Manufacturing Business Plan Template & PDF Example
- September 4, 2024

Creating a comprehensive business plan is crucial for launching and running a successful manufacturing business. This plan serves as your roadmap, detailing your vision, operational strategies, and financial plan. It helps establish your manufacturing business’s identity, navigate the competitive market, and secure funding for growth.
This article not only breaks down the critical components of a manufacturing business plan, but also provides an example of a business plan to help you craft your own.
Whether you’re an experienced entrepreneur or new to the manufacturing industry, this guide, complete with a business plan example, lays the groundwork for turning your manufacturing business concept into reality. Let’s dive in!
Our manufacturing business plan covers all essential aspects necessary for a comprehensive strategy. It details operations, marketing strategy, market environment, competitors, management team, and financial forecasts.
- Executive Summary : Provides an overview of the manufacturing company’s business concept, market analysis , management, and financial strategy.
- Facilities & Equipment: Describes the facility’s capabilities, machinery, and technological advancements.
- Operations & Supply: Outlines the production processes, supply chain logistics, and inventory management.
- Key Stats: Offers data on industry size , growth trends, and market positioning.
- Key Trends: Highlights significant trends impacting the industry, such as automation and localization.
- Key Competitors: Analyzes primary competitors and differentiates the company from these rivals.
- SWOT: Analyzes strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Marketing Plan : Outlines tactics for attracting new contracts and maintaining client relationships.
- Timeline : Sets out key milestones from inception through the first year of operations.
- Management: Information on the management team and their roles within the company.
- Financial Plan: Projects the company’s financial performance over the next five years, detailing revenue, profits, and anticipated expenses.


Manufacturing Business Plan Template (Download)

Fully editable 30+ slides Powerpoint presentation business plan template.
Download an expert-built 30+ slides Powerpoint business plan template
Executive Summary
The Executive Summary introduces your manufacturing business plan, offering a concise overview of your manufacturing facility and its products. It should detail your market positioning, the range of products manufactured, the production process, its location, size, and an outline of day-to-day operations.
This section should also explore how your manufacturing business will integrate into the local and broader markets, including the number of direct competitors within the area, identifying who they are, along with your business’s unique selling points that differentiate it from these competitors.
Furthermore, you should include information about the management and co-founding team, detailing their roles and contributions to the business’s success. Additionally, a summary of your financial projections, including revenue and profits over the next five years, should be presented here to provide a clear picture of your business’s financial plan.
Manufacturing Business Plan Executive Summary Example
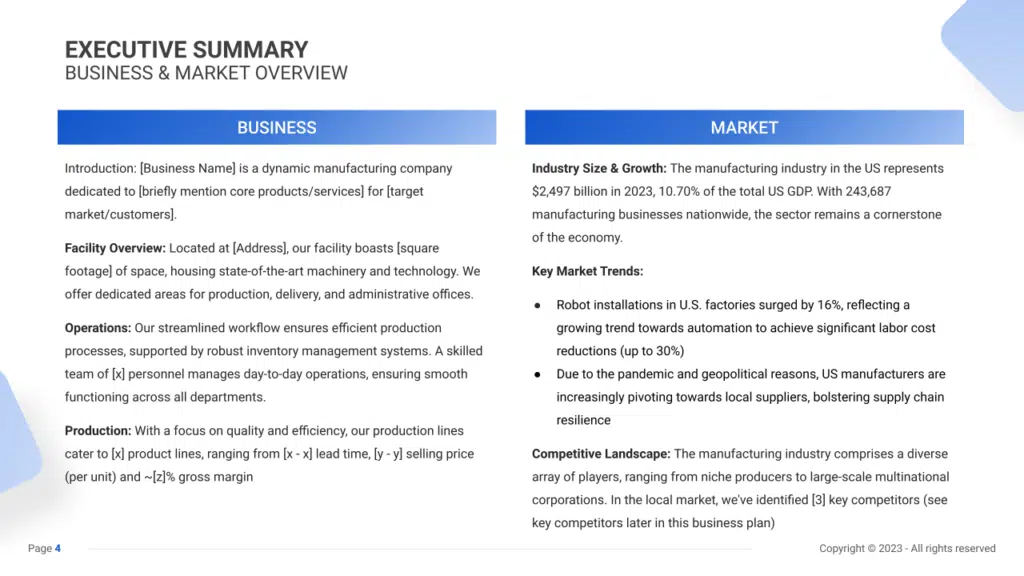
Business Overview
Detailing the business overview in your executive summary is essential to provide investors with a clear understanding of your manufacturing company. Include key details such as the company name, location, and core operations. Emphasize your unique selling proposition ( USP ) that sets your manufacturing business apart from competitors.
Example: “Precision Manufacturing Solutions” is a dynamic manufacturing company specializing in precision-engineered components for aerospace and automotive industries. Located at 123 Industrial Drive, our facility spans 50,000 square feet, equipped with state-of-the-art machinery and technology. Our facility is strategically organized to facilitate efficient production, logistics, and administrative functions. A skilled team of 75 personnel manages day-to-day operations, ensuring streamlined workflow and optimal resource utilization across all departments. Our production lines cater to a diverse range of precision components, delivering high-quality products with a focus on efficiency and reliability.
Market Overview
Understanding the broader manufacturing industry and market dynamics is crucial for positioning your company for success. Highlight industry size , growth trends, and key market insights to contextualize your business within the manufacturing landscape. Discuss emerging trends and competitive analysis to showcase your company’s market positioning.
Example: The manufacturing industry in the US represents a significant portion of the economy, with a valuation of $2,497 billion in 2023 and contributing 10.70% to the total US GDP. With over 243,687 manufacturing businesses nationwide, the sector remains a vital driver of economic growth and innovation. Recent trends indicate a surge in robot installations in U.S. factories, driven by the growing emphasis on automation to achieve cost efficiencies and enhance productivity. Additionally, manufacturers are increasingly pivoting towards local suppliers to strengthen supply chain resilience amidst global disruptions.
Management Team
Highlighting the expertise and experience of your management team instills confidence in potential investors and partners. Present key qualifications and achievements of your team members, emphasizing their contributions to the company’s success.
Example: John Smith (CEO): Provides strategic leadership and oversees manufacturing operations to ensure the highest standards of product quality and efficiency.Emily Johnson (CFO): Manages the company’s finances, including budgeting, financial planning, and risk management, driving business growth and profitability.
Financial Plan
Provide a clear financial plan outlining revenue targets, profit margins, and growth strategies to demonstrate your company’s financial viability.
Example:
We aim to achieve $31.7 million in annual revenue with a solid 15% operating profit margin ( EBITDA ) by 2028. This goal is supported by strategic investments in technology, talent, and operational efficiency. Our leadership team is committed to driving growth and maximizing shareholder value through prudent financial management and strategic decision-making.
Facilities & Equipment
Describe your manufacturing facility. Highlight its design, capacity, and technology. Mention the location, emphasizing accessibility to transport routes. Discuss advantages for efficiency and cost management. Detail essential equipment and its capabilities.
Operations & Supply Chain
Detail product range. Outline your operations strategy for efficiency and scalability. Discuss supply chain management. Highlight sourcing of materials, inventory control, and logistics. Emphasize strong partnerships with suppliers and distributors.

Industry Size & Growth
Start by examining the size of the manufacturing industry relevant to your products and its growth potential. This analysis is crucial for understanding the market’s scope and identifying expansion opportunities.
Key Market Trends
Proceed to discuss recent market trends , such as the increasing demand for sustainable manufacturing processes, automation, and advanced materials. For example, highlight the demand for products that utilize eco-friendly materials or energy-efficient production techniques, alongside the rising popularity of smart manufacturing.
Competitive Landscape
A competitive analysis is not just a tool for gauging the position of your manufacturing business in the market and its key competitors; it’s also a fundamental component of your business plan.
This analysis helps in identifying your manufacturing business’s unique selling points, essential for differentiating your business in a competitive market.
In addition, the competitive analysis is integral in laying a solid foundation for your business plan. By examining various operational aspects of your competitors, you gain valuable information that ensures your business plan is robust, informed, and tailored to succeed in the current market environment.
Identifying Your Manufacturing Competitors
The first step in conducting a competitive analysis for a manufacturing business is identifying direct and indirect competitors. Direct competitors are those producing similar products within your industry, while indirect competitors may offer substitute products or cater to overlapping market segments. Utilize market research and industry reports to compile a list of competitors, considering factors such as product range, target market , and geographical reach.
Online tools like industry databases and trade publications can provide valuable insights into competitor profiles and market dynamics. Additionally, networking within industry associations and attending trade shows can offer firsthand knowledge of key players in the manufacturing landscape.

Manufacturing Business Competitors’ Strategies
Once competitors are identified, analyzing their strategies is crucial for understanding market trends and identifying areas of competitive advantage. Key aspects to consider include:
- Product Portfolio: Assess competitors’ product offerings, including features, quality, and customization options. For example, a manufacturing company specializing in automotive components may face competition from both domestic and international suppliers offering similar parts.
- Technological Capabilities: Evaluate competitors’ technological infrastructure and capabilities, such as automation, digitalization, and advanced manufacturing processes. Companies leveraging cutting-edge technologies may have a competitive edge in terms of efficiency and product innovation.
- Supply Chain Management: Examine how competitors manage their supply chains, including sourcing of raw materials, manufacturing processes, and distribution networks. Understanding supply chain dynamics can uncover potential vulnerabilities or areas for improvement within your own operations.
- Pricing and Positioning: Analyze competitors’ pricing strategies and market positioning to determine how your manufacturing business stacks up in terms of value proposition and market positioning. Consider factors such as pricing tiers, discounts, and value-added services offered by competitors.
- Marketing and Branding: Evaluate competitors’ marketing tactics and brand perception within the market. Assess the effectiveness of their advertising campaigns, digital presence, and customer engagement strategies in building brand loyalty and market share.
- Operational Efficiency : Look for opportunities to optimize operational efficiency by benchmarking against industry leaders and identifying best practices in manufacturing processes, inventory management, and logistics. Consider investing in technologies or process improvements to enhance productivity and reduce costs.
What’s Your Manufacturing Business’s Value Proposition?
Armed with insights from the competitive analysis, articulate your manufacturing business’s unique value proposition and competitive advantages. Consider factors such as:
Highlight unique features, quality standards, or customization options that set your products apart from competitors. For example, a manufacturing company may differentiate itself through superior craftsmanship, innovative design, or eco-friendly materials.
Emphasize your commitment to customer satisfaction and responsiveness. Offering personalized support, timely delivery, and flexible solutions can strengthen customer relationships and foster loyalty in a competitive market.
Communicate your dedication to continuous improvement and innovation. Showcase initiatives to enhance product quality, streamline processes, and adapt to evolving customer needs and market trends.
Market Positioning: Position your manufacturing business strategically within the market, targeting niche segments or underserved markets where competitors may have limited presence or differentiation. Develop tailored marketing messages and value propositions to resonate with your target audience .

First, conduct a SWOT analysis for your manufacturing business. Highlight Strengths such as advanced production technology and a skilled workforce. Address Weaknesses, including potential supply chain vulnerabilities or high production costs. Identify Opportunities like emerging markets for your products or potential for innovation in production processes. Consider Threats such as global competition or economic downturns that may impact demand for your products.

Marketing Plan
Next, develop a marketing strategy that outlines how to attract and retain customers through targeted advertising, trade shows, digital marketing, and strategic partnerships. Emphasize the importance of showcasing product quality and technological advantages to differentiate your business in the market.
Marketing Channels
Identifying and leveraging effective marketing channels is critical for amplifying reach and visibility within the manufacturing sector.
Digital Marketing
Harnessing digital platforms for outreach is essential for modern businesses:
- Content Marketing: Developing high-quality and informative content, such as blogs, whitepapers, or case studies, showcasing industry expertise and problem-solving capabilities, establishes credibility and authority within the industry.
- Website Optimization: Creating a user-friendly website that prominently displays products, certifications, client testimonials, and case studies is imperative. Implementing SEO strategies enhances online visibility, ensuring that your business is discoverable in relevant online searches.
- Social Media Engagement : Leveraging platforms like LinkedIn for thought leadership, product launches, and industry insights, while utilizing visually engaging platforms like Instagram to showcase manufacturing processes and product innovations, amplifies brand visibility and engagement with potential clients.
Trade Shows and Industry Events
Participating in trade shows, industry exhibitions, and networking events offers invaluable opportunities for face-to-face interactions with potential clients, distributors, and partners. Utilizing these platforms to exhibit product samples, showcase innovations, and establish business relationships strengthens market presence and fosters partnerships within the industry.
Direct Sales and Networking
Building relationships through direct communication avenues:
- Cold Calling and Email Campaigns: Reach out directly to potential clients, emphasizing your manufacturing capabilities and solutions tailored to their unique needs, establish initial connections, and introduce your business offerings.
- Networking and Business Associations: Joining industry-specific associations, chambers of commerce, and business networks expands your reach and credibility within the manufacturing sector. Building relationships within these networks facilitates knowledge sharing and potential business collaborations.

Sales Channels
Implementing effective sales strategies is paramount for driving revenue growth and fostering long-term client relationships.
Consultative Selling
Emphasizing solutions over mere products:
- Solution-Oriented Approach: Understanding client pain points and offering tailored manufacturing solutions that specifically address their needs establishes your business as a partner rather than just a supplier.
- Technical Expertise: Equipping sales teams with technical insights and expertise demonstrates a deep understanding of client requirements, instilling confidence and trust in your business’s capabilities.
Client Relationship Management
Nurturing long-term relationships is critical for sustained success:
- After-Sales Support: Providing exceptional post-sales support, encompassing warranty services, maintenance, or technical assistance, nurtures client loyalty and satisfaction, fostering repeat business and referrals.
- Client Feedback Mechanism: Establishing a robust feedback loop enables continuous improvement of products and services based on client insights, ensuring that your offerings align with market demands and expectations.
Customized Offerings and Upselling
Upselling relevant products or tailored solutions enhances the value proposition:
- Tailored Solutions: Offering customized manufacturing solutions catering to unique client demands or industry-specific requirements adds value and fosters strong client relationships, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Add-On Services: Providing supplementary services or support packages beyond the standard offerings enhances the overall customer experience, elevating the perceived value of your business solutions.
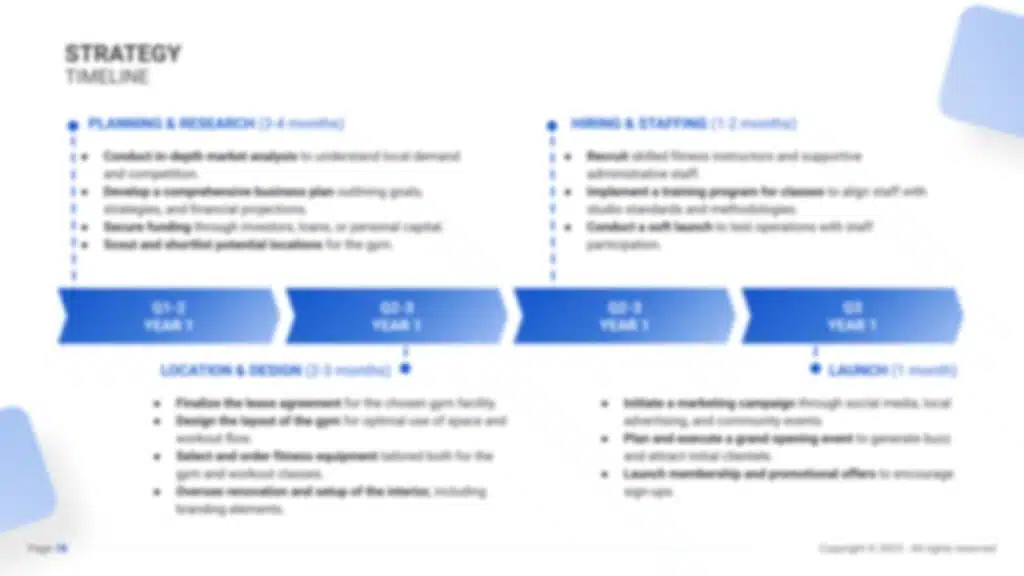
Strategy Timeline
Finally, create a detailed timeline that outlines critical milestones for your manufacturing business’s launch, marketing initiatives, customer acquisition, and expansion goals. Ensure the business progresses with clear direction and purpose, setting specific dates for achieving key operational and sales targets.
The Management section focuses on the manufacturing business’s management and their direct roles in daily operations and strategic direction. This part is crucial for understanding who is responsible for making key decisions and driving the manufacturing business toward its financial and operational goals.
For your manufacturing business plan, list the core team members, their specific responsibilities, and how their expertise supports the business.

The Financial Plan section is a comprehensive analysis of your financial projections for revenue, expenses, and profitability. It lays out your manufacturing business’s approach to securing funding, managing cash flow, and achieving breakeven.
This section typically includes detailed forecasts for the first 5 years of operation, highlighting expected revenue, operating costs and capital expenditures.
For your manufacturing business plan, provide a snapshot of your financial statement (profit and loss, balance sheet, cash flow statement), as well as your key assumptions (e.g. number of customers and prices, expenses, etc.).
Make sure to cover here _ Profit and Loss _ Cash Flow Statement _ Balance Sheet _ Use of Funds

Related Posts

Sit Still Franchise FDD, Profits, Costs & Fees (2025)
- December 4, 2024

Tapville Social Franchise FDD, Profits & Costs (2025)

Crisp & Green Franchise FDD, Profits & Costs (2025)
Privacy overview.

Manufacturing Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Manufacturing Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 7,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their manufacturing businesses. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through a manufacturing business plan template step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is a Manufacturing Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your manufacturing business as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategy for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for a Manufacturing Company
If you’re looking to start a new manufacturing business, or grow your existing manufacturing business, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your manufacturing business in order to improve your chances of success. Your business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Manufacturing Businesses
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for a manufacturing business are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans and angel investors. With regards to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to confirm that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business.
Personal savings is the other most common form of funding for a manufacturing business. Venture capitalists will usually not fund a manufacturing business. They might consider funding a manufacturing business with a national presence, but never an individual location. This is because most venture capitalists are looking for millions of dollars in return when they make an investment, and an individual location could never achieve such results. With that said, personal savings and bank loans are the most common funding paths for manufacturing businesses.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to Write a Business Plan for a Manufacturing Company
If you want to start a manufacturing business or expand your current one, you need a business plan. Below we detail what you should include in each section of your own business plan:
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of manufacturing business you are operating and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have a manufacturing business that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of manufacturing businesses?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan. For example, give a brief overview of the manufacturing industry. Discuss the type of manufacturing business you are operating. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target market. Provide a snapshot of your marketing strategy. Identify the key members of your team. And offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Analysis
In your company analysis, you will detail the type of business you are operating.
There are many types of manufacturing businesses, such as:
- Clothing manufacturing
- Garment manufacturing
- Food product manufacturing
- Diaper manufacturing
- Tile manufacturing
- Toy manufacturing
- Soap and detergent manufacturing
- Mobile accessories manufacturing
- Mattress manufacturing
- Bicycle manufacturing
- Pillow manufacturing
- Brick manufacturing
- Toilet paper manufacturing
- Furniture manufacturing
- Peanut butter manufacturing
- Cosmetics manufacturing
- Footwear manufacturing
In addition to explaining the type of manufacturing business you will operate, the Company Analysis section of your business plan needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to question such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of customers served, number of positive reviews, number of wholesale contracts, etc.
- Your legal structure. Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry or market analysis, you need to provide an overview of the manufacturing industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the manufacturing industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your strategy, particularly if your research identifies market trends.
The third reason for market research is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section:
- How big is the manufacturing industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential market for your manufacturing business? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of target market segments: wholesalers, other manufacturers, exports, retailers.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of manufacturing business you operate. Clearly, retailers would respond to different marketing promotions than export markets, for example.
Try to break out your target market in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, include a discussion of the ages, genders, locations and income levels of the customers you seek to serve. Because most manufacturing businesses primarily serve customers living in their same city or town, such demographic information is easy to find on government websites.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can understand and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Manufacturing Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other manufacturing businesses.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t direct competitors. This includes manufacturers in other niches, as well as those vertically integrated businesses that make their own product. You need to mention such competition as well.
With regards to direct competition, you want to describe the other manufacturing businesses with which you compete. Most likely, your direct competitors will be house flippers located very close to your location.
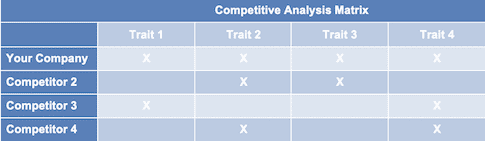
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their businesses and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as:
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What types of products do they manufacture?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide high quality manufacturing practices?
- Will you provide services that your competitors don’t offer?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a manufacturing business, your marketing strategy should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of manufacturing company that you documented in your Company Analysis. Then, detail the specific products you will be offering. For example, in addition to manufacturing, will you provide R&D, design, prototyping or any other services?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your marketing plan, you are presenting the services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the location of your manufacturing company. Document your location and mention how the location will impact your success. For example, is your manufacturing business located near a distribution hub, etc. Discuss how your location might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions : The final part is the promotions section. Here you will document how you will drive customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertising in local papers and magazines
- Reaching out to local websites
- Social media marketing
- Local radio advertising
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your manufacturing business, including sourcing inputs, designing processes, managing production, coordinating logistics and meeting with potential buyers.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to secure your 1,000 th contract, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your manufacturing business to a new city.
Management Team
To demonstrate your manufacturing business’ ability to succeed, a strong team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing manufacturing businesses. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act like mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in manufacturing or successfully running small businesses.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statements.
Income Statement : an income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenues and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you offer short-run production, or will you focus strictly on long-run? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets : Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your manufacturing business, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a bank writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement : Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and make sure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
In developing your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a manufacturing business:
- Location build-out including design fees, construction, etc.
- Cost of equipment and supplies
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Taxes and permits
- Legal expenses
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your production facility blueprint, or capabilities specifications.
Putting together a business plan for your manufacturing business is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert. You will really understand the manufacturing industry, your competition, and your customers. You will have developed a marketing plan and will really understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful manufacturing business.
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Manufacturing business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. See how Growthink’s professional business plan consulting services can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

Manufacturing Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Manufacturing Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your manufacturing business plan.
We have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their manufacturing businesses.
Sample Business Plan for a Manufacturing Business
Below is a manufacturing business plan example to help you create each section of your own business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
Perfect Snacks, located in Lincoln, Nebraska, is a food manufacturing company that specializes in the production of snack foods and packaged goods. We manufacture an extensive line of snack products, including trail mix, gummies, and chocolate. Our company focuses on quality and only uses the best natural ingredients in our products. We will primarily sell our products to grocery stores and other establishments that sell snacks, but will also sell bulk orders to individual customers through our website.
Perfect Snacks was founded by Joe Boseley. Joe has been working on the manufacturing concept over the past few years and began networking with grocery store clients and locating the land to build his manufacturing and distribution center. As a line manager that oversaw dozens of employees, Joe has the proper knowledge and experience to own, manage, and operate his own manufacturing company.
Product Offering
Perfect Snacks will manufacture an extensive list of sweet, salty, and healthy snacks. Some of our initial products will include:
We will primarily sell our products to grocery stores, recreation centers, and other businesses that sell snacks in bulk. Consumers can find our products in stores or buy them in bulk on our website.
Customer Focus
Perfect Snacks will primarily serve the residents of Lincoln, Nebraska. The community has a large population of families and children, who are the primary consumers of snack foods. Therefore, we will market our products to recreational centers, schools, grocery stores, and other establishments that sell snacks to children and their parents.
Management Team
Perfect Snacks is owned by Joe Boseley, a local entrepreneur who has worked in various warehouses and manufacturing companies in Lincoln, Nebraska. Working in the manufacturing industry and in warehouses, Joe is very familiar with the processing and distribution of packaged foods. As a line manager that oversaw dozens of employees, Joe has the proper knowledge and experience to own, manage, and operate his own manufacturing business.
Joe will utilize his past experience with developing staff roles and functions. He is also very familiar with the manufacturing equipment and plans to purchase the latest technology that is efficient and cost-effective. His contacts have allowed him to gain concrete Letters of Intent from local supermarket chains to have his manufactured goods in their stores.
Success Factors
Perfect Snacks will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Taste: Perfect Snacks’ snack products will be made with the highest quality ingredients and offer quality over quantity.
- Price: Perfect Snacks is able to offer the highest quality snacks at a competitive price point.
- Community Relations: Perfect Snacks will be a pillar in the community and be heavily involved in family-related activities in the area. It will sponsor events, provide snacks for schools and daycares at a discounted price, and donate a portion of its proceeds to area family-related charities and organizations.
- Proprietary Technology: Perfect Snacks will invest heavily on the latest technology to manufacture the snack foods for distribution. It will ensure the food products are made safely and free from any harmful chemicals and ingredients.
Financial Highlights
Perfect Snacks is seeking a total funding of $1,200,000 of debt capital to open its manufacturing business. The capital will be used for funding capital expenditures, salaries, marketing expenses, and working capital. Specifically, these funds will be used as follows:
- Manufacturing facility design/build-out: $400,000
- Equipment and supplies: $375,000
- Initial inventory: $100,000
- Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $250,000
- Marketing costs: $50,000
- Working capital: $25,000
The following graph below outlines the pro forma financial projections for Perfect Snacks.
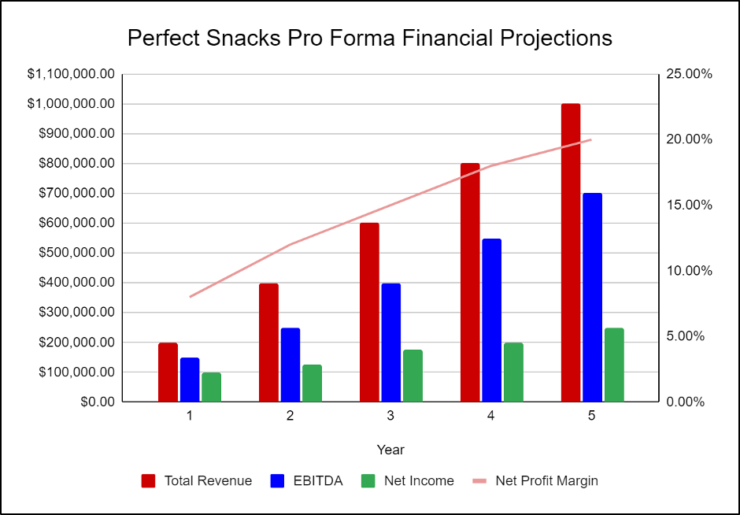
Company Overview
Who is perfect snacks, perfect snacks history.
After conducting a market analysis, Joe Boseley began surveying the local vacant warehouse space and decided on a parcel of land to construct the warehouse and distribution center. Joe incorporated Perfect Snacks as a Limited Liability Corporation on January 1st, 2023.
Once the land is acquired for the warehouse space, construction can begin to build-out the manufacturing facility.
Since incorporation, the Company has achieved the following milestones:
- Located a vacant lot that would be ideal for a manufacturing facility
- Developed the company’s name, logo, and website
- Hired a general contractor and architect for the build-out of the warehouse, small office, and distribution area
- Determined equipment and necessary supplies
- Determined beginning inventory
- Attained Letters of Intent from supermarket clients
- Began recruiting key employees
Perfect Snacks Services
Industry analysis.
The Manufacturing sector’s performance is largely attributable to the value of the US dollar, commodity prices, policy decisions and US manufacturing capacity. Food manufacturing has a history of success as it produces a basic human need. According to Grand View Research, the industry is currently valued at $121 billion and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate of 9.5% from now until 2030.
Commodity prices are currently stabilizing from coronavirus-induced volatility and renewed demand, both in the United States and global economies, which is anticipated to facilitate revenue expansion for manufacturers. Moreover, shifting technological change in the Manufacturing sector is anticipated to benefit large, developed economies, such as the United States. Therefore, now is a great time to start a new food manufacturing company in the U.S.

Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
Perfect Snacks will serve the community residents of Lincoln, Nebraska and its surrounding areas. The community of Lincoln, Nebraska has thousands of households that have children. Statistics show that the main consumers of snack products are children of all ages. They are regularly placed in school lunchboxes, afterschool snacks and programs, and at weekend sporting events. Therefore, we will market to locations where snacks are bought by children or their parents, such as grocery stores, recreational centers, and schools.
The precise demographics Lincoln, Nebraska is as follows:
Customer Segmentation
Perfect Snacks will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Grocery stores and recreational centers
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Perfect Snacks will face competition from other companies with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
Snacks N More
Snacks N More is another local manufacturing company that provides snack food to the immediate area. Established over thirty years ago, the company has the knowledge and expertise in food processing, commercialization, and packaging. They are known as a recognized ingredient supplier for the foodservice industry. Their portfolio of products includes a variety of nuts, snacks, confections, and dry-blend ingredients. As a private label manufacturer, Snack’s More produces a full line of non-chocolate candy, nuts, and fruit-flavored snacks. The company is known for their fruit flavored snacks, dried raisins, nut mixes, and producing ingredients for local restaurants and establishments. Their line of nuts and dried fruits are often used for baking purposes.
Jaxon’s Candy
Jaxon’s Candy is a manufacturer of all things candy related. As a contract manufacturer, the company works with many companies to create their custom designed confections. Their large 50,000 square foot facility produces over 300,000 pounds of candy every month. All of the products are highly concentrated either in sugar or chocolate, or both. Jaxon’s Candy also designs and manufactures their own custom packaging. The candy produced is also kosher certified, gluten-free, peanut free, and non-GMO.
Jaxon’s Candy currently manufactures candy for the following brands – Tommy Candy, Laffy Town, Chocowhoawhoa, Jellylicious, Healthee Candeee, and Sticky Teeth. Jaxon’s Candy can be found in grocery stores and convenient stores along the west coast of the United States.
Gimmy Candy
Gimmy Candy is located in the midwestern portion of the United States and boasts a facility of over 1 million square feet. Their fleet of transportation trucks distributes throughout the continental United States and is considered one of the largest candy manufacturers in the country. Their product portfolio includes assorted chocolates, gummy candy, hard candy, fruit candy, as well as gums and mints. Gimmy Candy was established in 1947 and has grown to be a model of manufacturing companies the industry uses as a model of sustainability and profitability. Their lineup of candy products can be found in every single grocery store and convenient store in the country. Gimmy Candy is considering expanding its distribution globally and start exporting its candy products to Asia, Canada, Europe, and South America. As one of the largest privately held companies in the United States, Gimmy Candy is also considered a top employer in the country and offers its employees a generous benefits package.
Competitive Advantage
Perfect Snacks will be able to offer the following advantages over their competition:
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
Perfect Snacks will offer the unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Fresh and comforting taste
- Community family advocate
- Developed with proprietary technology
- Manufactured with fresh, quality ingredients
- Affordable price
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for Perfect Snacks is as follows:
Social Media
Perfect Snacks will invest heavily in a social media advertising campaign. The brand manager will create the company’s social media accounts and invest in ads on all social media accounts. It will use a targeted marketing strategy to appeal to the target demographics.
Website/SEO
Perfect Snacks will invest heavily in developing a professional website that displays all of the features and benefits of the snack products. It will also invest heavily in SEO so that the brand’s website will appear at the top of search engine results.
Major Publications
We will also invest in advertising in selected larger publications until we have achieved significant brand awareness. Advertisements such as billboards and commercials will be shown during peak TV watching time and the billboards will be placed in highly trafficked areas.
Sponsorships
Perfect Snacks will also invest in sponsoring certain athletic and school events so that their banners and collateral material are displayed all over the event where numerous parents and children are at.
Perfect Snacks’ pricing will be moderate, so consumers feel they receive great value when purchasing our snack products.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for Perfect Snacks.
Operation Functions:
- Joe Boseley will be the CEO of Perfect Snacks. He will oversee the general operations and executive aspects of the business.
- Joe is joined by Candace Smith who will act as the warehouse manager. She will train and manage the staff as well as oversee general production of our products.
- Joe will hire an Administrative Assistant, Marketing Manager, and Accountant, to handle the administrative, marketing strategy, and bookkeeping functions of the company.
- Joe will also hire several employees to manufacture our products and maintain the equipment and machinery.
Milestones:
Perfect Snacks will have the following milestones complete in the next six months.
- 02/202X Finalize lease agreement
- 03/202X Design and build out Perfect Snacks
- 04/202X Hire and train initial staff
- 05/202X Kickoff of promotional campaign
- 06/202X Launch Perfect Snacks
- 07/202X Reach break-even
Perfect Snacks is owned by Joe Boseley, a local entrepreneur who has worked in various warehouses and manufacturing companies in Lincoln, Nebraska. Working in the manufacturing industry and in warehouses, Joe is very familiar with the processing and distribution of packaged foods. As a line manager that oversaw dozens of employees, Joe has the proper knowledge and experience to own, manage, and operate his own production business.
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
Perfect Snacks’ revenues will come primarily from its snack food sales. The company will sell the packaged snacks in local grocery stores, convenience stores, and other locations. As the company’s revenues increase, it will look to gain a wider distribution area.
The land purchase, equipment, supplies, opening inventory, and labor expenses will be the key cost drivers of Perfect Snacks. Other cost drivers include taxes, business insurance, and marketing expenditures.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
Key assumptions.
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and pay off the startup business loan.
- Average order value: $250
Financial Projections
Income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, manufacturing business plan faqs, what is a manufacturing business plan.
A manufacturing business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your manufacturing business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your Manufacturing business plan using our Manufacturing Business Plan Template here .
What are the Steps To Start a Manufacturing Business?
Starting a new manufacturing business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A Manufacturing Business Plan – The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed manufacturing business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include market research to define your local market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure – It’s important to select an appropriate legal entity for your manufacturing business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your manufacturing business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Manufacturing Business – Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your manufacturing business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options – It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your manufacturing business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location – Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees – There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Manufacturing Equipment & Supplies – In order to start your manufacturing business, you’ll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business – Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your manufacturing business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Start » strategy, how to build a manufacturing business plan.
A manufacturing business plan can help get your new venture off the ground and running smoothly.

A manufacturing business plan outlines the goals, strategies, and operations of a manufacturing company. Use this article as a road map for your business and to help recruit investors as your operation grows.
Manufacturing business plans vary slightly compared to business plans for other types of companies. Here's what goes into a manufacturing business plan and how to create one for your venture.
Why do companies need manufacturing business plans?
Manufacturing business plans are used for the same purpose as other companies' plans. These documents help set clear goals and objectives for internal stakeholders. They provide a framework for making decisions around financing, budgeting, hiring, and procurement. Additionally, investors and lenders often require a business plan to assess the venture's potential.
Business plans are meant to be flexible, living documents that are revisited periodically as the business grows. Writing a manufacturing business plan is a good exercise in understanding what equipment will be needed, evaluating the size of the market your business is based in, and assessing your competition. These things will change over time, so make sure you adjust your plan as your company matures.
[Read more: How to Use AI Tools to Write a Business Plan ]
What goes into a manufacturing business plan?
Manufacturing plans can be very detailed, but at a minimum should include the following sections:
- An executive summary.
- A company description.
- A production plan.
- An industry analysis.
- The target market.
- Compliance.
- A financial plan.
Some manufacturing plans also include sections for marketing, management, and operations. An operations plan can include the details of how you will source materials, your design process, how you will manage production, and ways to coordinate logistics with potential buyers. Marketing sections detail how you will position your product and reach potential buyers, while management identifies the key roles for which you will hire.
[Read more: 6 Product Design Software Programs for Beginners ]
While there's a lot of overlap with a normal business plan, manufacturing companies have unique processes and constraints they need to consider and address in their plan.
Why are manufacturing business plans unique?
The production plan section should provide a detailed outline of the manufacturing process, equipment, facilities, and supply chain. It should also include operational details that are crucial to the success of the manufacturing business: quality control, inventory management, and supply chain logistics, which should be covered extensively.
Manufacturing business plans also play an outsized role in recruiting funding. Manufacturers often require significant capital investments in equipment, machinery, and facilities. The financial projections included in the plan must accurately reflect these costs to ensure adequate funding for getting off the ground.
Finally, meeting global environmental, safety, and quality regulations is no easy feat. Identifying these requirements early positions the manufacturer to be compliant, as well as to assess which supply chain partners are also able to meet these rules. A manufacturing business plan should detail supply chain management, compliance demands, and steps to streamline both of these key elements.
How to write a manufacturing business plan
The easiest way to get started is to use a template. A few outlines are available online, like this one from Katana or this one from MoreBusiness.com . Start by defining your business and answering questions such as:
- What product will the business manufacture?
- Who is the target market of ideal customers?
- What makes this product unique?
- What business structure will be used?
From there, you can work through section by section to conduct market research, develop your operations plan, prototype your product, and identify supply chain partners. Include financial projections such as your startup costs, operational costs, revenue projections, and the break-even point.
"It's important to be optimistic when starting a new business, but you also need to be realistic. This is especially true when it comes to financial projections. Don't overestimate the amount of revenue you will generate or underestimate the costs of goods sold," wrote Katana .
Breaking your plan down into smaller sections can make it easier to identify areas where you need outside help too. Don't be shy about asking others in the industry for advice.
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .
Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
For more business strategies
Finding a small business attorney for your startup, how your business can have a successful giving tuesday, 15 ways your business can get ready for black friday (it's not just for the big guys).
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.
Manufacturing Business Plan Template & Guidebook
Starting a manufacturing business is an exciting endeavor, but it can be daunting to know where to start. Fortunately, the #1 Manufacturing Business Plan Template & Guidebook provides entrepreneurs and businesses with a detailed roadmap for success. With this template and guidebook, you will have the guidance you need to plan for success and develop a comprehensive business plan that outlines your vision and strategy.
Get worry-free services and support to launch your business starting at $0 plus state fees.
- How to Start a Profitable Manufacturing Business [11 Steps]
- 10+ Best & Profitable Manufacturing Business Ideas [2023]
- 25 Catchy Manufacturing Business Names:
- List of the Best Marketing Ideas For Your Manufacturing Business:
How to Write a Manufacturing Business Plan in 7 Steps:
1. describe the purpose of your manufacturing business..
The first step to writing your business plan is to describe the purpose of your manufacturing business. This includes describing why you are starting this type of business, and what problems it will solve for customers. This is a quick way to get your mind thinking about the customers’ problems. It also helps you identify what makes your business different from others in its industry.
It also helps to include a vision statement so that readers can understand what type of company you want to build.
Here is an example of a purpose mission statement for a manufacturing business:
Our mission at [Company Name] is to be the premier provider of innovative, high-quality manufacturing solutions that meet our customers' needs, while delivering superior customer service and providing a safe and rewarding workplace for our employees.

2. Products & Services Offered by Your Manufacturing Business.
The next step is to outline your products and services for your manufacturing business.
When you think about the products and services that you offer, it's helpful to ask yourself the following questions:
- What is my business?
- What are the products and/or services that I offer?
- Why am I offering these particular products and/or services?
- How do I differentiate myself from competitors with similar offerings?
- How will I market my products and services?
You may want to do a comparison of your business plan against those of other competitors in the area, or even with online reviews. This way, you can find out what people like about them and what they don’t like, so that you can either improve upon their offerings or avoid doing so altogether.

3. Build a Creative Marketing Stratgey.
If you don't have a marketing plan for your manufacturing business, it's time to write one. Your marketing plan should be part of your business plan and be a roadmap to your goals.
A good marketing plan for your manufacturing business includes the following elements:
Target market
- Who is your target market?
- What do these customers have in common?
- How many of them are there?
- How can you best reach them with your message or product?
Customer base
- Who are your current customers?
- Where did they come from (i.e., referrals)?
- How can their experience with your manufacturing business help make them repeat customers, consumers, visitors, subscribers, or advocates for other people in their network or industry who might also benefit from using this service, product, or brand?
Product or service description
- How does it work, what features does it have, and what are its benefits?
- Can anyone use this product or service regardless of age or gender?
- Can anyone visually see themselves using this product or service?
- How will they feel when they do so? If so, how long will the feeling last after purchasing (or trying) the product/service for the first time?
Competitive analysis
- Which companies are competing with yours today (and why)?
- Which ones may enter into competition with yours tomorrow if they find out about it now through word-of-mouth advertising; social media networks; friends' recommendations; etc.)
- What specific advantages does each competitor offer over yours currently?
Marketing channels
- Which marketing channel do you intend to leverage to attract new customers?
- What is your estimated marketing budget needed?
- What is the projected cost to acquire a new customer?
- How many of your customers do you instead will return?
Form an LLC in your state!

4. Write Your Operational Plan.
Next, you'll need to build your operational plan. This section describes the type of business you'll be running, and includes the steps involved in your operations.
In it, you should list:
- The equipment and facilities needed
- Who will be involved in the business (employees, contractors)
- Financial requirements for each step
- Milestones & KPIs
- Location of your business
- Zoning & permits required for the business
What equipment, supplies, or permits are needed to run a manufacturing business?
- Manufacturing equipment
- Raw materials
- Safety equipment and supplies
- Labor and skilled workers
- Legal permits and licensing as required by local ordinance
5. Management & Organization of Your Manufacturing Business.
The second part of your manufacturing business plan is to develop a management and organization section.
This section will cover all of the following:
- How many employees you need in order to run your manufacturing business. This should include the roles they will play (for example, one person may be responsible for managing administrative duties while another might be in charge of customer service).
- The structure of your management team. The higher-ups like yourself should be able to delegate tasks through lower-level managers who are directly responsible for their given department (inventory and sales, etc.).
- How you’re going to make sure that everyone on board is doing their job well. You’ll want check-ins with employees regularly so they have time to ask questions or voice concerns if needed; this also gives you time to offer support where necessary while staying informed on how things are going within individual departments too!
6. Manufacturing Business Startup Expenses & Captial Needed.
This section should be broken down by month and year. If you are still in the planning stage of your business, it may be helpful to estimate how much money will be needed each month until you reach profitability.
Typically, expenses for your business can be broken into a few basic categories:
Startup Costs
Startup costs are typically the first expenses you will incur when beginning an enterprise. These include legal fees, accounting expenses, and other costs associated with getting your business off the ground. The amount of money needed to start a manufacturing business varies based on many different variables, but below are a few different types of startup costs for a manufacturing business.
Running & Operating Costs
Running costs refer to ongoing expenses related directly with operating your business over time like electricity bills or salaries paid out each month. These types of expenses will vary greatly depending on multiple variables such as location, team size, utility costs, etc.
Marketing & Sales Expenses
You should include any costs associated with marketing and sales, such as advertising and promotions, website design or maintenance. Also, consider any additional expenses that may be incurred if you decide to launch a new product or service line. For example, if your manufacturing business has an existing website that needs an upgrade in order to sell more products or services, then this should be listed here.
7. Financial Plan & Projections
A financial plan is an important part of any business plan, as it outlines how the business will generate revenue and profit, and how it will use that profit to grow and sustain itself. To devise a financial plan for your manufacturing business, you will need to consider a number of factors, including your start-up costs, operating costs, projected revenue, and expenses.
Here are some steps you can follow to devise a financial plan for your manufacturing business plan:
- Determine your start-up costs: This will include the cost of purchasing or leasing the space where you will operate your business, as well as the cost of buying or leasing any equipment or supplies that you need to start the business.
- Estimate your operating costs: Operating costs will include utilities, such as electricity, gas, and water, as well as labor costs for employees, if any, and the cost of purchasing any materials or supplies that you will need to run your business.
- Project your revenue: To project your revenue, you will need to consider the number of customers you expect to have and the average amount they will spend on each visit. You can use this information to estimate how much money you will make from selling your products or services.
- Estimate your expenses: In addition to your operating costs, you will need to consider other expenses, such as insurance, marketing, and maintenance. You will also need to set aside money for taxes and other fees.
- Create a budget: Once you have estimated your start-up costs, operating costs, revenue, and expenses, you can use this information to create a budget for your business. This will help you to see how much money you will need to start the business, and how much profit you can expect to make.
- Develop a plan for using your profit: Finally, you will need to decide how you will use your profit to grow and sustain your business. This might include investing in new equipment, expanding the business, or saving for a rainy day.
Frequently Asked Questions About Manufacturing Business Plans:
Why do you need a business plan for a manufacturing business.
A business plan for a manufacturing business is essential because it serves as a guide to help the business plan its activities and reach its desired goals. It provides important information such as market analysis, strategy, financial projections, and operational plans. Additionally, it can serve as an important tool to attract potential investors or lenders and help secure funding.
Who should you ask for help with your manufacturing business plan?
You should consult a qualified business consultant, accountant, and/or lawyer who specialise in assisting companies with their manufacturing business plans. Additionally, it is a good idea to reach out to trade organisations, industry bodies, and experts in the manufacturing sector for guidance.
Can you write a manufacturing business plan yourself?
Yes, you can write a manufacturing business plan yourself. Depending on the complexity of your plan, you may want to research best practices and consult experts in the field if necessary. When writing a manufacturing business plan, it is important to include a market analysis, competitive analysis, operations plan, financial projections, and strategic plan. Additionally, you should also include key objectives, milestones and management strategies.
Related Business Plans

Home Inventory Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Home Inspection Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Home Decor Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Health And Wellness Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Hauling Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Hardware Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Handyman Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Hair Extension Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Handbag Business Plan Template & Guidebook
We're newfoundr.com, dedicated to helping aspiring entrepreneurs succeed. As a small business owner with over five years of experience, I have garnered valuable knowledge and insights across a diverse range of industries. My passion for entrepreneurship drives me to share my expertise with aspiring entrepreneurs, empowering them to turn their business dreams into reality.
Through meticulous research and firsthand experience, I uncover the essential steps, software, tools, and costs associated with launching and maintaining a successful business. By demystifying the complexities of entrepreneurship, I provide the guidance and support needed for others to embark on their journey with confidence.
From assessing market viability and formulating business plans to selecting the right technology and navigating the financial landscape, I am dedicated to helping fellow entrepreneurs overcome challenges and unlock their full potential. As a steadfast advocate for small business success, my mission is to pave the way for a new generation of innovative and driven entrepreneurs who are ready to make their mark on the world.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Use this manufacturing business plan as your template to start and grow your manufacturing company. This business plan for a manufacturing company includes market analysis, strategy, and more. Download this Manufacturing Business Plan free for easy editing in Microsoft Word, Google Docs or Apple Pages to make a PDF:
Sep 4, 2024 · Creating a comprehensive business plan is crucial for launching and running a successful manufacturing business. This plan serves as your roadmap, detailing your vision, operational strategies, and financial plan. It helps establish your manufacturing business’s identity, navigate the competitive market, and secure funding for growth.
Why You Need a Business Plan for a Manufacturing Company. If you’re looking to start a new manufacturing business, or grow your existing manufacturing business, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your manufacturing business in order to improve your chances of success.
A manufacturing business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your manufacturing business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
Aug 21, 2024 · A manufacturing business plan must address issues and elements specific to manufacturing goods, like supply chain management and regulatory compliance. — Getty Images/andresr A manufacturing business plan outlines the goals, strategies, and operations of a manufacturing company.
Starting a manufacturing business is an exciting endeavor, but it can be daunting to know where to start. Fortunately, the #1 Manufacturing Business Plan Template & Guidebook provides entrepreneurs and businesses with a detailed roadmap for success.