to serve and why?
While managing an in-school feeding program, I watched a 7-year-old boy take a modest meal at school, and save half for his siblings at home. Another girl expressed joy for the school meals she relied on. These encounters, and others like them, deeply impacted me, highlighting the critical issue of child hunger and food insecurity. My resolve to expand our school feeding program was fueled by these experiences, successfully growing it from 7 to 1,053 schools over five years.
After graduating, I joined the Philippine XXXXX in 2001, managing the Business and Peace Program in the XXXXX Region. Here, I worked with XXXXXX, identifying young Muslims for internships that fostered leadership and peace.
In 2008, I transitioned to the XXXXX Foundation, developing community programs and managing the in-school feeding program, which fed 40,000 children at its peak. These experiences solidified my commitment to child welfare and my belief in the power of social work.
Managing the feeding program, I faced ethical challenges, like discovering fund misappropriation by a local agency officer. I addressed this by establishing direct communication with schools and conducting random checks, ensuring program integrity.
Then in 2013, I took a break to focus on family and moved to XXXXX. Motherhood enriched my perspective, making me more empathetic, resilient, and dedicated to child welfare. Now ready to re-enter the social work field, I seek an MSW degree to update my skills and knowledge.
Post-MSW, I aim to influence policies and contribute to community-based solutions in the Philippines, aspiring to work with large non-profits and eventually with international agencies like UNICEF.
The COVID-19 pandemic has heightened child poverty in the Philippines, underscoring the urgency of my mission. At CSU Fullerton, I plan to study social work theories, understand child welfare systems, and apply these learnings to the Philippine context.
With a Master of Social Work degree, I am poised to join the effort to advance children’s welfare, equipped to make a significant difference in their lives. The Filipino children cannot wait. They need all the help they can get. And with a Master of Social Work degree from CSU Fullerton, the battle will have been half-won.
- Personal Narrative as Motivation : The statement effectively uses the applicant’s personal experiences with poverty, domestic violence, and addiction to illustrate a deep-rooted motivation for pursuing social work.
- Community Involvement and Professional Experience : Highlights significant community engagement and professional achievements, demonstrating a commitment to social justice and positive change.
- Challenges and Ethical Considerations : Discusses challenges faced during professional work, showing problem-solving skills and ethical awareness.
- Academic and Career Goals : Clearly articulates how an MSW will enrich the applicant’s knowledge and skills, aiming to influence policies and create community-based solutions.
- Personal Growth and Family Perspective : Reflects on the lessons learned from being a stay-at-home mother, tying this to a renewed enthusiasm for child welfare work.
Verdict: The statement presents a well-rounded candidate with a compelling personal connection to social work, reinforced by active community involvement, ethical professional practice, and clear career goals. The applicant’s experiences and aspirations align well with the MSW program at CSU Fullerton- making them a strong candidate.
Example 5: Cal State Long Beach MSW Personal Statement Sample
How did you become interested in social work? What motivated you to choose social work as a profession?
My passion for social work and advocacy for equality is rooted in a fundamental belief: no voice should be silenced in the pursuit of a just society. Throughout my life, I’ve witnessed how advocates for equality are often marginalized, their concerns unheard. This fuels my commitment to actively work towards a just world, where standing up for justice is a right for all.
As a child of Mexican immigrants, I experienced the harsh realities of a low-income household. This upbringing ingrained in me deep empathy and an intimate understanding of the struggles faced by underprivileged communities. My parents’ relentless hard work and sacrifices, despite economic hardships, have been a constant source of inspiration. They taught me resilience, compassion, and the importance of community support.
My professional journey in social work began at XXXX Community Development Corporation, where I took a lead role in organizing a landmark meeting with elected officials. We successfully voiced community concerns, addressing critical issues like infrastructure and public safety. This experience honed my skills in advocacy and highlighted the power of active listening and engagement.
Furthering my commitment, I volunteered at XXXX Volunteers in Medicine, assisting in providing healthcare to those unable to afford it. Here, I learned the critical role of accessible healthcare and the importance of educating communities about healthy living. These experiences have solidified my resolve to pursue a career in social work, focusing on advocating for essential services and support for underprivileged communities.
My aspiration to become a licensed clinical social worker, specializing in children’s mental health, aligns perfectly with the academic rigor and diverse environment offered by the Master of Social Work program at CSULB. As an undergraduate at CSULB, I was captivated by the program’s depth and the diverse perspectives it embraced. The experiences shared with students from varied backgrounds deepened my understanding of the multifaceted challenges in our society.
I am fully committed to investing my time and resources in the coursework and fieldwork placements at CSULB. The opportunity to study in a stimulating environment, surrounded by professionals who share my passion, will provide a solid foundation for my career. I bring with me a wealth of practical insights from working with low-income communities, the homeless, the elderly, and drug users. These experiences, I believe, will contribute significantly to our class discussions and align perfectly with CSULB’s mission of supporting vulnerable and oppressed populations.
My journey in social work is a commitment to those who struggle to be heard. At CSULB, I aim to further my skills, knowledge, and understanding, preparing myself to be a force for change and a voice for the voiceless. My goal is to ensure that every child, family, and community I work with gets the opportunity to thrive, just as I strive to make a meaningful impact in the field of social work.
- Strong Personal Connection : The statement effectively connects the candidate’s personal background as a child of Mexican immigrants to her empathy and understanding of underprivileged communities.
- Professional Experience : Highlights relevant work in community development and healthcare, which demonstrates practical skills in advocacy and community engagement.
- Academic and Career Goals : Clearly articulates the ambition to specialize in children’s mental health, aligning with CSULB’s program.
- Commitment to Social Work Values : Demonstrates a deep commitment to social justice, aligned with the mission of CSULB’s social work program.
Verdict: The personal statement is comprehensive and well-constructed, effectively demonstrating the candidate’s passion, relevant experience, and alignment with CSULB’s Master of Social Work program. The candidate’s background and professional aspirations make them a strong fit for the program.
Example 6: San Jose State University MSW Personal Statement Sample
In the heart of a small migrant community, where the sting of social inequities was a daily reality, my path toward a career in social work began to take shape. My childhood, marked by the challenges of racial discrimination and economic struggle, instilled in me not only resilience but a deep understanding of the complex social fabric that shapes communities. It was these formative experiences, coupled with my time volunteering at a local shelter, that solidified my dedication to advocating for social justice.
Professionally, my experiences have been closely aligned with the values at the core of social work. Serving as a community organizer, I worked alongside local leaders to tackle critical issues like housing affordability and healthcare accessibility, gaining valuable insights into the world of policy advocacy. Another pivotal role was as a counselor for at-risk youth, where I developed a keen understanding of the challenges faced by young people from diverse backgrounds. This role was instrumental in refining my skills in empathy and communication.
Looking ahead, my immediate goal is to become a Licensed Clinical Social Worker with a focus on trauma and PTSD. In the long run, I aspire to establish a non-profit dedicated to providing mental health services to marginalized communities. These ambitions are rooted in a deep-seated commitment to effecting lasting change for those society often overlooks.
San Jose State University’s MSW program, renowned for its emphasis on culturally competent practice, particularly with Latinx and other minority groups, aligns perfectly with both my personal and professional values. The program’s exceptional faculty and comprehensive curriculum stand out as ideal for nurturing my academic and professional growth.
In conclusion, I am confident that my time at San Jose State University will not only refine my existing skills but also expand my perspectives, equipping me to become an effective, empathetic social worker. I am eager to embrace the tools and knowledge that the program offers, to champion social justice and make a tangible difference in the lives of those most in need.
This MSW personal statement sample effectively showcases the candidate’s journey and motivation towards a career in social work. It does well in several key aspects:
- Personal Experience : The statement begins with a compelling narrative about the candidate’s upbringing in a diverse, challenging environment, effectively linking personal background to their interest in social work.
- Professional Alignment : The candidate skillfully ties their professional experiences, like community organizing and counseling, to the core values of social work- to demonstrate a clear understanding and commitment to the field.
- Future Goals & Alignment with the Program : The statement outlines specific short-term and long-term professional goals, aligning them with the strengths of San Jose State University’s MSW program. This demonstrates the candidate’s purposeful choice of program and their understanding of how it will support their career objectives.
- Flow and Clarity : The essay is well-structured, with each paragraph transitioning smoothly into the next, maintaining a clear and engaging narrative throughout.
Verdict: The statement presents a well-rounded, sincere, and focused candidate with a clear vision for their future in social work. It makes a strong case for their admission.
Example 7: Wayne State University MSW Personal Statement Sample
Your statement must address the following items:
- The National Association of Social Workers set forth important guiding principles to address social workers’ ethical responsibility to clients, colleagues, employers and employing organizations, the social work profession, and society.
- Describe how these ethical standards would shape your professional social work practice. How would you reconcile any conflicts between your personal values and the requirements of the profession?
- Describe why you believe you are a good fit with the mission of the Wayne State University School of Social Work, particularly its urban mission.
- Social workers are committed to social justice. Please describe your thoughts on a particular social and economic justice issue and how you intend to use your professional social work degree to address these issues.
As an African American with Native American roots, I have firsthand experience with the challenges faced by underserved communities. This background has deeply influenced my desire to pursue social work, driven by a belief in compassion, commitment, and competence. I aim to amplify my impact in this field by enhancing my skills, and I believe the MSW program at Wayne State University is the ideal setting for this growth.
My life in Detroit has exposed me to the myriad challenges of urban environments, from food deserts to unsafe public spaces and high crime rates. The city’s struggle with deindustrialization has led to job losses, property abandonment, and heightened poverty, which I believe positions me uniquely for Wayne’s urban mission. Understanding these issues firsthand, I feel equipped to contribute meaningfully to solutions.
In my current role with a youth assistance program, I work to prevent youths from entering the juvenile system and help rehabilitate those already involved. Our sessions include group counseling, academic enrichment, and life skills training, aimed at early intervention to improve life quality and academic performance.
My practice as a social worker is grounded in the ethical standards set forth by the National Association of Social Workers. I prioritize service above self-interest, as evidenced by my role as a Direct Care Worker for my sister with Autism Spectrum Disorder. I am committed to social justice and understand the importance of dignity and respect for every individual, regardless of their background. My experience with Wayne State University’s XXXXXX program has further reinforced the value of human relationships in social work.
I recognize the potential conflicts between personal values and professional responsibilities. In such cases, I intend to adhere to the profession’s ethical standards, ensuring that my personal beliefs do not hinder my ability to serve clients effectively.
The Wayne State University School of Social Work’s urban mission resonates with my experiences and aspirations. My understanding of Detroit’s unique challenges aligns with the school’s focus on urban social work. I am particularly interested in addressing issues of poverty and economic disparity, leveraging my post-masters degree to initiate impactful programs like fundraisers for low-income students and collaborations with local food banks.
I am aware of the challenges in understanding certain aspects of social work, such as the dynamics of gang involvement. To address this, I plan to engage in continuous learning about various community issues to enhance my ability to serve diverse populations effectively.
My journey has not been without its challenges. While I have been actively involved in addressing the needs of victims of gang violence, I recognize a gap in my understanding of gang culture. To bridge this gap, I am committed to learning more about gang dynamics, history, and the socioeconomic factors that influence gang membership. This knowledge will be crucial in my work with at-risk youth, allowing me to provide more targeted and effective interventions.
Balancing the demands of graduate studies with work, family, and financial responsibilities will be challenging, but my experience in the Wayne State University XXXXX program has equipped me with valuable skills in time management and prioritization. I am prepared to fully commit to the MSW program, confident that it will transform me into an impactful social work professional aligned with Wayne State’s mission.
- Alignment with University’s Mission : The statement effectively aligns the student’s personal and professional experiences with Wayne State University’s urban mission.
- Ethical Awareness : Demonstrates a clear understanding of social work ethics and a commitment to upholding these standards in practice.
- Conflict Resolution : Thoughtfully addresses potential conflicts between personal values and professional responsibilities, indicating maturity and professional readiness.
- Commitment to Social Justice : Shows a strong dedication to social justice, particularly in addressing economic disparities and poverty.
- Continuous Learning : Emphasizes a willingness to learn and grow, especially in areas like understanding gang dynamics, which is crucial for effective social work.
- Personal Experiences : Successfully uses personal experiences to illustrate a deep understanding of the challenges faced by underserved communities.
- Realistic Approach : Acknowledges and prepares for the challenges of balancing graduate studies with other life responsibilities.
Verdict: The applicant shows a strong alignment with the program’s focus, demonstrates ethical awareness, and possesses a clear commitment to social justice and continuous learning. The statement shows maturity and readiness for the challenges of graduate study in social work.
Example 8: University of Pittsburg MSW Personal Statement Sample
Please describe in your personal statement the following:
- Influences in your life that led you to select social work as a profession
- Why you are applying to the University of Pittsburg School of Social Work
- How an MSW will help you achieve your career goals
- Your special skills and abilities, your strengths as well as your limitations
- How your abilities will contribute to your development as a professional social worker
- Discuss a contemporary issue that is of concern to you
Printed on my grandfather’s funeral brochure was an old Irish proverb: “Death leaves a heartache no one can heal; love leaves a memory no one can steal.” This sentiment has resonated with me deeply, as I have experienced significant loss in my life, from cancer to accidents and suicide. These experiences have not only shaped my understanding of grief but also steered me towards a career in social work, specifically in gerontology and hospice care.
During my final quarter at XXXXXXX State College, I met a hospice social worker whose impact on families dealing with end-of-life situations was profound. Her approach to helping families accept, celebrate life, and find peace in farewells deeply inspired me. It was then that I realized the power of social work in providing comfort and dignity in life’s final stages.
I am applying to the University of Pittsburgh School of Social Work because of its strong gerontology program and its commitment to addressing contemporary issues like the impact of COVID-19 on the aging population. The pandemic has starkly highlighted the disparities in our healthcare system, especially concerning end-of-life care. I aim to contribute to this field by developing solutions to these emerging challenges, ensuring dignity and comfort for all in their final moments, regardless of their racial or socioeconomic status.
My work experience in childcare and hospitality has equipped me with patience, empathy, and a strong work ethic, qualities essential for a career in social work. Additionally, my volunteer work with XXXXXXX and the XXXXXXX has given me valuable experience in community service. However, I recognize my tendency to be overly trusting as a limitation. In the field of social work, discernment is crucial, and I am actively working on balancing empathy with professional objectivity.
At the University of Pittsburgh, I am particularly interested in courses like Grief and Loss: Interventions, Implications, and Understanding, and Direct Practice with Older Adults. These courses, coupled with field education in aging, hospice, or hospital settings, will be instrumental in achieving my career goals.
My commitment to serving the Pittsburgh community stems from my deep-rooted connection to the city. Witnessing the impact of the university’s alumni in the field has further motivated me to pursue my MSW here. I am fully aware of the challenges that lie ahead in the field of social work, but I am confident that the guidance and training offered by the University of Pittsburgh will equip me to tackle these challenges effectively.
My personal experiences with loss, combined with my professional aspirations and commitment to social justice, make me a suitable candidate for the MSW program. I am eager to contribute my skills, work ethic, and unique perspectives to the University of Pittsburgh School of Social Work and to grow into a compassionate and effective social worker.
- Connection of Personal Experience to Career Choice : Effectively links personal encounters with loss to a passion for social work, particularly in gerontology and hospice care.
- Alignment with Program’s Strengths : Clearly identifies why the University of Pittsburgh’s program, with its focus on gerontology, is a strong fit for the candidate’s career goals.
- Discussion of Contemporary Issues : Addresses the impact of COVID-19 on the aging population, showing awareness of current challenges in social work.
- Self-awareness and Growth : Acknowledges personal limitations, like being overly trusting, and the intention to work on balancing empathy with professional objectivity.
- Relevant Skills and Experience : Highlights experiences in childcare, hospitality, and volunteer work, which showcase skills valuable in social work.
Verdict: The statement demonstrates a clear connection between personal experiences and professional aspirations. It aligns effectively with the program’s focus, displays awareness of current social issues, and shows a commitment to personal growth- making the candidate a strong fit for the University of Pittsburgh’s MSW program.
Example 9: Case Western Reserve University MSW Personal Statement Sample
Discuss significant factors influencing your decision to pursue a Master of Science in Social Administration (MSSA).
- Your essay should include information regarding your interest in the social work profession, your intended concentration/specialization, and career goals.
- Please reflect on how any past school, community, volunteer, professional work, and leadership experiences will contribute to your success as a graduate student.
- Describe how you see yourself contributing to the vibrancy of our student body and school community.
- Describe any strengths or limitations that might influence you being successful in your field placement.
- Finally, please include why the Mandel School is a good fit for your educational goals.
My decision to pursue a Master of Science in Social Administration (MSSA) at the Mandel School is deeply rooted in personal and professional experiences that have highlighted the profound impact of social work. My journey began with observing the complexities of mental health within my family, which instilled in me a passion for understanding and advocating for mental health care.
Growing up, I watched a beloved family member struggle with mental health challenges. Witnessing their battle and the ripple effect it had on our family stirred in me a resolve to support others facing similar trials. This resolve only deepened with the birth of my daughter, Eve, when I encountered my postpartum mood disorders. Through receiving treatment and support, I was empowered to overcome these challenges, which further fueled my aspiration to assist women grappling with similar issues.
In my professional role as a Health Coach and Personal Trainer, I’ve had the privilege of supporting clients like John and Anna, whose mental well-being was intertwined with their physical health goals. These experiences have honed my ability to listen empathetically and devise holistic approaches to wellness that I believe will be invaluable in my social work practice.
My immediate career goal is to establish a private practice focused on women’s mental health, particularly addressing postpartum mood disorders. I am inspired to create a space where women can seek help without stigma or silence. In the long term, I aspire to influence mental health policy, advocating for accessible care and support systems that recognize and address the silent struggles many women face.
The Mandel School’s commitment to academic excellence and its vibrant student body resonate with my educational and professional ethos. The school’s innovative approach to social work education, particularly in mental health, makes it an exceptional fit for my aspirations. My compassion, coupled with my professional experience and personal journey through mental health challenges, will contribute to the rich tapestry of the Mandel School community.
Ultimately, I envision my time at the Mandel School as a transformative experience that will not only deepen my understanding of social work but also equip me with the skills to make significant contributions to the field. With a community that fosters diversity of thought and experience, I am confident that my educational journey here will prepare me for a fulfilling and impactful career in social work.
- Personal Connection : The statement effectively establishes a personal connection to social work through the candidate’s family experiences with mental health.
- Professional Relevance : It highlights relevant work experience that translates well into social work competencies, particularly in understanding clients’ holistic needs.
- Clear Career Objectives : The candidate articulates well-defined short-term and long-term goals that align with their personal experiences and professional aspirations.
- School Alignment : There is a strong emphasis on how the Mandel School’s ethos resonates with the candidate’s goals, suggesting a thoughtful choice in their application.
- Contribution to Community : The statement outlines how the candidate’s unique experiences and compassion will add value to the student body and fieldwork.
Verdict: The candidate’s personal statement is compelling, demonstrating a strong, authentic motivation for pursuing an MSSA and a clear vision for how the Mandel School will help fulfill their career objectives.
Example 10: University of Pittsburg MSW Personal Statement Sample
- Influences in your life that led you to select social work as a profession.
- Why you are applying to Pitt’s School of Social Work.
- How an MSW will help you achieve your career goals.
- How your abilities will contribute to your development as a professional social worker.
- discuss a contemporary issue that is of concern to you.
At just seven years old, I witnessed the harsh realities of poverty, domestic violence, and addiction within my family. These experiences instilled in me a passion for social work, especially after seeing how social workers supported our family through my parents’ mental health and addiction challenges. This inspired me to pursue a career in this field to use my background and skills gained from an MSW program to assist individuals and families in their recovery processes.
Growing up, our family was caught up in a custody battle, leading my siblings and me to frequently navigate foster care and courtrooms. My parents’ struggle with addiction was alleviated by the support of social workers and case managers, who provided housing, food assistance, service coordination, and counseling. Tragically, both my parents eventually succumbed to drug overdoses. Though painful, these experiences further reinforced my commitment to social work and helping others facing similar struggles.
In recent years, I have been actively involved in social justice activism. My roles as a community organizer and development director for XXXXX Summer Camp, a non-profit empowering girls and non-binary youth through music and mentorship, highlighted the need for improved mental and behavioral health services. Volunteering as a delivery driver and food packager with XXXXX Aid during the COVID-19 pandemic underscored the importance of community support for those in need.
My experience in event coordination, donor relationship building, and electoral campaign work has enabled me to contribute to meaningful change in my community, such as the successful XXXXX Wage initiative in Oregon, which improved the lives of countless workers. Serving on the XXXXX Democratic Committee for Ward Four, I have amplified community voices and supported candidates who advocate for accessible mental and behavioral health services, safe and affordable housing, and environmental protection.
A contemporary issue that concerns me is the effectiveness of harm reduction techniques in treating mental health and dual-diagnosis clients. I aim to explore how these techniques can be integrated into traditional substance abuse treatment models to better meet the mental health needs of individuals like my parents. Additionally, I am interested in how mental health professionals and addiction treatment providers can collaborate to provide comprehensive care for dual-diagnosis clients.
Obtaining an MSW will empower me to become a skilled, compassionate, and trauma-informed clinician. My goal is to contribute to accessible mental and behavioral health services, particularly for trauma survivors, and advocate for inclusive, culturally responsive, and restorative justice practices.
I am empathetic and easily connect with people, and my resilience in adversity will contribute to my development as a professional social worker. These qualities have supported me in helping my sister Cheyan and in my social justice work.
I chose the University of Pittsburgh’s School of Social Work for its highly-ranked program and specialization in mental health. This program aligns with my goal of employing harm reduction strategies for dual-diagnosis clients. Additionally, its proximity to my family will enable me to support them while pursuing my education.
I am eager to return to the University of Pittsburgh and embark on this transformative journey to become a professional social worker. The MSW program will enable me to make a significant difference in the lives of those who need compassionate and trauma-informed care. I am confident that this program will honor my family’s legacy and empower me to create positive change for countless individuals and families in need.
- Personal Experience as a Motivation : The applicant compellingly uses their personal history of overcoming poverty, domestic violence, and addiction to demonstrate a deep-rooted motivation for pursuing social work.
- Community Involvement : The statement highlights significant community engagement and activism, showcasing a commitment to social justice and change.
- Professional Development : Details about event coordination, campaign involvement, and leadership roles show the applicant’s ability to effect change and work collaboratively.
- Academic and Career Goals : The applicant clearly articulates their interest in harm reduction techniques and their intent to enhance their skills through the MSW program.
- Personal Qualities : Empathy and resilience are emphasized as strengths that will aid in their development as a social worker.
Verdict: The statement presents a well-rounded candidate with a powerful personal connection to social work, backed by active community involvement and clear professional goals. Their commitment to addressing complex social issues, coupled with their personal strengths, shines throughout the statement.

Before you go…
You should be inspired enough to craft your authentic MSW personal statement. But you still need experienced eyes to deeply review it for flow, tone, logical structure, and clarity! See how I can help you below…
I will proofread, polish, edit any personal statement, college application essay or sop.
Related Articles:
Social Work Personal Statement Guide (w/Examples)
Top 8 Cheapest Online MSW Programs
Best Online MSW Programs in California
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Advertise With Us
Advertising Disclosure
Privacy Policy
Cookie Policy
As an Amazon Associate (and a participant of other affiliate programs), this site earns from qualifying purchases.
© 2024 TheCollegeApplication.com, a Delicto Holdings Company | All Rights Reserved
Personal Social Work Practice Skills and Field Experience Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
The purpose of this blog is to discuss personal social work practice skills gained by participating in the field education experience. The practicum encouraged the social work intern to apply academic knowledge in real-life situations and understand the actual needs of diverse clients. The intern was expected to obtain social work skills at the practicum agency to offer effective interventions and quality service to their future clients.
The professional growth of the social work intern participating in the practicum at Vatsalya Adult Medical Daycare Center was assessed through self-reflection. The method allowed to analyze individual field education experience and social work skills acquired throughout the practicum (Laureate Education, 2013). The field education experience at Vatsalya provided the social worker with a set of essential professional skills and allowed them to acquire active listening, cultural competency, confidence, and problem-solving abilities during the practice at the agency. The generalist practice promoted at Vatsalya involved the social worker’s use of critical thinking skills to recognize truth and formulate opinions about certain situations (Kirst-Ashman & Hull, 2018).
The practicum setting including the sessions with vulnerable African American, Hispanic, and Asian clients taught the intern how to use the standards of the NASW Code of Ethics. The case of the rehabilitating client requiring occupational therapy taught the intern about the need to apply public policies and regulations for the benefit of vulnerable clients (Garthwait, 2017). It should be noted that ethical decision-making is an important social work skill allowing professionals to select appropriate interventions according to ethical principles.
In addition to the profession-specific skills and competencies, participation in field education experience helps master organizational and time-management abilities to improve the effectiveness and productivity of counseling sessions.
Reasonable time allocation enhanced the capacity of the intern to meet deadlines and avoid stress or burnout. The encounter with the speech-impaired dementia client taught the social work intern about the benefits of taking pauses and breaks during sessions. The measures helped build rapport and improve the client’s compliance with the implementation plan. Other general work skills included writing (reports, records) and information-processing skills, as well as the ability to work under supervision and utilize the instructor’s feedback for professional improvement.
Writing skills were efficiently employed by the social worker in process recording assignments used to analyze specific sessions and improve the interventions offered for vulnerable and diverse Vatsalya clients. Research skills were developed by the intern during field education experience to examine best practices available for particular cases and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions. Finally, the practicum explained how to use empathy, an open-minded attitude, and personal values for the benefit of clients and the agency. For instance, empathy helped establish trust and positively impact the confidence of the female client with age-related self-esteem issues.
To sum up, field education experience helped the social work intern learn essential skills and combine academic knowledge with real-life experience. Professional skills and competencies acquired at the agency included listening, problem-solving, cultural competency, and respect for diversity. The general work skills and the use of empathy and personal values were also learned and applied during the practicum.
Garthwait, C. L. (2017). The social work practicum: A guide and workbook for students (7th ed.). Pearson.
Kirst-Ashman, K. K., & Hull, G. H., Jr. (2018). Understanding generalist practice (8th ed.). Cengage Learning.
Laureate Education (Producer). (2013). Self-reflection . Web.
- Importance of Family in Society
- Reflecting on Your Own Business
- The Practicum Project in Nursing
- "The Intern" by Nancy Meyers
- Nursing Practicum Project Goals and Ideas
- Alice Walker’s Beauty: Accident From Childhood
- Experience and Resilience: Connection
- Personal Prosocial Behaviors During the Day
- Elusive Nature of Dreams: A Personal Exploration
- Cultural Competence and Cultural Humility
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, October 24). Personal Social Work Practice Skills and Field Experience. https://ivypanda.com/essays/personal-social-work-practice-skills-and-field-experience/
"Personal Social Work Practice Skills and Field Experience." IvyPanda , 24 Oct. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/personal-social-work-practice-skills-and-field-experience/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Personal Social Work Practice Skills and Field Experience'. 24 October.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Personal Social Work Practice Skills and Field Experience." October 24, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/personal-social-work-practice-skills-and-field-experience/.
1. IvyPanda . "Personal Social Work Practice Skills and Field Experience." October 24, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/personal-social-work-practice-skills-and-field-experience/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Personal Social Work Practice Skills and Field Experience." October 24, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/personal-social-work-practice-skills-and-field-experience/.

Why I Want to Be a Social Worker Essay: A Personal Reflection-2024

Choosing a career path is a deeply personal decision that often reflects one’s values, passions, and aspirations. For me, the decision to pursue a career in social work stems from a profound desire to make a positive impact on the lives of others and contribute to the well-being of my community. In this reflective essay, I will share the reasons why I want to be a social worker, exploring my motivations, experiences, and vision for the future in this rewarding and meaningful profession.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Role of a Social Worker
Before delving into my personal motivations, it’s important to understand the role of a social worker and the impact they have on individuals, families, and communities. Social workers are dedicated professionals who work with diverse populations to address social problems, advocate for social justice, and empower individuals to overcome challenges and achieve their full potential. They work in a variety of settings, including schools, hospitals, mental health clinics, child welfare agencies, and community organizations, providing support , resources, and interventions to those in need.
Motivations and Personal Experiences

1. Compassion and Empathy
At the core of my desire to become a social worker is a deep sense of compassion and empathy for others. Growing up, I witnessed firsthand the struggles and hardships faced by individuals in my community, from economic inequality to systemic injustice. These experiences ignited a passion within me to help those who are marginalized, vulnerable, or in need of support. I believe that every individual deserves to be treated with dignity, respect, and compassion, and I am committed to advocating for those whose voices may not be heard.
2. Commitment to Social Justice
Social justice is a fundamental principle that guides my values and beliefs. I am deeply committed to addressing systemic injustices and working towards a more equitable and inclusive society. As a social worker, I see myself as a catalyst for change, challenging oppressive systems and advocating for policies and practices that promote fairness, equality, and human rights. Whether it’s advocating for affordable housing, combating racial discrimination, or fighting for LGBTQ+ rights, I am dedicated to being an agent of social change and standing up for what is right.
3. Desire to Make a Difference
One of the most rewarding aspects of being a social worker is the opportunity to make a tangible difference in the lives of others. Whether it’s helping a struggling family find stable housing, supporting a survivor of domestic violence on their journey to healing, or empowering a young person to overcome adversity and pursue their dreams, each interaction has the potential to create positive change and inspire hope. The sense of fulfillment that comes from knowing that my work has made a meaningful impact is what drives me to pursue a career in social work.
4. Strengths and Skills
My capabilities and abilities, in my opinion, make me a good fit for a career in social work. With a sincere desire to comprehend and assist people, I am a cooperative problem-solver, good listener, and sympathetic communicator. I am resilient, flexible, and capable of doing well in a variety of demanding settings. In order to better serve my clients and the community, I also have a strong dedication to professional growth and lifetime learning. I work hard to increase my knowledge and abilities.
Vision for the Future
Looking ahead, I envision myself as a dedicated and compassionate social worker who is deeply engaged in my community and committed to social change. I see myself working collaboratively with individuals, families, and communities to address the root causes of social problems and create sustainable solutions. Whether it’s providing direct services , advocating for policy reform , or conducting research to inform evidence-based practices, I am committed to making a positive impact at both the micro and macro levels.

In addition to my direct practice work, I aspire to become a leader and advocate for the social work profession, promoting its values, ethics, and importance in addressing the complex challenges facing our society. I hope to inspire future generations of social workers to embrace their passion and commitment to social justice, and to recognize the profound impact they can have on the lives of others.
Conclusion: Embracing the Calling of Social Work
In conclusion, my decision to pursue a career in social work is rooted in a deep sense of compassion, commitment to social justice, and desire to make a positive difference in the world. I am drawn to the profession’s values of service, integrity, and empowerment, and I am excited about the opportunity to embark on this journey of learning, growth, and transformation. As I embark on this path, I am grateful for the opportunity to contribute my skills, strengths, and passion to the field of social work, and I am eager to embrace the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
FAQ: Why I Want to Be a Social Worker
1. what inspired you to pursue a career in social work.
My decision to pursue a career in social work was inspired by a combination of personal experiences, values, and aspirations. Growing up, I witnessed firsthand the struggles faced by individuals and families in my community, from poverty and homelessness to discrimination and social exclusion. These experiences ignited a passion within me to help those in need and advocate for social justice and equality.
2. What specific qualities or skills do you possess that make you well-suited for a career in social work?
I have a great sense of empathy, compassion, and a sincere desire to assist people. I can establish trustworthy relationships and connect with people from a variety of backgrounds because I am an effective communicator, problem-solver, and listener. In addition, I have resilience, adaptability, and a strong commitment to both professional and lifetime learning.
3. What do you hope to achieve as a social worker?
As a social worker, my primary goal is to make a positive impact on the lives of others and contribute to the well-being of my community. I aspire to address systemic injustices, empower individuals and families to overcome challenges, and advocate for policies and practices that promote social justice and equality. I also hope to inspire future generations of social workers and contribute to the advancement of the social work profession.
4. What are some challenges you anticipate facing in your career as a social worker?
While pursuing a career in social work is deeply rewarding, it also comes with its challenges. Some of the challenges I anticipate facing include navigating complex social systems and bureaucracies, managing the emotional toll of working with individuals in crisis, and advocating for change in the face of resistance or apathy. However, I am committed to overcoming these challenges and continuing to grow personally and professionally as a social worker.
5. How do you plan to continue your professional development as a social worker?
I plan to continue my professional development through ongoing education, training, and networking opportunities. This may include pursuing advanced degrees or certifications, participating in workshops or conferences, and engaging in supervision or mentorship relationships. I also plan to stay informed about current research, best practices, and emerging trends in the field of social work to enhance my skills and knowledge.
6. What advice would you give to others considering a career in social work?
My advice to others considering a career in social work is to follow your passion, stay true to your values, and never underestimate the impact you can have on the lives of others. It’s important to embrace challenges as opportunities for growth, seek support from colleagues and mentors, and practice self-care to avoid burnout. Remember that social work is not just a profession, but a calling to make a difference in the world.

Meet Manicka
I created The Social Work Success Path blog and podcast, during the pandemic of 2021 to provide online education and mentorship for Social Workers. I felt very isolated and disconnected being only in the second year of running my private practice. I strongly considered going back to work when everything shut down. The resources and tools that I share helped me to maintain my practice through the pandemic and plan a successful transition as a Social Work content creator, doing work that I love and connecting with Social Workers all around the world. I did this in the span of 1 year, but using the resources, trainings and tools that I have pulled together, and all my all lessons learned, you can make your career transition much sooner than I did!
Follow Along

You'll Also Love:

New Year, New Professional Resolutions: 20 Ideas for Social Workers in 2025
Social worker t shirt ideas for inspiration.

Motivational Tips: Motivate yourself by adopting these methods, you will not have to wait for success
Leave a comment.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This comprehensive list of careers every ambitious Social Worker should consider before entering the profession.
Email address:
What are you searching for?

What My Experience as a Social Work Student Taught Me

“God grant me serenity to accept the things I cannot change; courage to change the things I can; and the wisdom to know the difference.”
Since childhood, I have always known that I would grow up to find a job where I could make use of my natural ability to empathize with others and my strong desire to help people ease their pain. This is why, after completing college, I made the decision to apply to social work school and channel my energies and efforts into helping those less fortunate than I.
Graduate school was simultaneously a wonderful and terrifying experience. Wonderful in the sense that I was finally studying something I truly cared about and believed in; gone were the days of endless hours studying calculus and French literature, replaced by classes on social policy and family therapy. I met awesome new friends from vastly different backgrounds than myself, people I never would have had the opportunity to meet during my childhood in a beautiful but largely homogenous middle-class neighborhood of families with two college-educated parents and an average of 2.5 children.
But grad school was also terrifying, in the sense that I finally had the opportunity to discover what my decision to enter this field would truly entail. To say that social workers are under-appreciated and underpaid is putting it lightly. Over the course of my two-year master’s program, I had supervisors – supervisors! – who held at least one other job in addition to their main, full-time job, just to be able to pay the bills. It had never occurred to me that an employed adult putting in 40 hours a week might still not take home enough of a paycheck to cover her and her family’s basic needs. The fact that the US was in the midst of a recession only sought to make this problem even more relevant and apparent.
By this time I reached my second and final year of the program, my knowledge had increased exponentially – as had my stress level. Here I was, with all sorts of lofty plans for my future, and I didn’t even know if my choice of profession would allow me to pay rent. I was already working two part-time jobs on top of my full-time class schedule, plus three full days a week at my internship. If this was how difficult things were as a student, I didn’t even want to imagine what it’d be like trying to support and care for children, as many of my classmates were doing.
My second-year field placement took place, at my request, at an outpatient treatment center for chemically addicted men, women, and teens. The work was frustrating, and usually by the time I got home, I was not in the mood to see or speak to anyone for several hours while I unwound.
Weeks went by, then months, and soon enough it came time to start planning for graduation and my future licensing exam, which was drawing ever closer. I reminded my clients of my last day working at the center, and began the process of saying goodbye to them. They wished me all the best with my exams and my future. It struck me that after 10 months together, I would be leaving; some of these clients had been in therapy for years, while others were just starting out their respective journeys and had a long road ahead of themselves in their recovery – particularly for the majority of clients who had yet to accept that they did, in fact, have a problem.
The juxtaposition of my clients’ real, potentially life-threatening challenges with my own needless anxiety was startling. Don’t get me wrong – there is a very real concern in not being able to make enough money to support oneself and one’s family. But since I was not actually in that situation at that moment in time, there really was no need for me to be stressing.
The famous Serenity Prayer, often quoted in Alcoholics Anonymous meetings, implores God to: “grant me the serenity to accept the things I cannot change; courage to change the things I can; and the wisdom to know the difference”. That day, something finally clicked for me, and it became clear just how much I needed to let go of trying to be in control of everything. The decision to stop stressing, and the ability to carry it out, are two very different things, but at last I had a name to my goal – I needed to gain serenity.
Life throws a lot of challenges our way, some that we had anticipated and many that we had not. In worrying about the future, however, we all too often miss out on the present. Over the years following my experience as a social work student, there have been many trying times, but I always keep in the back of my mind the realization that there is a difference between the things I can change and the things I cannot – and that that’s ok.
Sometimes when we set out to help others, the experience ends up helping us in turn – have you ever experienced such a situation in your own life?
Photo by Francisco Osorio
About The Author
Rachel Schultz
Related posts.

How to Heal Anxiety

Five Pitfalls Anxiety Sufferers Fall into… and How to Get Past Them
Follow us on instagram.

possibilitychange

3 thoughts on “What My Experience as a Social Work Student Taught Me”
Great Article Rachel! I enjoyed reading about how you followed your passion to help others. I also enjoyed reading how at one point you had the realization that your career path my not held the lifestyle you dreamed about. I recently had a friend who is much younger then I am decide to go back to collage to study for a new career. He came to my house with his computer in hand and all the salary stats on the different career paths he had chosen. He and I looked through them all and I asked questions about the courses and got him to clarify his interpretation of the information. At the end of our discussion he asked me what I would do if I were making his choice. The only question I asked him was “which course focus gets you excited?” Being someone who has worked in a field that didn’t excite me, I can tell you it is draining in a different way. I will tell anyone I come across to first be true to your hearts calling. You will never feel unsuccessful by learning and focusing in an area that fills your spirit with joy. You will also find that when you focus on something that creates joy for you, then you can begin to innovate within that area. First take care of your own passions and then you can guide others to find what they are passionate about. Thank you for the read and the opportunity to comment! Cosimo
Thank you for being vulnerable with us and yet showcasing the strength in your convictions, through this article, Rachel :)
Wow you sure know how to use your words. Brilliant rendition of your journey and experience. I can say that I truly enjoyed the experience of returning to higher education after a half a century in doing stuff to get me by. I graduated with my bachelor of Social Work and wish now that I had done it before… however I can’t change that!!! So forward I go and know that I make a difference each and every day to my clients who have had serious health conditions and now need to rethink their “normal”… it fills my soul to be apart of their journey, the tears and the smile! I have no regrets and with my job the $$$ are very good…. If you work in non-profit it is less but in a government system its very good money! Do you live in USA?
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of followup comments via e-mail
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Buy Our Toolkit!
Social work scholarship essay examples
0 comments
In April 2016, I won a full scholarship from the National Council of Social Services (Singapore) to read Social Work in the University of Nottingham.

I thought I would take the chance to share the examples from my scholarship essay that helped me to get into the interview. I hope students reading this will have a clearer guide on how to write their own scholarship essays.
Whilst the scholarship essays from Singapore might differ to other countries, I provide principles here to guide your writing. Throughout this article, I will also include examples from my own personal scholarship essay application. Through this, I hope you gain better ideas on how to use them for yourself.
Writing a scholarship essay can seem unnerving. For one, they ask many why questions. They also seem to expect you to know what you are going to do with your life in 5 years’ time. You might not even know what you are going to do with your life tomorrow!
1. Include stories
A public speaking coach once told me, ‘Facts tell, stories sell.’ Humans are story-telling creature. Without stories, our lives would be less rich. But more importantly, without stories, we make less of an impact on the panel of assessors reading through our applications.
When you tell your story, try to keep it to one. Unless it’s a full essay, including only one will help you to go in-depth into the story.
Focus on the things you did that might relate to social work. What impact did it make?

Write about what others might have said of your contributions.
2. Ask someone else to read through your essay.
Example 1: about yourself.
During Sunday afternoons, I volunteer my time with the intellectually disabled, and see them as no more different from any of us. One of my most impactful moments came when I was teaching one of the trainees how to write in block letters. We are trying out the alphabet “A”. After the umpteenth time, he looks at me, bites his lip, and exclaims, “I don’t know how to write this!” Although he is bilingual and looks like you and me, such a simple alphabet has spawned so much difficulty. They may be obsessive, compulsive and impulsive, but their flaws are no less than our own, and their flaws do not change the fact that they are still fundamentally human and deserve respect and dignity. In my search for a future career, I wanted one that would be able to help me to make a positive impact in the lives of others. (LINK TO SOCIAL WORK) Whilst social work may often be seen as lowly paid, and the fruits of our labor often taking a much longer time to ripen, I believe that the process is what is to be cherished, rather than the end product itself.
We are all prone to our own biases. That is why sharing your essay with someone else is good. I shared my own essay with a social worker, who led me to see certain stereotypes I may have unknowingly conveyed through my essay.
Encourage someone to read your essay and tell you the good, and bad about it.
2. Use every experience you have had.
Some people think that direct social work or social care experience might be more useful. But for many younger students who might be applying for an undergraduate scholarship, you might not have this experience. It’s good to draw a link between your summer jobs and your future ambition of becoming a social worker.
For example, even though I didn’t have any social care experience, I used my experience in the army to illustrate how we shouldn’t hold stereotypes towards the disadvantaged. Social work was my way of reaching out to them.
Hopefully, the following social work scholarship essay examples, drawn from my own application, help.
Example 2: Current work experience
One of my fondest memories of National Service came in the cookhouse as I was speaking to one of the more notorious men. Big and bulky, it is not easy to order him around, especially when we know his connections outside. And especially when we have heard about how an imprint of his fist is still on a locker somewhere, landed in frustration after he was charged and sent to the detention barracks. But as he sits alone in the cookhouse, I feel compelled to speak to him, knowing that his past is no reason to isolate him or to treat him differently. As I awkwardly place my plate in front of him, he looks up, eyeing me suspiciously. I break into a smile and try to make small conversation. Unprompted, he shares about his experiences inside jail, and it is clear that he has not had it easy inside. But as I hear about his plans to begin work as a car salesman before eventually setting up a zi char store, whipping up dishes people love, I greatly admire the hope he holds deep within. His face is lit with optimism of a better future, and his scowl has disappeared. Army has indeed exposed me to a myriad of different characters and has taught me that far beyond the shelter of my privileged environment, lie many people who have not had the chance to enjoy life as fortunately as I have. Social work gives me that chance to touch these lives. (LINK TO SOCIAL WORK)

4. Be clear about who you are.
Applying for a scholarship can be a gruelling process. Application essays and interviews will ask you multiple questions about what your motivations are ( why social work?) , what you are interested in, what you are good at, what you can add, and where you want to be. You don’t have to know the answers to all these. But you need to show that you have at least thought about some of these questions.
If you have not, I would deeply recommend Richard Bolles’ What Color Is Your Parachute. This is a book that leads you on 7 separate exercises that help you elucidate more about who you. Try it. It is worth the effort.

5. Be linguistically and grammatically accurate.
Scholarship panels dislike reading grammatical errors and spelling mistakes. This will be the first sign that you might not have spent as much time as you should on an application. There is no second first impression. Your first impression counts. Before you submit that application, take the time to run through the spell check multiple times. To be safe, I would recommend 3 times!

6. Print it and read it out loud to yourself.
It is powerful to read what you have read, out loud to yourself. For one, the spelling and grammar mistakes will jump out at you. It also allows you to see if you are cogent.
Do your arguments flow well?
Do your points make sense?
Recommended by Cal Newport’s book How To Be A Straight-A student, I have found it invaluable in editing better.
I hope that these social work scholarship essay examples help make writing easier. Don’t forget, you are not defined by the outcome of this application. Even if you do not make it, that does not necessarily mean that you should not be a social worker. If you make it, check out my post on interview tips.
Getting a social work scholarship is hard. With the examples above, and the tips for getting a social work scholarship here, I hope you get yours. The world needs more social workers like you.

You may also like
5 best books on making case management less painful, 7 of the best social work books for students, subscribe to our newsletter now.
Session expired
Please log in again. The login page will open in a new tab. After logging in you can close it and return to this page.
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Advance articles
- Editor's Choice
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- About The British Journal of Social Work
- About the British Association of Social Workers
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Article Contents
Introduction, research design.
- < Previous
Social Work as a Human Rights Profession: An Action Framework
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Didier Reynaert, Siebren Nachtergaele, Nadine De Stercke, Hildegard Gobeyn, Rudi Roose, Social Work as a Human Rights Profession: An Action Framework, The British Journal of Social Work , Volume 52, Issue 2, March 2022, Pages 928–945, https://doi.org/10.1093/bjsw/bcab083
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Human rights are foundational to social work, as recognised in the global definition, leading many to consider social work a human rights profession. Although human rights has become an important compass for social work, comprehensive frameworks for understanding the ‘practice’ of human rights in social work are still limited. Only recently attempts have been made to fill this gap. This article seeks to continue these efforts and contribute to a better understanding of how social work constructs, deconstructs and reconstructs ideas of human rights in daily practice. We investigated the following research question: ‘How do social workers “act” when using human rights as a framework for practice?’ We used a qualitative research design consisting of ethnographic research and focus groups, with both social workers and service-users participating. Based on our research, we developed five building blocks for an action framework for human rights in social work: (i) systemworld-oriented action; (ii) lifeworld-oriented action; (iii) participatory action; (iv) joined-up action and (v) politicised action. These building blocks give a comprehensive account for the discursive practice of human rights in social work.
Human rights are foundational to social work, as recognised in the global definition, leading many to consider social work a human rights profession ( Healy, 2008 ; Staub-Bernasconi, 2016 ; Mapp et al. , 2019 ). Staub-Bernasconi (2016) , together with Gatenio Gabel (2015) , among others, acknowledges the historical connection of social work with human rights. In recent years, the recognition of social work as a human rights profession gained renewed attention in social work scholarship. In his book ‘ Practicing rights. Human rights-based approaches to social work practice ’, Androff (2016) makes a comprehensive account of the state of human rights in social work. He shows how (inter)national social work organisations adopted human rights in their codes of ethics, how social work scholars increasingly published books and articles on human rights or how social work education developed a range of training materials and educational programmes on human rights. Based on his analysis, Androff concludes that ‘The growth of scholarship and education focused on human rights suggests that the field is turning towards human rights, rediscovering its rights-based roots. It is now undeniable that there is a consensus that human rights are important and relevant to social work.’ ( Androff, 2016 , p. 10). These observations are in line with conclusions of Cubillos-Vega (2017) , who conducted a study on the scientific output on human rights in social work based on articles published in international indexed journals between 2000 and 2015. She notes that in recent years, the academic output on social work and human rights gradually increased. However, Cubillos-Vega’s (2017) study also reveals that published articles were primarily of theoretical nature. From the fifty-seven articles analysed, hardly one-third (sixteen) were of an empirical type. This trend is striking, Cubillos-Vega argues, because of the nature of the discipline of social work, taking a position between theory and practice. Already in 2012, Ife came to a similar conclusion: ‘Much of the academic debate about human rights remains at the theoretical level; less has been written about the practice of human rights. … There is little articulation of what it means in practice for professionals to claim that their work is based on human rights, and so human rights remain a “nice idea” rather than a solid foundation for the development of practice theories and methodologies.’ ( Ife, 2012 , pp. 10–11). Despite the ground-breaking work of several pioneers in the domain of social work and human rights (e.g. Reichert, 2003 ; Wronka, 2008 ; Ife, 2009 , 2012 ; Lundy, 2011 ), the practice of human right still remains a black box. To date, social work scholarship insufficiently succeed to gain practical knowledge showing how social workers ‘act’ when using the framework of human rights. Together with Ife, we acknowledge the presumption that human rights in social work have a discursive character, as they need to be permanently constructed, deconstructed and reconstructed throughout social work practice. ‘Social workers need to see themselves as active participants in this discursive process, and indeed social work practice itself can be seen as part of the ongoing process of the reconstruction of human rights. It is partly through social work practice that human rights are operationalised, and hence defined.’ ( Ife, 2012 , p. 133). Social work should recognise its actorship or agency in constructing human rights and social work scholarship should conscientiously scrutinise this construction process of human rights through social work practice.
Recent launches in social work scholarship rose to this challenge. In 2015, the SpringerBriefs in Rights-Based Approaches to Social Work were launched. The series aims to develop a social work practice grounded in human rights by presenting and reflecting on new methods ( Gatenio Gabel, 2015 ). The Journal of Human Rights and Social Work, established in 2016, has similar aims. In the inaugural issue, the editors-in-chief state that the journal ‘offers the opportunity for educators, practitioners, administrators, and students in this and related disciplines to have a voice and to expand their knowledge base on issues within human rights practice, knowledge of human rights tools, and to develop skills practicing from a human rights perspective’ ( Gatenio Gabel and Mapp, 2016 , p. 1). Additionally, several social work scholars have been developing practice approaches for human rights in social work. Androff (2016 , 2018 ), for instance, seeks to integrate the five-principles framework of human rights (human dignity, non-discrimination, participation, transparency and accountability) into the social work arena. According to Androff, this framework can offer an integrative account across a wide range of social work practices (see also Mapp et al. , 2019 ). One step further is the proposal of McPherson ( McPherson, 2015a ; Mapp et al. , 2019 ; McPherson and Abell, 2020 ), which contains a comprehensive framework for human rights practice in social work (HRPSW). It comprises three pillars of practice: a human rights lens, human rights methods and human rights goals. McPherson (2015a ) explains that the HRPSW model can be useful for both social work practice and social work education. What these practice models demonstrate is the increased academic interest in practice approaches of human rights in social work ( McPherson, 2015b ).
In this article, we build upon these efforts and present an action framework for human rights in social work. Our action framework expands the above mentioned models in an important way. It provides an understanding of human rights in social work in the context of a different welfare regime. Both the studies of Androff and McPherson are USA based, thereby confirming Cubillos-Vega’s (2017) observation of an Anglo-Saxon hegemony in social work scholarship on human rights. However, different social welfare regimes show different traditions of social work ( Lorenz, 2001 , 2008 ), associated with different understandings of human rights ( Alseth, 2020 ). Our study was conducted in Belgium, which is generally conceived as a conservative welfare state, distinct from the liberal welfare regime of the USA. Conservative welfare regimes have a certain tradition with social rights in particular. Additionally, conservative welfare regimes are characterised by a welfare state architecture of corporatism, balancing civil society’s interest and state power ( Esping-Andersen 1990 ; Lorenz, 2001 ; Dean, 2002 ). It is within this corporatist structure that human rights take shape with social workers developing a human right-based practice.
Because of the open character of our research question (‘How does social workers act when using human rights as a framework for practice?’), we chose a qualitative research design ( Shaw and Holland, 2014 ; Carey, 2012 ), developed in two parts. The first part consists of ethnographic research; the second, of focus groups.
Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research allows one to understand complex practices in their ‘natural setting’ ( D’Cruz and Jones, 2004 ) by being ‘ involved in the ongoing, daily world of the people being studied’ ( Fielding, 2008 , p. 269). Being part of and participating in human-rights-based practices in social work allows the ethnographer to get to know the logic, dynamics and meanings behind these practices. For this study, collaboration was set up with one of the eight regional institutions for community development in Flanders, Belgium. These institutions are recognised and subsidised by the Flemish government through the 1991 Act on Community Development. The overall mission of the institutions for community development is to contribute to realising the right to a decent life for people living in vulnerable life conditions. The institutions for community development explicitly use human rights as a framework to realise their mission. In particular, they focus on social rights as they are recognised in the Belgian Constitution: the right to decent housing, the right to education, the right to social security, the right to health care, the right to work, the right to a healthy living environment and the right to cultural and social development. The participatory approach is typical for the work of the institutions for community development. They are not working just ‘for’, but above all ‘with’ people living in vulnerable life conditions. Therefore, the institutions for community development are an interesting case for investigating the meaning of social work as a human rights profession. Our research took place in the institution for community development in East Flanders, one of the five Flemish provinces in Belgium. In collaboration with the institution, we decided to select two human rights domains to study: housing and education. These domains could be considered as exemplary to study social work as a human rights profession.
Research methods used in ethnographic research can be very diverse. For this study, we used a documentary review, participant observation and conversation-style interviews with key informants ( D’Cruz and Jones, 2004 ). For the documentary review, we used documents produced by social workers who are active in the institution for community development. These documents gave us an insight into the work of the institution regarding the role of social work in ‘doing’ human rights. Policy notes, minutes of meetings, annual reports, etc. were all considered. Because in ethnographic research, it is important to understand the particular historical and socio-cultural context of the practices being researched ( Bryman, 2012 ), additional documents produced outside the institution for community development were selected. They were used to develop an environmental analysis in order to ‘capture’ the work of the institution in relation to the broader policy context (demographic data, a ‘map’ of the available welfare organisations, the history of particular neighbourhoods, etc.).
For the participant observation, the relevant activities to understand the work of the institution for community development were selected in mutual consultation with a ‘gatekeeper’ ( Fielding, 2008 ) of the institution. Gradually, the researcher also spontaneously took part in a variety of activities. Participation by the researcher was always overt (see Bryman, 2012 ). Field notes were kept during or directly after the participant observation. These field notes took the form of detailed descriptions of particular events and of people’s actions in these events, as well as the researcher’s initial reflections on these events. In total, participant observations took four months and more than 400 h. Time was divided equally between the domains of education and housing.
The third method we used was conversation-style interviews with key informants. In order to guarantee the validity of the observations, provisional ideas on the findings, striking observations or remaining questions were ‘shared with the member’s world’ ( Fielding, 2008 ) and checked. These ‘ethnographic interviews’ often took the form of ‘interviews on the spot’ and gave a deeper understanding of the practice being studied. For both education and housing, 26 people participated in an interview (total n = 52). In the case of education, the group consisted of eight community development workers, twelve social workers from partner organisations (civil servants from the city, school social workers, school directors, social workers from the public centre for social welfare [PCSW], social workers from poverty-related organisations, etc.) and six service-users from the institution for community development. The service-users all had a background of living in poverty, and were selected as members of a parent group from a local school for primary education.
In the case of housing, the participants were six community development workers, eleven social workers from partner organisations (civil servants from the city, social workers from the social housing company, social workers from the PCSW, social workers from poverty-related organisations, etc.) and nine service-users. The service-users were selected based on their participation in the working group on housing that is organised by the institution for community development. This working group consists of people who all face problems with regard to housing. All interviews were audiotaped and transcribed. The researchers had no personal connection whatsoever with the institution for community development. The only professional link that the researchers had with the research context was expertise in the domain of community development and encounters with representatives of the institution in the context of education-related activities (e.g. internships).
Focus groups
In the second part of the study, focus groups were set up. While the general aim of a focus group is to discuss a specific topic ( Bryman, 2012 ), we had an additional 2-fold goal. First, we wanted to flesh out several issues that were not clear after the ethnographic research (deepening). Second, we wanted to explore whether the findings of our ethnographic research that took place in the context of community development were applicable in other domains of social work (broadening). We chose focus groups because they allow for creating rich data, enabling in-depth analysis. We selected people with a more expert profile in social work and human rights. The selection criteria used for participants were (i) being familiar with human rights in a social work context and (ii) having a generalist view on social work practice or policy. Participants from the focus group were senior staff members of various social work organisations, as well as lecturers and professors who teach social work at universities and universities of applied sciences in Flanders. Four focus groups of four to six people were organised (total n = 18). In addition, seven in-depth interviews were organised with experts who, because of practical considerations, were not able to attend the focus groups. All the focus groups were led by two people: the researcher who conducted the ethnographic research and whose role it was to bring up the content for discussion and a supervisor who was the moderator of the focus group. Each focus group lasted approximately an hour and a half, and each was organised around three statements: (i) Participatory action, as a foundation of a human rights-based approach in social work, can also exclude people; (ii) a human rights-based approach in social work contributes to individualisation and responsibilisation and (iii) a human rights-based approach that starts from rules and laws (a top-down perspective) obstructs an approach that starts from the needs of people (a bottom-up perspective). The discussion in the focus groups was organised based on the five-stage model proposed by Cronin (2008) : (1) introduction; (2) opening; (3) introductory statement; (4) key questions and (5) ending questions. Both the focus group discussions and interviews were audiotaped and transcribed.
Ethics statement
The study was approved and funded by the Research Council of the HOGENT University of Applied Sciences and Arts. It was carried out in collaboration with Ghent University in compliance with the ethical standards of both the institutions. Informed consent was obtained from all of the participants after an extensive explanation of the research project.
Data analysis
For the data analysis, an inductive approach was chosen ( Hodkinsons, 2008 ). More specifically, a thematic analysis was done on the materials obtained from the ethnographic research. The analysis was executed in two steps by the two first authors. In the first step, both authors separately analysed the same six interviews (two community development workers, two social workers form partner organisations and two service-users) for each domain (education and housing). The analysis was based on the six-step model developed by Braun and Clarke (2006 ; see also Teater, 2017 ). Initial codes were assigned to the materials and afterwards they were grouped around several themes or ‘building blocks’. To answer the question of how social work acts when using human rights, we were looking for themes or building blocks that constitute a comprehensive action-framework for human rights in social work. We were particularly looking for different or even conflicting interpretations or constructions of human rights by social work, as these different interpretations could clearly demonstrate the action component of our framework. After individual analysis by the two authors, the results were pooled and discussed. This working method increases the inter-rater reliability among the researchers ( Oluwatayo, 2012 ). The result of this first step was a first draft of an action framework for human rights in social work. In the second step, the second author continued the analysis of the remaining interviews and also analysed the documentary review and the participant observations.
Although the analysis was primarily data-driven, we, as researchers with an interest in social work and human rights, could not disengage from our pre-existing knowledge. As Braun and Clarke explain, ‘data are not coded in an epistemological vacuum’ (2006 , p. 14). So the research context of community development coloured our data to a certain extent. As explained earlier, the community development organisations explicitly use human rights as a framework for their practice. In recent years, they acquired a great deal of expertise in the field of human rights, which has been reflected in numerous reports, memoranda and suchlike. Furthermore, as social work is a practice characterised by interconnectedness with local communities, working with vulnerable people, both at the micro-level of individual support and at the macro-level of structural change, it is no coincidence that related themes emerged from the data. Altogether, the first phase analysis yielded five themes or building blocks for an action framework for human rights in social work: (i) systemworld-oriented action, (ii) lifeworld-oriented action, (iii) participatory action, (iv) joined-up action and (v) politicised action. In the next step, these findings were presented to all the authors and discussed. This did not result in any adjustments at the level of themes, but it did result in some changes to the topics included under each building block. The remaining points of discussion and things that were unclear were taken to the focus groups. After the focus groups were held, the same procedure was followed: the four transcribed focus groups and seven additional interviews were analysed by the two first authors, and then discussed with all the authors, until consensus was reached. Again, this did not result in any adjustments at the level of the building blocks.
Based on our data, an action framework for human rights in social work was developed, consisting of five building blocks. In the next part of this article, we present these five building blocks.
Systemworld-oriented action
The right to social support would be meaningless without social services; the right to education would be meaningless without schools; the right to decent housing would be meaningless without houses and the right to health care would be meaningless without hospitals. All these systems—social services, schools, houses, health care, social security, etc.—are considered parts of the systemworld . The systemworld can be defined as all the institutionalised societal resources necessary for the realisation of human rights. Access to these systems is often difficult for people living in vulnerable life conditions. They frequently experience high thresholds.
The problem is that you have to be well informed and to know the right person. … How many people know about the income guarantee for elderly people? A lot of people probably know about the premium for housing, but how many of them are actually applying for it? Definitely not that many, because it requires a lot of jargon that keeps people from applying . (a service-user)
It is a recurring complaint that social systems are inaccessible, because people who need care and support must deal with bureaucracy. The problem is not just the large number of forms that need to be filled in. Social workers also send people from pillar to post, so that ultimately people give up and do not apply for the support they are entitled to. In the end, social rights are often not realised.
We do not understand just how high the thresholds are for people who are already in a vulnerable position, who are living in difficult circumstances, and who are then confronted with a multitude of services that are not working in an integrated way, have cultural thresholds, etc. We have no idea what it means to live in poverty, how hard that is … so that support by social services and an emancipatory approach don’t mean anything. (a social worker, institution for community development)
An important topic related to creating accessible social institutions concerns the distinction between ‘universal’ and ‘selective’ social systems. Based on a human rights perspective, social workers often argue for universal social systems. However, some social workers point out the risks of this approach.
Human rights are of course for everyone. But I think that certain groups are more easily deprived of them. These are certainly socially vulnerable groups. … Other groups have more power to make their voices heard. In any case, they also have easier access to certain rights. Education, for example, is more in line with middle-class culture. (a social worker, institution for community development)
Another social worker puts it even more bluntly:
That is actually a waste of time and resources if we focus on all citizens. … In such an inclusive organisation, time and energy are not focused on the most vulnerable people. (a social worker, institution for community development)
To resolve the tension between a universal and a selective approach, some social workers argue for so-called progressive universalism. According to this line of thinking, social support should in principle be universal in orientation, and therefore should be addressed to everyone. However, these universal social systems should simultaneously develop ways of supporting people living in vulnerable life conditions who may fall through the cracks, by supplementing them with selective measures ‘within’ these universal systems. So a community centre can be open to everyone, but for people living in poverty, extra support should be provided ‘within’ this community centre to guarantee their participation.
We shouldn’t become the home of the poor either. We have to keep it a bit open without opening it up again to everyone, because then you know that the weakest people will fall out again. (a social worker, institution for community development)
Lifeworld-oriented action
Systemworld-oriented action has its counterpart in lifeworld-oriented action. Lifeworld-oriented action is about social workers making connections with the experiences from people’s everyday lifeworld. The focus is not so much on institutionalised resources, but rather on the practices that people themselves develop to cope with daily experiences of injustice and with violations of human rights.
Actually, being in the field, close to the people, makes you better able to understand the underlying causes … you can more easily contextualise situations. People don’t always say what they want to say or what they think. If you know the context, you can understand that people formulate things in a certain way but mean it differently. (a social worker, institution for community development)
People living in vulnerable life conditions often find that their living environments are insufficiently understood by social workers as well as others. At the same time, they experience difficulties in explaining their own situation to social work organisations.
A lifeworld orientation also requires that social workers facilitate the opportunities to connect different lifeworlds. Connecting lifeworlds can contribute to sharing diverse experiences and to creating connectedness.
One time there was a ‘week of empathisation’. This is good for involving citizens so they can also experience it that way. They cannot imagine what it is like. … It is good to involve them, so they get a very different view of our problems, because those people don’t normally have to deal with these problems. They should do this a lot more, through a campaign set up by the working group on housing, so these people are motivated to join our conversations and to experience what is going on. (a service-user)
Social workers also point out several risks that might be associated with a lifeworld approach. Specifically, they warn against a narrowing view on social problems where not only are social problems observed in the lifeworlds of people, but also solutions for these social problems are sought within the same lifeworlds. However, problems that manifest in the lifeworlds of people often originate from external causes, such as the labour market, the housing market or the school system. Therefore, social workers should always try to link issues raised in the lifeworld with the way social systems are organised.
That double movement has to be part of our work. That is why we say that you should not see our work merely as directed downwards. You have to work from the bottom up, but that movement must also go upwards. … You have to link the work with a broader movement of social organisations. They help to raise the issues of social inequality, and they can move society in the direction of redistribution. … It is even more necessary to set up broader alliances, so that all those little things that happen can become part of a broader context and become part of a wider environment. (a social worker, institution for community development)
The final crucial aspect of social work with lifeworld-oriented action is social duty in public deliberation.
The articulation of different needs of different groups is the core of democracy; that is a social issue. Which needs do we as a society recognise, and which not? Which needs can be defined as rights, how are they recognised, and can we organise ourselves accordingly? These are public debates. These are collective discussions, because not having your needs recognised, and, consequently, not being seen or heard in society, is usually a collective and structural problem. (a lecturer on social work)
Participatory action
Participation is a loose concept, but nevertheless a key notion when talking about an action framework for human rights in social work. After all, shaping human rights requires dialogue between social workers and citizens about how to construct human rights and for what purpose. Social workers point to two complementary features of participation. First, participatory action entails involvement, connection and reciprocity between social workers and citizens. Here, social workers focus on the ‘relational’ characteristic of the practice of participation.
Participative work cannot be one-sided. You cannot expect your client to participate in everything that comes out of your sleeve. I think the art is to participate with them, and to play it by ear: ‘What is going on here?’ If you as a social worker participate with them , you are going to exclude far fewer people than you would if you expect them to come and participate with you. (a social worker, institution for community development)
Social workers also recognise that participation is not simply a relational issue, but that it entails a ‘structural’ approach as well.
If I say that we have to be more individual, this doesn’t mean that we have to find an individual solution. What I mean is that we have to approach people individually and then hear from there what problems those people or those groups are experiencing. It is also important that policy acknowledges the stories of those people. (a social worker, institution for community development)
Participatory action comes with many pitfalls. One is the social exclusion caused by participatory practices. For social work, it is important to be aware of these processes of exclusion and to identify possible barriers and difficulties. In general, social workers indicate that ‘stronger’ people are the ones who participate in available activities, as these practices require a certain assertiveness or particular social or cultural skills.
Participation usually starts from a certain framework and not everyone fits into that framework. It also requires certain skills from clients—skills they don’t always have. So participatory practices exclude people, but at the same time, this makes us aware that we need to find a different way to involve those excluded. (social worker, institution for community development)
Another pitfall has to do with participation in social policy. One of the working methods of the institution for community development is to coach people who live in vulnerable life conditions to speak with policymakers. This involves a risk of instrumentalisation, not only by policymakers, but also by social workers, as these people adapt themselves to the preferences of social workers.
In everything we do, of course, it is important that we let people make their own choices. But to what extent we, as community workers, steer those choices … I’m not sure. … We wouldn’t say it like that, but we do come up with the solutions. … We start a project and then we involve people in it. (a social worker, institution for community development)
Joined-up action
Social work exists in many fields of practice. This can lead to physical or metaphorical borders between these fields. The over-organised professional field of social work often results in fragmentation or compartmentalisation. Social work from a human rights perspective should question these borders and even try to break through them. This is what is meant by joined-up action. Joined-up action aims to counteract structures and logic that withhold the realisation of human rights in social work.
A trend in the social field is to divide everything into separate human rights or compartments. That is how social policy is organised. A human-rights-based perspective implies an integrated or joined-up approach. This requires breaking through this administrative compartmentalisation of human rights. (a social worker, institution for community development)
Besides the limitations caused by the organisation of social work in different fields, social work is often restricted by the proliferation of rules, procedures, protocols, etc. From a human rights perspective, this requires social workers to push boundaries.
It is about pushing and crossing boundaries, looking outside the range of tasks, thinking outside the box. Laws are not violated, but rules are; these are agreements, and they can be interpreted more broadly or reinterpreted … . (a social worker, community health centre)
Social workers call for questioning rules and procedures. Joined-up action here means that social workers should use their professional discretion in order to be guided by their ethical duty instead of following fixed rules and arrangements.
Having sufficient professional discretion is very important, especially if you work with the most vulnerable groups. You need to take the side of these people instead of working with a double agenda. In any case, they will feel this immediately. But secondly, the more professional discretion social workers use in a system, the more they can defend the rights of vulnerable groups in society. … It is important that they make full use of their professional discretion in order to develop a social reflex as much as possible. (a social worker, institution for community development)
Politicising action
Politicisation concerns questioning and contesting power. Power is mostly conceived of as something that belongs to societal structures, like politics or the judiciary system. Exercising power may result in injustice and in inhuman living conditions. The role of social work is thought to be to collectivise individual experiences of human rights violations and to bring these to the public debate. Politicised social work should use political advocacy to denounce structures and systems of power that cause violations of human rights.
You can try to help the person on an individual level to realise his or her rights, but you will always come across structural issues. (a social worker, institution for community development)
Power is also something that is situated in speaking about particular social issues. These discourses of power have a significant impact on people. The role of social work is to question these dominant orders of society. A social worker from a poverty-related organisation working with young people explains:
Many of the young people who arrive at our organisation are caught up in the ‘it’s your own fault’ discourse … . These young people are caught in a system and therefore they often blame themselves: ‘I think it’s me’ … . For example, education is an often recurring subject: 90% have attended special education. How is that possible? Is it only because of the context of poverty that they are being referred to this type of education, largely determining their future? In our organisation, they learn that this is happening not only to them, but this is something systemic. We explain that it is caused by our educational system failing to give everyone equal opportunities. By doing this, we are ‘de-blaming’ them: there is an individual responsibility, but there is also a social responsibility. For them, this is a process of awareness-raising about how society works and about who decides what. In the beginning, this often alienates these young people, these issues of politics, policy, human rights. (a social worker, poverty organisation).
However, because of the often extensive subsidisation of social work organisations by the government, the politicising role of social work is frequently at odds with the autonomy and independence of the organisation.
You are actually in a sort of a split, which keeps you from going fully for human rights. We cannot just be a protest movement. We can never go full 100 per cent. We can do that, but only with the blessing of a minister. (a social worker, institution for community development)
Therefore, social workers should be aware of depoliticising tendencies that increasingly emphasise the controlling side of social work over its emancipatory character.
The pressure is increasing for social workers to exercise control. I think it is important that social workers be very conscious of this: what is my task? … You see that organisations that are not complying are experiencing consequences. … We owe it to ourselves to say why we stand for. If we don’t do that, we do not take our clients seriously. We must unite as social workers to make it clear to policymakers: this is social work and this is not social work. … We must be able to define our role as social workers: what do we serve? We cannot be used for everything. (a social worker, organisation supporting people with a migration background)
Social workers indicate that they should be much more concerned with their self-critical role. Their own actions as social workers should also be scrutinised in some form of ‘self-politicisation’.
Our qualitative research on how social work acts when aiming to realise human rights reveals five building blocks. They flesh out what it can mean for social work to be a human rights profession. It is important to consider these five building blocks in connection to one another as an action framework for human rights in social work. The key point of this framework is the recognition that human rights in social work are collectively constructed and that social workers play a crucial role in this construction process. To state that human rights are collectively constructed is to acknowledge the discursive, contested and complex nature of human rights in social work ( Cemlyn, 2008 ; Ife, 2012 ). There is no single way to construct human rights. On the contrary, trying to realise human rights is a process characterised by a plurality of potential constructions, based on the plurality of interests of the communities and community members involved. Part of our data also show opposing constructions of human rights ‘within’ building blocks. The discussion on systemworld-oriented action, for instance, demonstrates that some social workers are in favour of selective social services, while others defend universal ones. The same goes for participatory action: being recognised as an agent and being acknowledged as a partner in dialogue can conflict with instrumentalising tendencies. It is remarkable that the conflicting perspectives each underpin their opposite positions from the same framework of human rights. Another part of our data show opposing views on human rights ‘between’ building blocks. This is probably most obvious in the building blocks of lifeworld-oriented action and systemworld-oriented action, which can be considered opposites. The approach of starting from the needs experienced by communities seems to be difficult to reconcile with the bureaucratic procedures of institutions within a system, although both rely on human rights.
Our action framework has an ambiguous relationship with previous action models. It resonates only partially with Androff’s five-principles framework ( Androff, 2016 ), particularly regarding the principle of participation. The principle of accountability in Androff’s model is closely linked to the building block of politicised action. For the other principles, the two frameworks can be considered complementary. The same goes for McPhersons’s HRPSW framework (2015; see also McPherson and Abell, 2020 ). Some of the human rights methods in her model share similarities with our action framework: participation is a shared concern; accountability and activism correspond to politicised action; community and interdisciplinary collaboration are related to lifeworld-oriented action and micro/macro integration and capacity building resonate with systemworld-oriented action. On the other hand, the human rights lens and human rights goals are absent from our action framework. As for earlier research in the Flemish context, our action framework agrees with some aspects of it but not others. Vandekinderen et al. (2020) conducted a research project to explore the common ground of social work in Flanders. They identified five building blocks that are considered the DNA of social work in Flanders. Of these, politicising work is the only building block that both frameworks have in common. It is no surprise that this building block also shows up in our results, as politicising work is a main concern in the work of community development organisations in Flanders.
The observed divergences between our own action framework and the practice approaches of Androff and McPherson can be explained in different ways. In part, this is probably due to the different research contexts in which the projects took place. In our project, collaboration was set up with organisations in the field of community development. Although we included focus group discussions to see whether our findings were transferable, additional research in other social work domains could reveal different emphases or even different building blocks. Furthermore, comparative studies between countries could provide more insight into the international transferability of our action framework. As explained in the ‘Introduction’ section, the nature of social work is closely linked to the welfare regime of a country, which in turn ‘set the scene’ for understanding human rights. How different welfare regimes affect the translation of human rights in social work practice remains a blind spot in social work scholarship. However, this is of particular relevance as welfare regimes all over the world are facing far-reaching transformation that have a significant impact on how human rights in social work are understood. Further research might reveal the link between the nature of different welfare regimes and the way social workers use human rights in their practice. Finally, although we included the voices of service-users in our research project, they often remain left out of rights-based practice literature. Further research on human rights in social work should pay much more attention to the perspective of service-users and to the way that a human rights framework affects their situations and life conditions. These issues require an empirical shift in order to fully understand social work as a human rights profession. Understanding these issues could lend more nuance to the discussions on the relationship between social work and human rights, and would move this debate beyond empty slogans and catchphrases.
Alseth A. K. ( 2020 ) ‘ Human rights as an opportunity and challenge for social work in a changing Norwegian welfare state’, European Journal of Social Work , 23 ( 6 ), pp. 920 – 13 .
Google Scholar
Androff D. ( 2018 ) ‘ Practicing human rights in social work: Reflections and rights-based approaches’, Journal of Human Rights and Social Work , 3 ( 4 ), pp. 179 – 82 .
Androff D. ( 2016 ) Practicing Rights: Human Rights-Based Approaches to Social Work Practice , London , Routledge .
Google Preview
Braun V. , Clarke V. ( 2006 ) ‘ Using thematic analysis in psychology’, Qualitative Research in Psychology , 3 ( 2 ), pp. 77 – 101 .
Bryman A. ( 2012 ) Social Research Methods , New York , Oxford University Press .
Carey M. ( 2012 ) Qualitative Research Skills for Social Work: Theory and Practice , Ashgate, Farnham.
Cemlyn S. ( 2008 ) ‘ Human rights practice: Possibilities and pitfalls for developing emancipatory social work’, Ethics and Social Welfare , 2 ( 3 ), pp. 222 – 42 .
Cronin A. ( 2008 ) ‘Focus groups’, in Gilbert N. (ed.), Researching Social Life , London, Sage .
Cubillos-Vega C. ( 2017 ) ‘ Análisis de la producción científica sobre Derechos Humanos en Trabajo Social: perspectiva internacional (2000–2015 )’, Revista Española de Documentación Científica , 40 ( 1 ), p. 163 .
D’Cruz H. , Jones M. ( 2004 ) Social Work Research: Ethical and Political Contexts , London, Sage .
Dean H. ( 2002 ) Welfare Rights and Social Policy , Harlow, Prentice Hall.
Esping-Andersen G. ( 1990 ) The Three Worlds of Welfare Capitalism , Princeton, University Press .
Fielding N. ( 2008 ) ‘Ethnography’, in Gilbert N. (ed.), Researching Social Life , London, Sage .
Gatenio Gabel S. , Mapp S. ( 2016 , Editorial) Editorial . Journal of Human Rights and Social Work , 1 ( 1 ), pp. 1 – 2 .
Gatenio Gabel S. ( 2015 ) ‘Foreword,’ in Berthold S. M. (eds), Human Rights-Based Approaches to Clinical Social Work , New York, Springer .
Healy L. M. ( 2008 ) ‘ Exploring the history of social work as a human rights profession’, International Social Work , 51 ( 6 ), pp. 735 – 48 .
Hodkinsons P. ( 2008 ) ‘Grounded theory and inductive research’, in Gilbert N. (ed.), Researching Social Life , London, Sage .
Ife J. ( 2009 ) Human Rights from Below: Achieving Rights through Community Development , Cambridge, University Press .
Ife J. ( 2012 ) Human Rights and Social Work: Towards Rights-Based Practice , Cambridge, University Press .
Lorenz W. ( 2008 ) ‘ Towards a European model of social work’, Australian Social Work , 61 ( 1 ), pp. 7 – 24 .
Lorenz W. ( 2001 ) ‘ Social work responses to “New Labour” in continental European countries’, British Journal of Social Work , 31 ( 4 ), pp. 595 – 609 .
Lundy C. ( 2011 ) Social Work, Social Justice and Human Rights: A Structural Approach to Practice , Toronto, University of Toronto Press .
Mapp S. , McPherson J. , Androff D. , Gatenio Gabel S. ( 2019 ) ‘ Social work is a human rights profession’, Social Work , 64 ( 3 ), pp. 259 – 69 .
McPherson J. , Abell N. ( 2020 ) ‘ Measuring rights-based practice: Introducing the human rights methods in social work scales’, The British Journal of Social Work , 50 ( 1 ), pp. 222 – 42 .
McPherson J. ( 2015a ) Human Rights Practice in Social Work: A Rights-Based Framework and Two New Measures . Doctoral dissertation, Florida State University, Available online at: https://fsu.digital.flvc.org/islandora/object/fsu:273511/datastream/PDF/view (accessed 20 April 2021).
McPherson J. ( 2015b ) ‘ Human rights practice in social work: A US social worker looks to Brazil for leadership’, European Journal of Social Work , 18 ( 4 ), pp. 599 – 612 .
Oluwatayo J. A. ( 2012 ) ‘ Validity and reliability issues in educational research’, Journal of Educational and Social Research , 2 ( 2 ), pp. 391 – 400 .
Reichert E. ( 2003 ) Social Work and Human Rights: A Foundation for Policy and Practice , New York, Columbia University Press .
Shaw I. G. R. , Holland S. ( 2014 ) Doing Qualitative Research in Social Work , London, Sage .
Staub-Bernasconi S. ( 2016 ) ‘ Social work and human rights—linking two traditions of human rights in social work’, Journal of Human Rights and Social Work , 1 ( 1 ), pp. 40 – 9 .
Teater B. ( 2017 ) ‘ Social work research and its relevance to practice: “The gap between research and practice continues to be wide” ,’ Journal of Social Service Research , 43 ( 5 ), pp. 547 – 65 .
Vandekinderen C. , Roose R. , Raeymaeckers P. , Hermans K. ( 2020 ) The DNA of social work as a human rights practice from a frontline social workers’ perspective in Flanders . European Journal of Social Work , 23 ( 5 ), pp. 876 – 888 .
Wronka J. ( 2008 ) Human Rights and Social Justice: Social Action and Service for the Helping and Health Professions , Los Angeles, Sage Publications .
| Month: | Total Views: |
|---|---|
| May 2021 | 100 |
| June 2021 | 15 |
| July 2021 | 20 |
| August 2021 | 11 |
| September 2021 | 13 |
| October 2021 | 30 |
| November 2021 | 21 |
| December 2021 | 17 |
| January 2022 | 20 |
| February 2022 | 13 |
| March 2022 | 354 |
| April 2022 | 204 |
| May 2022 | 180 |
| June 2022 | 139 |
| July 2022 | 113 |
| August 2022 | 99 |
| September 2022 | 122 |
| October 2022 | 197 |
| November 2022 | 194 |
| December 2022 | 143 |
| January 2023 | 162 |
| February 2023 | 128 |
| March 2023 | 173 |
| April 2023 | 230 |
| May 2023 | 234 |
| June 2023 | 200 |
| July 2023 | 218 |
| August 2023 | 257 |
| September 2023 | 293 |
| October 2023 | 351 |
| November 2023 | 358 |
| December 2023 | 228 |
| January 2024 | 291 |
| February 2024 | 254 |
| March 2024 | 281 |
| April 2024 | 343 |
| May 2024 | 268 |
| June 2024 | 294 |
| July 2024 | 185 |
| August 2024 | 373 |
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1468-263X
- Print ISSN 0045-3102
- Copyright © 2024 British Association of Social Workers
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Review of: Olga Zhukova, An essay on Russian culture: philosophy of history, literature and art. Moscow: “Soglasie” Publisher house, 2019. 588 pages. Hardcover: ISBN 978-5-907038-50-9, € 17
- Open access
- Published: 08 December 2020
- Volume 72 , pages 407–411, ( 2020 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Alexei Alexeevich Kara-Murza ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0302-6500 1
This book review discusses the new research of the Russian philosopher and cultural study scholar Olga A. Zhukova. What is special about the Russian intellectual movement Russian Europeanism? Zhukova reconstructs the ideas of Russian Europeanism, and she evaluates the approaches of Russian thinkers to national cultural history. The author manages to introduce the reader to current discussions about the specifics of the Russian cultural and philosophical “project” and to propose new approaches for the interpretation of the intellectual and literary heritage of Russia. In addition to offering a critical analysis of Zhukova’s volume, the book review presents this thought provoking monograph as a great piece of scholarly work.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
This new book by Russian philosopher and cultural historian Olga A. Zhukova continues her long standing study of the history of Russian philosophy and culture (see Zhukova 2008 , 2013 , 2014 , 2017 ). The topic of this new monograph is the historical experience of Russia and the complex interplay between its cultural-political and spiritual-artistic traditions.
The central focus of Zhukova’s study is the issue of the discovery of self-awareness in Russian history and culture, posed in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries by authors (including emigrées) of the most influential and controversial Russian intellectual movement, namely, Russian Europeanism .
The author of the 600-page volume endeavors to explicate, evaluate and categorize the approaches of Russian thinkers to national cultural history and the various ways they characterize Russian philosophy, culture, literature, and art. Zhukova sees her task “in identifying the genesis and continuity of the forms of cultural creativity, in understanding the spiritual and intellectual foundations of its traditions and practices” (p. 7). The author defines this intellectual procedure as “an analytical reconstruction of the social and spiritual history of Russia” (ibid.).
Zhukova understands “culture” as “the process of formation and transmission of social practices and structures of individual and collective consciousness with their own mechanism of self-organization and reproduction at the level of connotations and meanings” (p. 10). Conceiving “culture” in this way, she recognizes a certain similarity between her own definition and the concept of “semiosphere,” formulated by a prominent semiotician and cultural historian, Yuri M. Lotman. It is worth emphasizing in this regard that Zhukova's book contains a significant amount of the author's well-developed ideas, and its framework is based on her original philosophical concept of culture, which she prefers to call ideal-centric .
As Zhukova points out, its central tenet is that “culture is considered as a sum of individual and collective actions (acts) of sense-givings, which are the most common expressions of a person as an intelligent being, and which ensure the reproduction and development of a social community within the horizon of ideal notions of oneself” (p. 14). This allows the author to consider such cultural practices as religion, philosophy, literature, art, and science in their continuous interaction, and include spiritual (transcendental) ideals into the cultural horizon. The author’s approach corresponds significantly to the Russian spiritual and intellectual tradition with its special attention to the issues of religious metaphysics, to the identification of the key problem for European thought: the relationship between mind and faith.
Reconstructing the ideas of Russian Europeanism, Zhukova demonstrates both the virtuoso work of a scholar, masterfully working with various primary and secondary sources, and the high analytical ability of a philosophical theorist of culture. In tackling the complex issues of the history of Russian thought the author applies her original theoretical models and updated methodological tools, thereby providing not only an understanding of Russian culture as an “already established” phenomenon of history but also projecting its ongoing development.
Keeping at distance between the science and philosophy of Russian Europeanists, Zhukova insists that her interpretation is one of the possible ways to read Russian culture, in a way that is free from the tasks of advocacy and, even more so, apology for this line of national culture (p. 11). Zhukova certainly accomplishes her primary research aim very successfully, thus allowing for her monograph to be commended as a significant contribution to the study of Russian philosophy and culture and for placing this book among the leading ranks of the latest research on this subject (quite a limited number, I must say).
However, the intention of the book’s author is not limited to the task of creating a typological model of Russian culture as a mode of existence of the nation in history. First, Zhukova's scholarly position and her historical–critical approach stand in sharp opposition to a variety of attempts to mythologize Russian culture as such. By removing rushed, superficial (and, in essence, politically dogmatic) ideologemes that often accompany various discussions of Russian culture, the author manages to create a more accurate (and an even, level-headed) image of such a complex phenomenon as the Russian cultural and philosophical tradition, which remains in a constant process of self-identification and search for new affirmations of its “Russianness.”
Further, Zhukova's book significantly expands the arsenal of conceptual and methodological tools for the establishment of a critical history of Russian thought and actualizes the discourse about Russian culture in the context of Modernity. The author manages to introduce the reader to current discussions about the specifics of the Russian cultural and philosophical “project” and, what is especially important, to propose new approaches for the interpretation of the intellectual and literary heritage of Russia. The significance of this book also lies in the fact that it further enriches and conceptualizes the language of description and interpretation, precisely “translating” the “archetypal” ideas and intuitions central to Russian thought into the language of contemporary philosophy, thus revealing their actual meaning.
The book itself is very ambitious. It conceptualizes key themes of Russian culture, formulated by Russian authors “as meaningful questions of national existence, historical creativity of the nation and spiritual self-improvement of the individual” (p. 2). The author specifically notes that it is not her intent to give a “ready-made” definition of Russian culture. Instead, she sees her goal as the clarification and reinterpretation of philosophical, artistic, and aesthetic narratives of national culture in the diverse creative work of “Russian Europeans.”
To accomplish this goal, Zhukova (who has already proved herself as a master of the “intellectual portrait”) turns to the analysis of the lives and intellectual legacies of the great Russian thinkers who, in their works, synthesized philosophical and literary ideas, often acting as practical politicians. Among them are Pyotr J. Chaadaev, Pyotr A. Vyazemsky, Alexander S. Pushkin, Alexander I. Herzen, Timofey N. Granovsky, Ivan S. Turgenev, Nikolai G. Chernyshevsky, Vasily O. Klyuchevsky, Pyotr B. Struve, Vasily A. Maklakov, Semyon L. Frank, Boris P. Vysheslavtsev, Alexander N. Benois, Sergei P. Diaghilev, and Boris K. Zaitsev.
The first part of the book, “Philosophy of Russian History: Dilemmas of National Existence” (pp. 33–299), examines the most important philosophical and historical concepts of Russian thinkers and their specific takes on the problem of Russia and Europe. Of special interest in this section is an analysis of the concept of “Russian freedom” (in its various connotations), and a discussion of the religious roots of the confrontation between “autocratic” and “emancipatory” projects in Russian political history.
The heading of the second part of the book is “Russian Culture in Search of an Ideal: Literature and Art as an Experience of Philosophical Self-knowledge” (pp. 303–505). This section offers a philosophical reconstruction of the artistic, religious and political ideals of Russian culture in the nineteenth and first half of the twentieth centuries, how they are expressed in the works of the writers, philosophers and artists of the Golden and Silver Age.
Viewed in its entirety, the book shows precisely how the ideal-axiological core of Russian culture really “works.” This “work,” according to Zhukova, takes place in the hereditary continuity of the social, historical and spiritual-creative experience, including the conditions of powerful socio-cultural transformations of our time, which is convincingly demonstrated in the final section of the book (pp. 506–537).
The most significant and impressive feature of the book is its ability to view each of its many “characters” both as a “collector of Russian common cultural meanings” (Zhukova’s term) and as an acute, polemically charged author creating her own direction in the history of Russian culture and, in this way, testing Russian cultural integrity “to its breaking point.” It is indeed an intellectual pleasure to follow the author’s analytical thought, who looks at the twists and turns of life and creative searches of such different “Russian Europeans” as, for example, Chaadaev, Herzen, Struve, or Maklakov.
This is a highly informative and thought-provoking book, which I highly recommend to all specialists in Russian thought and culture. Everyone who wants to learn about Russian culture would benefit enormously from this book. It is a valuable and engaging contribution to the study of Russian philosophical and cultural tradition.
Zhukova, O. A. (2008). Metafizika tvorchestva. Iskusstvo i religiia v istorii kul'tury Rossii [Metaphysics of creativity. Art and religion in Russian culture]. Moscow: SFGA.
Zhukova, O. A. (2013). Na puti k Russkoi Evrope: intellektualy v bor'be za svobodu i kul'turu v Rossii [On the way to Russian Europe. Intellectuals and their struggle for freedom and culture in Russia]. Moscow: Liberal Mission Foundation.
Zhukova, O. A. (2014). Izbrannye raboty po filosofii kul'tury. Kul'turnyi kapital. Russkaia kul'tura i social'nye praktiki sovremennoi Rossii [Selected works on the philosophy of culture. Cultural capital. Russian Culture and the Social Practices of Modern Russia]. Moscow: Soglasie.
Zhukova, O. A. (2017). Filosofiia russkoi kul'tury. Metafizicheskaia perspektiva cheloveka i istorii [Philosophy of Russian culture. Metaphysical perspective of the human being and history]. Moscow: Soglasie.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Philosophy, Russian Academy of Sciences, 12/1 Goncharnaya Str., Moscow, 109240, Russian Federation
Alexei Alexeevich Kara-Murza
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Alexei Alexeevich Kara-Murza .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
I approve the Journal policy in ETHICAL RESPONSIBILITIES OF AUTHORS.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Kara-Murza, A.A. Review of: Olga Zhukova, An essay on Russian culture: philosophy of history, literature and art. Moscow: “Soglasie” Publisher house, 2019. 588 pages. Hardcover: ISBN 978-5-907038-50-9, € 17. Stud East Eur Thought 72 , 407–411 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11212-020-09400-3
Download citation
Accepted : 17 November 2020
Published : 08 December 2020
Issue Date : December 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11212-020-09400-3
Selected philosophical, social, and political essays.
By dmitriĭ ivanovich pisarev.
- 0 Want to read
- 0 Currently reading
- 0 Have read
My Reading Lists:
Use this Work
Create a new list
My book notes.
My private notes about this edition:
Buy this book
This edition doesn't have a description yet. Can you add one ?
Showing 1 featured edition. View all 1 editions?
| 1 |
Add another edition?
Book Details
Edition notes, classifications, the physical object, community reviews (0).
- Created November 1, 2008
- 2 revisions
Wikipedia citation
Copy and paste this code into your Wikipedia page. Need help?
| Edited by | link works | |
| Created by | Imported from |

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Two papers with high burst strengths emerged ... the UK has extensive experience in social welfare and aging research, providing valuable theoretical guidance and practical experience ...
HUNTSVILLE, Ala. — Social media timelines lit up over the weekend with images of gleeful Chase Bank customers running to ATMs, debit cards and checks in hand, then walking or running away throwing cash into the air - cash that apparently wasn't theirs to withdraw. Financial experts are warning ...
A recent experience in a social work class reinforced these concerns, as I found myself struggling to balance paraphrasing with maintaining a natural, engaged conversation (McGann, 2020). Recognizing that perfectionism can initially feel mechanical, I acknowledge the necessity of practice to enhance my skills and overcome this challenge.
This essay was written by Adrian Bloxham and was the winning social work entry in this year's Critical Writing Prize 2019. Adrian is studying for an MA at Anglia Ruskin University and he was nominated by his lecturer Dr Wendy Coxshall. I am currently on placement in a Supported Housing Hostel for adults in Cambridgeshire.…
My experience as a Social Work student. 19 January 2022 by Charlotte. I have always been the type of person to care about those around me and always wanted a career where I could help people to improve themselves and/or the situation they are in. I felt social work was the perfect career path for me as the whole nature of the job is to support ...
The realm of social work is a dynamic and impactful field that demands a blend of empathy, resilience, and practical skills. Undertaking a social work internship provided me with an immersive opportunity to translate theoretical knowledge into real-world practice. This essay offers a reflection on my social work internship experience ...
Social work is a profession that aims to promote social change, alleviate suffering, and improve the well-being of individuals, families, and communities. It encompasses a wide range of activities, including direct practice with individuals and families, community organizing, policy advocacy, and research. The implications of... Social Work.
Therefore, choosing social work as a career equips an intern with ambition, desire, vision, and the desire to do the best things. My internship opportunity provided a more significant career opportunity for me to grow as more emphasis was put offering guidance and supporting the disadvantaged communities. As a social worker, I pride myself in ...
My experience will guide me in understanding the different interventions used by social workers and enhance my knowledge of social work theories and methods. I have a fair understanding around the Children Act 1989/2004, Human Rights Act and the Care Act 2014.
Commentary: Clarity of Motivation: The essay effectively communicates the candidate's personal experiences and observations of disparities in their community as key motivators for pursuing social work.; Goal-Oriented: Clearly outlines immediate and long-term goals, demonstrating a focused vision for a career in social work.; Understanding of a Social Issue: The candidate's insight into the ...
The field education experience at Vatsalya provided the social worker with a set of essential professional skills and allowed them to acquire active listening, cultural competency, confidence, and problem-solving abilities during the practice at the agency. The generalist practice promoted at Vatsalya involved the social worker's use of ...
1. Compassion and Empathy. At the core of my desire to become a social worker is a deep sense of compassion and empathy for others. Growing up, I witnessed firsthand the struggles and hardships faced by individuals in my community, from economic inequality to systemic injustice. These experiences ignited a passion within me to help those who ...
Advocacy for Social Justice. Another reason why I am drawn to social work is the opportunity to advocate for social justice and fight against inequality. Social workers have the privilege and responsibility to stand up for marginalized individuals and communities, challenging oppressive systems and working towards a more equitable society.
Prepare an Outline and Conduct Research. Create an outline of the points you want to include. Fill in your points with relevant research and examples from your personal and professional experience. Don't worry about having too much research or too many points in your outline. You can always cut it down later.
Social work is a profession that is dedicated to helping individuals, families, and communities navigate through challenging circumstances and improve their overall well-being. It requires a unique combination of empathy, problem-solving skills, and a commitment to social justice. In this application essay, I will explore my personal ...
Bell, Linda, Maria Appel Nissen, and Jorunn Vindegg, 'The construction of professional identity in social work: experience, analytical reflection and time', in Björn Blom, Lars Evertsson, and Marek Perlinski (eds), Social and Caring Professions in European Welfare States: Policies, Services and Professional Practices (Bristol, 2017; online edn ...
What My Experience as a Social Work Student Taught Me. By Rachel Schultz. "God grant me serenity to accept the things I cannot change; courage to change the things I can; and the wisdom to know the difference.". Since childhood, I have always known that I would grow up to find a job where I could make use of my natural ability to empathize ...
I shared my own essay with a social worker, who led me to see certain stereotypes I may have unknowingly conveyed through my essay. Encourage someone to read your essay and tell you the good, and bad about it. 2. Use every experience you have had. Some people think that direct social work or social care experience might be more useful.
Satisfactory Essays. 1231 Words. 5 Pages. Open Document. Since my experience as a Social Worker has mainly been focused with the youth population, during the course of my career I had to develop very creative skills to engage such population. They experienced inevitable unremitting stress, such as poverty, failing education and exposure to ...
A student contacted me recently wanting tips on how to write on the topic; 'why I want to be a social worker'. I explained the great benefits of being a social worker.I also embedded myself in this task and wrote with my own experiences and views on why I became a social worker in an essay format.. Picture a world where compassion and empathy are the guiding forces, where individuals ...
Social work is a challenging profession that also helps one make a difference in the lives of others (CUW 2011). It aims at improving the overall functioning and well-being of people served. A social worker must have a genuine and special concern for the poor, marginalized, and the vulnerable.
Introduction. Human rights are foundational to social work, as recognised in the global definition, leading many to consider social work a human rights profession (Healy, 2008; Staub-Bernasconi, 2016; Mapp et al., 2019).Staub-Bernasconi (2016), together with Gatenio Gabel (2015), among others, acknowledges the historical connection of social work with human rights.
This "work," according to Zhukova, takes place in the hereditary continuity of the social, historical and spiritual-creative experience, including the conditions of powerful socio-cultural transformations of our time, which is convincingly demonstrated in the final section of the book (pp. 506-537).
Abstract. The goal of this work is the study of psychological-pedagogical approaches to the understanding of the idea of professional competence of social work specialists as well as the role of study in the system of additional educations in professional-personal development of the listeners. In the process of study of this problem we define ...
Selected philosophical, social, and political essays by Dmitriĭ Ivanovich Pisarev, 1958, Foreign Languages Pub. House edition, in English