- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy

Joint Variation – Formula, Examples | How to Solve Problems Involving Joint Variation?
Joint Variation definition, rules, methods and formulae are here. Check the joint variation problems and solutions to prepare for the exam. Refer to problems of direct and inverse variations and the relationship between the variables. Know the different type of variations like inverse, direct, combined and joint variation. Go through the below sections to check definition, various properties, example problems, value tables, concepts etc.
Joint Variation – Introduction
Joint Variation refers to the scenario where the value of 1 variable depends on 2 or more and other variables that are held constant. For example, if C varies jointly as A and B, then C = ABX for which constant “X”. The joint variation will be useful to represent interactions of multiple variables at one time.
Most of the situations are complicated than the basic inverse or direct variation model. One or the other variables depends on the multiple other variables. Joint Variation is nothing but the variable depending on 2 or more variables quotient or product. To understand clearly with an example, The amount of busing candidates for each of the school trip varies with the no of candidates attending the distance from the school. The variable c (cost) varies jointly with n (number of students) and d (distance).
Joint Variation problems are very easy once you get the perfection of the lingo. These problems involve simple formulae or relationships which involves one variable which is equal to the “one” term which may be linear (with just an “x” axis), a quadratic equation (like “x²) where more than one variable (like “hr²”), and square root (like “\sqrt{4 – r^2\,}4−r2”) etc.
Functions of 2 or More Variables
It is very uncommon for the output variable to depend on 2 or more inputs. Most of the familiar formulas describe the several variables functions. For suppose, if the rectangle perimeter depends on the length and width. The cylinder volume depends on its height and radius. The travelled distance depends on the time and speed while travelling. The function notation of the formulas can be written as
P = f(l,w) = 2l + 2w where P is the perimeter and is a function of width and length
V = f(r,h) = Πr²h where V is the volume and is a function of radius and height
d = f(r,t) = rt where d is the distance and is a function of time and rate.
Tables of Values
Just for the single variable functions, we use the tables to describe two-variable functions. The heading of the table shows row and column and it shows the value if two input variables and the complete table shows the values of the output variable.
You can easily make graphs in three dimensions for two-variable functions. Instead of representing graphs, we represent functions by holding two or one variable constants.
Also, Read:
- What is Variation
- Practice Test on Ratio and Proportion
How to Solve Joint Variation Problems?
Follow the step by step procedure provided below to solve problems involving Joint Variation and arrive at the solution easily. They are along the lines
Step 1: Write the exact equation. The problems of joint variation can be solved using the equation y =kxz. While dealing with the word problems. you should also consider using variables other than x,y and z. Use the variables which are relevant to the problem being solved. Read the problem carefully and determine the changes in the equation of joint variation such as cubes, squares or square roots.
Step 2: With the help of the information in the problem, you have to find the value of k which is called the constant of proportionality and variation.
Step 3: Rewrite the equation starting with 1 substituting the value of k and found in step 2.
Step 4: Use the equation in step 3 and the information in the problem to answer the question. While solving the word problems, remember including the units in the final answer.
Joint Variation Problems with Solutions
The area of a triangle varies jointly as the base and the height. Area = 12m² when base = 6m and height = 4m. Find base when Area = 36m² and height = 8m?
The area of the triangle is represented with A
The base is represented with b
Height is represented with h
As given in the question,
A = 12m² when B = 6m and H = 4m
We know the equation,
A = kbh where k is the constant value
12 = k(6)(4)
Divide by 24 on both sides, we get
12/24 = k(24)/24
The value of k = 1/2
As the equation is
To find the base of the triangle of A = 36m² and H = 8m
36 = 1/2(b)(8)
Dividing both sides by 4, we get
36/4 = 4b/4
The value of base = 9m
Hence, the base of the triangle when A = 36m² and H = 8m is 9m
Wind resistance varies jointly as an object’s surface velocity and area. If the object travels at 80 miles per hour and has a surface area of 30 square feet which experiences 540 newtons wind resistance. How much fast will the car move with 40 square feet of the surface area in order to experience a wind resistance of 495 newtons?
Let w be the wind resistance
Let s be the object’s surface area
Let v be the object velocity
The object’s surface area = 80 newtons
The wind resistance = 540 newtons
The object velocity = 30
w = ksv where k is the constant
(540) = k (80) (30)
540 = k (2400)
540/2400 = k
The value of k is 9/40
To find the velocity of the car with s = 40, w = 495 newtons and k = 9/40
Substitute the values in the equation
495 = (9/40) (40) v
The velocity of a car is 55mph for which the object’s surface area is 40 and wind resistance is 495 newtons
Hence, the final solution is 55mph
For the given interest, SI (simple interest) varies jointly as principal and time. If 2,500 Rs left in an account for 5 years, then the interest of 625 Rs. How much interest would be earned, if you deposit 7,000 Rs for 9 years?
Let i be the interest
Let p be the principal
Let t be the time
The interest is 625 Rs
The principal is 2500
The time is 5 hours
i = kpt where k is the constant
Substituting the values in the equation,
(625) = k(2500)(5)
625 = k(12,500)
Dividing 12,500 on both the sides
625/12,500 = k (12,500)/12,500
The value of k = 1/20
To find the interest where the deposit is 7000Rs for 9 years, use the equation
i = (1/20) (7000) (9)
i = (350) (9)
Therefore, the interest is 3,150 Rs, if you deposit 7,000 Rs for 9 years
Thus, the final solution is Rs. 3,150
The volume of a pyramid varies jointly as its height and the area of the base. A pyramid with a height of 21 feet and a base with an area of 24 square feet has a volume of 168 cubic feet. Find the volume of a pyramid with a height of 18 feet and a base with an area of 42 square feet?
Let v be the volume of a pyramid
Let h be the height of a pyramid
Let a be the area of a pyramid
The volume v = 168 cubic feet
The height h = 21 feet
The area a = 24 square feet
V = Kha where K is the constant,
168 = k(21)(24)
168 = k(504)
Divide 504 on both sides
168/504 = k(504)/504
The value of k = 1/3
To find the volume of a pyramid with a height of 18 feet and a base with an area of 42 square feet
h = 18 feet
a = 42 square feet
V = (1/3) (18) (42)
V = (6) (42)
V = 252 ft³
The volume of the pyramid = 252 ft³ which has a height of 18 feet and a base with an area of 42 square feet
Therefore, the final solution is 252 ft³
The amount of oil used by a ship travelling at a uniform speed varies jointly with the distance and the square of the speed. If the ship uses 200 barrels of oil in travelling 200 miles at 36 miles per hour, determine how many barrels of oil are used when the ship travels 360 miles at 18 miles per hour?
No of barrels of oil = 200
The distance at which the oil is travelling = 200 miles
The distance at which the ship is travelling = 36 miles per hour
A = kds² where k is constant
200 = k.200.(36)²
Dividing both sides by 200
200/200 = k.200.(36)²/200
1 = k.(36)²
The value of k is 1/1296
To find the no of barrels when the ship travels 360 miles at 18 miles per hour
A = 1/1296 * 360 * 18²
Therefore, 90 barrels of oil is used when the ship travels 360 miles at 18 miles per hour
Thus, the final solution is 90 barrels
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Chapter 6: Proportions and Modeling Using Variation
Solve problems involving joint variation.
Many situations are more complicated than a basic direct variation or inverse variation model. One variable often depends on multiple other variables. When a variable is dependent on the product or quotient of two or more variables, this is called joint variation . For example, the cost of busing students for each school trip varies with the number of students attending and the distance from the school. The variable c , cost, varies jointly with the number of students, n , and the distance, d .
A General Note: Joint Variation
Joint variation occurs when a variable varies directly or inversely with multiple variables.
For instance, if x varies directly with both y and z , we have x = kyz . If x varies directly with y and inversely with z , we have [latex]x=\frac{ky}{z}[/latex]. Notice that we only use one constant in a joint variation equation.
Example 4: Solving Problems Involving Joint Variation
A quantity x varies directly with the square of y and inversely with the cube root of z . If x = 6 when y = 2 and z = 8, find x when y = 1 and z = 27.
Begin by writing an equation to show the relationship between the variables.
Substitute x = 6, y = 2, and z = 8 to find the value of the constant k .
Now we can substitute the value of the constant into the equation for the relationship.
To find x when y = 1 and z = 27, we will substitute values for y and z into our equation.
x varies directly with the square of y and inversely with z . If x = 40 when y = 4 and z = 2, find x when y = 10 and z = 25.
Candela Citations
- Precalculus. Authored by : Jay Abramson, et al.. Provided by : OpenStax. Located at : http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected] . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download For Free at : http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected].
- Joint Variation
If more than two variables are related directly or one variable changes with the change product of two or more variables it is called as joint variation .
If X is in joint variation with Y and Z, it can be symbolically written as X α YZ. If Y is constant also then X is in direct variation with Z. So for joint variation two or more variables are separately in direct variation. So joint variation is similar to direct variation but the variables for joint variation are more than two.
Equation for a joint variation is X = KYZ where K is constant.
One variable quantity is said to vary jointly as a number of other variable quantities, when it varies directly as their product. If the variable A varies directly as the product of the variables B, C and D, i.e., if.A ∝ BCD or A = kBCD (k = constant ), then A varies jointly as B, C and D.
For solving a problems related to joint variation first we need to build the correct equation by adding a constant and relate the variables. After that we need determine the value of the constant. Then substitute the value of the constant in the equation and by putting the values of variables for required situation we determine the answer.
We know, area of a triangle = ½ × base × altitude. Since ½ is a constant, hence area of a triangle varies jointly as its base and altitude. A is said to vary directly as B and inversely as C if A ∝ B ∙ \(\frac{1}{C}\) or A = m ∙ B ∙ \(\frac{1}{C}\) (m = constant of variation) i.e., if A varies jointly as B and \(\frac{1}{C}\) .
If x men take y days to plough z acres of land, then x varies directly as z and inversely as y.
1. The variable x is in joint variation with y and z. When the values of y and z are 4 and 6, x is 16. What is the value of x when y = 8 and z =12?
The equation for the given problem of joint variation is
x = Kyz where K is the constant.
For the given data
16 = K × 4 × 6
or, K = \(\frac{4}{6}\) .
So substituting the value of K the equation becomes
x = \(\frac{4yz}{6}\)
Now for the required condition
x = \(\frac{4 × 8 × 12}{6}\)
= 64
Hence the value of x will be 64.
2. A is in joint variation with B and square of C. When A = 144, B = 4 and C = 3. Then what is the value of A when B = 6 and C = 4?
From the given problem equation for the joint variation is
From the given data value of the constant K is
K = \(\frac{BC^{2}}{A}\)
K = \(\frac{4 × 3^{2}}{144}\)
= \(\frac{36}{144}\)
= \(\frac{1}{4}\) .
Substituting the value of K in the equation
A = \(\frac{BC^{2}}{4}\)
A = \(\frac{6 × 4^{2}}{4}\)
= 24
3. The area of a triangle is jointly related to the height and the base of the triangle. If the base is increased 10% and the height is decreased by 10%, what will be the percentage change of the area?
We know the area of triangle is half the product of base and height. So the joint variation equation for area of triangle is A = \(\frac{bh}{2}\) where A is the area, b is the base and h is the height.
Here \(\frac{1}{2}\) is the constant for the equation.
Base is increased by 10%, so it will be b x \(\frac{110}{100}\) = \(\frac{11b}{10}\) .
Height is decreased by 10%, so it will be h x \(\frac{90}{100}\) = \(\frac{9h}{10}\) .
So the new area after the changes of base and height is
\(\frac{\frac{11b}{10} \times \frac{9h}{10}}{2}\)
= (\(\frac{99}{100}\) )\(\frac{bh}{2}\) = \(\frac{99}{100}\) A.
So the area of the triangle is decreased by 1%.
4. A rectangle’s length is 6 m and width is 4 m. If length is doubled and width is halved, how much the perimeter will increase or decrease?
Formula for the perimeter of rectangle is P = 2(l + w) where P is perimeter, l is length and w is width.
This is joint variation equation where 2 is constant.
So P = 2(6 + 4) = 20 m
If length is doubled, it will become 2l.
And width is halved, so it will become \(\frac{w}{2}\) .
So the new perimeter will be P = 2(2l + \(\frac{w}{2}\) ) = 2(2 x 6 + \(\frac{4}{2}\) ) = 28 m.
So the perimeter will increase by (28 - 20) = 8 m.
● Variation
- What is Variation?
- Direct Variation
- Inverse or Indirect Variation
- Theorem of Joint Variation
- Worked out Examples on Variation
- Problems on Variation
11 and 12 Grade Math
From Joint Variation to Home Page
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math . Use this Google Search to find what you need.
New! Comments
Share this page: What’s this?
- Preschool Activities
- Kindergarten Math
- 1st Grade Math
- 2nd Grade Math
- 3rd Grade Math
- 4th Grade Math
- 5th Grade Math
- 6th Grade Math
- 7th Grade Math
- 8th Grade Math
- 9th Grade Math
- 10th Grade Math
- 11 & 12 Grade Math
- Concepts of Sets
- Probability
- Boolean Algebra
- Math Coloring Pages
- Multiplication Table
- Cool Maths Games
- Math Flash Cards
- Online Math Quiz
- Math Puzzles
- Binary System
- Math Dictionary
- Conversion Chart
- Homework Sheets
- Math Problem Ans
- Free Math Answers
- Printable Math Sheet
- Funny Math Answers
- Employment Test
- Math Patterns
- Link Partners
- Privacy Policy

Recent Articles
3rd Grade Number Worksheet |Practice the Questions on Numbers with Ans
Dec 23, 24 03:10 AM

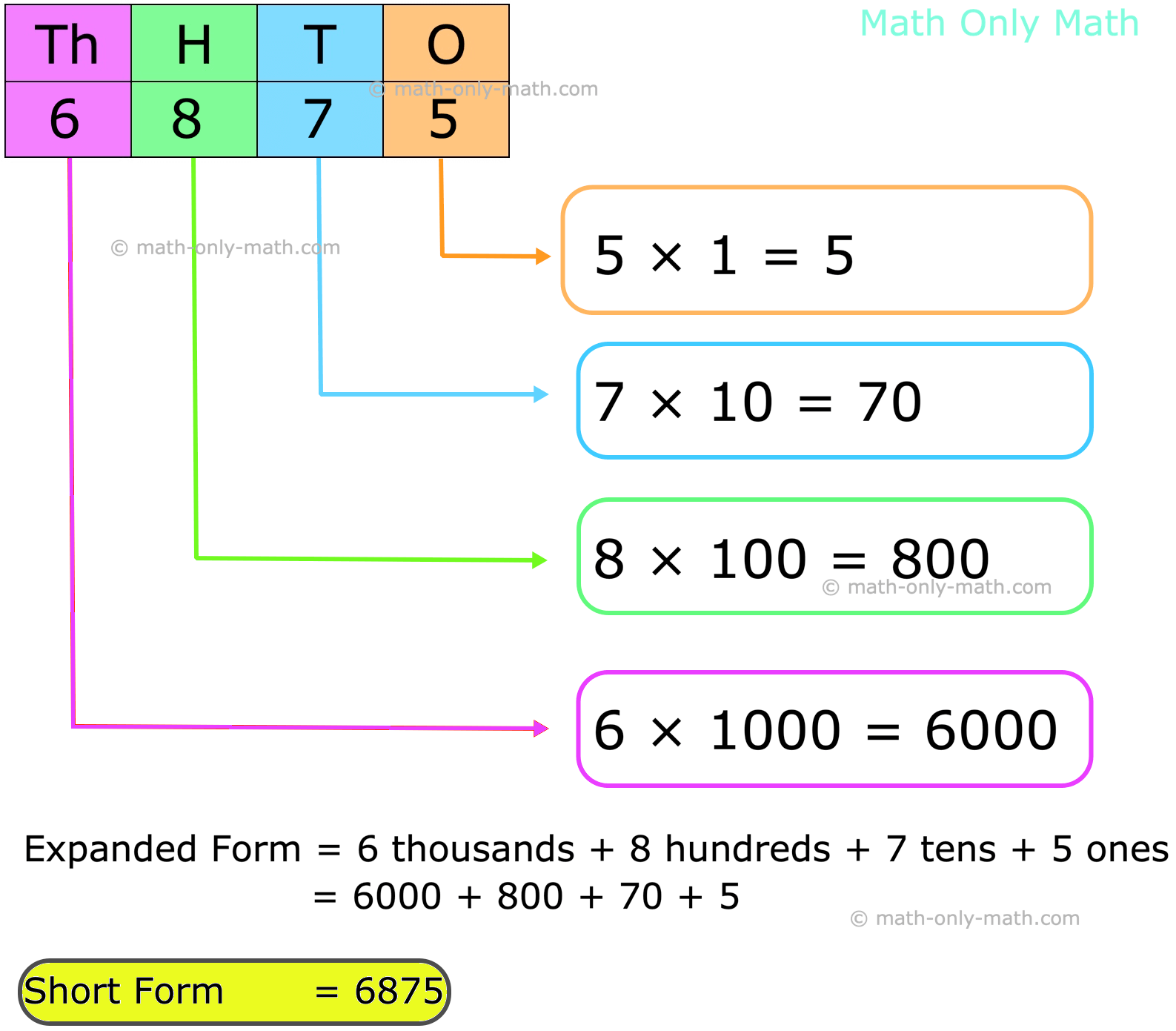
Expanded Form and Short Form of a Number | Numbers in Expanded Form
Dec 23, 24 02:39 AM

Rounding off Numbers | Nearest Multiple of 10 | Nearest Whole Number
Dec 22, 24 04:09 PM

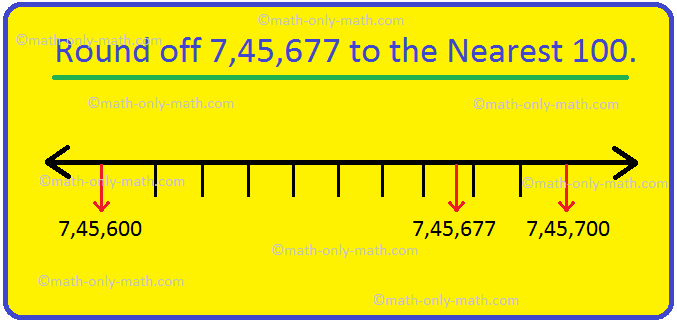
Round off to Nearest 100 | Rounding Numbers To Nearest Hundred | Rules
Dec 22, 24 03:40 PM
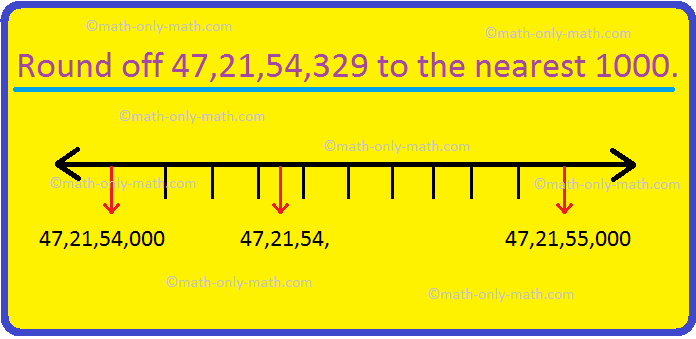
Round off to Nearest 1000 |Rounding Numbers to Nearest Thousand| Rules
Dec 22, 24 03:39 PM
© and ™ math-only-math.com. All Rights Reserved. 2010 - 2024.
- Solutions Integral Calculator Derivative Calculator Algebra Calculator Matrix Calculator More...
- Graphing Line Graph Calculator Exponential Graph Calculator Quadratic Graph Calculator Sine Graph Calculator More...
- Calculators BMI Calculator Compound Interest Calculator Percentage Calculator Acceleration Calculator More...
- Geometry Pythagorean Theorem Calculator Circle Area Calculator Isosceles Triangle Calculator Triangles Calculator More...
- Tools Notebook Groups Cheat Sheets Worksheets Study Guides Practice Verify Solution
Study Guides > College Algebra
Solve problems involving joint variation.
Many situations are more complicated than a basic direct variation or inverse variation model. One variable often depends on multiple other variables. When a variable is dependent on the product or quotient of two or more variables, this is called joint variation . For example, the cost of busing students for each school trip varies with the number of students attending and the distance from the school. The variable c , cost, varies jointly with the number of students, n , and the distance, d .
A General Note: Joint Variation
Joint variation occurs when a variable varies directly or inversely with multiple variables.
For instance, if x varies directly with both y and z , we have x = kyz . If x varies directly with y and inversely with z , we have [latex]x=\frac{ky}{z}[/latex]. Notice that we only use one constant in a joint variation equation.
Example 4: Solving Problems Involving Joint Variation
A quantity x varies directly with the square of y and inversely with the cube root of z . If x = 6 when y = 2 and z = 8, find x when y = 1 and z = 27.
Begin by writing an equation to show the relationship between the variables.
Substitute x = 6, y = 2, and z = 8 to find the value of the constant k .
Now we can substitute the value of the constant into the equation for the relationship.
To find x when y = 1 and z = 27, we will substitute values for y and z into our equation.
x varies directly with the square of y and inversely with z . If x = 40 when y = 4 and z = 2, find x when y = 10 and z = 25.
Licenses & Attributions
Cc licensed content, shared previously.
- Precalculus. Provided by: OpenStax Authored by: Jay Abramson, et al.. Located at: https://openstax.org/books/precalculus/pages/1-introduction-to-functions. License: CC BY: Attribution . License terms: Download For Free at : http://cnx.org/contents/ [email protected] ..
We want your feedback
Please add a message.
Message received. Thanks for the feedback.
Joint or Combined Variation
These lessons help Algebra students learn about joint or combined variation.
Related Pages: Proportions Joint Variation Word Problems Direct Variation Inverse Variation More Algebra Lessons
The following figure shows Joint Variation. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions of Joint and Combine Variations.
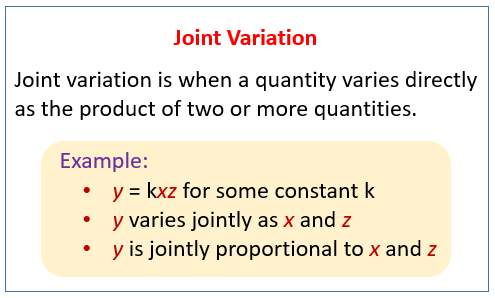
What is Joint Variation or Combined Variation?
Joint Variation or Combined Variation is when one quantity varies directly as the product of at least two other quantities.
For example: y = kxz y varies jointly as x and z, when there is some nonzero constant k
Joint Variation Examples
Example: Suppose y varies jointly as x and z. What is y when x = 2 and z = 3, if y = 20 when x = 4 and z = 3?
Example: z varies jointly with x and y. When x = 3, y = 8, z = 6. Find z, when x = 6 and y = 4.
Joint Variation Application
Example: The energy that an item possesses due to its motion is called kinetic energy. The kinetic energy of an object (which is measured in joules) varies jointly with the mass of the object and the square of its velocity. If the kinetic energy of a 3 kg ball traveling 12 m/s is 216 Joules, how is the mass of a ball that generates 250 Joules of energy when traveling at 10 m/s?
Distinguish between Direct, Inverse and Joint Variation
Example: Determine whether the data in the table is an example of direct, inverse or joint variation. Then, identify the equation that represents the relationship.
Combined Variation
In Algebra, sometimes we have functions that vary in more than one element. When this happens, we say that the functions have joint variation or combined variation. Joint variation is direct variation to more than one variable (for example, d = (r)(t)). With combined variation, we have both direct variation and indirect variation.
How to set up and solve combined variation problems?
Example: Suppose y varies jointly with x and z. When y = 20, x = 6 and z = 10. Find y when x = 8 and z =15.
Lesson on combining direct and inverse or joint and inverse variation
Example: y varies directly as x and inversely as the square of z, and when x = 32, y = 6 and z = 4. Find x when y = 10 and z = 3.
How to solve problems involving joint and combined variation?
If t varies jointly with u and the square of v, and t is 1152 when u is 8 and v is 4, find t when v is 5 and u is 5.
The amount of oil used by a ship traveling at a uniform speed varies jointly with the distance and the square of the speed. If the ship uses 200 barrels of oil in traveling 200 miles at 36 miles per hour, determine how many barrels of oil are used when the ship travels 360 miles at 18 miles per hour.
Designer Dolls found that its number of Dress-Up Dolls sold, N, varies directly with their advertising budget, A, and inversely proportional with the price of each doll, P. When $54,00 was spent on advertising and the price of the doll is $90, then 9,600 units are sold. Determine the number of dolls sold if the amount of advertising budget is increased to $144,000.
Example: y varies jointly as x and z and inversely as w, and y = 3/2, when x = 2, z =3 and w = 4. Find the equation of variation.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.
JOINT VARIATION WORKSHEET
Problem 1 :
Write the equation for the following joint variation.
"x varies jointly as y and z"
Problem 2 :
"z varies jointly as x and the square root of y"
Problem 3 :
"w varies jointly as x and y and inversely as z"
Problem 4 :
Suppose y varies jointly with x and z. If y = 36 when x = 4 and z = 3, find y when x = 12 and z = 36.
Problem 5 :
Suppose x varies directly as y and z. If y = 3 and z = 4, then x = 24. Find the value of x when y = 7 and z = 4.
Problem 6 :
Suppose y varies jointly with the square of x and the cube root of z. If x = 5 and z = 8, then y = 25. Find y, if x = 2 and z = 27.
Problem 7 :
Suppose x varies directly with y and inversely with z. If x = 3 and y = 10, then z = 9. Find x when y = 12 and z = 18.
Problem 8 :
The surface area of a cylinder varies jointly as the radius and the sum of the radius and the height. A cylinder with radius 4 cm and height 8 cm has a surface area 96 π cm 2 . Find the surface area of a cylinder with radius 3 cm and height 10 cm.

1. Answer :
x varies jointly as y and z
2. Answer :
z varies jointly as x and the square root of y
3. Answer :
w varies jointly as x and y and inversely as z
4. Answer :
Since y varies jointly with x and z,
y = kxz ----(1)
Substitute y = 36, x = 4 and z = 3 to find the value of k.
36 = k(4)(3)
Divide both sides by 12.
Substitute k = 3 in (1).
Substitute x = 12, z = 36 and evaluate y.
y = 3(12)(36)
5. Answer :
Since x varies directly as y and z,
x = kyz ----(1)
Substitute x = 24, y = 3 and z = 4 to find the value of k.
24 = k(3)(4)
Divide both sides by 24.
Substitute k = 2 in (1).
Substitute y = 7, z = 4 and evaluate x.
x = 2(7)(4)
6. Answer :
y ∝ (x 2 )( 3 √z)
y = k( x 2 )( 3 √z) ----(1)
Substitute x = 5, z = 8 and y = 25 to find the value of k.
25 = k(5 2 )( 3 √8)
25 = k(25)(2)
Divide both sides by 50.
Substitute k = 0.5 in (1).
y = 0.5(x 2 )( 3 √z)
Substitute x = 2, z = 27 and evaluate y.
y = 0.5(2 2 )( 3 √27)
y = 0.5(4 )(3)
7. Answer :
Since x varies directly with y and inversely with z,
x = ky /z ----(1)
Substitute x = 3, y = 10 and z = 9 to find the value of k.
3 = k(10)/9
Multiply both sides by 9.
Divide both sides by 2.7.
Substitute k = 2.7 in (1).
Substitute y = 12, z = 18 and evaluate x.
x = 2.7(12)/18
8. Answer :
Let S represent surface area of the cylinder, r represent radius and h represent height.
Since S varies jointly as r and (r + h),
S ∝ r(r + h)
S = kr(r + h) ----(1)
Substitute S = 96 π , r = 4 and h = 8 to find the value of k.
96 π = k(4)(4 + 8)
96 π = k(4)(12)
96 π = 48k
Divide both sides by 48.
2π = k
Substitute k = 2 π in (1).
S = 2 π r(r + h)
Substitute r = 3, h = 10 and evaluate S.
S = 2 π(3) (3 + 10)
S = 2 π(3) (13)
Surface area = 78 π cm 2
Kindly mail your feedback to [email protected]
We always appreciate your feedback.
© All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
- Sat Math Practice
- SAT Math Worksheets
- PEMDAS Rule
- BODMAS rule
- GEMDAS Order of Operations
- Math Calculators
- Transformations of Functions
- Order of rotational symmetry
- Lines of symmetry
- Compound Angles
- Quantitative Aptitude Tricks
- Trigonometric ratio table
- Word Problems
- Times Table Shortcuts
- 10th CBSE solution
- PSAT Math Preparation
- Privacy Policy
- Laws of Exponents
Recent Articles
SAT Math Resources (Videos, Concepts, Worksheets and More)
Dec 23, 24 03:47 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 91)
Dec 23, 24 03:40 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 90)
Dec 21, 24 02:19 AM

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Sep 25, 2024 · How to Solve Joint Variation Problems? Follow the step by step procedure provided below to solve problems involving Joint Variation and arrive at the solution easily. They are along the lines. Step 1: Write the exact equation. The problems of joint variation can be solved using the equation y =kxz.
A General Note: Joint Variation. Joint variation occurs when a variable varies directly or inversely with multiple variables. For instance, if x varies directly with both y and z, we have x = kyz. If x varies directly with y and inversely with z, we have [latex]x=\frac{ky}{z}[/latex]. Notice that we only use one constant in a joint variation ...
When this happens, we say that the functions have joint variation or combined variation. Joint variation is direct variation to more than one variable (for example, d = (r)(t)). With combined variation, we have both direct variation and indirect variation. How to set up and solve combined variation problems? Example:
For solving a problems related to joint variation first we need to build the correct equation by adding a constant and relate the variables. After that we need determine the value of the constant. Then substitute the value of the constant in the equation and by putting the values of variables for required situation we determine the answer.
Dec 9, 2023 · Below are some examples to solve "joint variation" problems using the joint variation formula. Example 1: Finding an Equation of Joint Variation Find an equation of variation where a varies jointly as b and c, and a = 30 when b = 2 and c =3.
Solve problems involving joint variation. Many situations are more complicated than a basic direct variation or inverse variation model. One variable often depends on multiple other variables. When a variable is dependent on the product or quotient of two or more variables, this is called joint variation. For example, the cost of busing ...
Joint Variation Word Problems. JOINT VARIATION WORD PROBLEMS. Problem 1 : ... Solving Trigonometric Equations Problems and Solutions. Dec 18, 24 10:53 AM.
When this happens, we say that the functions have joint variation or combined variation. Joint variation is direct variation to more than one variable (for example, d = (r)(t)). With combined variation, we have both direct variation and indirect variation. How to set up and solve combined variation problems? Example:
Joint and Combined Variation Practice Problems *Make sure to use correct UNITS, when applicable 1) If f varies jointly as g and the cube of h, and f = 200 when g = 5 and h = 4, find f when g = 3 and h = 6. 2) If y varies jointly as x and z, and y = 33 when x = 9 and z = 12, find y when x = 16 and z = 22.
Problem 2 : Write the equation for the following joint variation. "z varies jointly as x and the square root of y" Problem 3 : Write the equation for the following joint variation. "w varies jointly as x and y and inversely as z" Problem 4 : Suppose y varies jointly with x and z. If y = 36 when x = 4 and z = 3, find y when x = 12 and z = 36 ...